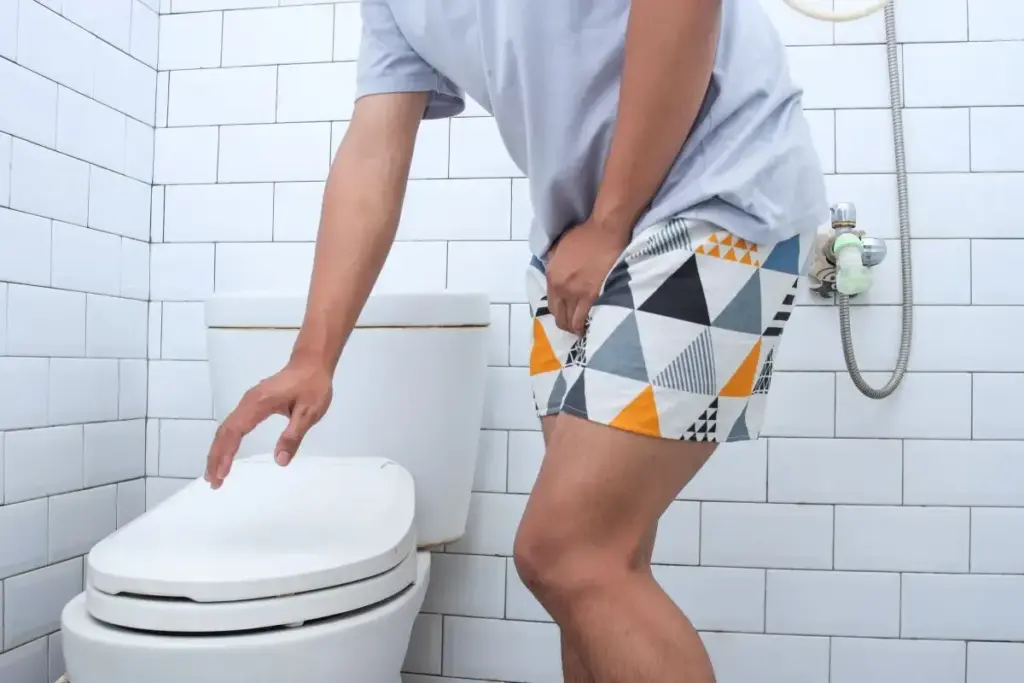
Feeling painful or difficult urination can really upset you. It’s a problem that can happen to anyone, at any age. This issue makes many people go to the doctor. Dysuria is a painful condition. Discover the amazing medical meaning and how to find a powerful cure for your burning urination today.
Dysuria is the medical term for this painful urination. It’s not a disease itself but a sign of something else going on. This something needs to be found and fixed.
Knowing what dysuria definition means is key. We’ll look into what dysuria is, why it happens, and why you should see a doctor.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the meaning of dysuria is essential for identifying its causes.
- Dysuria is a symptom that can be associated with various underlying medical conditions.
- It is a common issue affecting a wide range of individuals.
- Recognizing the significance of dysuria can prompt timely medical intervention.
- Seeking medical care is critical for addressing the root cause of dysuria.
Understanding Dysuria: Definition and Overview
Dysuria is a common problem that affects millions globally, causing a burning or pain sensation when you pee. It’s important to understand dysuria to manage the discomfort it brings during micturition. We’ll look into its medical definition, symptoms, and how common it is among different groups.
Medical Definition of Dysuria
Dysuria is when urination is painful or hard. It feels like a burning sensation while you pee. This could mean there’s an issue that needs a doctor’s attention. The reasons can be from infections to other health problems.
Common Symptoms Associated with Dysuria
People with dysuria might also feel like they need to pee a lot, or feel urgent. They might also have stomach pain. These signs can make everyday life hard. Spotting these symptoms is key to getting the right medical help.
Prevalence and Demographics
Dysuria affects many people, no matter their background. Studies show it’s common in those with urinary tract infections. Who gets it can depend on age, gender, and health. For example, women are more likely to get UTIs, which cause dysuria.
Knowing about dysuria helps us tackle the root problems and get the right medical care. It’s not just a symptom; it’s a warning sign of a possible health issue.
Causes of Dysuria: Identifying the Underlying Issues

Dysuria, or painful urination, can come from many sources. It’s important to know what causes it to treat it right. We’ll look at infections and other conditions that lead to dysuria.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are a big reason for dysuria, mainly in women. These infections happen when bacteria get into the urinary tract. This leads to pain and frequent need to pee. Azo UTIs are usually treated with antibiotics.
|
Symptoms |
Causes |
Treatment |
|---|---|---|
|
Burning sensation while urinating |
Bacterial infection |
Antibiotics |
|
Frequent urination |
Infection and inflammation |
Increased fluid intake |
|
Abdominal pain |
Spread of infection |
Medical consultation |
STIs and Other Infections
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) also cause dysuria. Chlamydia and gonorrhea can lead to painful urination. Men might notice urine in pee male symptoms, showing they have an infection.
Non-Infectious Causes of Dysuria
Not all dysuria comes from infections. Other reasons include bladder stones, some medicines, and interstitial cystitis. Some people might feel burns when i pee because of these reasons. This shows we need to look at all possible causes.
In summary, dysuria can stem from UTIs, STIs, or other issues. Knowing the cause is essential for the right treatment and relief.
Symptoms of Dysuria: What to Look For
Dysuria symptoms can be quite distressing. Recognizing them is the first step towards seeking appropriate medical care. We will outline the common symptoms associated with dysuria, helping you understand what to look for and when to seek help.
Painful Urination
Painful urination is a hallmark symptom of dysuria. It is characterized by a burning or stinging sensation while urinating. This discomfort can range from mild to severe and may be persistent or occur only during certain times.
“The pain can be quite intense, which makes everyday activities uncomfortable; thus, it’s crucial to stress the need for prompt medical evaluation as this symptom significantly impacts one’s quality of life.
Frequent Urination
Frequent urination is another common symptom of dysuria. Individuals may feel the need to urinate more often than usual, even when there’s little urine in the bladder. This can be disruptive, affecting daily routines and sleep patterns.
It’s essential to note that frequent urination can be accompanied by other urinary tract symptoms, such as urgency or a feeling of incomplete bladder emptying. These symptoms together can indicate an underlying issue that needs medical attention.
Other Associated Symptoms
In addition to painful and frequent urination, dysuria can be associated with other symptoms. These may include:
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Blood in the urine
- Pelvic pain or discomfort
- Fever or chills
These symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause of dysuria. For instance, if the cause is a urinary tract infection (UTI), symptoms may include cloudy urine or blood in the urine. Recognizing these associated symptoms is key for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.
We stress the importance of seeking medical care if you experience any of these symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Diagnosing Dysuria: Medical Approaches
Diagnosing dysuria requires a detailed strategy. This includes initial consultations, lab tests, and sometimes, imaging studies. Finding the cause of dysuria is key to effective treatment.
Initial Consultations and Tests
When someone has dysuria symptoms, we start with a detailed medical history and physical exam. We look at the pain’s duration and severity, and any other symptoms like fever or stomach pain.
We might do a urinalysis to check for infections or other issues. This test can show blood, protein, or bacteria in the urine. It helps us decide what to do next.
Laboratory Tests for Diagnosis
Laboratory tests are vital for finding the cause of dysuria. We might do:
- Urine culture to find bacterial infections
- Blood tests for infection or inflammation signs
- STI testing if infections are suspected
These tests help us figure out the best treatment. It could be antibiotics, other meds, or more tests.
Imaging and Further Investigations
In some cases, we need imaging studies to find the cause of dysuria. We might use:
- Ultrasound to look at the kidneys and bladder
- CT scans for detailed urinary tract images
- Cystoscopy to see inside the bladder and urethra
These studies can show structural problems, stones, or other causes of dysuria.
If symptoms are severe or don’t get better, we might do more tests. This helps rule out complex conditions.
|
Diagnostic Approach |
Description |
Potential Findings |
|---|---|---|
|
Initial Consultation |
Medical history and physical examination |
Symptoms assessment, fever, abdominal tenderness |
|
Urinalysis |
Laboratory test to analyze urine |
Presence of blood, protein, bacteria, or other abnormalities |
|
Imaging Studies |
Ultrasound, CT scans, or cystoscopy |
Structural abnormalities, stones, tumors, or other conditions |
We use different diagnostic methods to find the cause of dysuria. This helps us create a good treatment plan. Some might find relief with azo urinary pain relief, while others need more medical help.
Treatment Options for Dysuria: A Complete Guide
Finding the right treatment for dysuria can greatly improve your life. Dysuria, or painful urination, can stem from many causes. The key is to find and treat the cause.
Antibiotics and Medications
For UTI-related dysuria, antibiotics are often prescribed. Azo-UTI can ease bladder pain and discomfort. It’s important to finish all antibiotics as told by your doctor to clear the infection.
For other infections, like STIs, treatment is specific. Non-infectious causes might need symptom-managing meds or treatments for underlying issues.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Adjustments
Medical treatments aren’t the only solution. Home remedies and lifestyle changes can also help. Drinking lots of water helps flush out bacteria and dilutes urine, easing bladder irritation.
- Avoiding spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol can lessen bladder irritation.
- Good hygiene, like proper wiping and urinating after sex, can prevent infections.
- Warm compresses on the lower abdomen can ease discomfort.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Knowing when to get medical help is vital. If you have severe pain, fever, or blood in your urine, seek help right away. These signs could mean a serious infection or condition needing quick treatment.
Understanding dysuria treatments and knowing when to get help can greatly improve your condition. By using medical treatments and making lifestyle changes, you can reduce symptoms and enhance your life quality.
Preventing Dysuria: Healthy Practices
Understanding dysuria’s causes is key to preventing it. Simple habits and health awareness can lower painful urination risks.
Hydration and Diet Recommendations
Drinking enough water is vital for urinary health. It helps remove harmful bacteria and pathogens. Aim for eight glasses of water daily, more if you’re active or in a hot place.
Eating a balanced diet with fruits, veggies, and whole grains also helps. Foods like cranberries and blueberries can prevent infections by stopping bacteria from sticking to the bladder and urinary tract walls.
|
Food |
Benefits |
|---|---|
|
Cranberries |
May prevent UTIs by inhibiting bacterial adhesion |
|
Blueberries |
Rich in antioxidants and may help reduce inflammation |
|
Water |
Flushes out bacteria and pathogens from the urinary tract |
Personal Hygiene Tips
Good personal hygiene is key to avoiding dysuria. For those with a urethra, wiping from front to back helps prevent bacteria. Also, urinating after sex can flush out bacteria.
Men should clean their genital area regularly and retract the foreskin if applicable. Women should avoid scented soaps and bubble baths to prevent irritation and dysuria.
Sexual Health Considerations
Sexual health is important for preventing dysuria, mainly by avoiding STIs. Using condoms and knowing your partner’s STI status can help a lot.
Regular STI testing is also vital, more so for those with many partners. Catching and treating STIs early can prevent dysuria and other complications.
By following these healthy practices, we can lower dysuria risks and keep our urinary tracts healthy.
Dysuria in Men vs. Women: Key Differences
Dysuria, or painful urination, shows up differently in men and women. It can come from many causes, affecting both sexes but in different ways. Knowing these differences is key to understanding and treating dysuria.
Causes Specific to Women
In women, painful urination often means they have a urinary tract infection (UTI). UTIs are more common in women because their urethra is shorter. Other causes include yeast infections and hormonal changes during menopause, which can cause vaginal dryness and irritation.
Women are also more likely to have interstitial cystitis. This is a chronic condition that causes bladder pressure and pain. We’ll look into these conditions further to understand their effects.
Causes Specific to Men
Men face different reasons for painful urination, like prostatitis or inflammation of the prostate gland, and sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Their longer urethra can sometimes lower the risk of some infections but also poses unique challenges.
Conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), or enlarged prostate, can also cause dysuria in men. This is because an enlarged prostate can block the flow of urine. It’s important to know these gender-specific causes for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Impact on Quality of Life
Dysuria can greatly affect a person’s quality of life, no matter their gender. The pain and discomfort can cause anxiety and stress, making daily activities and sleep hard. For some, the fear of painful urination can lead to not drinking enough water, which can make things worse.
It’s not just about treating the physical symptoms of dysuria. It’s also about improving the person’s overall well-being. By understanding the gender-specific aspects of dysuria, healthcare providers can offer more personalized and effective care.
Potential Complications of Untreated Dysuria
Untreated dysuria can lead to serious health problems. Dysuria means painful or hard urination, often due to underlying issues. It’s key to understand dysuria and seek medical help early.
Progression to More Serious Conditions
Ignoring dysuria can cause bigger health issues. For example, urinary tract infections (UTIs) can spread to the kidneys. This can lead to pyelonephritis, a serious infection.
There’s also a risk of kidney damage from untreated UTIs. Kidney damage can make it hard for the body to remove waste, causing toxin buildup.
|
Condition |
Description |
Potential Complications |
|---|---|---|
|
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) |
Infections occurring in any part of the urinary system |
Kidney damage, sepsis |
|
Pyelonephritis |
Infection of the kidney |
Impaired kidney function, kidney scarring |
|
Kidney Damage |
Impaired kidney function due to infection or other causes |
Chronic kidney disease, end-stage renal disease |
Psychosocial Effects
Dysuria’s impact on mental health is significant. Chronic conditions can cause anxiety and stress, lowering quality of life. The pain from dysuria can make people avoid social and intimate activities, leading to feelings of loneliness.
Long-term Health Risks
Untreated dysuria can lead to long-term health issues. In men, conditions like prostatitis can cause infertility or chronic prostatitis.
It’s vital to get medical help to avoid these problems. Early treatment can greatly improve outcomes for those with dysuria.
Seeking Medical Help: When to Consult a Physician
Dysuria can be a sign of an underlying issue that requires medical attention. We’re here to guide you on when to seek help. It’s important to recognize the severity of your symptoms and know when to consult a healthcare provider.
Red Flags to Watch For
Certain symptoms indicate a need for immediate medical attention. If you experience severe pain while urinating, difficulty urinating, or notice blood in your urine, seek help right away. Other red flags include fever, chills, or a strong, persistent urge to urinate.
These symptoms could signify a more serious condition, such as a severe urinary tract infection (UTI) or bladder pain syndrome. They require prompt treatment.
Preparing for Your Appointment
Before your consultation, gather information about your symptoms. Keep a record of when your symptoms started, their severity, and any factors that seem to trigger or relieve them. Also, list any medications you’re currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs like azo urinary pain relief medication.
Being prepared will help ensure a productive discussion with your healthcare provider.
Questions to Ask Your Healthcare Provider
During your appointment, don’t hesitate to ask questions about your condition. Some essential questions include: “What is causing my dysuria?” “What tests do I need to undergo to determine the cause?” “What treatment options are available for my condition?” and “Are there any lifestyle changes or home remedies that can help alleviate my symptoms?”
Asking these questions will help you understand your diagnosis and the best course of treatment.
Dysuria and Mental Health: The Overlooked Connection
Painful urination can be really tough to deal with. Knowing what it means is key. Dysuria, or painful urination, is more than just a physical problem. It can really mess with your mental health too.
The stress and worry from dysuria can be too much. It can change how you live your day-to-day life. It affects your overall happiness and well-being.
The Psychological Impact
People with dysuria often feel anxious. They wonder if it hurts to have this condition. The pain makes simple tasks hard to do.
This issue can happen to anyone. It causes a lot of worry and can really hurt your mental health.
Support and Resources
It’s important to address the mental health side of dysuria. Support groups and resources can offer a lot of help. We need to make sure care includes mental health support.
Mental Health Matters
Dealing with dysuria needs a complete approach. This includes medical treatment and mental health support. Understanding the link between dysuria and mental health helps us provide better care. It improves the lives of those affected.
FAQ
What is dysuria?
Dysuria is when you feel pain when you pee. It can mean you have an infection or something else is wrong.
What are the common causes of dysuria?
Dysuria can be caused by infections or injuries. This includes UTIs and STIs, as well as irritation.
How is dysuria diagnosed?
Doctors use tests and scans to find out why you’re in pain. They start with a check-up and then do more tests.
What are the treatment options for dysuria?
Doctors might give you medicine for infections. You can also try home remedies and change your habits to feel better.
How can dysuria be prevented?
To avoid dysuria, drink lots of water and eat well. Keep clean and protect your health when you’re intimate.
Are there any differences in dysuria between men and women?
Yes, men and women face different issues with dysuria. Some problems are more common in one gender than the other.
What are the possible complications of untreated dysuria?
If you don’t treat dysuria, it can get worse. This can affect your mental health and lead to serious health problems.
When should I seek medical help for dysuria?
See a doctor if you have severe pain or trouble peeing. These are signs you need help right away.
How can I prepare for a medical appointment for dysuria?
Before your appointment, write down your symptoms and medical history. Also, think about any questions you want to ask your doctor.
Is there a connection between dysuria and mental health?
Yes, dysuria can make you feel anxious or stressed. It’s important to talk about your mental health with your doctor.
What is the role of Azo in urinary pain relief?
Azo helps with the pain of peeing. It can make you feel better by reducing burning sensations.
Why does it burn when I pee?
Burning when you pee can be from infections or irritation. It’s important to see a doctor to find out why.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/urethritis.htmhttps://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/urethritis.htm



































