Hematology focuses on diseases of the blood, bone marrow, and lymphatic system. Learn about the diagnosis and treatment of anemia, leukemia, and lymphoma.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
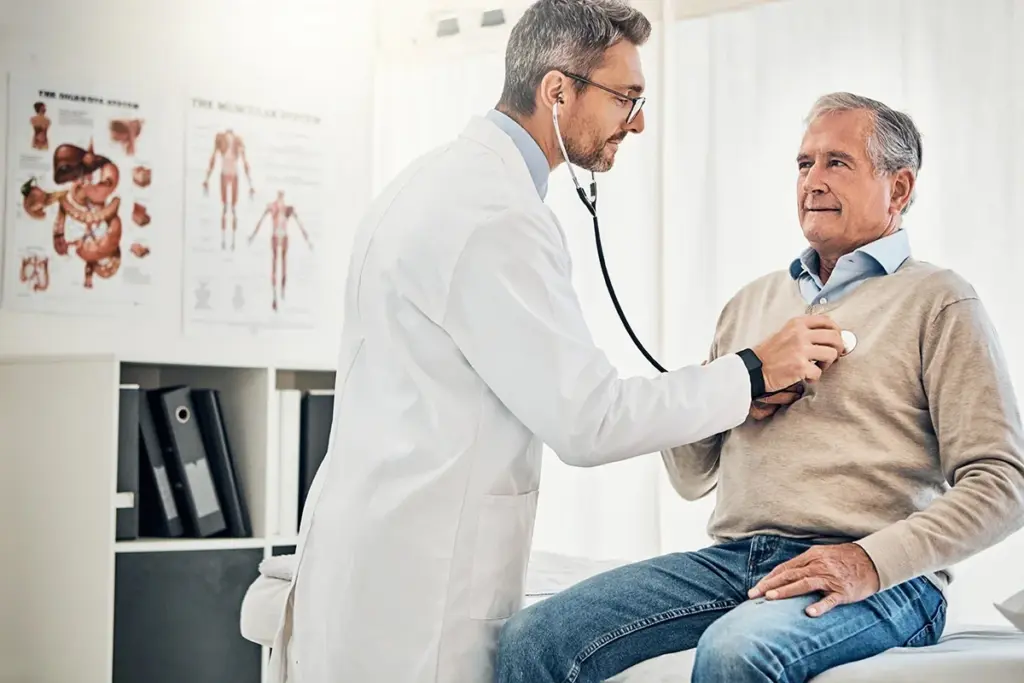
The management of hemochromatosis is one of the distinct success stories in medicine. Unlike many genetic disorders that have no cure, the complications of hemochromatosis can be completely prevented, and often reversed, with simple and effective therapy. The cornerstone of treatment is the physical removal of excess iron from the body. At Liv Hospital, we provide a comprehensive treatment environment that supports patients through the intensive induction phase and helps them establish a sustainable maintenance routine, ensuring a normal life expectancy and optimal health.
Phlebotomy, or venesection, is the removal of blood from the body. It is essentially identical to the process of voluntary blood donation.
Red blood cells are rich in hemoglobin, a protein that contains iron. When blood is removed, the body must produce new red blood cells to replace the loss. To do this, it pulls stored iron out of the organs (liver, pancreas, heart) and transports it to the bone marrow. This process gradually depletes the toxic iron reserves.
Approximately 450 to 500 mL of blood is removed during each session. This amount of blood contains about 200 to 250 mg of iron. Since the body creates new blood cells relatively quickly, the procedure can be repeated frequently.
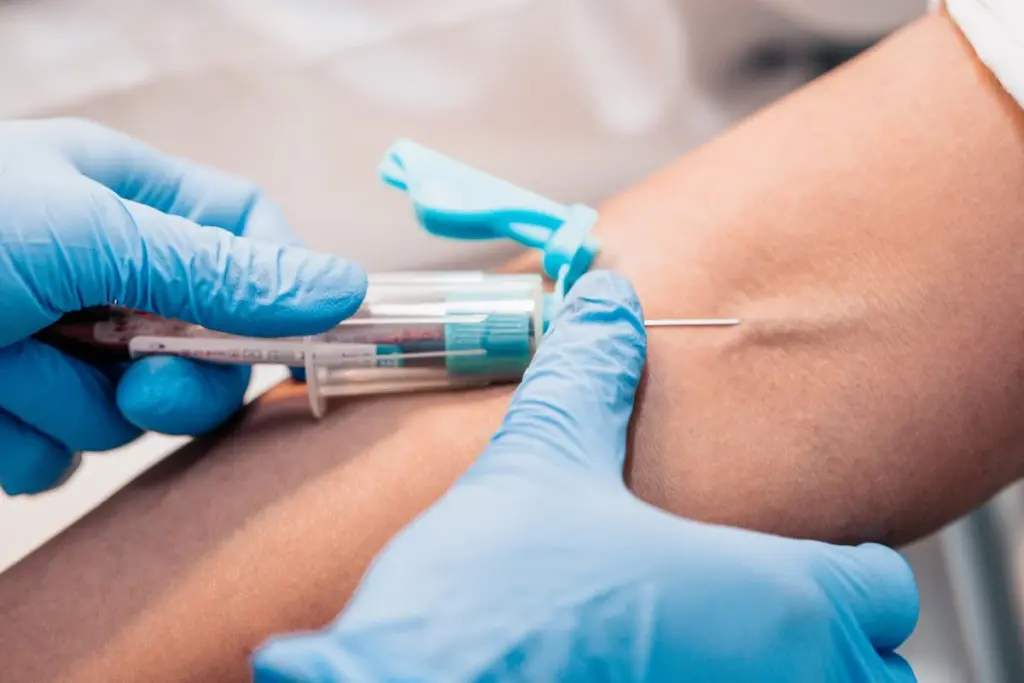
This is the initial, intensive phase of treatment aimed at rapidly reducing iron stores to a safe level.
Once the excess iron is cleared, the goal shifts to keeping it low.
Blood Donation: In many countries, patients in the maintenance phase can donate their blood at standard blood banks, turning their treatment into a life saving gift for others.
For some patients, phlebotomy is not an option. This includes those with severe anemia, congestive heart failure, or poor venous access.
These are medications that bind to iron in the bloodstream and tissue, forming a complex that the body can excrete through urine or feces.
Chelation therapy is generally slower than phlebotomy, more expensive, and carries a risk of side effects such as kidney toxicity and hearing loss. It is strictly reserved for patients who cannot tolerate blood removal.
While diet cannot cure the disease, it plays a supportive role in management.
Heme iron, found in red meat, is absorbed very efficiently. Patients are advised to limit their intake of red meat (beef, lamb, venison). Non heme iron, found in vegetables and grains, is absorbed poorly and does not need to be strictly restricted. A balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables is encouraged.
Patients should read labels to avoid highly iron fortified breakfast cereals and snack bars.
Patients with hemochromatosis are uniquely susceptible to a bacterium called Vibrio vulnificus, which thrives in warm seawater and concentrates in shellfish. In a person with high iron levels, this bacteria can multiply explosively, causing overwhelming and often fatal sepsis. Therefore, patients must strictly avoid raw oysters and uncooked shellfish.

Certain substances can interfere with treatment or worsen organ damage.
Vitamin C acts as a catalyst for iron absorption in the gut. While the Vitamin C naturally occurring in fruit is safe, high dose supplements (e.g., 1000 mg) can be dangerous. They can mobilize large amounts of iron from storage, causing heart arrhythmias.
For patients with elevated liver enzymes or cirrhosis, complete abstinence from alcohol is crucial. Alcohol works synergistically with iron to destroy liver cells. For those without liver damage, moderate consumption may be permissible, but it should be discussed with a specialist.
Multivitamins containing iron are strictly contraindicated.
Treating the iron overload stops the progression of disease, but existing damage requires specific management.
Patients with cirrhosis require surveillance for complications like esophageal varices and fluid retention.
The diabetes associated with hemochromatosis often requires insulin, as the beta cells may be permanently destroyed. However, better glycemic control is often achieved once iron levels are reduced.
Unfortunately, joint pain and arthritis often do not improve with phlebotomy and can sometimes worsen. Management relies on analgesics (NSAIDs or acetaminophen), physiotherapy, and occasionally joint replacement surgery for severe damage.
Testosterone replacement therapy can be highly effective for men suffering from low libido and fatigue, improving quality of life significantly.

In select cases, a procedure called erythrocytapheresis (red cell apheresis) may be used.
This procedure uses a specialized machine to remove only the red blood cells while returning the plasma and platelets to the patient.
It can remove twice the amount of red cells (and thus iron) per session compared to standard phlebotomy, potentially shortening the induction phase. However, it is more expensive and complex, so it is not standard for all patients.

Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
It is no more painful than a regular blood test or blood donation; there is a brief pinch when the needle is inserted.
No, if you stop, iron will build up again. Maintenance treatment is needed for life to keep levels safe.
Raw oysters may contain a bacteria that feeds on iron and can cause a deadly infection in people with hemochromatosis.
Yes, exercise is encouraged, but you should stay well hydrated and avoid strenuous activity immediately after a phlebotomy session.
Generally, no. Phlebotomy is faster, safer, and more effective for most people. Pills are used only when blood cannot be removed.
 Hematology
Hematology Hematology
Hematology Hematology
Hematology Hematology
Hematology
Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)