ASGS (Parotidectomy) is the surgical removal of part or all of the parotid gland, usually to treat tumors. It is a complex procedure due to nearby nerves.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Auricular Salivary Gland Surgery is the common name for a procedure called a Parotidectomy. This surgery involves removing part or all of the parotid gland, which is the largest of your salivary glands. The parotid gland is located in front of and just below your ear.
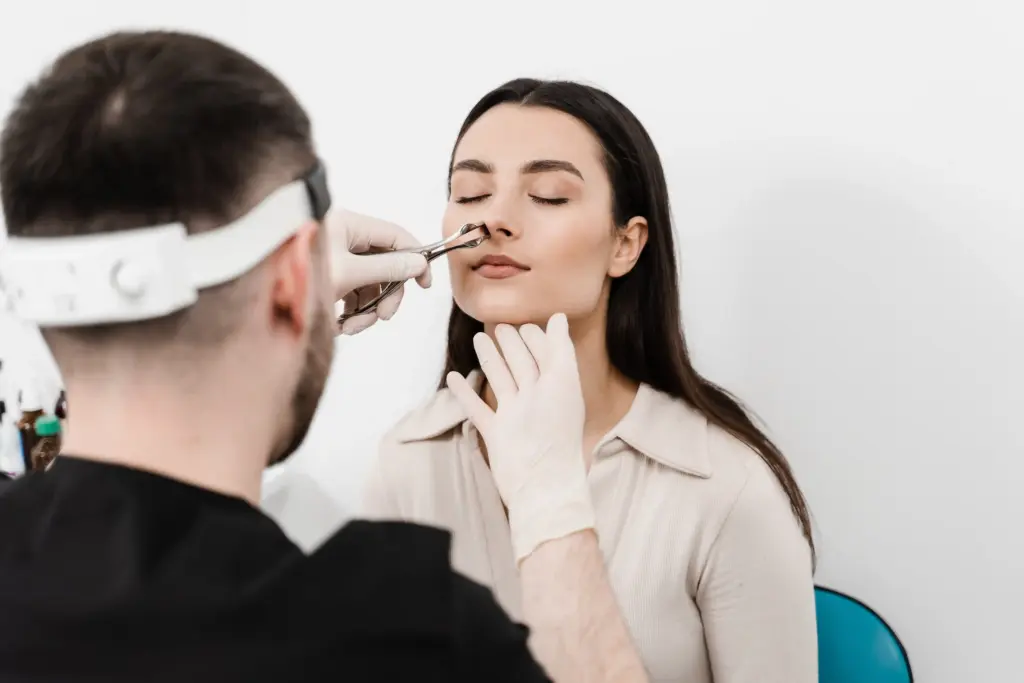
The scope of the Parotidectomy procedure is defined by the depth of the gland and the critical nature of the facial nerve. The parotid gland is divided into a superficial lobe and a deep lobe by the facial nerve, which branches out to control the muscles of the face. The need to find and protect every branch of this nerve makes the surgery complex.
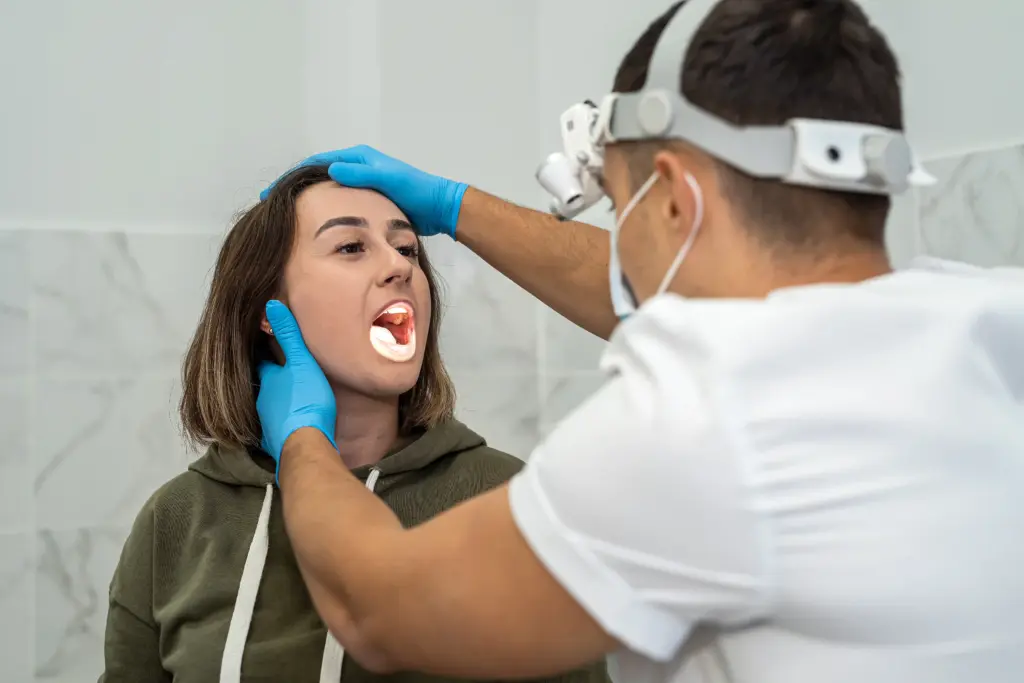
It is essential to distinguish Auricular Salivary Gland Surgery (Parotidectomy) from other similar procedures and conditions to ensure patients understand what they are facing.
The main reason for performing Auricular Salivary Gland Surgery (Parotidectomy) is to diagnose and treat growths found in the gland. The specific tumor type dictates the urgency and extent of the surgery.
The primary focus of a Parotidectomy is the salivary and nervous systems, but the procedure has implications for several related areas of the head and neck.
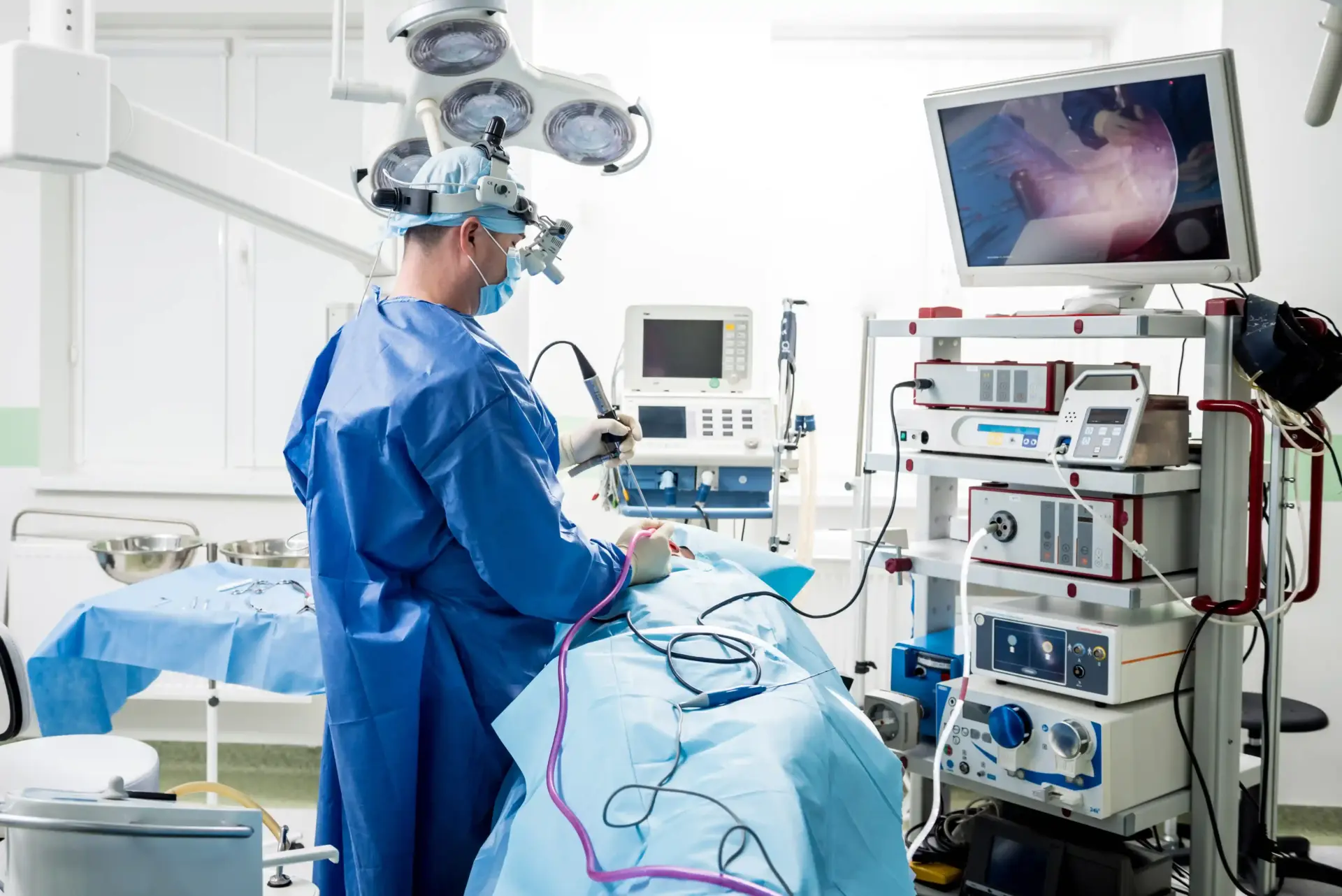
Auricular Salivary Gland Surgery (Parotidectomy) holds critical importance in medicine because the failure to correctly diagnose and treat parotid masses can lead to severe facial disfigurement, high rates of cancer recurrence, or uncontrolled systemic disease.
The complex, sensitive nature of the Parotidectomy mandates an intensely collaborative multidisciplinary care (MDC) approach coordinated by surgeons with advanced training.
Early and accurate assessment of a parotid mass is vital. Waiting to diagnose a mass can allow a slow-growing benign tumor to become technically complex to remove or, worse, allow a small cancer to spread aggressively.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Auricular Salivary Gland Surgery (Parotidectomy) is the removal of the salivary gland located near the ear (the parotid gland). It is usually done to remove a tumor.
The most significant risk is temporary or permanent weakness of the facial nerve, which runs through the gland. This nerve controls movement in the face (e.g., smiling, closing the eye).
The surgery covers two main categories: benign (non-cancerous) tumors like pleomorphic adenoma, and malignant (cancerous) tumors that require more extensive removal.
You should consult an ENT or head and neck surgeon immediately upon noticing any painless lump or swelling in front of or below the ear that does not go away.
Yes, the parotid gland is the largest salivary gland. However, after its removal, the other glands usually increase their production to compensate, so overall saliva production remains mostly normal.


Why do you have a deviated septum? Learn easy ultimate cause facts and find effective ways to treat the pain and breathe better instantly. A

Millions of people worldwide suffer from allergic rhinitis. This condition can really affect their quality of life. Using an air purifier might help manage its

Allergic rhinitis affects millions worldwide, causing significant discomfort and impacting quality of life. Research has shown that certain nutrients can play a key role in

Did you know millions of people worldwide have a condition where their immune system attacks their own tissues? This leads to ongoing allergic reactions. Autoimmune

Listing common causes for extended hoarseness and addressing hoarseness timing concern (laryngitis, GERD, vocal abuse). hoarseness timing concern Having a hoarse voice for months can

Did you know that sinusitis sickness can make you feel really tired and exhausted? It’s not just the usual congestion and facial pressure. Many people

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)