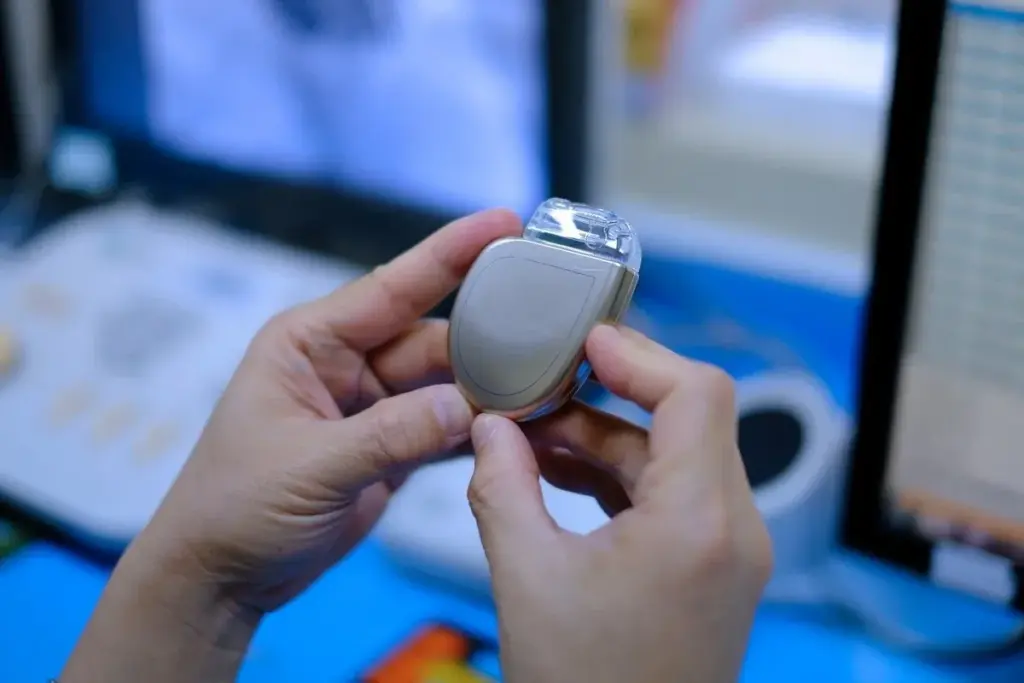
Heart rhythm disorders affect millions worldwide. Arrhythmias are a major cause of heart problems. In the United States, about 4.5 million people have arrhythmias. This shows we need good treatment options.
What pacemaker do you need? Get best 3 vital options. From single to biventricular, find the amazing device that suits your heart best.
An implantable cardiac device called a pacemaker is key in treating heart rhythm issues. We will look at the three main types of pacemakers. They help bring back a normal heart rhythm.
Key Takeaways
- Pacemakers are a crucial treatment option for heart rhythm disorders.
- There are three main types of pacemakers used in arrhythmia treatment.
- These implantable devices help regulate heart rhythm and restore normal heart function.
- Understanding the different types of pacemakers is essential for effective treatment.
- Pacemakers have revolutionized the management of arrhythmias worldwide.
Understanding Heart Rhythm Disorders
It’s important to know about heart rhythm disorders to diagnose and treat them. These disorders, or arrhythmias, happen when the heart’s electrical system gets disrupted. This leads to irregular heartbeats.
“The heart’s electrical system is a complex network that controls the heartbeat,” says a leading cardiologist. “When it works right, the heart beats regularly, pumping blood well throughout the body.”
Common Arrhythmias That Require Pacemaker Intervention
Some common arrhythmias that may need a pacemaker include:
- Atrial fibrillation, characterized by rapid and irregular heartbeats
- Bradycardia, or a slow heart rate
- Heart block, a condition where the electrical signals between the heart’s chambers are delayed or blocked
These conditions can cause symptoms like dizziness, fatigue, and shortness of breath. They can really affect a person’s quality of life.
How the Heart’s Electrical System Works

The heart’s electrical system is a complex network. It generates and conducts electrical impulses, controlling the heartbeat. This system includes the sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and the bundle of His, among others.
The SA node acts as the heart’s natural pacemaker, starting electrical impulses that trigger heart contractions. The AV node and bundle of His then send these impulses to the ventricles, ensuring a coordinated heartbeat.
When this system works right, the heart beats regularly, pumping blood well. But, when it gets disrupted, arrhythmias can happen. In these cases, a pacemaker might be needed to get the heart rhythm back to normal.
Heart Blockages: Symptoms and Diagnosis
diagnostic tests for heart blockage
It’s important to know the symptoms and how to diagnose heart blockages. These blockages, often caused by coronary artery disease, can be serious if not treated quickly.
Signs of Heart Blockage
The signs of heart blockage can vary. But common symptoms include chest pain or discomfort, known as angina. This pain feels like pressure or tightness in the chest and can spread to the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
Other symptoms might be shortness of breath, feeling very tired, and feeling lightheaded.
As one expert notes, “Recognizing the symptoms of heart blockage is the first step towards getting the necessary medical care.”
“The earlier you identify the symptoms, the sooner you can seek help,” says a cardiologist.
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Lightheadedness
Diagnostic Tests for Heart Blockage
Diagnosing heart blockage involves several tests. The most common include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): Measures the electrical activity of the heart.
- Stress Test: Evaluates how the heart functions under stress.
- Coronary Angiogram: Uses dye and X-rays to show the inside of the coronary arteries.
These tests help doctors find blockages and decide the best treatment.
How Pacemakers Regulate Cardiac Function
pacemaker technology
Pacemakers are implantable electronic devices that help manage heart rhythm disorders. They directly affect how the heart works. This shows the complexity and innovation in these devices.
The Evolution of Pacemaker Technology
Pacemaker technology has seen big changes over time. The first pacemaker was implanted in the late 1950s. Now, we have devices that can adjust heart rate based on activity.
Today’s pacemakers are smaller, last longer, and work better. These improvements have made them more efficient and less invasive. This has greatly helped patients.
Components of Modern Pacemakers
Modern pacemakers have several important parts. These parts work together to control the heart’s rhythm.
- The pulse generator is the main part. It has the battery and electronics that control the device.
- Leads are insulated wires that connect the pulse generator to the heart. They deliver electrical impulses.
- Electrodes are at the tip of the leads. They send the electrical impulses to the heart muscle.
These components help the pacemaker watch the heart’s rhythm. It steps in when needed to keep the heart rate right. The electronic device is set up for each patient’s needs, offering personalized care.
Single-Chamber Pacemaker: Features and Applications
single-chamber pacemaker
The single-chamber pacemaker is a high-tech medical device. It’s made to meet specific heart pacing needs. It works by sending electrical impulses to regulate the heartbeat.
Structure and Functioning Mechanism
A single-chamber pacemaker has a pulse generator and a lead. The pulse generator is small and battery-powered. It controls the pacing with its electronics. The lead is a wire that connects the pulse generator to the heart, sending the impulses.
When implanted, it’s usually connected to the right atrium or ventricle. It watches the heart’s rhythm and steps in when needed to keep a proper beat.
Ideal Candidates for Single-Chamber Devices
Single-chamber pacemakers are good for patients with arrhythmias like bradycardia. This is when the heart beats too slowly. They’re best for those needing pacing in just one heart chamber.
Advantages and Limitations
These pacemakers are easy to implant and have fewer hardware issues. But, they might not fit all patients. This includes those needing pacing in both chambers or with certain heart failure.
|
Feature |
Description |
Benefit |
|---|---|---|
|
Simple Implantation |
Less complex procedure |
Reduced risk of complications |
|
Single Lead |
Fewer hardware components |
Lower risk of lead-related issues |
|
Effective Pacing |
Reliable heart rhythm regulation |
Improved quality of life |
Single-chamber pacemakers are a key treatment for certain heart rhythm issues. They’re simple yet effective, making them crucial in cardiac care.
Dual-Chamber Pacemaker: Features and Applications
dual-chamber pacemaker
Dual-chamber pacemakers are a big step forward in heart pacing technology. They help patients with heart issues by regulating heart rhythm better. These devices manage both the atria and ventricles, making pacing more natural.
Structure and Functioning Mechanism
A dual-chamber pacemaker has a pulse generator and two leads. One lead is in the right atrium, and the other is in the right ventricle. This setup lets the device control both chambers, making heartbeats more coordinated and natural.
The pulse generator is where the device’s electronics are. It sends out pacing pulses and checks the heart’s electrical signals. The leads have electrodes that send pulses to the heart and send signals back to the pulse generator.
Ideal Candidates for Dual-Chamber Devices
Dual-chamber pacemakers are great for patients with heart blockages. They help those with symptomatic bradycardia or certain AV block types. They’re also good for patients needing a natural pacing mode.
Patients with sinus node dysfunction can also benefit. This condition makes the heart’s natural pacemaker not work right. The device helps keep a normal heart rhythm, reducing symptoms like dizziness and fatigue.
Advantages and Limitations
The main plus of dual-chamber pacemakers is their natural pacing. This improves heart output and reduces heart failure symptoms.
But, there are downsides. Having two leads can raise the risk of complications. The device’s programming is also more complex, needing careful adjustments.
Despite these challenges, dual-chamber pacemakers are a key treatment for many. They offer better heart rhythm control and improve life quality for patients with heart rhythm disorders.
Biventricular Pacemaker: Features and Applications
Biventricular Pacemaker
For those with certain heart failure types, biventricular pacemakers offer a life-changing treatment. These devices are part of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). They help the heart’s ventricles beat in sync, improving life quality.
Structure and Functioning Mechanism
A biventricular pacemaker is an implantable device with three leads. One is in the right atrium, one in the right ventricle, and one in the left ventricle. This setup ensures both ventricles contract together, boosting heart efficiency and reducing heart failure symptoms.
The device uses advanced algorithms to monitor and adjust the heart’s electrical activity. It sends timed electrical impulses to both ventricles. This makes them contract at the same time, increasing cardiac output.
Ideal Candidates for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
Those best suited for CRT have:
- Advanced heart failure (NYHA Class III or IV)
- Left ventricular dysfunction with an ejection fraction of 35% or less
- Evidence of ventricular dyssynchrony
- Symptoms despite optimal medical therapy
These patients often see big improvements in symptoms, quality of life, and survival rates with CRT.
Advantages and Limitations
The benefits of biventricular pacemakers include:
- Improved heart function and reduced heart failure symptoms
- Enhanced quality of life
- Potential decrease in hospital stays
But, there are also downsides and possible complications, such as:
|
Limitation/Complication |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Surgical Risks |
Infection, bleeding, and reaction to anesthesia |
|
Device-Related Issues |
Lead malfunction, device recall, or battery depletion |
|
Not Suitable for All Patients |
Some patients may not respond to CRT or have anatomical limitations |
Choosing to get a biventricular pacemaker should be a careful decision. It’s important to weigh the benefits and risks with a healthcare provider.
“The introduction of cardiac resynchronization therapy has been a game-changer for many patients with heart failure, offering them a renewed chance at a more normal life.” – A Cardiologist
Comparing the Three Types of Pacemakers
pacemaker comparison
Today, we have three types of pacemakers, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. It’s important to know how they differ. We’ll look at their effectiveness for various heart conditions, battery life, size, and how they’re placed in the body.
Effectiveness for Different Heart Conditions
Single-chamber pacemakers help with irregular heartbeats. Dual-chamber pacemakers can treat more conditions, including those needing both atria and ventricles to work together. Biventricular pacemakers, or CRT devices, help heart failure by making ventricles contract in sync.
Comparison of Pacemaker Effectiveness
|
Pacemaker Type |
Heart Condition |
Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
|
Single-Chamber |
Irregular heartbeat |
Effective for consistent arrhythmias |
|
Dual-Chamber |
Various arrhythmias |
Highly effective for coordinating atrial and ventricular contractions |
|
Biventricular |
Heart failure |
Effective in synchronizing ventricular contractions |
Battery Life and Device Longevity
Battery life is key when choosing a pacemaker. Batteries last 5 to 15 years, depending on the device and patient. Single-chamber pacemakers usually last longer because they’re simpler. But, dual-chamber and biventricular pacemakers, though more complex, have better battery technology now.
Size and Placement Considerations
The size and where the pacemaker is placed can affect comfort and the implantation process. Today’s pacemakers are small and less invasive. The choice between types depends on the patient’s body and heart condition.
Programming Flexibility and Adaptability
Modern pacemakers can be programmed to meet specific patient needs. Dual-chamber and biventricular pacemakers have more options because they’re more complex. This flexibility is key for improving device performance and patient results.
In conclusion, each type of pacemaker has its own strengths and considerations. Understanding these differences helps healthcare providers and patients make the best choice for treatment.
The Pacemaker Implantation Procedure
Learning about the pacemaker implantation process can ease worries and get patients ready. We’ll look at the main steps, from getting ready to recovering.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before the pacemaker implant, patients have tests to see if they’re a good fit. These tests include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to check heart rhythm
- Echocardiogram to look at heart function
- Blood tests to find any health issues
They’re also told to follow some rules before the procedure. This includes not eating or drinking beforehand, telling their doctor about medicines, and having someone drive them home.
What Happens During Implantation
The pacemaker implant process has several important steps. First, local anesthesia is given to numb the area. Then, a small incision is made in the chest for the pacemaker.
The pacemaker leads are guided into the heart with X-ray imaging. The pacemaker is then connected to these leads. Finally, the pacemaker’s work is checked to make sure it’s working right.
Recovery and Immediate Aftercare
After the procedure, patients are watched closely to make sure the pacemaker is working well. They’re told to rest and let their body heal. They also need to watch the incision site for infection signs and follow their doctor’s recovery plan.
Potential Risks and Complications of Pacemakers
Pacemakers are crucial for many people, but they come with risks. It’s important for patients and doctors to know about these risks.
Procedure-Related Complications
Getting a pacemaker involves surgery. This surgery can lead to problems like infection or bleeding. Some people might also react to the anesthesia.
Common procedure-related complications:
- Infection
- Bleeding or hematoma
- Reaction to anesthesia
- Pneumothorax (collapsed lung)
- Cardiac perforation
Even though these issues can happen, they are not common. Thanks to better technology and techniques, they are less frequent.
Device-Related Complications
After a pacemaker is put in, it can face problems. These might include issues with the leads, the device itself, or the battery and programming.
|
Complication |
Description |
Typical Solution |
|---|---|---|
|
Lead Malfunction |
Issues with the pacing lead that can affect the device’s ability to properly pace the heart. |
Lead revision or replacement |
|
Device Failure |
Rare instances where the pacemaker itself fails to function correctly. |
Device replacement |
|
Battery Depletion |
The battery life is limited, and depletion requires replacement. |
Generator replacement |
Regular check-ups with a doctor are key. They help keep the device working right and catch any problems early.
Knowing about the risks of pacemakers is important. While there are risks, many people find the benefits of pacemakers worth it.
Living with a Pacemaker: Lifestyle Adjustments
Living with a pacemaker means making some lifestyle changes. These changes help the device work right and keep you safe. They also make your life better overall.
Activity Recommendations and Restrictions
Most people with pacemakers can do their usual activities again after they recover. But, some activities might need to be changed or avoided. For example, contact sports that involve significant physical contact or risk of collision should be avoided to prevent damage to the device.
Heavy lifting or bending should be avoided, especially in the first few weeks. As you heal, you can start doing more activities. Walking and light exercise are good for recovery and heart health.
Electronic Device Interference Concerns
Pacemakers can be affected by some electronic devices, but the risk is low with today’s technology. It’s important to be careful around strong magnetic fields. These are found in MRI machines, some industrial equipment, and certain household appliances.
Devices like microwaves, televisions, and computers are usually safe. But, it’s a good idea to stay away from them a bit. Always tell your healthcare providers about any new devices you start using.
Travel Considerations
Traveling with a pacemaker needs some planning. Always carry your pacemaker identification card. Tell your airline or travel provider about your pacemaker. Airport security is usually safe, but let them know about your pacemaker.
Look up medical facilities at your destination in case you need help. Keep a list of your medications and medical history handy.
Medical ID and Emergency Information
Wearing a medical alert ID is a good idea. It gives important information to doctors in emergencies. Make sure your emergency contacts know about your pacemaker and how to reach your doctor.
Keep a record of your pacemaker settings, appointments, and any device info. This is very helpful in emergencies.
Patient Experiences and Quality of Life with Different Pacemaker Types
Pacemakers do more than just regulate heartbeats. They improve patients’ lives in many ways. They help with physical health, mental state, and getting back to normal activities.
Physical Improvements After Implantation
Many patients feel better after getting a pacemaker. They have more energy, breathe easier, and feel less pain from irregular heartbeats. This lets them do more in their daily lives and get healthier.
A study on heart failure patients with CRT pacemakers showed big improvements. They could do more and went to the hospital less. These changes make life better for those with heart issues.
Psychological Aspects of Living with a Cardiac Device
Having a pacemaker can affect the mind. It can ease worries about heart problems but also bring concerns about device issues. Yet, many patients feel safer and happier with their pacemakers.
Help from doctors, family, and support groups is key. Learning about the device helps reduce anxiety and improves how patients feel.
Return to Normal Activities
Pacemakers let people do what they love again. Most can go back to their usual activities, like exercise and hobbies, after they heal. How much they can do depends on the pacemaker and their health.
Doctors guide patients on what activities are safe. They advise avoiding heavy lifting and sports to protect the pacemaker.
Patient Testimonials
Real stories from patients show how pacemakers change lives. They talk about feeling more independent and enjoying activities again.
“Since getting my pacemaker, I’ve been able to resume hiking and spending time with my grandchildren without feeling held back by my heart condition. It’s been a game-changer.”
— Emily, age 62, dual-chamber pacemaker recipient
These stories highlight the good effects of pacemakers. They show how these devices help both physically and emotionally.
|
Pacemaker Type |
Physical Improvements |
Psychological Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Single-Chamber |
Moderate improvement in symptoms |
Reduced anxiety about heart rhythm |
|
Dual-Chamber |
Significant improvement in heart function |
Enhanced sense of security and well-being |
|
Biventricular (CRT) |
Marked improvement in heart failure symptoms |
Improved mental health and reduced hospitalization |
Advancements in Pacemaker Technology
The field of cardiology has seen big changes in pacemaker technology. These changes are making life better for patients with heart rhythm problems. They offer new hope to people all over the world.
Leadless Pacemakers
Leadless pacemakers are a big step forward. They don’t need leads like old pacemakers do. Instead, they are tiny devices put right in the heart. This makes them safer and better for patients.
Key Features of Leadless Pacemakers:
- Minimally invasive implantation procedure
- Reduced risk of lead-related complications
- Potential for reduced recovery time
MRI-Compatible Devices
MRI-compatible pacemakers are another big win. They let patients safely get MRI scans, which was a big no-no before. These devices are made to be safe during MRI scans, avoiding problems like device failure or lead heating.
|
Feature |
Traditional Pacemakers |
MRI-Compatible Pacemakers |
|---|---|---|
|
MRI Safety |
No |
Yes |
|
Device Malfunction Risk |
High |
Low |
|
Lead Heating Risk |
Yes |
Minimized |
Remote Monitoring Capabilities
Remote monitoring has changed how we care for pacemaker patients. It lets doctors check on the device and the patient’s heart rhythm from afar. This means fewer doctor visits and quicker help when needed.
The benefits of remote monitoring include:
- Reduced need for hospital visits
- Early detection of device or heart rhythm issues
- Improved patient outcomes through timely intervention
Future Innovations on the Horizon
The future of pacemaker technology looks bright. Scientists are working on new materials and designs to make devices better. Some ideas include:
- Biodegradable pacemaker components
- Artificial intelligence (AI) integrated devices
- Enhanced battery life technologies
These new ideas will keep making cardiac care better. They promise safer, more effective, and easier treatments for patients.
Insurance Coverage and Cost of Pacemaker Therapy in the United States
Insurance coverage is key to making pacemaker therapy available. It’s important for patients and their families to understand the costs involved.
Medicare and Medicaid Coverage
For many, Medicare and Medicaid are crucial for pacemaker therapy coverage. Medicare covers pacemaker implantation for those with certain heart conditions. Medicaid coverage varies by state but usually includes necessary pacemaker procedures.
A study in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found benefits for Medicare beneficiaries with heart failure. Those who got CRT or ICD with a pacemaker did better than those without.
“The use of CRT in appropriate patients has been shown to improve symptoms, reduce hospitalizations, and decrease mortality.”
Private Insurance Considerations
Private insurance plans also cover pacemaker therapy, but coverage varies. It’s important for patients to check their policies. They should know what’s covered and what they’ll have to pay out of pocket.
|
Insurance Type |
Coverage for Pacemaker Therapy |
Out-of-Pocket Expenses |
|---|---|---|
|
Medicare |
Generally covers medically necessary pacemaker procedures |
20% of Medicare-approved amount after deductible |
|
Medicaid |
Varies by state; generally covers medically necessary procedures |
Minimal to no out-of-pocket expenses for eligible beneficiaries |
|
Private Insurance |
Varies by plan; often covers pacemaker therapy |
Depends on plan details; may include deductibles, copays, and coinsurance |
Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Even with insurance, patients may still face costs for pacemaker therapy. These can include deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. Knowing these costs helps with financial planning.
Financial Assistance Programs
For those struggling with pacemaker therapy costs, financial help is available. These programs can make treatment more affordable.
We suggest patients look into these options. They should also talk to their healthcare provider about their financial concerns.
Conclusion
Knowing how pacemakers help with heart health is key for those with heart rhythm issues. We’ve looked at the main types of pacemakers: single-chamber, dual-chamber, and biventricular. Each one is made for different heart problems, and picking the right one is vital for good heart care.
New pacemaker tech has made a big difference for patients. Today’s devices last longer, work better, and fit each patient’s needs. This change has made life better for people with heart rhythm problems, letting them live more active and happy lives.
As we keep improving in heart care, making treatment plans just for each patient is crucial. This way, patients get the best pacemaker therapy for their specific needs. It helps improve their heart health and life quality.
Healthcare pros can give top-notch care by knowing the pacemaker types and the latest tech. This helps meet the complex needs of patients with heart rhythm issues.
FAQ
What are the signs of blocked arteries?
Signs of blocked arteries include chest pain and shortness of breath. You might also feel tired or have pain in your legs or arms. The symptoms depend on where and how bad the blockage is.
How do I know if I have a heart blockage?
Doctors use tests like ECGs and coronary angiograms to find heart blockages. If you have chest pain or trouble breathing, see a doctor right away.
What are the symptoms of a clogged artery?
A clogged artery can cause chest pain or discomfort. You might also feel pain or weakness in your legs or arms. Shortness of breath and fatigue are other signs. In serious cases, it can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
How do pacemakers help with heart blockages?
Pacemakers help keep your heart rhythm steady. They don’t fix blockages but can manage symptoms of heart rhythm problems linked to blockages.
What are the different types of pacemakers?
There are single-chamber, dual-chamber, and biventricular pacemakers. Each type treats different heart rhythm issues and has its own benefits.
How long do pacemakers last?
Pacemakers can last from 5 to 15 years. The exact time depends on the type and how much it’s used.
Are there any risks or complications associated with pacemakers?
Pacemakers might cause infection or malfunction. There’s also a chance of a reaction to the materials. But these risks are low, and most people with pacemakers live normally.
Can I lead a normal life with a pacemaker?
Yes, most people with pacemakers can live active lives. But, it’s important to follow your doctor’s advice on lifestyle changes and safety precautions.
How do advancements in pacemaker technology impact patient care?
New pacemaker tech, like leadless pacemakers, has improved care. It offers more options, reduces risks, and boosts quality of life for those with heart rhythm issues.
Will insurance cover the cost of a pacemaker?
In the U.S., many insurance plans, including Medicare and Medicaid, cover pacemaker therapy. But, coverage can vary based on your plan and situation.
What are the latest innovations in pacemaker technology?
Recent advancements include leadless pacemakers and MRI-compatible devices. There’s also better remote monitoring. These aim to make pacemaker therapy safer and more effective.
Reference
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459196/



































