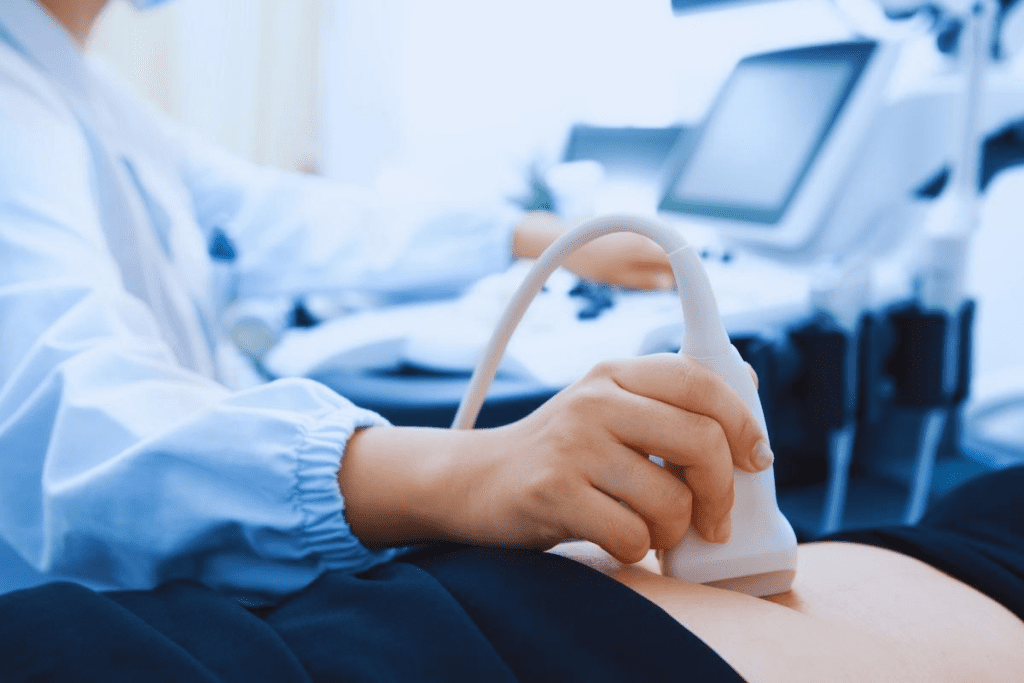
Ovarian cancer is a big health worry, with nearly 20,000 new cases in the United States each year. It often grows quietly, making early detection key for treatment. Understanding the possibility of an early ovarian cancer cure is important for both patients and doctors, as it offers hope and guides treatment decisions.
Early detection can greatly improve the five-year survival rate for ovarian cancer. We will look at the different treatments and why finding cancer early is so important for success.
Key Takeaways
- Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed late, making early detection critical.
- The five-year survival rate improves a lot with early detection.
- There are many treatment options, based on the cancer’s stage and type.
- Understanding early detection’s importance can lead to better results.
- We are dedicated to giving full support to international patients.
Understanding Ovarian Cancer
It’s important to know about ovarian cancer to catch it early and treat it well. Ovarian cancer starts in the ovaries, which are key parts of the female body.
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer happens when cells in the ovary grow too much and don’t stop. This forms a tumor. These cells can harm the area around them. If not treated, they can spread to other parts of the body.
Types of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer comes in different types, based on where it starts. The main types are:
- Epithelial ovarian cancer: This is the most common, starting from the outer ovary layer.
- Germ cell ovarian cancer: These cancers start in egg-producing cells.
- Stromal ovarian cancer: This starts in the tissue that supports the ovary.
Risk Factors
Some things can make a woman more likely to get ovarian cancer. These include:
- Family history: Having a close relative with ovarian cancer raises your risk.
- Genetic mutations: Having certain genes, like BRCA1 and BRCA2, increases your risk a lot.
- Age: Your risk goes up with age, more so after 50.
- Reproductive history: Not having kids or having them late can raise your risk.
Knowing these risk factors helps you understand your own risk. It can guide you in making health choices.
Stages of Ovarian Cancer
Early detection is vital in managing ovarian cancer. The disease progresses through different stages. Knowing these stages helps doctors choose the right treatment.
Cancer Limited to Ovaries
Stage 1 ovarian cancer is treatable and has a better prognosis. Survival rates for Stage 1 are higher. We’ll look at Stage 1’s subtypes and treatment options.
Cancer Spread Within Pelvis
Stage 2 ovarian cancer has spread to the pelvis. It’s considered early but more complex. Treatment may include surgery and other therapies.
Cancer Spread to Abdomen
Stage 3 ovarian cancer has spread to the abdomen. It’s divided into subcategories. Cancer may reach the abdomen’s lining or lymph nodes, requiring aggressive treatment.
Distant Metastasis
Stage 4 is the most advanced stage. Cancer has spread to distant areas like the liver or lungs. Treatment aims to improve quality of life at this stage.
Knowing the cancer’s stage is key for treatment and prognosis. We’ll discuss how stage impacts treatment and outcomes next.
Early Ovarian Cancer Cure: Is It Possible?

Early detection is key to curing ovarian cancer. When caught early, treatment success rates soar. We’ll look at what makes early-stage ovarian cancer treatable and the outcomes for patients.
Definition of “Cure” in Cancer Treatment
In cancer, “cure” means no cancer cells left, making the patient cancer-free. But, “cure” doesn’t always mean cancer won’t come back. Remission is more common, showing cancer has shrunk or gone away. We use “cure” carefully, as it means no cancer for a long time.
Cure Rates for Stage 1 Ovarian Cancer
Stage 1 ovarian cancer has better cure rates. Studies show a five-year survival rate of 70% to over 90%. This depends on the tumor and the patient’s health.
Factors Affecting Curability
Several things impact ovarian cancer’s curability:
- The stage at diagnosis
- Tumor grade and histology
- Patient’s age and overall health
- Effectiveness of the treatment plan
Knowing these factors helps us create better treatment plans. This boosts patients’ chances of long-term remission or cure.
Symptoms and Early Detection
Spotting ovarian cancer early can save lives. But, it’s hard because the symptoms are not always clear. Knowing the early signs helps people get help faster.
Common Early Symptoms
Ovarian cancer’s symptoms are often not obvious. They can be like other health issues. Early signs include:
- Pelvic or abdominal pain
- Bloating or swelling in the abdomen
- Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly
- Urinary symptoms such as urgency or frequency
These signs don’t just mean ovarian cancer. They can also point to other health problems. But, if they keep happening or get worse, see a doctor.
Why Early Detection is Challenging
Finding ovarian cancer early is hard. The symptoms are not clear and can be mistaken for other issues. There’s no good screening test for everyone yet.
Scientists are working on better tests. They want to find new ways to spot cancer early. Until then, knowing the risks and symptoms is key.
When to See a Doctor
If you keep feeling bad and it worries you, see a doctor. They can check you out and suggest tests if needed.
People with a family history or genetic risk should talk about screening with their doctor. It’s very important.
| Symptom | Description | Action |
| Pelvic or abdominal pain | Persistent pain or discomfort in the pelvic or abdominal region | Consult a healthcare provider if the pain persists |
| Bloating or swelling | Noticeable bloating or swelling in the abdomen | Seek medical attention if the symptom doesn’t resolve |
| Urinary symptoms | Urgency or frequency in urination | Discuss with a healthcare provider if symptoms are persistent or severe |
Diagnostic Methods for Early Ovarian Cancer
There are several ways to find ovarian cancer early. Finding it early is key to better treatment and survival. Let’s look at how we can detect it early.
Physical Examination
A physical check is often the first step. A healthcare provider looks for any unusual things in the pelvic area. Pelvic exams are important for finding tumors that might be ovarian cancer.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are very important for diagnosing ovarian cancer. They help find out how big and where tumors are. Some common tests are:
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to see the ovaries.
- CT Scan: Gives detailed pictures of the belly and pelvis.
- MRI: Shows detailed pictures of inside structures.
Blood Tests and Biomarkers
Blood tests check for certain markers linked to ovarian cancer. The main marker is CA-125. High CA-125 levels might mean ovarian cancer, but it’s not the only disease it shows up in.
| Biomarker | Description | Significance |
| CA-125 | A protein often elevated in ovarian cancer | Used for monitoring treatment response and detecting recurrence |
| HE4 | A protein that can be elevated in ovarian cancer | Used in conjunction with CA-125 for improved diagnostic accuracy |
Surgical Diagnosis
Surgery is used to get tissue samples for tests. Laparoscopy or laparotomy let doctors see and take samples from the ovaries. This method gives a clear diagnosis and helps figure out how far the cancer has spread.
Knowing about these methods is key for early detection and managing ovarian cancer. By using physical exams, imaging, blood tests, and surgery, doctors can create a treatment plan that fits each patient’s needs.
Treatment Options for Early Stage Ovarian Cancer
Being diagnosed with early-stage ovarian cancer can feel overwhelming. Let’s look at the treatment options available. The right treatment depends on several factors. These include the cancer’s stage and type, the patient’s health, and their preferences.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is often the first step in treating early-stage ovarian cancer. The goal is to remove the tumor and any affected tissue. We perform surgical staging to determine the extent of the cancer, which helps in planning further treatment.
The types of surgical interventions include:
- Total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy
- Unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy for fertility preservation
- Omentectomy to remove the omentum, a layer of tissue that can be affected by cancer
- Lymph node dissection to check for cancer spread
Chemotherapy Protocols
Chemotherapy may be recommended after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells. The choice of chemotherapy drugs depends on the type and stage of ovarian cancer. Common chemotherapy protocols for early-stage ovarian cancer include:
| Chemotherapy Regimen | Description | Cycle Duration |
| Carboplatin + Paclitaxel | A combination of carboplatin and paclitaxel is a standard first-line treatment | 21 days |
| Carboplatin + Docetaxel | An alternative regimen that may be used based on patient tolerance and response | 21 days |
Targeted Therapies
Targeted therapies target specific genes or proteins involved in cancer growth. PARP inhibitors are an example of targeted therapy used in ovarian cancer treatment, mainly for patients with BRCA mutations.
We are always working to improve our understanding and use of targeted therapies. This is to better outcomes for patients with early-stage ovarian cancer.
Fertility-Sparing Surgery for Young Women
Fertility-sparing surgery is a big deal for young women with ovarian cancer. It lets them keep their ability to have kids. This gives them hope and options for the future.
Candidates for Fertility Preservation
Not every woman with ovarian cancer can have fertility-sparing surgery. The choice depends on the cancer’s stage, type, and the woman’s health.
Women with early-stage ovarian cancer (Stage I) might be good candidates. We look at each case carefully. We consider the woman’s health and if she wants kids in the future.
Surgical Techniques
This surgery removes the bad ovary but keeps the healthy one and uterus. There are different ways to do this, like:
- Unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy: Taking out one ovary and fallopian tube.
- Conservative management: Keeping the uterus and part of one ovary.
The right technique depends on the cancer’s size and where it is.
Pregnancy Outcomes After Treatment
Research shows women who have this surgery can get pregnant. Here are some results:
| Study | Number of Patients | Number of Pregnancies | Pregnancy Rate |
| Study A | 50 | 15 | 30% |
| Study B | 75 | 25 | 33.3% |
| Study C | 100 | 40 | 40% |
These numbers show fertility-sparing surgery works for young women with ovarian cancer who want kids.
Survival Statistics for Early Ovarian Cancer
Early ovarian cancer survival stats give us important insights. They show how well treatments work. Knowing these stats helps patients and doctors make better choices.
5-Year Survival Rates by Stage
The 5-year survival rate is a key measure for ovarian cancer patients. It shows the percentage of people who live at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
| Stage at Diagnosis | 5-Year Survival Rate |
| Stage I | 90% |
| Stage II | 70% |
| Stage III | 39% |
| Stage IV | 17% |
The table shows how survival rates change with the stage of cancer. For Stage I, the survival rate is about 90%. This shows how critical early detection is.
Factors Affecting Survival
Many things can change a patient’s survival chances. These include:
- Age: Older patients often face a tougher fight.
- Overall Health: Patients with other health problems may struggle more.
- Tumor Characteristics: The type and grade of the tumor matter a lot.
- Treatment Response: How well the cancer responds to treatment is key.
Long-term Outlook
The outlook for early ovarian cancer patients is usually good. This is thanks to better treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies. These have helped increase survival rates.
We keep watching survival stats to learn more about the disease. This helps us improve care for ovarian cancer patients. By staying up-to-date with new research and treatments, we can offer the best care possible.
Recurrence Risk and Monitoring
Knowing the risk of cancer coming back is key for those with early-stage ovarian cancer. After treatment, the worry of cancer returning is big for both patients and doctors.
Recurrence Patterns in Early-Stage Disease
How often cancer comes back in early-stage ovarian cancer can change. It depends on the first stage, tumor type, and treatment used. Usually, the risk of coming back is higher in the first few years after treatment.
Key factors influencing recurrence risk include:
- The stage and grade of the tumor at diagnosis
- The effectiveness of the initial treatment
- Genetic factors, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations
Follow-up Protocols
Regular check-ups are vital for watching for cancer coming back and finding problems early. These check-ups include:
- Regular physical exams and checking medical history
- Imaging tests, like ultrasound or CT scans, as the doctor suggests
- CA-125 blood tests to watch tumor marker levels
These visits get less frequent over time but are a big part of caring for ovarian cancer survivors long-term.
Living with the Emotional Impact
Ovarian cancer can bring many emotions, like fear and hope. It affects patients and their families deeply. We must recognize the emotional burden it carries.
Coping with Diagnosis and Treatment
Dealing with ovarian cancer needs a mix of physical and emotional care. Support from family, friends, and healthcare providers is key. Looking for support groups can help find comfort with others facing similar challenges.
One survivor shared,
“The diagnosis was like a storm that shook my world, but finding support was like finding an anchor that held me steady.”
This shows how vital a strong support system is.
Managing Fear of Recurrence
Fear of cancer coming back is common. To manage it, regular check-ups, mindfulness, and staying in touch with others help. Talking about fears with healthcare teams can offer reassurance and advice.
Support Resources
Many resources help with ovarian cancer’s emotional side. These include:
- Counseling for cancer patients
- Online forums and support groups
- Materials on managing stress related to cancer
- Mindfulness and relaxation techniques
Using these resources can greatly improve life for those with ovarian cancer. By acknowledging the emotional impact and providing support, we help them face this tough journey better.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing ovarian cancer involves managing risk factors and using genetic testing. We can’t remove all risk, but we can lower it by tackling things we can control.
Risk Factors You Can Control
Some lifestyle choices and health conditions can raise your risk. For example, being overweight can increase your risk of ovarian cancer. Eating well and exercising can help keep your weight in check.
Smoking also raises your risk, even more so if you have certain genetic mutations. It’s linked to many health problems, including ovarian cancer.
Key controllable risk factors include:
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Use of certain hormone therapies
Protective Factors
Some things can help protect you from ovarian cancer. Taking birth control pills, for instance, can lower your risk. The more you use them, the more protection you get.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding also offer some protection. The more children you have, the lower your risk becomes.
| Protective Factor | Description | Impact on Risk |
| Oral Contraceptives | Use of birth control pills | Reduces risk, effect increases with duration |
| Pregnancy | Having children | Reduces risk, more pregnancies = lower risk |
| Breastfeeding | Nursing infants | May reduce risk |
“The use of oral contraceptives has been one of the most consistent and well-documented protective factors against ovarian cancer.” – American Cancer Society
Genetic Testing and Counseling
Women with a family history of ovarian or breast cancer should consider genetic testing. This can reveal mutations in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2, which increase ovarian cancer risk. Genetic counseling helps make sense of these results and guides risk management.
Genetic testing is a blood test for specific gene mutations. If a mutation is found, your doctor can discuss ways to lower your risk. This might include preventive surgery or closer monitoring.
By managing risk factors, using protective measures, and getting genetic testing and counseling, women can reduce their ovarian cancer risk.
Latest Research and Treatment Advances
Recent breakthroughs in ovarian cancer research have opened new avenues for treatment and improved patient outcomes. We are witnessing a significant shift in the approach to ovarian cancer treatment, driven by advances in medical research and technology.
Immunotherapy Developments
Immunotherapy, which harnesses the power of the immune system to fight cancer, has shown great promise in treating ovarian cancer. Checkpoint inhibitors, a type of immunotherapy, work by releasing the brakes on the immune system, allowing it to attack cancer cells more effectively.
- PD-1 inhibitors: These have shown efficacy in ovarian cancer, particular in patients with specific genetic markers.
- Cancer vaccines: Researchers are working on developing vaccines that can prevent or treat ovarian cancer by stimulating the immune system.
PARP Inhibitors
PARP inhibitors are a class of drugs that have revolutionized the treatment of ovarian cancer, particular for patients with BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. These drugs work by blocking an enzyme called PARP, which cancer cells use to repair their DNA.
- Maintenance therapy: PARP inhibitors are used as maintenance therapy after initial chemotherapy to reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Combination therapy: Researchers are exploring the use of PARP inhibitors in combination with other treatments, such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy.
Promising Clinical Trials
Several clinical trials are underway, investigating new and innovative treatments for ovarian cancer. Some of the most promising areas of research include:
- Targeted therapies: Drugs that target specific genetic mutations or pathways involved in ovarian cancer.
- Angiogenesis inhibitors: Drugs that prevent the formation of new blood vessels, which feed the growth of tumors.
These advances in ovarian cancer research and treatment are giving new hope to patients and their families. As we continue to push the boundaries of medical knowledge, we are optimistic about the future of ovarian cancer treatment.
Conclusion
Early detection is key to beating ovarian cancer. Knowing about treatment options helps patients make better choices. We’ve looked at ovarian cancer’s stages, symptoms, and how to find it early.
Thanks to new treatments, survival rates are getting better. This includes surgery, chemo, and targeted therapies. Young women can even keep their ability to have kids with special surgeries.
Early detection and the right treatment are vital. Knowing the risks and symptoms helps people get help fast. We urge everyone to stay informed and talk to doctors if they’re worried about ovarian cancer.
FAQ
Can ovarian cancer be cured if caught early?
Yes, catching ovarian cancer early can lead to a cure. The cure rate for Stage 1 ovarian cancer is much higher.
What are the symptoms of ovarian cancer?
Symptoms of ovarian cancer include bloating, pelvic pain, and trouble eating. They can also cause frequent urination. But, these signs are often not specific and may appear late.
How is ovarian cancer diagnosed?
Doctors use physical exams, imaging tests like ultrasound and CT scans, and blood tests. They also perform surgical diagnosis to find ovarian cancer.
What are the treatment options for early-stage ovarian cancer?
Early-stage ovarian cancer can be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, or targeted therapies. The best option depends on the cancer’s stage, type, and the patient’s health.
Can fertility be preserved in young women with ovarian cancer?
Yes, young women with early ovarian cancer can try fertility-sparing surgery. This method helps keep fertility while treating the cancer.
What are the survival statistics for early ovarian cancer?
The 5-year survival rate for Stage1 ovarian cancer is high. It ranges from 70% to over 90%, depending on the stage and other factors.
What is the risk of recurrence in early-stage ovarian cancer?
The risk of recurrence in early-stage ovarian cancer varies. It depends on the stage, cancer type, and other factors. Regular follow-ups are key to catch any recurrence early.
How can ovarian cancer be prevented?
While we can’t prevent ovarian cancer entirely, we can lower the risk. Maintaining a healthy weight and using oral contraceptives help. Genetic testing also plays a role.
What are the latest research and treatment advances in ovarian cancer?
New treatments for ovarian cancer include immunotherapy and PARP inhibitors. Clinical trials are also showing promise. These advances offer hope for better treatment outcomes.
What is the long-term outlook for ovarian cancer survivors?
The long-term outlook for ovarian cancer survivors varies. It depends on the stage at diagnosis, treatment success, and overall health. Regular follow-up care is vital to manage any long-term effects and watch for recurrence.
References
- Patni, R., & Skates, S. J. (2019). Screening for Ovarian Cancer: An Update. Current Oncology Reports, 21(3), 25. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6459072/
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. (2025). NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Ovarian Cancer. https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail?category=1&id=1459
- British Gynaecological Cancer Society. (2017). BGCS Ovarian Cancer Guidelines. https://www.bgcs.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/BGCS-Guidelines-Ovarian-Guidelines-2017.pdf




































