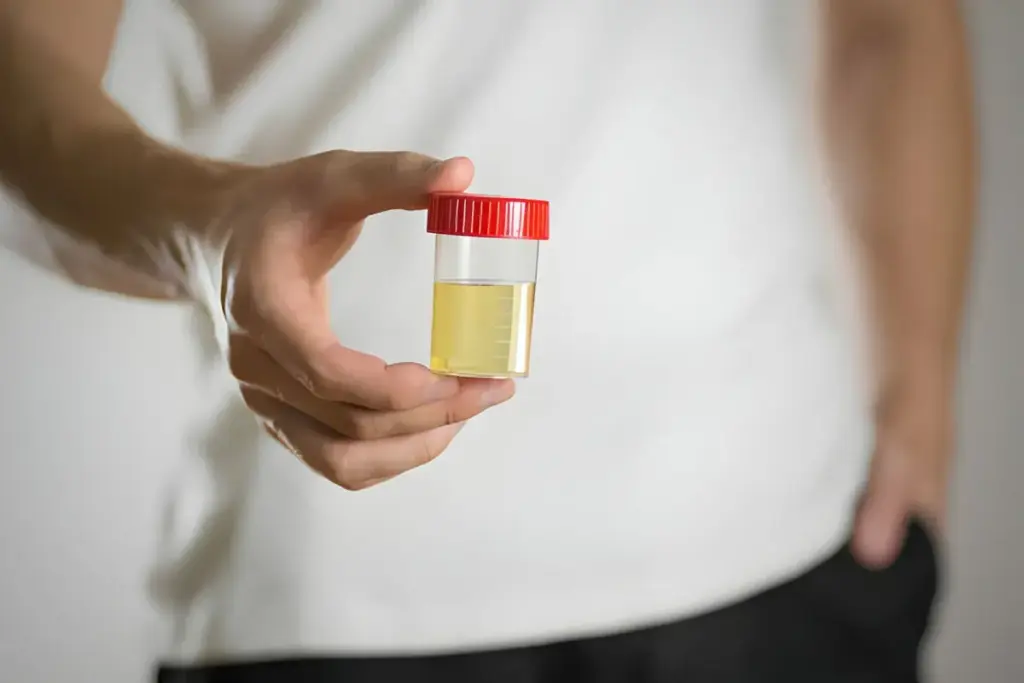
Urinary retention is a common problem after a prostate biopsy procedure. Medical Expert. Castle, MD, says it can be very upsetting. It can really mess up your daily life. Post-test symptoms: Blood in urine after a prostate biopsy is common. We explain how long bleeding lasts and when it becomes a concern.
Many people struggle to pee normally after this procedure. We’ll look into why this happens and how to fix it.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the causes of urinary retention after a biopsy.
- Recognizing the symptoms and when to seek medical help.
- Exploring available treatments to alleviate urinary issues.
- Learning how to manage and prevent future complications.
- Discovering the importance of post-procedure care.
Understanding Prostate Biopsy
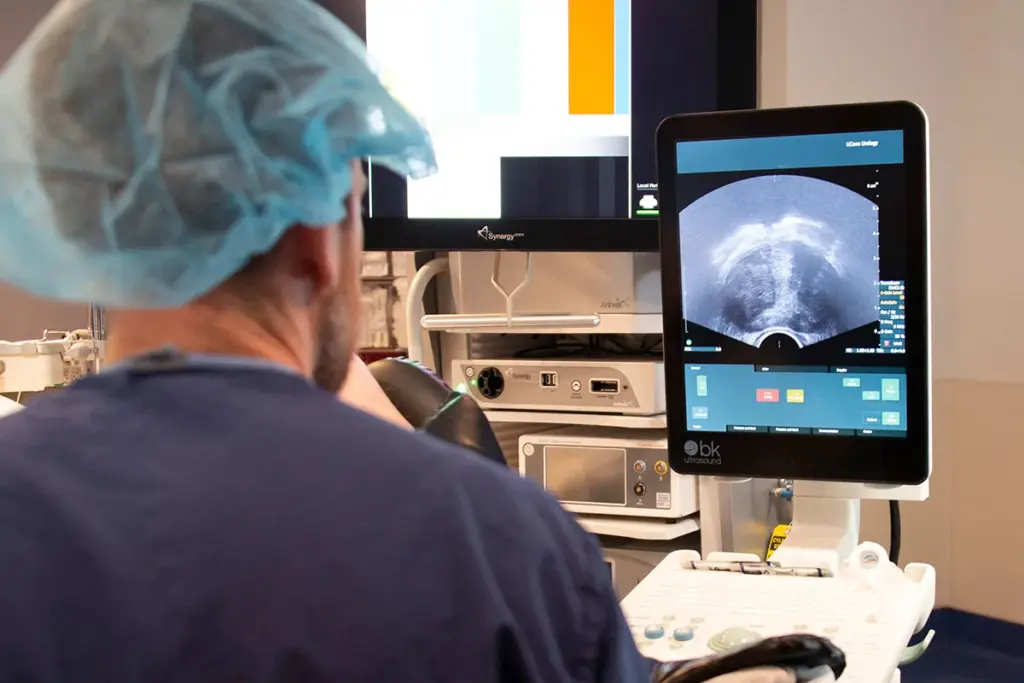
Prostate biopsy is a key test to find cancer or other issues in the prostate gland. We’ll dive into the details to help you understand it better.
What is a Prostate Biopsy?
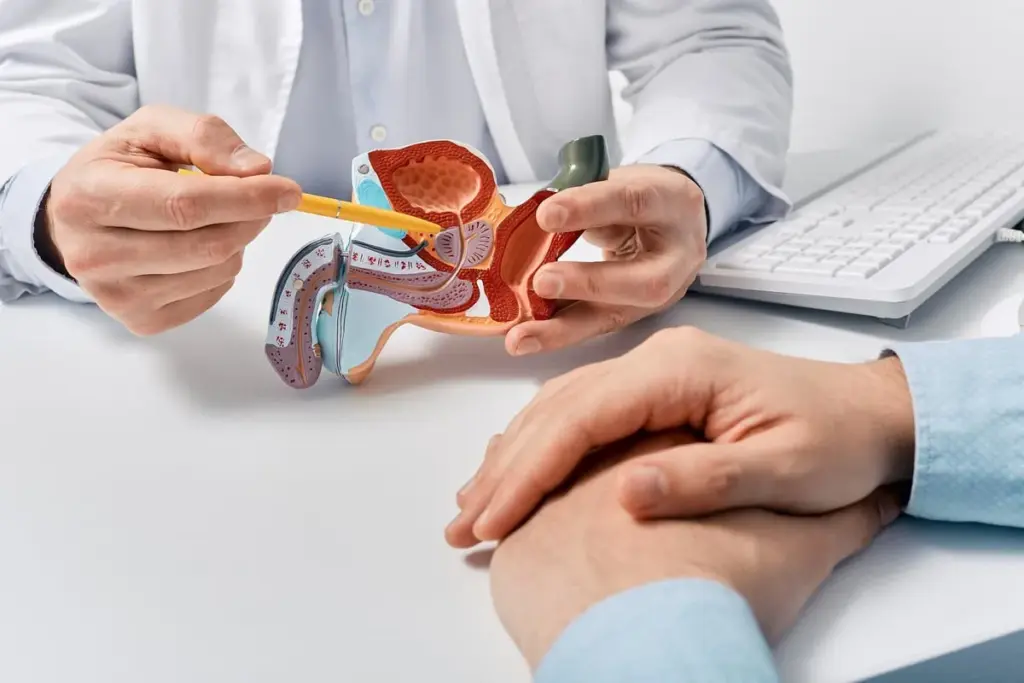
A prostate biopsy takes small tissue samples from the prostate gland for a microscope check. It’s done to look for cancer cells or other problems.
A urologist uses special tools to get the tissue. The method used can vary based on the patient’s situation and the doctor’s advice.
Common Reasons for the Procedure
Doctors might suggest a biopsy if your PSA level is high or if a DRE shows something odd. Other reasons include a family history of prostate cancer or past abnormal biopsies.
Medical Expert. Castle says, “A prostate biopsy is key for finding prostate cancer and figuring out treatment.” [1]
|
Reason for Biopsy |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Elevated PSA Level |
A high PSA level can mean prostate issues, like cancer. |
|
Abnormal DRE |
An odd DRE result might point to prostate problems. |
|
Family History |
Having a family history of prostate cancer means you’re at higher risk, so a biopsy is wise. |
Types of Prostate Biopsy Techniques
There are different biopsy methods, like TRUS, transperineal, and MRI-guided biopsies. Each has its own benefits and is picked based on the patient’s needs.
TRUS biopsy is common. It uses ultrasound to guide the urologist in getting tissue samples through the rectum. It’s quick and can be done with local anesthesia.
“The choice of biopsy technique depends on various factors, including the patient’s overall health and the suspected location of the abnormal tissue.”
— Medical Expert, Urologist
Knowing about prostate biopsy helps understand why some people might have urinary issues after it. We’ll cover this in more detail later.
Symptoms Following a Prostate Biopsy
It’s important to know the symptoms after a prostate biopsy. Patients might feel different things, some of which go away quickly. Others might need a doctor’s help.
Temporary Urinary Issues
Urinary problems are common after a prostate biopsy. You might find it hard to pee, feel pain while peeing, or need to pee a lot. Medical Expert.
These problems usually don’t last long and might go away in a few days. But, it’s key to watch your symptoms and see a doctor if they don’t get better or get worse.
Other Common Side Effects
Patients might also feel other things like blood in the urine or semen, discomfort in the rectum, or mild pain. These symptoms are usually short-lived but can be scary if you don’t expect them.
“It’s not uncommon for patients to experience some level of discomfort or urinary issues following a prostate biopsy. But knowing about these side effects can really help reduce worry and improve how things turn out.”
Expert Opinion
When to Seek Medical Attention
Even though many symptoms after a prostate biopsy are short-term, some need a doctor’s help. You should get medical help if you have severe pain, a lot of bleeding, or if your symptoms get worse over time.
- Severe or persistent pain
- Heavy bleeding or blood clots
- Increasing difficulty urinating
- Fever or chills
Knowing about these symptoms and when to get help can really help your recovery. Always follow what your healthcare provider tells you to do.
|
Symptom |
Typical Duration |
When to Seek Help |
|---|---|---|
|
Urinary Issues |
A few days to a week |
If persists or worsens |
|
Blood in Urine/Semen |
A few days to several weeks |
If heavy or accompanied by pain |
|
Rectal Discomfort |
A few days |
If severe or persistent |
The Anatomy of the Prostate Gland
The prostate gland is a vital part of the male reproductive system. It sits below the bladder and surrounds the urethra. This gland is key for producing fluids that help with urination and sperm movement.
Understanding the prostate gland’s anatomy is essential. It’s shaped like a doughnut and has different zones. The central zone is where most of the gland’s tissue is found. The transition zone is where the gland gets bigger with age. The peripheral zone is where most prostate cancers start.
Knowing where the PSA is located is also important. PSA is a protein made by the prostate gland. It’s found in the fluid of the gland and in the blood. High levels of PSA in the blood can be a sign of prostate issues.
Here’s a quick look at the prostate gland’s anatomy:
|
Zone |
Function |
|---|---|
|
Central Zone |
Produces most of the gland’s tissue |
|
Transition Zone |
Grows with age |
|
Peripheral Zone |
Where most prostate cancers start |
By understanding the prostate gland’s anatomy, we can better grasp its role in the body. This knowledge helps in diagnosing and treating prostate issues.
Causes of Urinary Retention Post-Biopsy
Having trouble urinating after a prostate biopsy can be scary. But knowing why it happens can help ease worries. Urinary retention, or not being able to fully empty the bladder, can stem from several biopsy-related reasons.
Swelling and Inflammation
Swelling and inflammation in the prostate and nearby areas are big culprits. This swelling can block the urethra, making it hard to pee. Inflammation is a natural reaction to the biopsy, but it can lead to temporary issues.
Medical Expert. Castle says managing inflammation with proper care can lower the risk of urinary retention. We’ll look into post-procedure care later.
Pain and Discomfort Factors
Pain and discomfort after a biopsy can also lead to urinary retention. The pain might make the urinary sphincter contract involuntarily, making it harder to pee. It’s key to manage pain well to avoid urinary retention.
- Pain management through medication
- Relaxation techniques to reduce discomfort
- Adequate rest and avoiding strenuous activities
Psychological Factors Impacting Urination
Psychological factors like anxiety and stress from the biopsy can also affect urination. Stress can tighten the pelvic floor muscles, making it harder to pee. Using counseling or relaxation techniques can help.
|
Cause |
Description |
Management Strategy |
|---|---|---|
|
Swelling and Inflammation |
Obstruction of the urethra due to swelling |
Post-procedure care, anti-inflammatory medication |
|
Pain and Discomfort |
Involuntary contraction of the urinary sphincter |
Pain management medication, relaxation techniques |
|
Psychological Factors |
Tension in the pelvic floor muscles due to stress |
Counseling, relaxation techniques |
Knowing the causes of urinary retention after a prostate biopsy can help manage it. By tackling these causes, people can lower their risk of this problem.
Risk Factors for Urinary Issues
Several health and demographic factors can raise the risk of urinary problems after a biopsy. Knowing these factors helps doctors take better care of their patients.
Pre-existing Conditions
Having urinary or prostate issues before a biopsy can make recovery harder. Problems like BPH, urinary tract infections, or incontinence can complicate things. Patients with these conditions should talk to their doctors about their risks.
Age and Prostate Size
Older men often face urinary problems due to aging and prostate growth. Prostate size also plays a role; a bigger prostate might lead to urinary retention or other issues after a biopsy.
Medication Influences
Some medicines can mess with urine flow and raise the risk of biopsy complications. Anticoagulants might cause bleeding, while alpha-blockers can affect how urine flows. It’s important for patients to tell their doctors about all their medications before the biopsy.
Understanding these risk factors helps doctors prepare patients for possible problems. This way, they can improve patient outcomes and lower the chance of urinary issues after a biopsy.
Diagnostic Tests for Urinary Incontinence
To find out why someone has urinary incontinence, we need to do a detailed check. We use many tests to see what’s wrong and figure out the best way to fix it.
Physical Examination
A physical check is the first step to find out about urinary incontinence. We look at the patient’s overall health and check for any signs of brain or nerve problems. We also do a pelvic exam to see how strong the pelvic muscles are and if there are any problems.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests help us see inside the urinary system. We use ultrasound and MRI to look for any problems like tumors or stones. These tests show us what’s going on with the bladder and urethra.
Types of Imaging Tests:
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the bladder and urethra.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of the urinary tract and surrounding tissues.
Urinary Flow Tests
Urinary flow tests check how well urine flows. They help find blockages or problems with the bladder emptying. These tests can spot issues like BPH in men or urethral stricture in both men and women.
With the results of these tests, we can make a treatment plan that fits each patient’s needs.
Treatment Options for Urinary Retention
Dealing with urinary retention after a biopsy can be tough. There are many ways to tackle it. The right treatment depends on why it’s happening and how bad it is.
Medication Management
Medicine might help with urinary retention. These drugs relax the prostate and bladder neck. This makes it easier to pee.
Some common medicines include:
- Alpha-blockers, which relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck.
- 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, which can shrink the prostate over time.
It’s important to follow your doctor’s advice and tell them about any side effects or worries.
Self-Care Strategies
There are self-care steps that can help with urinary retention. These include:
- Double voiding: Trying to pee again a few minutes after the first try.
- Relaxation techniques: Using warm baths or listening to calming music to relax.
- Fluid management: Adjusting how much you drink to avoid overloading your bladder.
Using these strategies can help manage symptoms and improve how you pee.
Surgical Interventions
In serious cases, surgery might be needed. This can include:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): A procedure to remove part of the prostate.
- Urethral dilation: Stretching the urethra to improve urine flow.
These surgeries are usually considered when other treatments don’t work.
|
Treatment Option |
Description |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Medication Management |
Using medications to relax the prostate and bladder neck. |
Non-invasive, can be effective for mild to moderate urinary retention. |
|
Self-Care Strategies |
Lifestyle adjustments to improve urinary function. |
Low risk, can be done at home, complements other treatments. |
|
Surgical Interventions |
Procedures to correct anatomical issues causing urinary retention. |
Can provide significant relief for severe urinary retention. |
Talking to a healthcare provider is key to finding the right treatment. They will consider your specific situation and how bad the urinary retention is.
“The key to managing urinary retention is understanding the underlying cause and selecting the most appropriate treatment option.”
— Medical Expert, Urologist
Lifestyle Changes to Support Recovery
Recovering from a prostate biopsy is more than just medical treatment. It’s about making lifestyle changes. By changing our daily habits, we can improve our recovery and health.
Importance of Hydration
Drinking enough water is key after a prostate biopsy. It helps clear out the system and lowers infection risk. Aim for eight glasses of water a day. Also, eat hydrating foods like watermelon and cucumbers.
Dietary Considerations
Eating a balanced diet is important for recovery. Include foods high in antioxidants, like berries and leafy greens. They help with healing. Omega-3 fatty acids in foods like salmon also help. Avoid spicy or acidic foods that can irritate the prostate.
|
Food Group |
Recommended Foods |
Foods to Avoid |
|---|---|---|
|
Fruits |
Berries, Watermelon |
Citrus Fruits (in excess) |
|
Vegetables |
Leafy Greens, Cucumbers |
Spicy Vegetables |
|
Proteins |
Salmon, Lean Meats |
Processed Meats |
Regular Physical Activity
Regular exercise is important for recovery. Start with gentle activities like walking or yoga. They improve circulation and reduce discomfort. Always listen to your body and your healthcare provider.
By making these lifestyle changes, you can support your recovery after a prostate biopsy. It’s good to talk to your healthcare provider before starting any new habits or exercise.
Recovery Timeline After a Prostate Biopsy
The recovery after a prostate biopsy can vary. Knowing what to expect can make it easier. We’ll cover normal recovery, signs of complications, and the importance of follow-up appointments.
Normal Recovery Expectations
Most men can get back to normal in a few days after a prostate biopsy. But, it takes several weeks for the prostate gland to fully heal. During this time, some men might feel mild side effects like discomfort, bleeding, or trouble urinating.
These symptoms are usually short-lived and can be managed with medication and self-care.
Signs of Complications
While most men recover well, it’s important to know the signs of complications. These include:
- Severe pain or trouble urinating that gets worse
- Heavy bleeding or clots
- Fever or chills
- Infection signs like redness, swelling, or discharge at the biopsy site
If you notice any of these symptoms, contact your healthcare provider right away.
Follow-Up Appointments
Follow-up appointments are key to recovery. They let your healthcare provider check on your healing, address any issues, and talk about the biopsy results. Usually, you’ll have a follow-up within a few weeks.
During this visit, your provider might do a physical exam, review your symptoms, and guide you on when to start normal activities.
As one healthcare professional noted,
“Follow-up care is not just about checking for complications; it’s also an opportunity for patients to ask questions and receive reassurance about their recovery.”
|
Timeframe |
Expected Recovery Stage |
|---|---|
|
1-3 days |
Mild discomfort, possible bleeding or spotting |
|
3-7 days |
Gradual improvement in symptoms, resumption of light activities |
|
1-3 weeks |
Most symptoms resolve, return to normal activities |
|
Several weeks |
Full recovery, including prostate healing |
In conclusion, understanding the recovery timeline after a prostate biopsy is key for a smooth recovery. Knowing what to expect and when to seek medical help can help patients feel confident during this time.
Preventing Future Urinary Issues
Reducing the risk of urinary problems after a prostate biopsy is possible with the right steps. We know patients worry about these issues after the test.
Best Practices Before and After Biopsy
To lower the risk of urinary problems, follow some key steps before and after the biopsy. Before, talk to your doctor about any urinary issues you have. After, follow their advice on rest, medication, and follow-up care closely.
Important practices include:
- Drink plenty of water to help flush your urinary system.
- Avoid activities that put pressure on your prostate area.
- Take any prescribed medication as directed to manage pain and prevent infection.
Monitoring Symptoms
Keep a close eye on your urinary symptoms after the biopsy. Some discomfort is normal, but certain signs can mean trouble. Watch for increased pain, trouble urinating, or fever, and see a doctor if you notice these.
Regular self-monitoring can catch problems early, allowing for quick action.
Engaging with Healthcare Providers
Talking openly with your healthcare team is key to preventing and managing urinary issues after a biopsy. Don’t be shy about reaching out with concerns or questions.
At follow-up visits, share any symptoms or worries with your doctor. This helps address problems quickly and lowers the risk of long-term urinary issues.
By following these steps, patients can greatly reduce the risk of urinary problems after a prostate biopsy. This ensures a smoother recovery.
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Talking to healthcare providers is key for handling urinary health after a biopsy. It’s tough to deal with urinary health issues alone. A good partnership between patients and healthcare providers is vital.
Communicating Your Concerns
It’s important for patients to share their symptoms, no matter how small, with their doctors. Open communication is key to spotting problems early. Keeping a symptom journal can help track changes and concerns.
- Record the severity and frequency of symptoms.
- Note any factors that alleviate or exacerbate symptoms.
- Share this information with your healthcare provider.
The Importance of Follow-Up Care
Follow-up care is essential for recovery. Regular check-ins with healthcare providers help monitor urinary health. It’s important to stick to the follow-up schedule set by your doctor.
|
Follow-Up Activity |
Purpose |
Timeline |
|---|---|---|
|
Post-Biopsy Check-Up |
Assess healing and address concerns |
1-2 weeks post-biopsy |
|
Urinary Health Monitoring |
Monitor urinary function and detect complications |
Ongoing, as advised by healthcare provider |
When to Consult a Specialist
If urinary issues don’t get better, seeing a specialist might be needed. Urologists can handle complex urinary health problems. If standard care doesn’t work, getting a specialist’s opinion is a good idea.
In summary, healthcare providers are critical in managing urinary health after a biopsy. By talking openly, following up, and knowing when to see a specialist, patients can feel more confident in their recovery.
Resources and Support Groups
Dealing with urinary issues after a prostate biopsy can be tough. But, patients don’t have to go through it alone. We offer access to reliable resources and support groups to help on this journey.
Reliable Sources of Information
Patients can find trustworthy info from places like the American Cancer Society or the National Cancer Institute. These groups give advice on managing urinary issues and keeping prostate health in check.
Support Networks
Online forums and local support groups connect patients with others facing similar challenges. These groups offer a safe place to share worries and get support.
Managing Urinary Issues
There are coping strategies like pelvic floor exercises and stress management that can help with urinary symptoms. We suggest patients try these and talk about them with their healthcare provider.
FAQ
What is a prostate biopsy, and why is it performed?
A prostate biopsy is a procedure where tissue from the prostate gland is taken for examination. It’s done to find prostate cancer or other issues.
What are the common symptoms after a prostate biopsy?
After a prostate biopsy, you might experience urinary problems, pain, discomfort, and swelling. These symptoms are usually temporary but can vary in severity.
Why do I experience urinary retention after a prostate biopsy?
Urinary retention can happen due to swelling, pain, discomfort, or psychological factors from the biopsy. Knowing these causes can help manage the issue.
What are the risk factors for urinary issues after a prostate biopsy?
Risk factors include health conditions, age, prostate size, and certain medications. Being aware of these can help prevent issues.
How is urinary incontinence diagnosed after a prostate biopsy?
Diagnosis involves physical exams, imaging tests, and urinary flow tests. These help assess the condition and guide treatment.
What are the treatment options for urinary retention?
Treatment options include medications, lifestyle changes, and surgery. The choice depends on the cause and severity of the condition.
How can I support my recovery after a prostate biopsy?
Stay hydrated, make dietary changes, and exercise regularly to support recovery. These lifestyle changes can help alleviate symptoms and improve health.
What is the typical recovery timeline after a prostate biopsy?
The recovery time varies, but most patients can get back to normal in a few days to a week. It’s important to monitor for complications and attend follow-up appointments.
How can I prevent future urinary issues?
Follow best practices before and after the biopsy, monitor symptoms, and communicate with healthcare providers. This can help prevent future urinary issues.
What is the role of healthcare providers in managing urinary issues after a prostate biopsy?
Healthcare providers are key in addressing concerns, providing follow-up care, and guiding patients on when to see a specialist.
Where can I find resources and support for urinary issues after a prostate biopsy?
Reliable information, online and local support networks, and coping strategies are available. They help patients manage urinary issues and related challenges.
What are the benefits of not ejaculating for 30 days?
Some studies suggest that not ejaculating for a period may reduce the risk of certain prostate issues. More research is needed to confirm this.
How does a urologist examine ejaculation?
A urologist may assess ejaculation as part of a thorough evaluation. This may include questions about ejaculatory function, pain, or other symptoms.
What is anal intraepithelial neoplasia?
Anal intraepithelial neoplasia is abnormal cell growth in the anal canal. It can potentially lead to cancer and requires medical monitoring.
How is a prostate biopsy performed?
A prostate biopsy is usually done using ultrasound guidance. A needle is inserted to collect tissue samples from the prostate gland.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29974188/



































