Did you know millions of people worldwide face ear problems like hearing loss, vertigo, and tinnitus? These issues really affect their lives. At our place, we get how hard it is to figure out these problems and why it’s key to test them right.
Neuro-oto tests are top-notch tools for audiologists to check how the ear works with the brain. They’re vital for finding out what’s causing ear, nose, and throat issues. This helps doctors create the best treatment plans.
We’re all about giving the latest neuro otological tests. We want to make sure patients get the right diagnosis and care for their problems.
Key Takeaways
- Neuro-oto tests diagnose ear-related disorders.
- These tests assess the ear’s connection to the brain.
- Accurate diagnosis enables effective treatment plans.
- Our institution provides cutting-edge neuro otological tests.
- Specialized care is available for various ear, nose, and throat conditions.
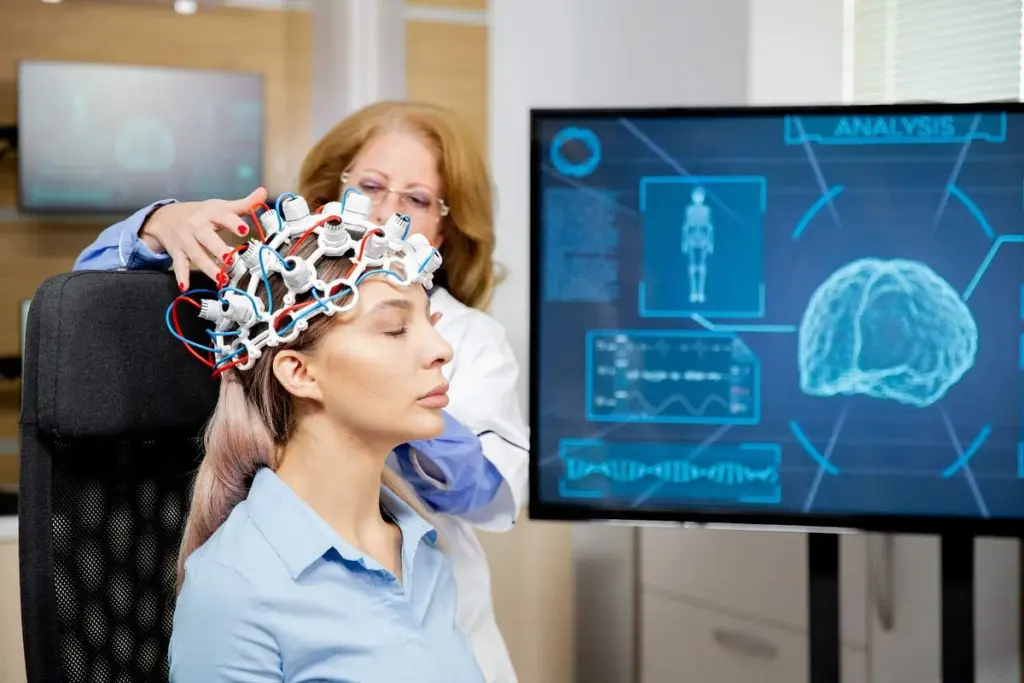
The Science Behind Neuro-Otological Examinations
The science of neuro-otological exams links the ear to the brain. These tests check how well the ear and balance systems work. They are key for hearing and staying balanced.
Definition and Purpose of Neuro-Oto Tests
Neuro-oto tests are special exams for the ear and brain. They help find and fix problems with hearing, balance, and equilibrium. This is done by checking how the ear and brain work together.
These tests aim to find the cause of ear symptoms like dizziness or hearing loss. Knowing the cause helps doctors create better treatment plans.
When These Tests Are Typically Recommended
These exams are suggested for ear or balance issues. Signs include ongoing dizziness, balance problems, or sudden hearing loss. They also check if treatments are working or if a condition is getting worse.
Advanced tests help us understand ear and brain connections better. This leads to more accurate diagnoses and better treatments.
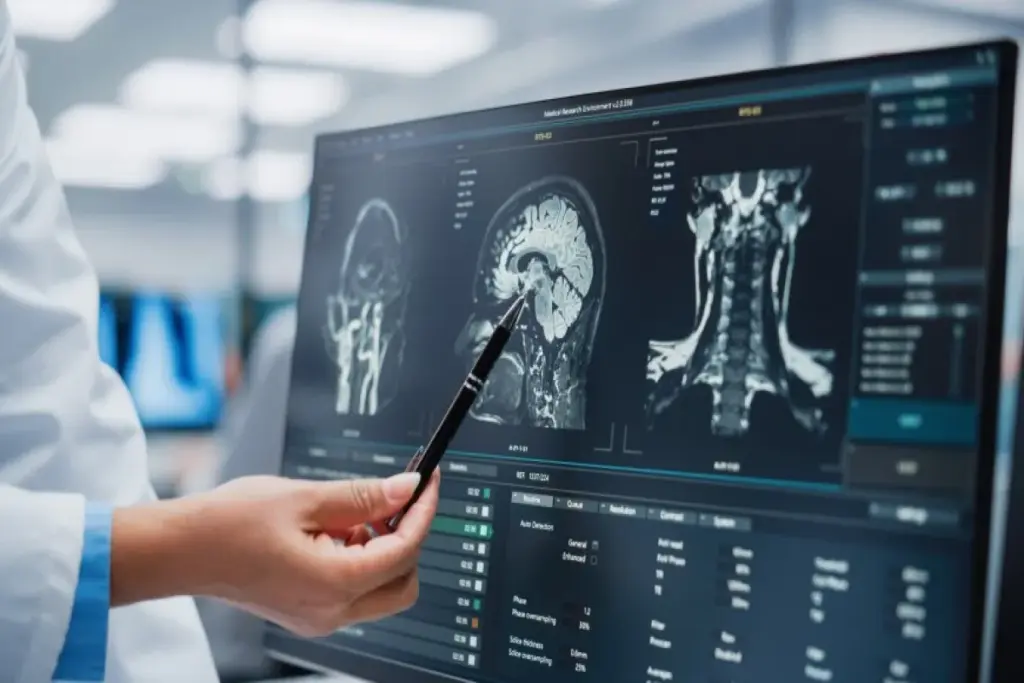
Otology: The Study of the Ear and Its Disorders
Otology is a key part of medicine that focuses on ear disorders. It studies, diagnoses, and treats ear problems. This field looks into the ear’s complexities, from hearing loss to balance issues.
Definition and Scope of Otology
Otology is the medical field that deals with ear disorders. It covers a wide range of issues, like infections and hearing loss. Specialists in otology work with other doctors to give full care.
The otologic meaning goes beyond just studying the ear. It’s about understanding the ear’s detailed structures and how they work. This knowledge is key for treating ear problems well.
The Evolution of Otological Medicine
Otology has seen big changes over time, thanks to new technology and knowledge of the ear. In the past, treating ear issues was hard. But now, thanks to modern tools, otology has grown a lot.
Today, otologists and other doctors have many ways to diagnose and treat ear problems. They can give better care and teach patients about ear health. An otologist does more than just treat ear issues. They also focus on prevention and teaching patients.
The term otological meaning shows how wide-ranging otology is. It’s all about understanding and fixing ear health problems. As we learn more about the ear, otology keeps growing, bringing new hope and treatments for ear issues.
Neurootology: Where Neurology Meets Ear Science
Neurootology is a field that combines ear and nervous system studies. It helps diagnose and treat complex ear issues. It’s key for understanding ear and brain connections, mainly when neurological factors play a role in hearing and balance problems.
What is Neurootology?
Neurootology is a part of otolaryngology that deals with ear and brain disorders. It covers a wide range of issues, like balance and hearing problems. Neurootologists are experts in handling complex cases that involve both ear and brain aspects.
The Role of Neuro-Otologists
Neuro-otologists are vital in treating complex ear disorders. They use special tests to find the cause of symptoms. Their knowledge helps manage conditions that need both ear and brain understanding. They offer care that fits each patient’s needs.
Differences Between Otologists and Neurootologists
Otolaryngologists and neurootologists both work with ear issues, but they focus differently. Otologists mainly treat ear diseases like hearing loss and infections. Neurootologists, though, focus on ear and nervous system disorders. They handle balance issues and conditions with neurological ties. Neurootology is a specialized field that looks at the neurological side of ear problems.
Common Ear Disorders Requiring Neuro-Otological Testing
Ear disorders are complex and need advanced testing for a correct diagnosis. These disorders affect the ear and its functions. They often require special tests to find the cause and the right treatment.
Vestibular Disorders and Balance Issues
Vestibular disorders mess with the inner ear’s balance system. Symptoms include dizziness, vertigo, and imbalance. These issues can really affect someone’s life, making it key to get a correct diagnosis through neuro-otological testing.
Some common vestibular disorders are:
- Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
- Meniere’s disease
- Vestibular neuritis
- Labyrinthitis
Neuro-otological testing helps find the exact cause of these symptoms. It guides the best treatment options.
Hearing Loss and Auditory Processing Disorders
Hearing loss and auditory processing disorders are serious issues that can be diagnosed with neuro-otological testing. Hearing loss can vary from mild to severe. It can be conductive, sensorineural, or mixed.
Auditory processing disorders make it hard to process sound. This can make it tough to understand speech and other sounds.
|
Type of Hearing Loss |
Description |
Common Causes |
|---|---|---|
|
Conductive Hearing Loss |
Involves issues with the middle ear |
Ear infections, otosclerosis |
|
Sensorineural Hearing Loss |
Relates to problems with the inner ear or auditory nerve |
Aging, noise exposure, certain medications |
|
Mixed Hearing Loss |
Combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss |
Various factors including infections and trauma |
Tinnitus and Other Auditory Symptoms
Tinnitus is when you hear noise or ringing in your ears. It’s a common ear disorder that might need neuro-otological testing. Tinnitus can be linked to hearing loss, earwax buildup, or certain medicines.
Finding the real cause of tinnitus and other ear symptoms is key for good treatment.
Dealing with ear disorders can be tough. With detailed neuro-otological testing, we can find the cause of your symptoms. Then, we can create a treatment plan that fits your needs.
The Ear-Brain Connection: Understanding the Auditory Pathway
Our ears and brain work together to help us hear and stay balanced. This system is complex, involving many parts and pathways.
Anatomy of the Ear
The ear has three main parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The outer ear catches sound waves. The middle ear sends these vibrations to the inner ear.
The inner ear has the cochlea for hearing and the vestibular system for balance.
Neural Pathways for Hearing
Sound vibrations turn into electrical signals in the cochlea. These signals go to the brain through the auditory nerve. In the brain, they help us understand different sounds.
The Vestibular System and Balance
The vestibular system in the inner ear is key for balance and spatial awareness. It works with the visual and proprioceptive systems to help us move around.
Knowing how our ears and brain connect is vital for diagnosing and treating hearing and balance issues. Doctors can better help with hearing loss, tinnitus, and balance problems by understanding ear anatomy and neural pathways.
Comprehensive Types of Neuro-Otological Tests
It’s important to know about different neuro-otological tests for good ear care. These tests help find and treat ear problems. This ensures patients get the right treatment.
Audiometric Evaluations
Audiometric evaluations are key for checking hearing loss. They show the type and how bad the hearing loss is. Tests like pure tone audiometry, speech audiometry, and tympanometry give a full picture of hearing.
Audiometric Test Types:
|
Test Type |
Description |
Clinical Use |
|---|---|---|
|
Pure Tone Audiometry |
Measures the faintest tones a person can hear at different frequencies. |
Diagnoses hearing loss and determines its severity. |
|
Speech Audiometry |
Assesses the ability to hear and understand speech. |
Evaluates the effectiveness of hearing aids and cochlear implants. |
|
Tympanometry |
Examines the middle ear function by varying air pressure. |
Identifies middle ear disorders such as otosclerosis. |
Vestibular Function Assessments
Vestibular function assessments are key for checking balance problems. They help find issues with dizziness, vertigo, and imbalance. These tests are important for diagnosing balance disorders.
Vestibular Test Types:
- Electronystagmography (ENG) or Videonystagmography (VNG)
- Rotational Chair Testing
- Computerized Dynamic Posturography
Neuroimaging in Ear Diagnostics
Neuroimaging is vital for finding ear and brain problems. MRI and CT scans give detailed images. They help see the inner ear and auditory pathways.
Neuroimaging Techniques:
|
Technique |
Description |
Clinical Use |
|---|---|---|
|
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) |
Provides detailed images of soft tissues, including nerves. |
Diagnoses acoustic neuromas and other soft tissue abnormalities. |
|
CT (Computed Tomography) Scan |
Offers high-resolution images of bone structures. |
Evaluates bony abnormalities and temporal bone fractures. |
Using these tests together, doctors can fully understand a patient’s ear health. This helps them create effective treatment plans.
Detailed Audiometric Testing Procedures
In audiology, detailed testing is key for diagnosing hearing issues. We use various tests to check how well someone can hear.
Pure Tone Audiometry Process
Pure tone audiometry tests how well someone can hear different sounds. We use headphones to play sounds at low volumes and increase them until they are heard.
The results show on an audiogram. This chart helps us see how well someone can hear at different sound levels. It’s important for figuring out hearing loss.
Speech Recognition and Discrimination Tests
These tests check how well someone can understand speech. We play words at different volumes and see if they can repeat them.
These tests show how well someone can hear speech. This is important for understanding how hearing loss affects talking. The results help us create a plan to help with hearing.
Acoustic Reflex and Immittance Measurements
Acoustic reflex testing checks how the middle ear muscles react to sound. It tells us about the middle ear and the nerve pathway.
Immittance measurements, like tympanometry, look at the eardrum and middle ear muscle reflexes. These tests help find problems like otosclerosis and eustachian tube issues.
By combining these tests, we get a full picture of someone’s hearing. This helps us create a good treatment plan.
Vestibular Testing Techniques and Protocols
Diagnosing vestibular disorders needs special tests. These tests help doctors understand the vestibular system. This way, they can make accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
Electronystagmography (ENG) and Videonystagmography (VNG)
Electronystagmography (ENG) and Videonystagmography (VNG) test the vestibular system by looking at eye movements. ENG uses electrodes around the eyes to record these movements. VNG uses infrared cameras for more precise tracking.
Key aspects of ENG/VNG include:
- Assessment of nystagmus (abnormal eye movements)
- Evaluation of the vestibular-ocular reflex
- Identification of peripheral or central vestibular dysfunction
These tests are key for diagnosing conditions like benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), vestibular neuritis, and other vestibular disorders.
Rotational Chair Testing
Rotational chair testing is a valuable tool for assessing the vestibular system. The patient sits in a rotating chair, and their eye movements are recorded during the rotation.
|
Test Component |
Description |
Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|
|
Rotation Stimulus |
Chair rotation stimulates the vestibular system |
Evaluates vestibular response to different frequencies |
|
Eye Movement Recording |
Records nystagmus in response to rotation |
Assesses vestibular-ocular reflex function |
|
Gain and Phase Measurements |
Quantifies the vestibular response |
Helps diagnose bilateral vestibular loss or asymmetry |
Computerized Dynamic Posturography
Computerized dynamic posturography (CDP) is a complex test. It checks a patient’s balance function and how they use sensory inputs for balance. It sees how well someone can keep their posture under different conditions.
The test involves:
- Standing on a movable platform with a visual surround
- Varying the platform and visual surround to challenge balance
- Measuring the patient’s ability to maintain balance
This test gives important info on how a patient uses vestibular, visual, and proprioceptive inputs for balance. It helps guide rehabilitation strategies.
Advanced Electrophysiological Diagnostic Methods
We use the latest electrophysiological diagnostic techniques to check how well the ears and balance work. These methods give us detailed insights into the ear and balance systems. This helps us make accurate diagnoses and manage related health issues well.
Electrocochleography (ECochG)
Electrocochleography (ECochG) is a test that looks at the electrical signals from the cochlea and auditory nerve when we hear sounds. It’s very helpful in spotting Meniere’s disease.
Key applications of ECochG include:
- Diagnosing Meniere’s disease
- Checking how well the cochlea and auditory nerve work
- Watching the inner ear during surgeries
Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Testing
Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) testing is a safe way to check the auditory nerve and brainstem. It looks at the electrical signals from the ear and brain when we hear sounds.
ABR testing is commonly used for:
- Checking hearing in babies and young kids
- Finding out if someone has auditory neuropathy
- Keeping an eye on brain function during surgeries
Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (VEMP)
Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (VEMP) testing helps us see how well the vestibular system works. It looks at the muscle responses to sound or vibration. This is important for the saccule and the inferior vestibular nerve.
|
Test |
Primary Use |
Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
ECochG |
Diagnosing Meniere’s disease |
Directly measures cochlear and auditory nerve function |
|
ABR |
Checking auditory nerve and brainstem function |
Safe, clear look at hearing function |
|
VEMP |
Evaluating vestibular function |
Looks at saccule and inferior vestibular nerve function |
The Medical Team Behind Ear Health
Ear health is a complex field that needs the help of many healthcare professionals. Doctors and specialists work together to diagnose, treat, and manage ear disorders. This team approach ensures patients get the best care possible.
Otolaryngologists and ENT Specialists
Otolaryngologists, or ENT specialists, are doctors who focus on ear, nose, and throat issues. They are key in treating hearing, balance, and related problems.
Key Responsibilities of Otolaryngologists/ENT Specialists:
- Diagnosing and treating ear infections and other ear-related disorders
- Performing surgeries such as cochlear implantation and tumor removal
- Managing conditions like tinnitus and hearing loss
Audiologists and Their Clinical Role
Audiologists are experts in hearing and balance disorders. They help diagnose and treat hearing loss, fit hearing aids, and offer rehabilitation.
Audiologists do more than just fit hearing aids. They also help with balance disorders through vestibular assessment and rehabilitation.
|
Services Provided by Audiologists |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Hearing Assessments |
Comprehensive tests to evaluate hearing loss |
|
Hearing Aid Services |
Fitting, adjusting, and maintaining hearing aids |
|
Vestibular Rehabilitation |
Therapy to alleviate balance disorders |
Interdisciplinary Approach to Ear Disorders
Managing ear disorders often needs a team effort. This team includes otolaryngologists, audiologists, neurologists, primary care physicians, and rehabilitation specialists.
“The collaboration among different specialists ensures that patients receive complete care. This care addresses symptoms and the underlying causes of their condition.”
— Expert in Otolaryngology
Together, these professionals can make a more accurate diagnosis. They can also create a treatment plan that meets the patient’s specific needs.
Patient Experience: Preparing for Neuro-Otological Tests
We’re here to help you feel at ease during neuro-otological testing. Our team works hard to make sure you’re ready for your visit. We want your experience to be as comfortable as possible.
Before Your Appointment
There are a few things you can do before your test. Always follow any instructions from your healthcare provider. They might ask you to avoid certain medicines or get your ears ready for the test.
- Get to your appointment 15 minutes early to fill out any paperwork.
- Don’t use hair products or wear too much makeup, as they can affect the tests.
- Bring any medical records, like past test results and your current medications.
During the Testing Process
Our team will walk you through each step during the test. The tests are designed to be non-invasive and as comfortable as possible. You might feel some discomfort or dizziness, but it’s usually temporary.
Some tests you might have include:
- Audiometric evaluations to check your hearing.
- Vestibular function assessments to test your balance.
- Neuroimaging tests, like MRI or CT scans, to see your ear and brain structures.
Post-Test Recovery and Considerations
After the test, you might get advice on how to recover. In most cases, you can go back to your normal activities right away. But, some tests might need you to rest or be watched for a bit.
We’ll talk about your test results with you. We’ll explain what they mean and what you might need to do next. We’re here to support you every step of the way.
Understanding Your Test Results
It’s important to understand your neuro-otological test results to diagnose and treat ear problems well. When you get your test results, knowing what they mean is key to your ear health.
Interpreting Diagnostic Reports
Diagnostic reports from neuro-otological tests can be complex. They detail your ear health and function. We’ll make these reports easy to understand, highlighting important findings and their meanings.
Your report may show results from audiometric and vestibular function tests. Each part of the report talks about a different ear health aspect. This includes hearing, balance, or neural responses.
Key Components of a Diagnostic Report:
- Audiometric test results, including pure tone thresholds and speech recognition scores.
- Vestibular test findings, such as electronystagmography (ENG) or videonystagmography (VNG) results.
- Any additional tests performed, like auditory brainstem response (ABR) or vestibular evoked myogenic potentials (VEMP).
Common Abnormal Findings and Their Significance
Abnormal findings in your test results can point to various ear disorders. It’s vital to understand these findings to choose the right treatment.
|
Abnormal Finding |
Possible Indication |
Significance |
|---|---|---|
|
Elevated hearing thresholds |
Hearing loss |
May require hearing aids or other interventions |
|
Abnormal vestibular test results |
Vestibular dysfunction |
Could indicate balance disorders or vertigo |
|
Abnormal ABR or VEMP results |
Neural pathway issues |
May suggest problems with auditory processing or nerve damage |
By grasping your test results and what abnormal findings mean, we can craft a treatment plan tailored to you.
Treatment Approaches Following Diagnosis
Getting a diagnosis is the first step in finding the right treatment. Healthcare experts then create a plan based on the diagnosis. This plan is made to fit the patient’s unique needs.
Every patient is different, and so are their treatments. We aim to give full care. This includes medical treatments, surgeries, and rehabilitation.
Medical Management Options
Medical management is often the first treatment for ear problems. It can include medicines to ease symptoms, fight infections, or reduce swelling. For example, antibiotics treat bacterial infections, and corticosteroids help with swelling in conditions like vestibular neuritis.
Some treatments also involve changing your lifestyle or using home remedies. For Meniere’s disease, a low-sodium diet and avoiding triggers are recommended.
Surgical Interventions for Ear Disorders
If medicines don’t work, surgery might be needed. The type of surgery depends on the problem. For example, cochlear implants can help those with severe hearing loss.
Other surgeries include fixing perforated eardrums or removing infected bone cells. Deciding on surgery is a big choice, made after talking to an ear specialist.
Vestibular and Auditory Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is key for recovering from ear issues. Vestibular rehabilitation helps with balance problems. It includes exercises to improve balance.
Auditory rehabilitation helps with hearing loss. It includes hearing aids, training, and speech therapy. Our team creates personalized plans for each patient.
Innovations in Neuro-Otology: Current Research and Future Directions
The field of neuro-otology is on the verge of a big change. New diagnostic tools and treatments are leading the way. We’re learning more about how the ear and brain work together. This is opening up new ways to diagnose and treat ear problems.
Emerging Diagnostic Technologies
Diagnostic tools in neuro-otology are getting better fast. This helps doctors diagnose and treat ear issues better. Some new technologies include:
- Advanced Imaging Techniques: High-resolution MRI and CT scans help us see the inner ear and auditory pathways better. This leads to more accurate diagnoses.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Audiology: AI is being used to analyze hearing data. This could mean finding hearing problems sooner and getting treatments that fit each person better.
- Vestibular Testing Innovations: New tests like video head impulse testing (vHIT) and vestibular evoked myogenic potentials (VEMP) are helping us understand vestibular function and disorders better.
These new technologies are making diagnosis more accurate. They also help in finding more effective treatments.
Promising Treatment Advances
Treatment options in neuro-otology are also changing a lot. This is thanks to new medical technology and a better understanding of ear disorders. Some exciting new treatments include:
|
Treatment Area |
Current Advances |
Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Hearing Loss |
Cochlear implants with advanced signal processing |
Improved speech recognition in noisy environments |
|
Vestibular Disorders |
Vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT) tailored to individual needs |
Enhanced balance and reduced dizziness |
|
Tinnitus Management |
Personalized sound therapy and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) |
Reduced tinnitus severity and improved quality of life |
As research keeps moving forward, we’ll see even more new treatments. These will offer hope to those with ear-related disorders.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve looked at how important neuro-otological tests are. They help find and treat ear problems. These tests check ear health and find issues like vestibular disorders and hearing loss.
These tests have changed how we deal with ear problems. They help doctors understand how the ear works with the brain. This knowledge is key to treating ear issues.
We’re always working to improve care for ear health. We use the latest tests and treatments to help our patients. Our goal is to give the best care possible for ear health needs.
FAQ
Common Ear Disorders
What are some common ear disorders that require neuro-otological testing?
Ear disorders needing neuro-otological tests include vestibular problems, hearing loss, and tinnitus. These can really affect someone’s life.
What is the auditory pathway, and how does it relate to hearing?
The auditory pathway is how sound gets from the ear to the brain. It lets us hear and understand sound.
Testing and Preparation
What types of tests are used in neuro-otological evaluations?
Tests in neuro-otological evaluations include audiometric tests and vestibular function checks. They also use neuroimaging to fully assess ear function.
How do I prepare for a neuro-otological test?
To get ready for a neuro-otological test, follow your doctor’s instructions. This might mean avoiding certain meds, arriving early, and sharing your medical history.
Care Professionals and Treatments
What is the role of an audiologist in ear care?
An audiologist is vital in ear care. They diagnose and treat hearing and balance issues. They also provide hearing aids and therapies to help people communicate better.
What treatment options are available for ear disorders diagnosed through neuro-otological tests?
Treatment for ear disorders includes medical care, surgery, and therapies. These can be vestibular rehab or auditory therapy. They aim to improve symptoms and quality of life.
Future Developments
What advancements are being made in the field of neuro-otology?
Neuro-otology is always getting better. New diagnostic tools and treatments, like medications and surgeries, are being developed. They aim to better diagnose and treat ear problems.
Reference
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9422724/