Appendicitis is an acute inflammation of the appendix, a small pouch attached to the large intestine. a medical emergency requiring prompt diagnosis & surgical removal.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix, a small finger-like pouch attached to the large intestine in the lower right abdomen. This condition often arises from a blockage, leading to infection and swelling that can become a medical emergency if untreated. It commonly affects people aged 10-30 and requires prompt evaluation to prevent rupture.
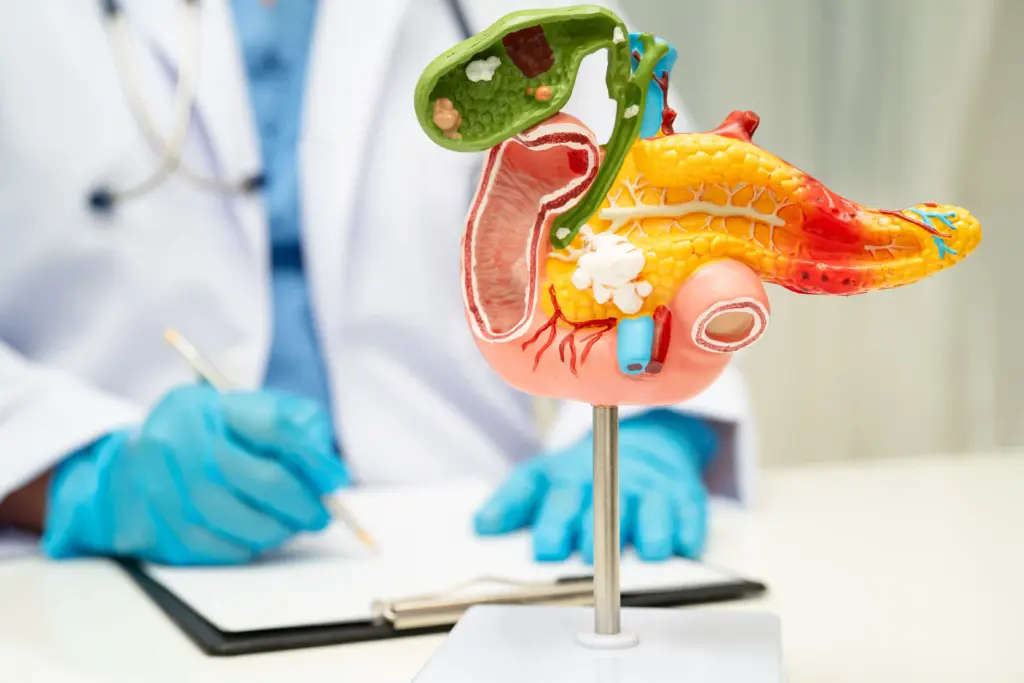
Appendicitis is a sudden and painful swelling (inflammation) of the appendix. The appendix is a small, tube-shaped pouch attached to the first part of the large intestine, near the lower right side of the abdomen. Appendicitis is one of the most common causes of emergency abdominal surgery worldwide. If it is not treated quickly, the swollen appendix can burst (rupture). This releases infectious material into the abdomen, which can lead to a serious, life-threatening infection called peritonitis.

The medical term Appendicitis clearly explains the condition through its root words. The first part, “appendix,” comes from the Latin word appendix, meaning “an addition” or “something attached,” which describes the small, pouch-like structure attached to the large intestine. The second part, the suffix “-itis,” is derived from Greek and is universally used in medicine to signify “inflammation.” Therefore, when combined, Appendicitis precisely means the “inflammation of the appendix,” a term that became formalized in the late 19th century as medical understanding of this condition grew.
The scope of appendicitis covers the acute care of a specific, painful infection within the digestive system.
It is important to understand what appendicitis is and what conditions should not be confused with it:
It is not the cause of general abdominal pain, but a specific cause that must be ruled out in the emergency room.
Appendicitis is mainly categorized by the severity and the presence of complications.

Appendicitis itself is not a dedicated medical specialty. However, its diagnosis, treatment, and management involve several critical areas and subspecialties within medicine:
These specialities work together quickly because the condition can change from simple inflammation to a life-threatening emergency in a short period.
Appendicitis is important because it is a race against time. The condition poses a rapidly increasing danger if not treated quickly, making it a major concern in emergency medicine.

Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Appendicitis is the sudden swelling of the appendix, a small pouch attached to the large intestine. A general surgeon performs an appendectomy, which is the surgical removal of the inflamed appendix, usually through a minimally invasive (laparoscopic) procedure.
Appendicitis itself is the condition. Treatment focuses on resolving the severe inflammation and infection caused by a blockage in the appendix and preventing it from rupturing.
The main types are Acute Appendicitis (sudden inflammation) and Perforated Appendicitis (where the appendix has ruptured, which is a medical emergency).
You should see a doctor immediately, usually by going to the emergency room, if you have severe abdominal pain that starts near the belly button and moves to the lower right abdomen, especially if it is accompanied by fever or vomiting.
Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix (a small pouch). Diverticulitis is the inflammation of diverticula (small pouches) that form in the lining of the large intestine. Both cause abdominal pain, but in different areas and require different treatments.

Medical mistakes in hospitals are a big worry. The Institute of Medicine says up to 98,000 deaths annually in the U.S. are due to these
Did you know that nearly 40% of adults worldwide are overweight or obese? Many are looking for effective ways to lose weight. While bariatric surgery
An expert guide on how hernia mesh stays in place. We explore the amazing technology of stitches, tacks, and self-gripping mesh. The choice of technique
It’s estimated that a significant number of patients worldwide are deemed ineligible for hernia surgery due to various health concerns. At our institution, we’ve encountered numerous
Our ultimate guide to hernia treatment success. Discover the amazing 100% curable facts and which repair options are best. With over 700,000 hernia repairs performed
Having a mastectomy can change your life in big ways. Many women worry about how their breasts will look after surgery. Keeping a natural look

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)