Surgical care is a complex process. It involves many stages to ensure patient safety and optimal recovery.
The journey of surgical care has five distinct stages. These are preoperative, pre-anesthesia, intraoperative, post-anesthesia, and postoperative. Each stage is key to the success of a surgical procedure.
It’s important for healthcare providers to know these stages. This knowledge helps them deliver high-quality care and reduce complications. As surgery rates go up worldwide, hospitals are finding new ways to improve patient outcomes and experiences.
Key Takeaways
- The five stages of surgical care are preoperative, pre-anesthesia, intraoperative, post-anesthesia, and postoperative.
- Each stage is vital for patient safety and recovery.
- Understanding these stages is key to delivering top-notch surgical care.
- Hospitals are innovating to improve patient outcomes and experiences.
- The surgical care pathway covers every step from scheduling to full recovery.
The Complete Surgical Care Pathway
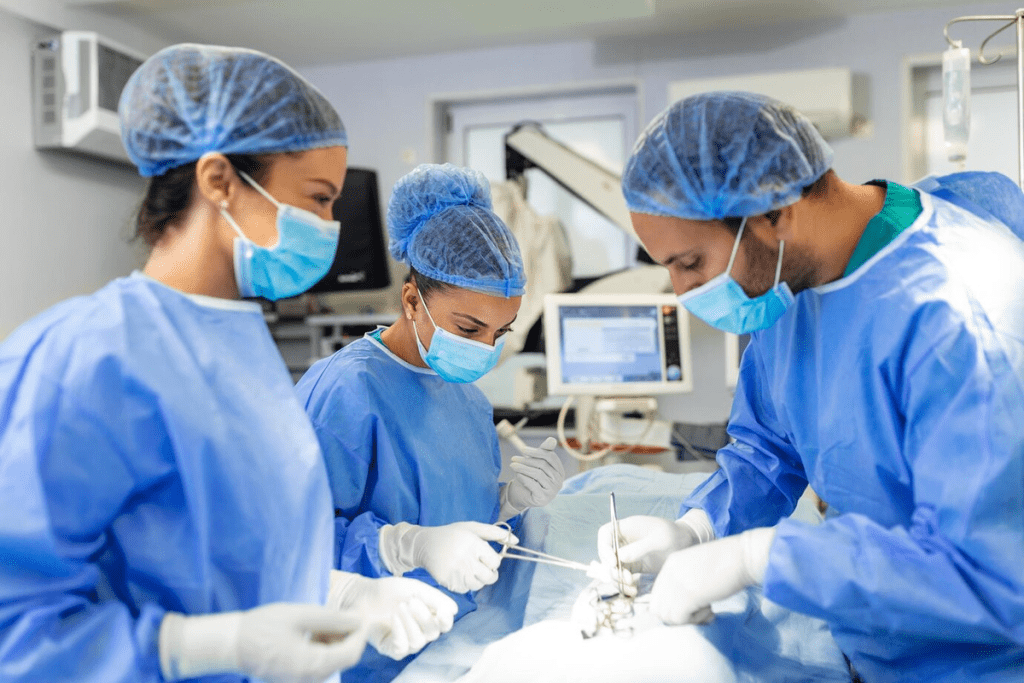

Surgical procedures happen over 313 million times worldwide each year. They need a well-planned care pathway to lower risks. A structured approach ensures patient safety and the best results.
Global Statistics on Surgical Procedures
The World Health Organization points out the big problem of surgical complications. Over 14% of hospital adverse events are due to surgery. This shows we need a strong surgical care pathway.
Worldwide, half a million deaths from surgery could be avoided each year. This is with safety checklists and clear care plans. It shows how vital a complete surgical care pathway is.
Why Structured Surgical Care Matters
A structured surgical care pathway is key to better patient results. It makes care more consistent, lowering the chance of problems during and after surgery.
The WHO Surgical Safety Checklist is a big part of this. It has been proven to cut down on complications and make patients safer. It makes sure all important steps are taken.
- Enhances patient safety
- Reduces surgical complications
- Improves communication among the surgical team
Stage 1: Preoperative Care – Preparing for Surgery
Preoperative care is the first step in the surgical journey. It focuses on checking the patient and getting ready for surgery. This stage is key to making sure patients are ready, reducing risks, and improving results.
Patient Assessment and Medical History
Checking the patient thoroughly is important at this stage. Doctors look at the patient’s medical history and current health. They also check for any risks related to the surgery. Diagnostic tests and examinations help find any hidden conditions that might affect the surgery.
The patient’s past health is closely examined. This includes any past surgeries, allergies, or ongoing health issues. Knowing this helps doctors plan the surgery better and reduces the chance of problems.
Patient Education and Informed Consent
Teaching patients is a big part of preoperative care. They learn about their surgery, including what will happen, possible risks, and what to expect. This helps them make smart choices about their care and get ready for recovery.
Informed consent comes after patients are fully informed. This makes sure they understand their treatment and agree to it. It’s a big part of caring for the patient and letting them make their own health choices.
By focusing on patient checks, medical history, and education, the preoperative stage lays the groundwork for a good surgery. Good preoperative care can greatly improve patient outcomes. It can lower the risk of problems and make patients happier with their surgery experience.
Stage 2: Pre-anesthesia Phase – Final Preparations
In the pre-anesthesia phase, careful planning and checks are done to ensure the best surgical conditions. This stage is key to making sure the patient is ready for anesthesia and the surgery that follows.
Pre-surgical Checklists and Safety Protocols
Pre-surgical checklists are vital for safety in the pre-anesthesia phase. They help confirm the patient’s identity, the surgical site, and that all needed equipment is ready and working. By using these checklists, surgical teams can lower the risk of problems during surgery.
It’s also important to follow safety protocols, like checking the patient’s medical history and current medications. This helps spot any risks related to anesthesia and surgical procedures. It allows for the right steps to be taken.
Anesthesia Planning and Patient Preparation
Anesthesia planning is about choosing the right type of anesthesia for the patient. This depends on the patient’s health, the surgery type, and what the patient prefers. Good planning is essential for the patient’s comfort and safety during the surgery.
Preparing the patient is also critical in this phase. This includes teaching them about the anesthesia process, discussing risks and benefits, and getting their consent. Proper preparation can help reduce anxiety and improve results.
By focusing on detailed checklists, safety protocols, and thorough anesthesia planning, healthcare providers can make the transition to surgery smooth and safe. This helps lead to a successful surgery and recovery.
Stage 3: Intraoperative Care – The Surgery Process
Intraoperative care is when the surgery happens. It’s all about watching the patient closely and following safety rules. This part is key because it’s when the surgery plan is put into action. The team must work together and stay alert.
Surgical Team Roles and Responsibilities
The surgical team is very important in this stage. Teamwork is essential for a successful surgery. The team includes:
- The surgeon and surgical residents
- Anesthesiologist and nurse anesthetist
- Surgical nurses and surgical technologists
Each team member has their own job. They do everything from the surgery itself to keeping the patient safe. Good communication is crucial to avoid problems.
Patient Monitoring During Active Surgery
Keeping an eye on the patient is key during surgery. The anesthesiologist and nurses watch the patient’s heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. Advanced monitoring technologies help get real-time data for quick decisions.
They also watch the anesthesia levels to keep the patient comfortable and pain-free. They adjust as needed to keep everything right.
Intraoperative Safety Measures and Protocols
Safety is the top priority during surgery. Checklists and safety timeouts help make sure everything is correct. They check the patient’s identity, the surgical site, and that all equipment is ready and working.
“The use of checklists in surgery has been shown to reduce complications and improve patient outcomes by ensuring that critical steps are not missed.”
Following sterilization and hygiene protocols is also key to avoiding infections. The team follows strict rules for dressing, gloving, and keeping everything clean.
By focusing on teamwork, careful patient watching, and following safety rules, the surgery can go well. This leads to good results for the patient.
Stage 4: Post-anesthesia Care – Immediate Recovery
The post-anesthesia phase is a key part of the surgical procedure journey. It focuses on making sure the patient is stable and recovering well. Good care during this time is essential to avoid problems and make the next steps smoother.
Post-Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU) Management
The Post-Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU) is where patients are watched closely as they recover from anesthesia. Effective PACU management needs a team that can handle the challenges of recovery.
The main goals of PACU care are to keep patients comfortable, watch their vital signs, and catch any issues early. This is done by:
- Keeping an eye on vital signs and oxygen levels
- Managing pain and discomfort
- Using oxygen therapy when needed
- Acting fast if complications arise
Identifying and Managing Post-surgical Complications
Even with the best care, complications can happen after surgery. It’s important to spot these problems early to deal with them quickly. Issues like breathing problems, heart issues, and infections at the surgery site are common.
Effective management means having plans in place for quick detection and action. This includes:
- Regular checks on the patient’s health
- Using scoring systems to spot issues early
- Getting specialists involved when needed
By focusing on these areas, healthcare teams can greatly improve how patients do after anesthesia.
Stage 5: Postoperative Care – Long-term Recovery
The final stage of surgical care is key to a patient’s full recovery. It includes many activities to help the patient get back to health.
Hospital Recovery and Discharge Planning
Good hospital care and planning for discharge are very important. Healthcare teams must give patients the right treatment and support while they’re in the hospital. This means managing pain, watching for problems, and teaching patients about care after they leave.
A smooth discharge process helps avoid going back to the hospital. It makes sure patients can easily move to home care.
Follow-up Care and Rehabilitation
Follow-up care and rehab are essential after surgery. Regular visits help doctors check on patients and make changes to care plans if needed. Rehab, like physical therapy, helps patients get stronger and move better.
Putting a focus on rehabilitation and long-term care is important. With the right support, patients can fully recover and get back to their daily lives.
Improving Patient Outcomes Through Modern Surgery Protocols
Modern surgery protocols have changed patient care for the better. They have made patient safety and outcomes much better. This is thanks to the use of standardized protocols in surgical care.
WHO Surgical Safety Checklist Implementation
The World Health Organization’s (WHO) surgical safety checklist is a key tool in modern surgery. It has been shown to cut down on complications by over 30%. The checklist makes sure surgical teams follow a set process, reducing errors and oversights.
The WHO surgical safety checklist includes important parts:
- Preoperative checks to verify patient identity and the surgical site
- Review of patient medical history and allergies
- Confirmation of surgical plans and equipment readiness
How Standardized Protocols Reduce Complications
Standardized protocols in surgical care are vital in cutting down complications. By sticking to established guidelines, surgical teams can lower surgery risks. Standardized protocols help in several ways:
- They improve communication among the surgical team
- They ensure thorough preoperative checks
- They enhance patient monitoring during and after surgery
Standardized protocols not only improve patient outcomes but also make surgery safer and more efficient. By using these protocols, healthcare facilities can greatly lower surgical complication rates.
The benefits of modern surgery protocols are clear. By adopting these protocols, the surgical community can keep improving patient care and outcomes. The WHO surgical safety checklist’s success shows the big impact of standardized protocols.
Conclusion
The five stages of surgical care are key to patient safety and recovery. Knowing what surgery means is important for everyone involved. A structured surgical care pathway helps hospitals lower complications and improve results.
Liv Hospital is a great example of putting patient safety first. They use the latest surgical methods and focus on the patient. This shows how important a well-planned surgical process is.
Healthcare places that focus on safety and use modern surgery methods improve care quality. This leads to better results for patients and builds trust in healthcare.
FAQ’s:
What are the five stages of surgical care?
The five stages are preoperative care, pre-anesthesia phase, intraoperative care, post-anesthesia care, and postoperative care. These stages are key to patient safety and recovery.
Why is structured surgical care important?
It’s vital for reducing complications and improving patient outcomes. Safety protocols, like the WHO checklist, ensure quality care throughout the process.
What happens during the preoperative stage?
Patients are assessed, their medical history reviewed, and they’re educated. This stage prepares them for surgery and ensures informed consent.
What is the role of the surgical team during intraoperative care?
The team ensures patient safety and optimal outcomes. They monitor patients, maintain a sterile environment, and follow safety protocols.
What is post-anesthesia care, and why is it important?
It’s the immediate recovery phase after surgery. Patients are closely monitored for complications. This stage is critical for managing post-surgical issues.
How do modern surgery protocols improve patient outcomes?
Protocols like the WHO checklist reduce complications and improve safety. They standardize care, ensuring high-quality treatment throughout the process.
What is the significance of follow-up care after surgery?
Follow-up care is vital for monitoring patients’ progress and addressing concerns. It supports rehabilitation and ensures optimal recovery and long-term health.
What is the surgical care pathway?
It’s a structured plan outlining the stages of surgical care. It ensures patients receive coordinated care from preparation to recovery. Surgery involves manual or instrumental treatment of bodily parts, often through incision or excision.
What is a surgical procedure?
A surgical procedure is a medical intervention that treats bodily parts. It can be diagnostic, therapeutic, or reconstructive, aiming to treat various medical conditions.
References
- Davrieux, C. F. (2019). Stages and factors of the “perioperative period and the surgical process. Revista de CirugÃa, 70(1), 47-53. Retrieved fromhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6368165/
- Vickers, R. (2010). Five steps to safer surgery. BMJ Quality & Safety, 19(Suppl 1), i3“i4. Retrieved fromhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3604917/


































