Plastic surgery restores form and function through reconstructive procedures, cosmetic enhancements, and body contouring.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
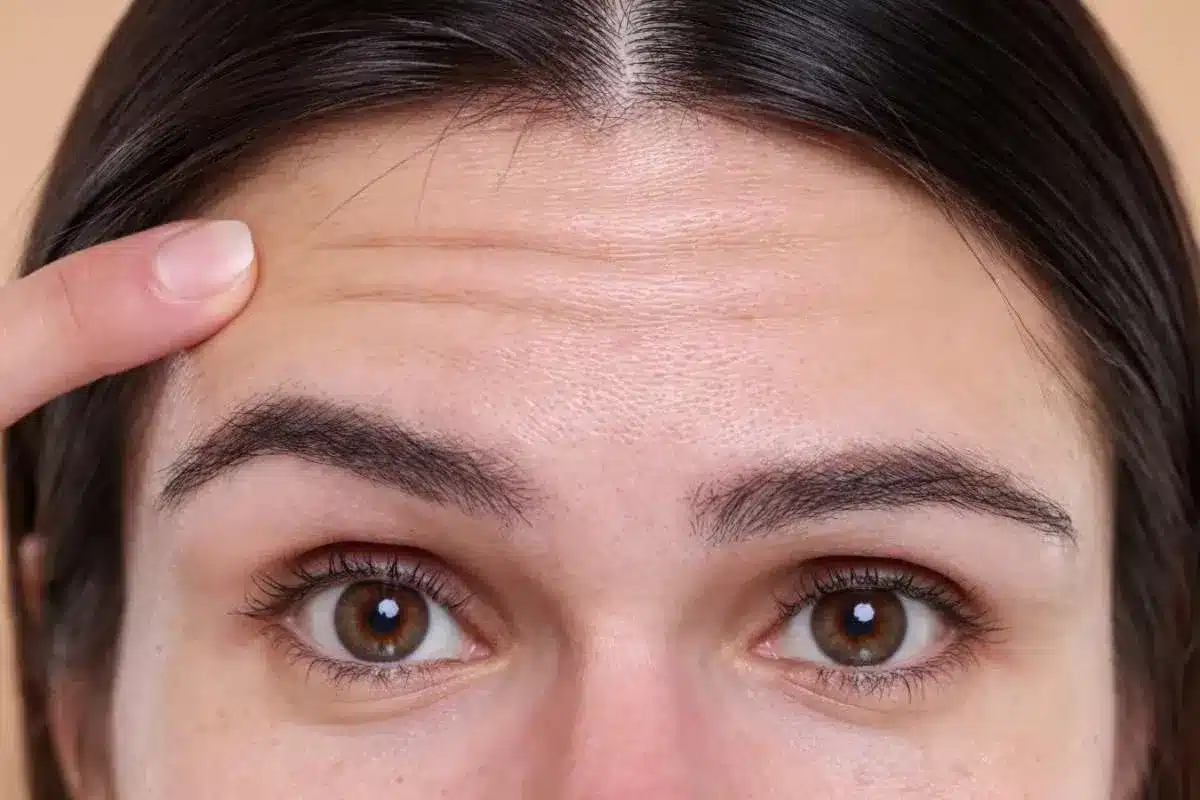
A forehead lift, or brow lift, is a key procedure for refreshing the upper face. It lifts the brow and forehead tissues that have gradually dropped over time. The surgery raises the eyebrows to a more youthful, alert position and smooths the forehead.
Surgeons see this surgery as a way to restore the entire upper third of the face. It does more than just tighten skin it helps bring the eyebrows, eyelids, and hairline back into balance. The aim is to reduce the heavy, tired, or angry look that can come from a low brow.
This surgery works deep under the skin to release the ligaments and muscles that pull the brow down. By changing these muscles, the lift lasts longer and stands up to gravity and repeated facial movements. It acts as a reset for the aging forehead.
Today’s techniques focus on a gentle, natural-looking lift instead of an overly tight look. Surgeons now use methods that fit each person’s unique features and gender, so your appearance is refreshed but still looks like you.
The forehead and upper eyelids work closely together. Sometimes, what looks like extra skin on the upper eyelid is actually caused by the eyebrow dropping and pushing the skin down. If only the eyelid is treated and the brow is not lifted, the results may not be as good, and the brow could drop even more.
A forehead lift takes the weight off the upper eyelids. This often means less skin needs to be removed if you have eyelid surgery. Sometimes, lifting the brow alone tightens the skin enough that eyelid surgery is not needed.
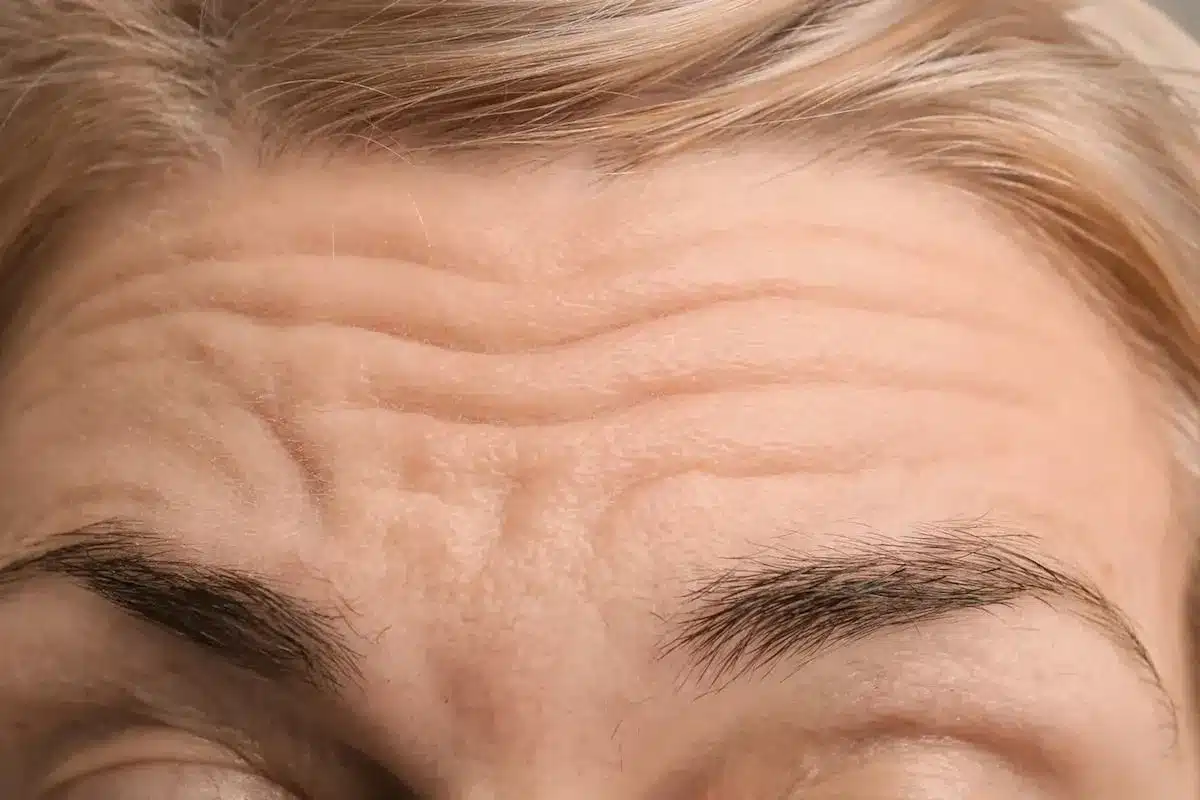
The forehead muscles also play a role. If the brow is heavy, the frontalis muscle has to work harder to keep your eyes open, which can cause deep horizontal worry lines.
Lifting the brow with surgery takes away the need for the frontalis muscle to keep contracting. This lets the forehead skin smooth out on its own and may mean you need fewer future treatments like Botox. The surgery addresses the root cause of the wrinkles, not just the lines themselves.
The endoscopic forehead lift is now the top choice for minimally invasive upper facial surgery. It uses small cuts hidden in the hairline and a tiny camera to see the tissues underneath. This lets the surgeon release and move tissues without making a long incision across the scalp.
Surgeons use special tools to free the brow from the bone and adjust the muscles that cause frown lines. The tissues are lifted and held in place with small internal devices. This approach leads to less scarring, less numbness, and a quicker recovery than older open surgeries.
A temporal brow lift targets just the outer third, or tail, of the eyebrow. This part often drops first, making you look sad or tired. This method works well for people whose central brow is still high but who have sagging at the sides.
The surgeon makes cuts in the hair at the temples, then lifts the skin and tissue diagonally. This opens up the eyes and smooths crow’s feet. It’s a less invasive option and can sometimes be done with just local anesthesia.

The coronal brow lift is the classic open method, using a long incision from ear to ear across the top of the head. Although it’s less common now because of endoscopic lifts, it’s still useful for certain cases. It works especially well for people with a low forehead who want their hairline raised.
This approach lets the surgeon see and adjust the forehead muscles and skin directly. A strip of scalp is removed, which lifts the eyebrows and smooths the forehead. It gives the most dramatic and long-lasting lift, but leaves a longer scar and may change how the scalp feels.
The gliding brow lift is a newer, less invasive way to lift the brow. The surgeon loosens the skin of the forehead and brow through small entry points, without going deep under the bone. The skin is then moved up and held in place with a special suture net.
This method works by letting the skin settle and stick in its new position. It’s a good choice for people with thin hair or those who can’t have deeper surgery. It gives a moderate lift and has little risk to the deeper nerves.
If you have a naturally high forehead, lifting the brow can move the hairline back even more, which may look unbalanced. The pretrichial, or hairline, incision solves this by placing the cut right along the front hairline.
This lets the surgeon remove skin from the upper forehead instead of the scalp. It lifts the brow and can lower or keep the hairline in place. This is important for keeping facial balance in people with a high forehead.
The position of your brow affects how you express emotions without words. A low, flat brow can make you look tired or sad, while deep lines between the brows can look like anger or stress. A forehead lift helps reset these signals.
The goal is to give you a neutral, pleasant look at rest. Lifting the brow and relaxing the muscles that pull it down makes your face look more open and friendly. This helps your appearance match how you feel inside, which is important for satisfaction.
Today’s standards focus on a natural brow shape, not an overly high one. Lifting the brow too much can make you look surprised. Surgeons plan the lift so your brow sits just right for your face, usually on or just above the bone around the eye.
Symmetry is important, but most people naturally have some unevenness in their brows. The surgery can lift one side more than the other to improve balance, but perfect symmetry isn’t natural. The aim is to create a balanced, harmonious look.
The forehead is just one part of the upper third of your face. When planning a forehead lift, surgeons also consider the middle and lower face. Lifting the upper face can make aging in other areas more noticeable, so a full-face assessment is important.
Surgeons use the rule of thirds to keep the forehead in proportion with the nose and chin. They also adjust the brow’s curve to match the cheekbones and jawline. This approach helps create a balanced, natural-looking result.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
The primary difference lies in the cancer’s origin and central location. Leukemia originates in the bone marrow and primarily affects the blood and bone marrow, circulating as liquid cancer. Lymphoma also originates from blood cells, but typically forms solid tumors in lymph nodes and other lymphoid tissues.
Lymphoma is generally not considered an inherited condition passed directly from parent to child. While having a close family member with lymphoma may slightly increase risk, the vast majority of cases arise from acquired genetic mutations that occur during a person’s lifetime due to environmental factors, infections, or random errors in cell division.
The main types are Metabolic Acidosis (too much acid, often kidney-related), Metabolic Alkalosis (too much base), Respiratory Acidosis (too much carbon dioxide from slow breathing), and Respiratory Alkalosis (too little carbon dioxide from fast breathing).
You should see a nephrologist if blood tests show a persistent acid-base problem, especially if you have an existing kidney condition like Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) or if the disorder is metabolic. They specialise in the complex role the kidneys play in regulating pH.
Nephrology focuses on the kidney’s role in the long-term regulation of base (bicarbonate) and acid excretion. Pulmonology focuses on the lung’s role in the rapid regulation of carbon dioxide levels. Both are vital, but handle different parts of the Acid-Base control system.


Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)