Is cardiac catheterization serious? It addresses vital health needs. While low risk, knowing the serious benefits is amazing for your peace of mind.
Over a million heart catheterization procedures happen every year in the United States. It’s a common way to check for heart problems.
Getting a cath lab procedure might seem scary, but it’s very important. It helps doctors find and fix heart issues. Coronary angiography, a big part of the cardiac cath procedure, lets doctors see the heart’s blood vessels. They can spot any blockages this way.
We’ll look into why heart catheterization is so important. We’ll talk about what happens during the procedure and how it keeps your heart healthy.
Key Takeaways
- Heart catheterization is a common and generally safe procedure.
- It’s used to diagnose and treat various heart conditions.
- The procedure involves inserting a catheter into the heart’s blood vessels.
- Coronary angiography is a key component of the cardiac cath procedure.
- Understanding the process can help alleviate patient concerns.
What Is Cardiac Catheterization and Why Is It Performed
Cardiac catheterization is a key tool in cardiology. It helps diagnose and treat heart issues. A thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel. It’s then guided to the heart.
This procedure lets us see the heart’s structure. We can spot blockages or abnormalities. We can also fix these problems to make the heart work right again.
Definition and Medical Purpose
Cardiac catheterization is a minimally invasive procedure. It helps us diagnose and treat heart conditions. The main goal is to:
- See the coronary arteries and find blockages or narrowing
- Check the pressure inside the heart chambers
- Look at how well the heart pumps
- Do interventions like angioplasty and stenting to improve blood flow
This procedure gives us a clear view of the heart. It helps us create specific treatment plans for heart disease patients.
Common Conditions Requiring Cardiac Catheterization
Many heart conditions need cardiac catheterization for diagnosis and treatment. These include:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): When the coronary arteries narrow or block due to plaque, leading to angina or heart attack.
- Angina: Chest pain or discomfort from reduced blood flow to the heart, often a sign of CAD.
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction): When blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing heart muscle damage.
Cardiac catheterization is essential for managing these conditions. It lets us see how bad the artery blockage is. We can then assess the heart’s function and do interventions to improve blood flow and prevent more damage.
The Cardiac Catheterization Procedure Step by Step
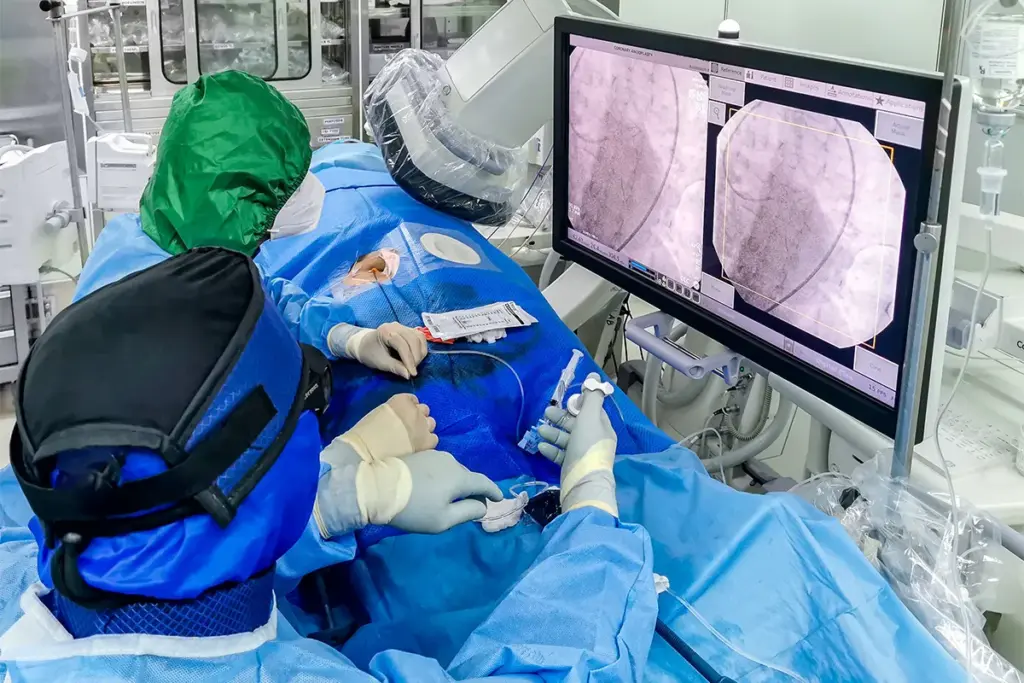
Cardiac catheterization is a key test for heart health. We’ll guide you through it step by step. It helps diagnose and sometimes treat heart issues. Knowing what to expect can make it less scary.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Getting ready for cardiac catheterization is important. Patients are usually told to:
- Fast for a certain period before the procedure
- Tell their doctor about any medications, like blood thinners
- Bring a friend or family member to drive them home
Following specific instructions from your healthcare team is also vital. These are made just for you.
What Happens During the Procedure
During the cardiac catheterization procedure, local anesthesia numbs the area. This is usually in the groin or arm. The procedure happens in a cath lab with special imaging.
The doctor puts a thin, flexible tube called a catheter into the artery. They use X-ray imaging to guide it to the heart. Then, they inject contrast dye to see the heart’s arteries on the X-ray. This helps spot any problems.
Duration and Immediate Aftermath
The heart cath procedure takes about 30 to 60 minutes. It can take longer if more steps are needed, like placing a stent.
After, patients are watched for a few hours for any issues. They might feel sore or bruised where the catheter was inserted. This usually goes away in a few days. Most patients go home the same day, with care instructions and follow-up plans.
Knowing the steps of cardiac catheterization helps prepare patients. It makes the experience less overwhelming.
Assessing the Seriousness of Cardiac Catheterization
Looking at cardiac catheterization’s seriousness means checking its type, how it compares to other treatments, and its safety. It’s a key tool in cardiology for both diagnosing and treating heart issues.
Classification as a Minimally Invasive Procedure
Cardiac catheterization is seen as a minimally invasive procedure. It involves a small cut in a blood vessel, usually in the groin or arm, to put in a catheter. This makes it different from more invasive surgeries.
Comparison to Open Heart Surgery
Unlike open heart surgery, which opens the chest, cardiac catheterization is done with much less disruption. It leads to quicker recovery times and fewer risks of complications.
Statistical Safety Profile
The safety record of cardiac catheterization is good, with few serious side effects. Here are some important numbers:
- Low mortality rate: Less than 1% in most studies
- Major complication rate: About 1-2%
- Minor complication rate: Varies, but generally higher than major complications
Thanks to new technology and techniques, cardiac catheterization is considered safe. But, like any medical procedure, it carries some risks. The benefits usually outweigh these risks for those needing it.
In summary, cardiac catheterization is a serious but valuable procedure in cardiology. Its status as minimally invasive and its good safety record make it a key tool.
Potential Risks and Complications
Cardiac catheterization is a key tool for diagnosing and treating heart issues. Yet, it carries risks and complications that patients should know about. Most people do well without major problems. But, knowing the risks helps you make informed decisions about your health.
Common Minor Complications
Most people feel little discomfort during and after the procedure. Some might face minor issues, such as:
- Bruising or hematoma at the catheter insertion site
- Temporary discomfort or pain
- Allergic reactions to the contrast dye used during the procedure
These issues are usually short-lived and often fix themselves or need only simple treatment.
Serious but Rare Complications
Though rare, serious complications can happen. These include:
- Heart attack or stroke
- Arrhythmias or other heart rhythm disturbances
- Coronary artery perforation
- Severe allergic reactions to the contrast dye
A study in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that major complications occur in less than 1% of patients.
“The risk of major complications from cardiac catheterization is low, but not negligible. It’s vital for patients to be aware of these risks and talk about any worries with their healthcare provider.”
Risk Factors That Increase Complication Rates
Some factors can up the risk of complications during or after the procedure. These include:
|
Risk Factor |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Age |
Older patients may have a higher risk of complications |
|
Pre-existing kidney disease |
Patients with kidney issues may be at higher risk for contrast-induced nephropathy |
|
Diabetes |
Diabetic patients, specially those with poor glucose control, may face increased risks |
|
Heart failure |
Patients with advanced heart failure may be at higher risk for complications |
Knowing these risk factors helps healthcare providers take extra steps and keep a closer eye on patients during and after the procedure.
Being aware of the possible risks and complications helps patients prepare better for the procedure. It also lets them work closely with their healthcare team to reduce these risks.
Benefits of Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac catheterization has changed how we diagnose and treat heart problems. It’s a key part of cardiology, giving doctors valuable insights and treatment options for heart diseases.
Diagnostic Benefits
Cardiac catheterization is great for diagnosing heart issues. It lets doctors see the heart’s structure and function. They can spot blockages and check the health of the coronary arteries. This info is key for planning treatment.
The diagnostic benefits of cardiac catheterization include:
- Accurate visualization of coronary arteries
- Identification of blockages and narrowing
- Assessment of heart function and structure
Treatment Benefits
Cardiac catheterization also offers treatment benefits. Doctors can do things like angioplasty and stent placement during the procedure. These help restore blood flow to the heart. They can ease symptoms, improve heart function, and prevent future heart problems.
|
Treatment Benefit |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Angioplasty |
A procedure to widen narrowed or blocked coronary arteries |
|
Stent Placement |
Insertion of a small mesh tube to keep the artery open |
Quality of Life Improvements
Cardiac catheterization can greatly improve a patient’s life. It helps diagnose and treat heart issues, reducing symptoms like chest pain and shortness of breath. This lets patients get back to their normal activities. Plus, the procedure is less invasive than open-heart surgery, so recovery time is shorter.
The overall benefits of cardiac catheterization can be summarized as follows:
|
Benefit |
Impact |
|---|---|
|
Diagnostic Accuracy |
Improved treatment planning |
|
Effective Treatment |
Restored blood flow, alleviated symptoms |
|
Minimally Invasive |
Less recovery time, fewer complications |
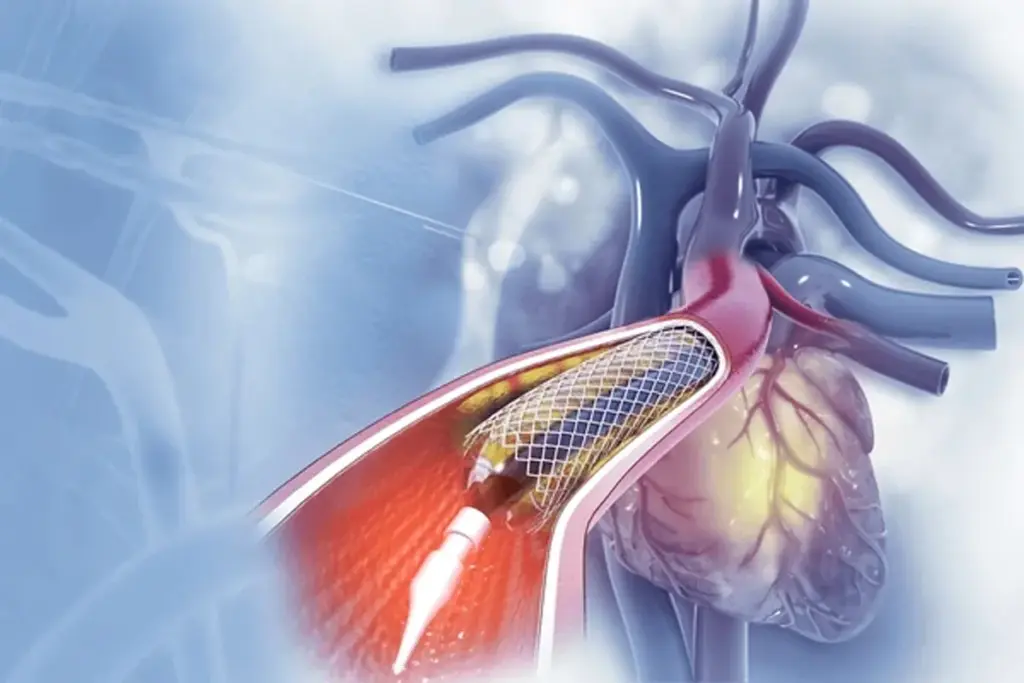
Heart Stent Placement During Catheterization
Heart stent placement during catheterization is a key treatment for coronary artery disease. This method is used during cardiac catheterization. It’s a minimally invasive way to diagnose and treat the disease.
What Are Coronary Stents and How Do They Work
Coronary stents are small, mesh-like tubes made of metal or other materials. They are designed to keep coronary arteries open. When a coronary artery is blocked or narrowed, a stent is placed to restore blood flow to the heart.
Stents work by expanding within the artery to push aside the plaque, improving blood flow and reducing symptoms such as chest pain.
According to the American Heart Association, stents have become a critical tool in managing coronary artery disease. They significantly improve patient outcomes.
“Stent placement has revolutionized the treatment of coronary artery disease, providing a minimally invasive solution. It reduces recovery time and improves quality of life.”
Cardiovascular Research Foundation
The Stent Placement Process
The stent placement process occurs during cardiac catheterization. Here’s an overview of the steps involved:
- A catheter with a balloon tip is guided to the blocked coronary artery.
- The balloon is inflated to widen the artery.
- A stent is placed over the balloon and expanded to fit the artery.
- The balloon is deflated and removed, leaving the stent in place.
Types of Stents and Their Durability
There are several types of stents, including bare-metal stents and drug-eluting stents. Bare-metal stents are made of metal and work by keeping the artery open. Drug-eluting stents release medication to prevent the artery from re-narrowing.
|
Type of Stent |
Description |
Durability |
|---|---|---|
|
Bare-Metal Stents |
Made of metal, keeps artery open |
High durability, but higher risk of re-narrowing |
|
Drug-Eluting Stents |
Releases medication to prevent re-narrowing |
High durability, lower risk of re-narrowing |
Advances in stent technology have led to the development of newer stents. The choice of stent depends on various factors, including the patient’s medical history and the complexity of the blockage.
Recovery After Heart Catheterization
Knowing what to expect during recovery can make it easier after a heart catheterization. The recovery phase is key and needs careful attention for the best results.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
After the procedure, you’ll be in a recovery area where medical staff watch over you. It’s normal to feel groggy or tired as the sedation wears off. They’ll check your vital signs to make sure everything is okay.
Hospital Stay Duration
The time you spend in the hospital varies based on your health and the procedure. Some patients can go home the same day, while others might need to stay overnight. Your doctor will decide based on your condition.
- Same-day discharge for uncomplicated procedures
- Overnight stay for observation in some cases
- Extended stay for patients with complications or other health issues
Activity Restrictions and Return to Normal Life
It’s important to follow your doctor’s advice on activity levels during recovery. Avoid heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous activities for a few days to prevent bleeding. Most people can get back to normal activities in a week, but it depends on the individual.
To help with a smooth recovery, consider these tips:
- Keep the catheter insertion site clean and dry
- Follow your medication regimen as prescribed
- Attend follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider
By following these guidelines and your healthcare provider’s advice, you can reduce the risk of complications. This ensures a successful recovery after heart catheterization.
Life Expectancy After Cardiac Catheterization and Stent Placement
Knowing how long you might live after cardiac catheterization and stent placement is key. This procedure can save lives but comes with risks and outcomes to understand.
Statistical Outcomes and Survival Rates
Research shows that survival rates after these procedures vary. This depends on the heart condition’s severity and the patient’s overall health.
A study in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that survival rates are affected by age and health conditions. This is important to know.
|
Age Group |
1-Year Survival Rate |
5-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|
|
Less than 60 |
95% |
80% |
|
60-69 |
90% |
70% |
|
70-79 |
85% |
60% |
|
80 and above |
80% |
50% |
Factors Affecting Long-Term Prognosis
Many things can affect how well you do long-term after these procedures. These include:
- Underlying Health Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, or kidney disease can make outcomes worse.
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, diet, and exercise levels play a big role in long-term health.
- Medication Adherence: Taking medications as directed is key to avoiding complications.
Life After a “Widowmaker” Heart Attack and Stent Placement
A “widowmaker” heart attack is very serious. It happens when the left anterior descending artery gets blocked. Stent placement can save lives in such cases.
Studies show that timely stent placement can greatly improve survival and quality of life. It’s vital to follow up and make lifestyle changes to get the best results.
Multiple Stent Placements: What You Need to Know
It’s important for patients and doctors to understand the effects of multiple stents. As new techniques in cardiac catheterization emerge, more people are getting multiple stents.
Patients with complex heart disease often need multiple stents. Doctors decide on this based on how bad the blockages are and where they are.
Number of Stents a Person Can Have
The number of stents needed varies a lot. There’s no fixed limit on how many stents can be used.
Some patients might get up to five or more stents. But, each case is different. The decision depends on the patient’s health and their specific situation.
|
Number of Stents |
Patient Profile |
Typical Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
|
1-2 Stents |
Simple coronary artery disease |
Improved blood flow, reduced symptoms |
|
3-5 Stents |
Complex coronary artery disease |
Significant improvement in quality of life |
|
More than 5 Stents |
Advanced or diffuse coronary artery disease |
Variable outcomes, close monitoring required |
Impact on Prognosis
The effect of multiple stents on a patient’s future is a big concern. Studies show that more stents can help by opening up more blood flow. But, they also add more challenges.
Patients with multiple stents might need more care. This includes regular check-ups and changes to their medication.
Living With Multiple Stents: Patient Experiences
Managing health with multiple stents is a big job. But, many patients see a big improvement in their life after the procedure.
It’s also key for patients to know about the risks. This includes the chance of needing more procedures in the future.
By knowing about the effects of multiple stents, patients can make better choices. They can work with their doctors to get the best results.
Long-Term Considerations: How Long Do Stents Last?
Knowing how long stents last is key for those who’ve had cardiac catheterization. It’s important to think about what makes stents last longer and when you might need more procedures.
Stent Longevity and Durability
Stent durability has grown thanks to new medical tech. Modern stents are made to last longer and reduce risks. Drug-eluting stents release medicine to stop arteries from narrowing.
Most stents work well for years. But, your health, lifestyle, and medicine use can affect how long they last.
What Happens to Stents After 10 Years
Research shows stents can last a long time. Many stents keep working well for 10 years or more.
A study in a cardiology journal found most patients with drug-eluting stents did well after 10 years. But, they need to keep getting checked and might need more treatments.
Need for Repeat Procedures
Even with stents, some people might need more treatments. This could be because of disease growth, stent failure, or new blockages.
The table below talks about stent longevity and when you might need more procedures.
|
Factor |
Influence on Stent Longevity |
Potential for Repeat Procedures |
|---|---|---|
|
Patient Health |
Overall health affects stent durability |
Poor health may increase the need for additional treatments |
|
Stent Type |
Drug-eluting stents generally have better outcomes |
Choice of stent may reduce the need for repeat procedures |
|
Lifestyle Factors |
Diet, exercise, and smoking affect stent longevity |
Healthy lifestyle choices can minimize the need for additional interventions |
By knowing these factors and taking care of your heart, you can make your stent last longer. This can also lower the chance of needing more procedures.
Special Considerations for High-Risk Patients
Patients with health issues or who are older face special challenges with cardiac catheterization. We must carefully check if the benefits are worth the risks.
Elderly Patients and Age Considerations
Elderly patients often have many health problems. We look at their kidney function, blood vessel access, and any brain issues when planning their care.
Age alone is not a reason to avoid cardiac catheterization. But we do think about it when assessing risks.
Patients With Existing Health Conditions
Patients with conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, or kidney disease need careful checks before the procedure. We try to get their health as good as possible before doing the catheterization.
Watching them closely during and after is key. This helps us quickly handle any problems.
Alternative Options for High-Risk Individuals
For those at high risk, we might look at other ways to diagnose and treat. This could include tests like cardiac MRI or CT angiography.
In some cases, treating with medicine might be better than invasive procedures. This depends on the patient’s health and what they prefer.
Living Well After Cardiac Catheterization
A cardiac catheterization is a big step towards better heart health. But what happens next is just as important. It involves medical care, follow-up, and healthier habits.
Medication Requirements and Compliance
After the procedure, you might need to take medications. These help manage your heart, prevent clots, or control symptoms. It’s important to take your meds as told.
- Take your medications at the same time every day to maintain consistency.
- Understand the purpose of each medication and its possible side effects.
- Never stop taking your medications without talking to your healthcare provider.
Medication adherence is key to avoiding problems and making your treatment work. If you have side effects or concerns, talk to your doctor.
Follow-Up Care and Monitoring
Follow-up care is vital for watching your heart health. Your doctor will check on you to address any issues early.
Regular check-ups help your healthcare team adjust your treatment and offer support. Make sure to keep these appointments and report any new symptoms.
Lifestyle Modifications for Optimal Outcomes
Healthy lifestyle choices can greatly improve your recovery and heart health. Here are some changes to consider:
- Dietary Changes: Eat a heart-healthy diet with lots of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Physical Activity: Do regular exercise as advised by your doctor.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is a huge benefit for your heart.
- Stress Management: Try stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing.
By making these lifestyle changes and following your care plan, you can improve your recovery and life quality.
When to Seek Emergency Care After Catheterization
Cardiac catheterization is usually safe, but there are warning signs that mean you need to see a doctor right away. Knowing these signs is key to avoiding and handling any problems.
Warning Signs of Complications
Keep a close eye on how your body is feeling after a cardiac catheterization. Some symptoms could mean you’re facing a complication that needs quick medical help. Look out for:
- Severe pain or discomfort in the chest, arm, or jaw
- Shortness of breath or trouble breathing
- Weakness or numbness in the legs or arms
- Confusion or trouble speaking
- Severe bleeding or swelling at the catheter site
- Coldness or paleness in the limb where the catheter was inserted
If you notice any of these signs, don’t wait to get emergency care. Quick action can make a big difference if you’re facing a complication.
Normal vs. Abnormal Recovery Symptoms
It’s important to know the difference between normal and abnormal symptoms after a procedure. A little discomfort, bruising, or swelling at the catheter site is okay. But severe or getting worse symptoms are not normal and need to be checked out.
Here’s a look at what’s normal versus what’s not:
|
Normal Symptoms |
Abnormal Symptoms |
|---|---|
|
Mild discomfort or bruising at the catheter site |
Severe pain or swelling that gets worse over time |
|
Small amount of bleeding that stops with pressure |
Heavy or continuous bleeding |
|
Mild fatigue or soreness |
Severe weakness or numbness |
Knowing these differences helps you react right if you have any symptoms after the procedure.
In summary, while cardiac catheterization is generally safe, it’s important to watch out for signs of trouble after it’s done. Spotting the warning signs and knowing the difference between normal and abnormal symptoms can help you get the right care when you need it.
Conclusion: Balancing the Risks and Benefits of Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac catheterization is a key medical procedure that has changed how we diagnose and treat heart issues. It has both risks and benefits, and knowing these is vital for both patients and doctors.
This procedure helps diagnose and treat heart problems effectively, improving life quality. Yet, it also comes with risks, from small issues to rare but serious problems. By weighing these, patients can make better choices about their care.
In the end, cardiac catheterization is a valuable tool for heart health. It offers a less invasive way to diagnose and treat heart conditions. By understanding its risks and benefits, patients can make informed decisions. They can work with their healthcare team to get the best results.
FAQ
What is cardiac catheterization?
Cardiac catheterization is a procedure where a catheter is inserted into the heart. It helps doctors see the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood vessels. This is to diagnose and treat heart conditions.
How serious is a heart catheterization procedure?
This procedure is considered safe and less invasive than open-heart surgery. While it has some risks, they are low. Most patients can go home the same day or the next day.
What are the common conditions that require cardiac catheterization?
It’s used for conditions like coronary artery disease, angina, and heart valve problems. It helps find blockages and place stents to keep arteries open.
How long does a cardiac catheterization procedure take?
The procedure itself takes 30 minutes to an hour. But, preparation and recovery can take several hours.
What are the risks and complications associated with cardiac catheterization?
Risks include bleeding, infection, and allergic reactions to dye. Serious issues like heart attack or stroke are rare.
How many stents can a person have?
There’s no limit to the number of stents. It depends on the person’s condition and disease severity.
How long do stents last?
Stent longevity varies by type, location, and health. On average, they can last 10-15 years or more.
What happens to stents after 10 years?
After 10 years, stents can narrow or block due to plaque buildup. This increases heart attack risk. Regular care can help spot issues.
How can I minimize the risks associated with cardiac catheterization?
Follow your doctor’s advice, disclose allergies or health issues, and attend follow-ups. A healthy lifestyle also helps.
What is the life expectancy after cardiac catheterization and stent placement?
Life expectancy varies based on disease severity and overall health. Studies show good long-term outcomes for stent patients.
How can I live well after cardiac catheterization?
Stick to medication, attend appointments, and make lifestyle changes. Quit smoking, exercise, and eat well.
When should I seek emergency care after catheterization?
Seek emergency care for severe chest pain, breathing trouble, or severe bleeding. Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor.
Can I have multiple stent placements?
Yes, multiple stent placements are possible. The decision depends on your condition and disease severity.
What are the benefits of cardiac catheterization?
It offers accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. It can reduce heart attack risk and improve quality of life.
Reference
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531461/[2




































