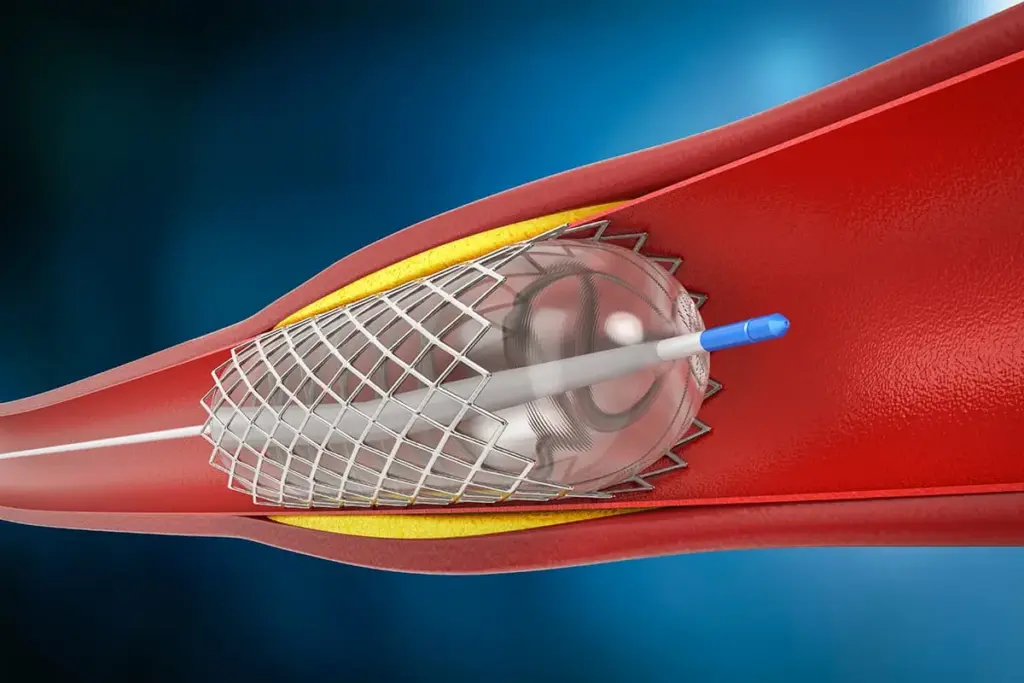
When a coronary artery stent is placed, patients often wonder if they’ll feel better right away. We understand that undergoing a heart stent procedure can be a significant experience. It’s natural to have questions about the outcome.
A stent is a small, mesh tube that’s used to keep the arteries open. This improves blood flow to the heart. By understanding the role of a stent in heart health, patients can better appreciate the benefits of this life-saving treatment.
We will explore the effects of stent placement and what patients can expect during their recovery.
Stent in heart relief? Get best recovery facts. Many feel amazing instantly! Chest pain vanishes as vital blood flow returns to safety.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the purpose of a coronary artery stent
- The role of stent placement in treating heart conditions
- What to expect during recovery from a heart stent procedure
- The benefits of improved blood flow to the heart
- How a cardiac stent can impact overall health
Understanding What a Stent in Heart Does
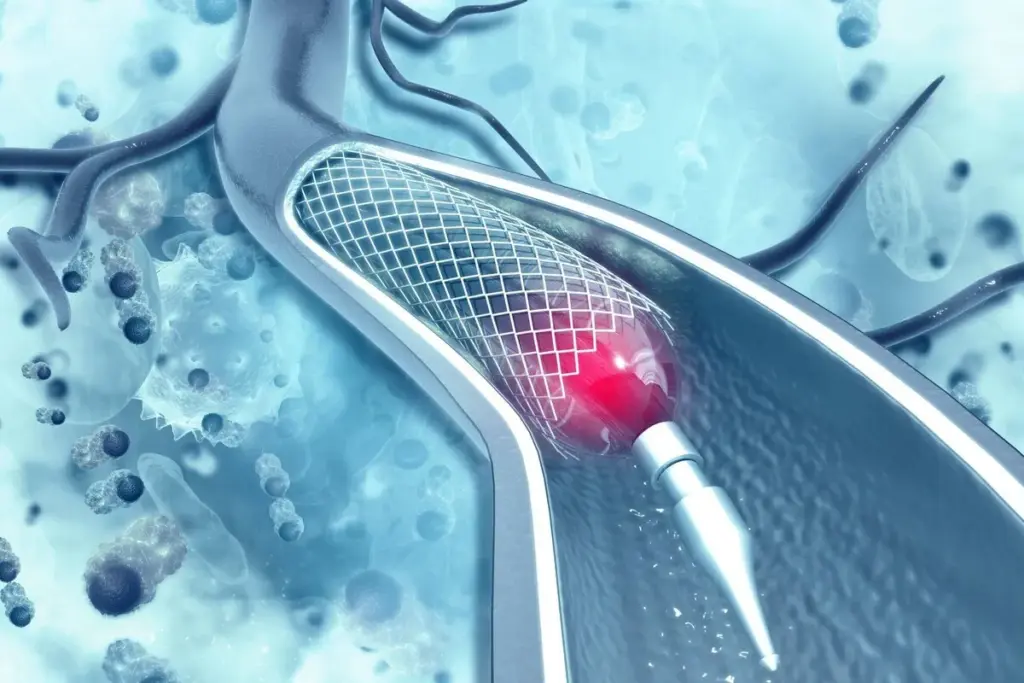
A stent in the heart is a small, mesh-like device. It helps keep blood flowing to the heart muscle. When a coronary artery gets narrowed or blocked, a stent keeps it open. This improves blood flow and lessens symptoms of coronary artery disease.
Definition and Types of Cardiac Stents
A cardiac stent, or coronary artery stent, is a tiny, expandable tube. It’s put into a narrowed or blocked coronary artery. There are different types of cardiac stents, including:
- Bare-metal stents: These are made from metal mesh and are designed to keep the artery open.
- Drug-eluting stents: These stents release medication that prevents cell growth, reducing the risk of the artery becoming blocked again.
- Bioresorbable stents: These stents are made from materials that dissolve over time, potentially reducing long-term complications.
“The use of stents has revolutionized the treatment of coronary artery disease,” says a leading cardiologist. “By restoring blood flow to the heart, stents can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life.”
How Stents Improve Blood Flow to the Heart
Stents improve blood flow to the heart by keeping the coronary arteries open. When a stent is placed in a narrowed or blocked artery, it:
- Restores normal blood flow to the heart muscle, reducing symptoms such as chest pain (angina).
- Improves overall heart function by ensuring that the heart receives the oxygen and nutrients it needs.
- Reduces the risk of heart attack by preventing the artery from becoming completely blocked.
By understanding how a stent in the heart works, patients can better appreciate the importance of this lifesaving device in managing coronary artery disease.
When Is a Coronary Artery Stent Necessary?
Doctors decide on a coronary artery stent based on a few key factors. These factors mainly focus on the patient’s heart health and how severe their coronary artery disease is.
Conditions That May Require Stent Placement
Some conditions might need a coronary artery stent. These include:
- Atherosclerosis: This is when plaque builds up in the arteries, causing them to narrow or block.
- Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS): This includes heart attacks or unstable angina, where quick action is needed.
- Stable Angina: For those with stable angina, a stent might be considered if symptoms don’t improve with medicine and lifestyle changes.
These conditions show how important it is to act quickly to get blood flowing to the heart again.
Diagnostic Tests Leading to Stent Recommendations
Several tests help figure out if a coronary artery stent is needed. These tests are:
- Coronary Angiography: This uses dye and X-rays to see the coronary arteries and find blockages.
- Stress Test: This test checks how the heart works under stress, usually through exercise or medicine.
- Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR): A method used during angiography to measure pressure differences across a stenosis.
These tests are key in deciding if a stent is needed and in choosing the best treatment plan.
Figuring out when a coronary artery stent is needed involves a detailed look at the patient’s condition and test results. This careful approach makes sure the treatment fits the patient’s needs. It helps improve heart health and outcomes.
The Heart Stent Procedure Explained
Learning about the heart stent procedure can help ease your worries. We’re here to walk you through it, from start to finish. You’ll know what to expect, making you feel more at ease.
Preparation for Stent Placement
Before your heart stent procedure, several steps are taken to keep you safe and ensure success. Pre-procedure preparation includes:
- Diagnostic tests like angiograms to check the blockage.
- Talking about your medical history, allergies, and current meds with your doctor.
- Getting advice on which meds to stop or keep taking before the procedure.
- Arranging for a ride home, as you might be sleepy from sedatives.
It’s also key to follow any fasting instructions given by your healthcare team.
Step-by-Step Process of Stent Insertion
The heart stent procedure is detailed and involves several steps:
- Accessing the Artery: The procedure starts with accessing the blocked artery through a small incision, usually in the groin or arm.
- Guiding the Catheter: A thin, flexible tube is guided to the blocked artery using X-ray imaging.
- Placing the Stent: A stent is placed to keep the artery open once the blockage is found.
- Inflating the Balloon: If a balloon angioplasty is done, the balloon is inflated to expand the stent and clear the plaque.
- Final Check: Angiography is used to make sure the stent is in the right place and the artery is open.
Your healthcare team watches your vital signs closely to keep you safe.
Types of Anesthesia Used
The heart stent procedure usually uses local anesthesia to numb the area where the catheter is inserted. You might also get conscious sedation to help you relax. Conscious sedation keeps you awake but relaxed, so you can respond to commands.
“The use of local anesthesia and conscious sedation during stent placement procedures has significantly improved patient comfort and outcomes,” says a leading cardiologist.
Explaining the heart stent procedure in detail shows it’s complex but effective. Knowing the preparation, steps, and anesthesia types helps patients feel more confident and ready for their treatment.
Do You Feel Immediately Better After a Stent?
Many people wonder when they’ll start feeling better after getting a cardiac stent. It’s normal to want to know what happens right after the procedure.
Immediate Physical Sensations Post-Procedure
Right after the stent is placed, you might feel some things. These can include:
- Mild discomfort or soreness at the catheter insertion site
- A feeling of relief as the blockage is cleared
- Possible bruising or swelling at the site
These feelings are usually short-lived and can be managed with medicine.
Timeline of Symptom Improvement
How fast you start feeling better can vary. Some might notice changes in a few hours, while others might take a few days.
Key milestones in symptom improvement include:
- Reduced chest pain or angina within the first 24-48 hours
- Improved energy levels over the first week
- Enhanced overall physical capability as the heart function improves
Factors Affecting Immediate Relief
Several things can affect how quickly you feel better after a stent. These include:
- The severity of your condition before the stent placement
- Overall heart health and presence of other cardiac conditions
- Adherence to post-procedure rehabilitation programs and rehab care
Following your healthcare provider’s advice for rehab can really help your recovery. It makes the stent work better for you.
By knowing these factors and working with your healthcare team, you can get the most out of your stent. This will help improve your heart health.
The First Week After Getting a Stent in Heart
Understanding what to expect in the first week after a stent can make recovery easier. This time is key for managing your health and setting up for long-term success.
Common Physical Experiences
In the first week, you might feel some normal healing sensations. These can include:
- Mild discomfort or soreness at the catheter insertion site
- Fatigue or feeling more tired than usual
- Bruising or swelling at the site where the catheter was inserted
These symptoms usually go away as you heal. But, it’s important to watch them and talk to your doctor if you have any worries.
Medication Management
Medicine is very important for healing after a stent. You’ll likely get:
- Anti-platelet therapy to stop blood clots on the stent
- Medications for high blood pressure, cholesterol, or diabetes
It’s very important to take your medicine as your doctor tells you. Not taking it can lead to serious problems.
Activity Restrictions and Recommendations
It’s important to balance rest and activity in the first week. You should avoid hard activities but some light movement is good:
- Avoid heavy lifting, bending, or hard exercise
- Take short walks to help blood flow and prevent clots
- Start doing more activities as your doctor says it’s okay
Rehabilitation therapy, like cardiac rehab, might be suggested. It helps with recovery and heart health. These programs include exercise, heart-healthy tips, and stress counseling.
Potential Complications Following Stent Placement
Stent placement is common but comes with risks. It’s important to know these risks for good patient care. While safe most of the time, complications can happen right away or later.
Early Complications (First 30 Days)
Early issues might include bleeding at the site, dye allergy, or stent thrombosis. Stent thrombosis is a serious clot inside the stent that needs quick medical help.
Kidney damage from dye is a concern, more so for those with kidney problems. We also watch for infection at the site, though it’s rare.
Warning Signs That Require Medical Attention
It’s key for patients to know when to seek help fast. Look out for severe chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or fainting. Also, watch for bleeding signs like bruising or bleeding at the site.
Fever, chills, or redness at the site could mean infection. If you see these signs, get medical help right away.
How Common Are Stent Complications?
The chance of stent complications depends on many things. These include the patient’s health, other medical conditions, and the stent procedure details. While rare, serious issues can happen.
|
Complication |
Frequency |
Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|
|
Stent Thrombosis |
Rare ( |
Premature discontinuation of antiplatelet therapy, small stent diameter |
|
Bleeding at Access Site |
Common (2-6%) |
Use of anticoagulation therapy, larger sheath size |
|
Kidney Damage |
Uncommon (1-2%) |
Pre-existing kidney disease, diabetes, contrast dye volume |
Knowing about these complications and their risks helps both patients and doctors. It helps in reducing risks and getting the best results after stent placement.
Stent Recovery Timeline: Week by Week Progress
Knowing what to expect after a stent placement can ease anxiety. The healing process is slow, but knowing what’s ahead can help. It makes your journey to full recovery smoother.
Weeks 1-2: Initial Recovery Phase
The first two weeks are key for healing. Resting and letting your body mend is essential. You might feel some pain, tiredness, and bruising at the catheter site. But these symptoms usually go away in a few days.
It’s important to stick to your medication and follow your doctor’s advice.
When you start feeling better, you can slowly do more. But, avoid heavy lifting, bending, or hard work that could hurt your heart.
Weeks 3-4: Expanding Activities
By weeks 3-4, you’ll likely feel more energetic and can do more. You might go back to work, depending on your job, and start with light exercise like walking. Remember to listen to your body and not overdo it.
Keep doing what your doctor says about exercise and how hard you should work. You might also notice your health getting better and symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath lessening.
Months 2-3: Returning to Normal Life
In two to three months, you can usually get back to your usual activities, including harder exercise. This is a big step in your recovery. But, keep following your doctor’s advice on how hard and how often you should exercise.
At this point, you should also pay more attention to your body’s signals. Know when to get medical help if you notice anything strange. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider will help track your progress and address any worries.
Remember, everyone’s recovery is different. Your health, other medical conditions, and how well you follow your treatment plan can affect how fast you recover.
“Recovery is not just about the physical healing; it’s also about regaining your emotional and mental well-being.”
By understanding the stent recovery timeline and following your healthcare provider’s advice, you can make your recovery better. This will also improve your long-term health.
Cardiac Rehabilitation After Stent Surgery
Stent surgery is just the start. Cardiac rehabilitation is key for a full recovery. After stent placement, it’s vital to join a cardiac rehab program. This ensures your heart health and overall wellbeing.
Definition and Purpose of Cardiac Rehabilitation
Cardiac rehabilitation is a program supervised by doctors. It’s for patients with heart issues or who have had stent placement. Its main goal is to help patients recover, lower future heart risks, and improve their life quality.
The American Heart Association says these programs are customized. They focus on exercise, heart-healthy living education, and stress reduction counseling.
“Cardiac rehabilitation is a vital component of the care plan for patients with cardiovascular disease, helping them to achieve a better quality of life and reduce the risk of future cardiac events.”
American Heart Association
Components of a Complete Rehab Program
A complete cardiac rehab program has several parts:
- Exercise Training: Sessions tailored to the patient’s fitness and health.
- Education: Tips on heart-healthy diet, lifestyle, and risk management.
- Counseling: Help with stress and emotional needs.
- Medical Monitoring: Ongoing health checks and treatment plan adjustments.
|
Component |
Description |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Exercise Training |
Supervised exercise sessions |
Improves cardiovascular health, increases stamina |
|
Education |
Heart-healthy diet and lifestyle information |
Empowers patients to manage their condition |
|
Counseling |
Stress management and emotional support |
Reduces stress, improves mental wellbeing |
When to Start Rehabilitation
The right time to start rehab varies. It depends on your health and your doctor’s advice. Usually, it’s a few days to a week after stent placement, when you’re stable and cleared by your doctor.
Always follow your doctor’s advice on when and how to start your cardiac rehab program.
Exercise Guidelines Following Heart Stent Procedure
Exercise is key in recovering after a heart stent procedure. It helps in healing and improves heart health. Understanding this is vital.
Safe Activities in the First Month
In the first month, focus on low-intensity activities. These activities should promote blood flow without straining your heart too much. Safe activities include:
- Short walks, gradually increasing in duration
- Light stretching exercises
- Breathing exercises
These activities help prevent complications and ensure a smooth recovery. Always watch how your body reacts and report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider.
Gradually Increasing Exercise Intensity
As you get better, you can increase the intensity of your exercises. Always do this under the guidance of a healthcare professional or a cardiac rehabilitation program. A typical progression might include:
|
Week |
Activity Level |
Examples |
|---|---|---|
|
1-2 |
Low intensity |
Short walks, light stretching |
|
3-4 |
Moderate intensity |
Brisk walking, cycling on flat ground |
|
5 and beyond |
Higher intensity |
Swimming, jogging, or other aerobic exercises |
Increasing exercise intensity should be based on your individual tolerance and comfort level. It’s essential to listen to your body and not push yourself too hard.
Activities to Avoid After Stent Placement
While recovering from a heart stent procedure, there are certain activities that you should avoid. These include:
- Heavy lifting or bending
- High-intensity exercises, such as those that strain or require holding your breath
- Contact sports or activities that risk a blow to the chest
Avoiding these activities will help ensure that your heart has the best chance to heal properly. Always consult with your healthcare provider before resuming any strenuous activities.
By following these exercise guidelines, you can significantly contribute to your recovery and long-term heart health. Remember, every individual’s recovery process is unique. It’s essential to work closely with your healthcare team to develop a personalized exercise plan.
Dietary Changes to Support Heart Health
Changing your diet is key to keeping your heart healthy after a stent. Eating well can help manage risks and improve your health. It’s important to make smart food choices for your heart.
Heart-Healthy Eating Patterns
Eating heart-healthy means focusing on whole foods. Include a variety of foods in your diet, like:
- Fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread
- Lean protein sources, like poultry, fish, and legumes
- Healthy fats, including nuts, seeds, and avocados
These foods are full of nutrients and fiber. They help keep your heart healthy and lower disease risk.
Foods to Embrace and Limit
It’s important to watch what you eat for heart health. Limit or avoid:
- Processed and packaged foods high in salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats
- Red and processed meats
- Refined grains, such as white bread and sugary snacks
- Foods high in saturated and trans fats
Choose whole, nutrient-rich foods instead. They give you energy and support your health. Making these changes can help manage your heart health.
Importance of Dietary Adherence
Sticking to a heart-healthy diet takes effort. We suggest getting help from a healthcare professional or dietitian. They can create a plan that fits your lifestyle.
Benefits of sticking to a heart-healthy diet include:
- Lowering blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Reducing the risk of future heart problems
- Improving overall health and well-being
- Supporting a healthy weight
By focusing on your diet, you can actively manage your heart health. This improves your overall well-being.
Essential Medications After Receiving a Stent
After getting a stent, patients take certain medicines to help them heal and keep their heart healthy. These medicines are key to avoiding problems and making sure the stent works right.
Anti-Platelet Therapy: Purpose and Duration
Anti-platelet therapy is a main medicine given after a stent. It stops blood platelets from clumping, which can block the stent. Common drugs include:
- Aspirin: Taken in small doses forever to stop clots.
- P2Y12 inhibitors (e.g., clopidogrel, prasugrel, ticagrelor): Taken for 6 to 12 months, based on the stent type and patient risk.
How long you take anti-platelet therapy depends on your health and the stent type. Always follow your cardiologist’s advice on how long to take it.
Other Common Medications
Other medicines may be given to help with heart health and other conditions. These include:
- Beta-blockers: Help the heart work less and need less oxygen.
- Statins: Lower cholesterol to prevent more plaque buildup.
- ACE inhibitors or ARBs: Control blood pressure and ease heart strain.
Managing Side Effects
These medicines are important for heart health after a stent, but they can have side effects. Common ones are:
- Bleeding or bruising
- Headaches or dizziness
- Fatigue
Talking to your doctor about side effects is key. They can often change your medicine or dose to help.
Following your medicine plan can greatly improve your recovery after a stent. It’s also important to keep up with doctor visits. This helps make sure the medicines are working well and addresses any side effects.
Emotional and Psychological Recovery After Stent Placement
Getting a stent can change your life, but the emotional journey is just as key as the physical healing. Patients on their road to recovery face many emotions. It’s important to recognize and tackle these feelings.
Common Emotional Responses
Patients often feel a mix of emotions after getting a stent. Some feel relieved the procedure is done and their heart health is improving. Others worry about future complications or more medical steps. Acknowledging these feelings is the first step to managing them.
Strategies for Mental Wellbeing
Several strategies can help with mental wellbeing during recovery. Staying connected with family and friends offers emotional support and fights loneliness. Relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can also reduce stress and anxiety.
- Practice mindfulness to stay present and focused.
- Engage in activities that bring joy and fulfillment.
- Consider joining a support group to connect with others who have experienced similar situations.
When to Seek Professional Support
While it’s normal to feel a range of emotions after a stent, some may need extra help. If anxiety, depression, or feeling overwhelmed gets worse, it’s time to seek professional help. Mental health experts can offer guidance, support, and treatment plans that fit your needs.
By acknowledging the emotional side of recovery and taking steps to support mental wellbeing, patients can improve their overall recovery. This can lead to a better quality of life after stent placement.
Long-Term Outcomes and Lifestyle With a Stent
Knowing about the long-term effects of a heart stent is key for patients. A stent can really help your heart health. But, it’s important to think about how it affects your life expectancy, quality of life, and lifestyle changes.
Life Expectancy and Quality of Life
Getting a stent can make your life better by improving blood flow to your heart. Studies show that stent patients often feel less pain and breathe easier. This lets them do more things without getting tired.
Key factors influencing long-term outcomes include:
- Adherence to prescribed medications
- Participation in cardiac rehabilitation programs
- Lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise
- Regular follow-up care with healthcare providers
Preventing Future Blockages
To avoid future blockages, heart stent patients need to live a healthy lifestyle. This means:
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming
- Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke
- Managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga
It’s also important to work closely with your healthcare team to monitor your condition and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Follow-up Care Schedule
Having a regular follow-up care plan is essential for heart stent patients. This usually includes:
- Regular check-ups with your cardiologist
- Periodic stress tests or other diagnostic tests to monitor heart health
- Adjustments to medications as necessary
By following these guidelines and staying in touch with your healthcare providers, patients can enjoy better long-term outcomes and a higher quality of life with a heart stent.
Conclusion: Living Well With Your Heart Stent
Getting a heart stent can change your life, easing symptoms of coronary artery disease. It’s important to know about the procedure, recovery, and lifestyle changes needed for the best results.
Living with a stent means focusing on heart health. This includes eating right, exercising regularly, and taking your meds as directed. Cardiac rehab is key, helping you get stronger, manage stress, and boost your heart health.
By making these changes and working with your doctors, you can improve your life and lower heart disease risks. We’re here to support you, providing care and advice for the best outcomes.
With the right care and support, life with a heart stent can be healthier and more active. Our goal is to offer top-notch healthcare with compassion and expertise, helping you thrive.
FAQ
What is a stent and how does it work?
A stent is a small, mesh-like device put into a narrowed or blocked artery. It helps improve blood flow to the heart. By keeping the artery open, it allows for normal blood flow.
What are the different types of stents available?
There are several stent types, like bare-metal, drug-eluting, and bioresorbable stents. Each has its own benefits and characteristics.
How long does it take to recover from a stent placement procedure?
Recovery time varies, but most can get back to normal in a few days to a week. It’s important to follow your doctor’s advice and keep up with follow-up appointments.
Will I feel immediately better after getting a stent?
Some people feel better right away, while others may take longer. How quickly you feel better depends on many factors.
What are the possible complications of stent placement?
Complications like bleeding, blood clots, and restenosis can happen. But, these are rare. Most people do well without major issues.
What is cardiac rehabilitation, and why is it necessary after stent surgery?
Cardiac rehab is a program with exercise, education, and support. It helps patients recover from heart conditions and improve health. It’s key after stent surgery.
What kind of exercise can I do after getting a stent?
Start with light activities and avoid heavy lifting at first. As you get better, you can do more. Always follow your doctor’s advice.
What dietary changes should I make to support heart health after stent placement?
Eat lots of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid foods high in saturated fats, salt, and sugar.
What medications will I need to take after receiving a stent?
You might need anti-platelet therapy and other meds for conditions like high blood pressure or diabetes. Always take your meds as your doctor says.
How can I manage stress and emotional changes after stent placement?
It’s normal to feel anxious or depressed after a heart event. Try stress-reducing activities like meditation. Also, talk to loved ones or mental health experts for support.
What is the long-term outlook for someone with a stent?
With proper care, many people with stents can live active, fulfilling lives. Regular check-ups and sticking to treatment plans are key to staying healthy.
How often should I have follow-up appointments after stent placement?
Your doctor will tell you when to come back for check-ups. These visits are important to track your progress and address any concerns.





