Neurology diagnoses and treats disorders of the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, as well as thought and memory.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Doctors may suggest seeing a neurosurgeon when there are changes in the brain, spine, or nerves that stop them from working normally. These changes can happen because of pressure, injury, unusual growths like tumors, problems with stability, or trouble with blood flow to the nerves. Not every nerve problem needs surgery, but sometimes surgery is needed to keep things from getting worse or to stop lasting damage.
Symptoms can start slowly over time or come on quickly, depending on what is causing the problem and how fast it is happening.

Changes in brain function are clinically significant.
When the brain is affected by structural abnormalities, symptoms may involve higher neurological functions as well as basic motor and sensory control.
Brain-related symptoms may include
• Persistent or worsening headaches
• Seizures or seizure-like activity
• Changes in memory, attention, or behavior
• Weakness or numbness affecting one side of the body
• Visual disturbances or speech difficulties
Such symptoms often prompt advanced imaging and specialist evaluation.
Spinal involvement affects movement and sensation.
Structural problems involving the spinal cord or vertebral column can disrupt neural transmission, leading to progressive neurological impairment.
Spinal-related symptoms may include
• Neck or back pain associated with neurological changes
• Limb weakness or stiffness
• Numbness, tingling, or altered sensation
• Difficulty with balance or walking
• Changes in bladder or bowel control
These symptoms may worsen if compression persists.
Peripheral nerves support daily function.
Conditions affecting peripheral nerves may cause focal symptoms related to specific nerve pathways.
Peripheral nerve symptoms may include
• Localized pain or burning sensations
• Muscle weakness in a specific distribution
• Loss of sensation or coordination
• Functional limitation in affected limbs
Surgical intervention may be considered when nerve compression or injury is persistent.

Cranial nerves control critical functions.
Cranial nerve involvement may produce distinct neurological symptoms depending on the nerve affected.
Cranial nerve symptoms may include
• Facial weakness or asymmetry
• Difficulty swallowing or speaking
• Hearing changes or imbalance
• Visual impairment or eye movement abnormalities
Such symptoms often indicate localized neurological pathology.
Pressure affects brain function globally.
Structural conditions that increase pressure within the skull can impair brain function and may require urgent neurosurgical evaluation.
Symptoms of increased pressure may include
• Severe or persistent headaches
• Nausea or vomiting
• Altered consciousness or confusion
• Visual changes related to pressure effects
These symptoms require prompt assessment.
Risk reflects exposure and biology.
Certain underlying factors increase the likelihood of conditions that may require neurosurgical intervention.
Risk factors may include
• Degenerative changes of the spine
• Congenital neurological abnormalities
• Prior trauma to the head or spine
• Vascular abnormalities affecting the brain
• Progressive structural conditions
Awareness of risk supports early detection.
Injury alters neural integrity.
Traumatic events involving the head or spine significantly increase the risk of structural neurological injury that may require surgical care.
Risk increases with
• High-impact accidents
• Repetitive injury exposure
• Delayed evaluation after trauma
Early assessment reduces long-term damage.
Age influences vulnerability.
Children and older adults may face different neurosurgical risks due to developmental factors, degenerative changes, or reduced physiological reserve. Age-specific evaluation supports appropriate care planning.
Pattern recognition guides referral.
Neurosurgical evaluation is often considered when
• Neurological symptoms are progressive or severe
• Imaging reveals structural abnormalities
• Conservative treatment fails to control symptoms
• Neurological function is at risk
Timely referral supports optimal outcomes.

Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
No, many are managed non-surgically.
Progressive weakness, seizures, or pressure-related symptoms.
Only if it is associated with neurological impairment.
No, some conditions develop without clear risk factors.
When structural causes are suspected or symptoms worsen.


Every year, thousands of people around the world have brain tumor removal surgery. Craniotomy surgery is a common method. It involves temporarily removing a part
Get the hopeful facts about life expectancy brain surgery. Discover the amazing survival rates and critical factors that influence prognosis. Getting a diagnosis of a
The jackknife position is key in many medical procedures, like colorectal surgeries. The STERIS guide on patient positioning calls it the Kraske position. The patient
Medical treatments can make people anxious, and wondering if stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) hurts is common. We know how scary any medical procedure can be. That’s
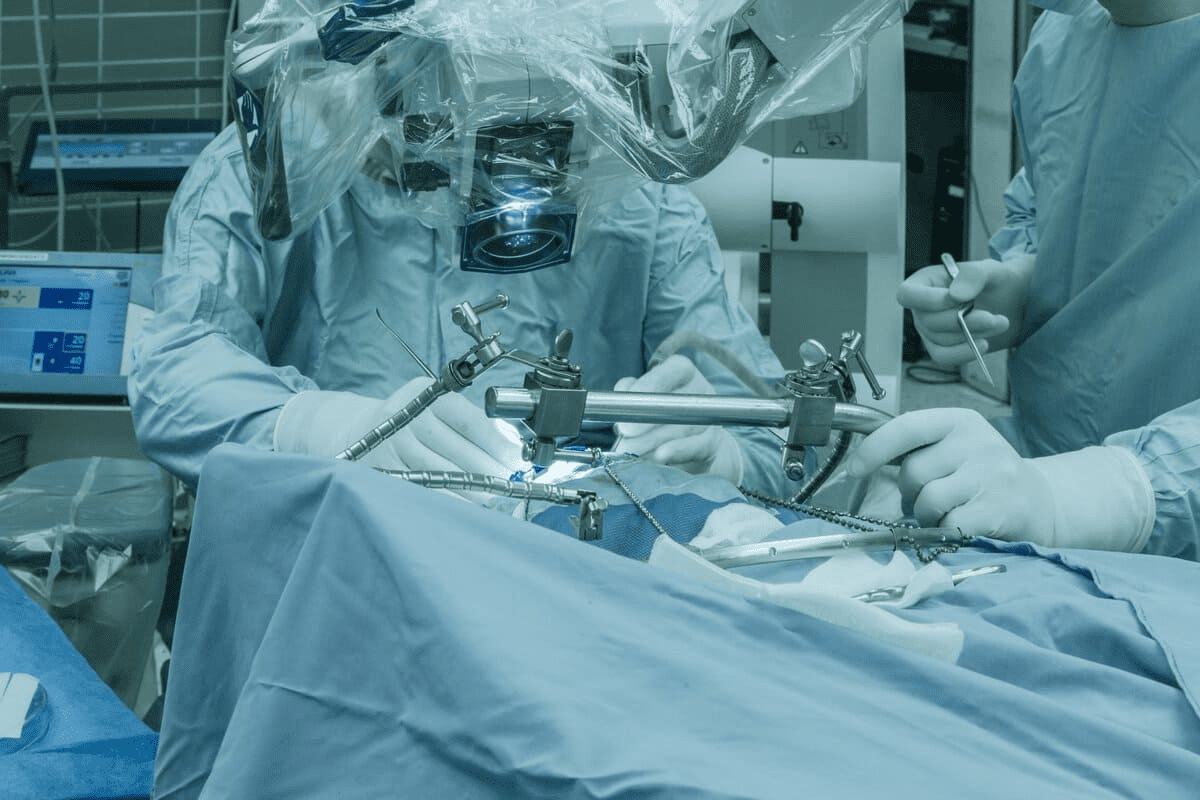
Craniotomy Survival Rate Nearly 50,000 craniotomies are done every year in the United States. A craniotomy involves temporarily removing a portion of the skull to
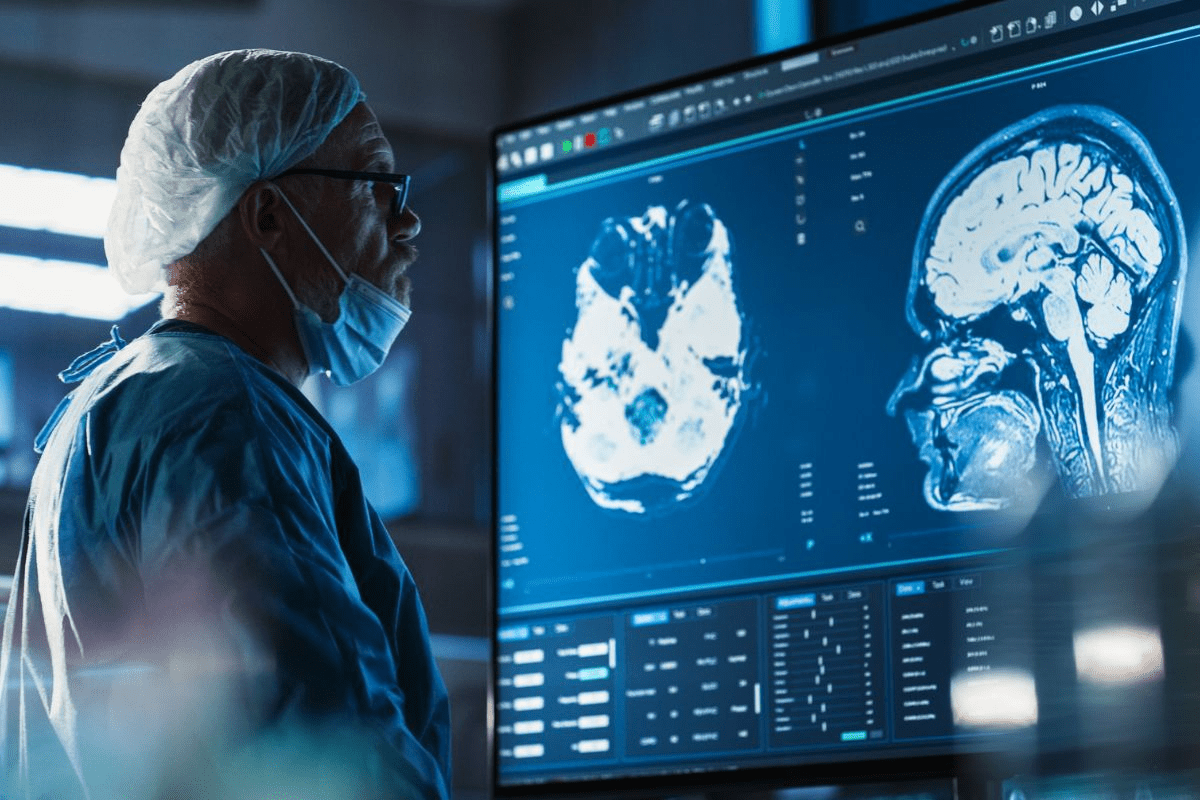
Did you know over 200,000 brain surgeries happen every year in the United States? This shows how important and complex neurosurgical procedures are. Neurosurgery is a

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)