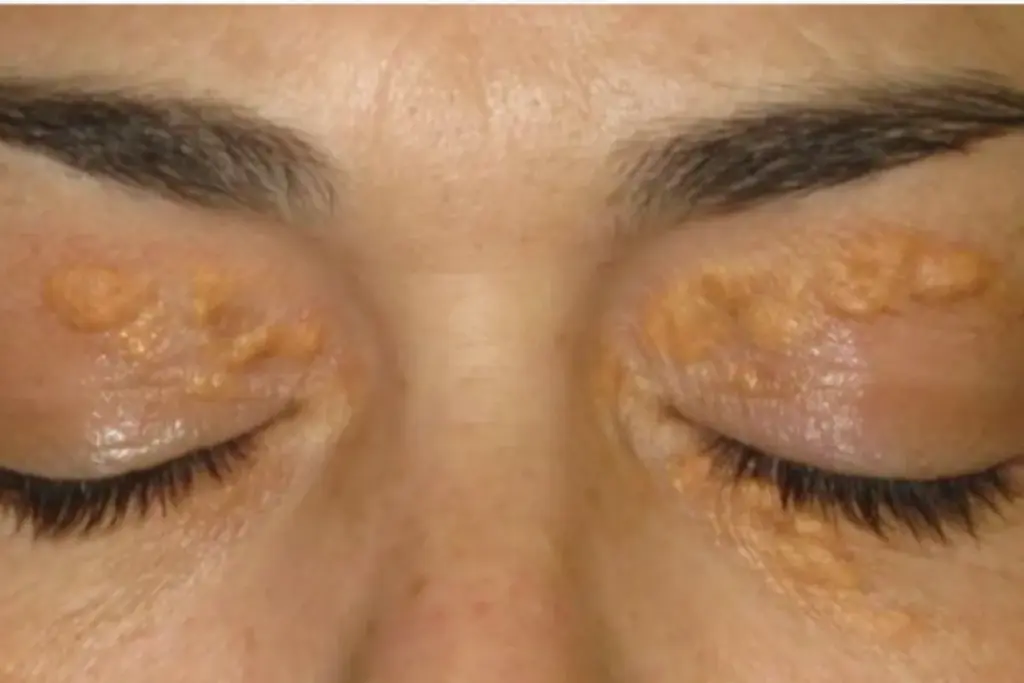
Are you seeing small, yellowish bumps on your skin, like around your elbows or buttocks? This could mean your cholesterol and triglyceride levels are too high. It’s a big warning, even more so if you have diabetes or metabolic disorders.
Eruptive xanthomatosis is a serious condition that needs quick medical help. It can lead to heart disease and pancreatitis. At Liv Hospital, we focus on treating this rare skin issue caused by high blood lipids.
We’ll dive into the details of this condition. We’ll talk about its causes, symptoms, how to diagnose it, and treatment options. You’ll learn how to manage it effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the causes and symptoms of eruptive xanthomatosis is key to treating it well.
- Controlling lipid levels is essential in managing this condition.
- It’s important to tackle underlying metabolic issues to avoid serious problems.
- Getting medical help quickly can greatly improve your chances of recovery.
- A good treatment plan includes making lifestyle changes and using medical treatments.
Understanding Eruptive Xanthomatosis
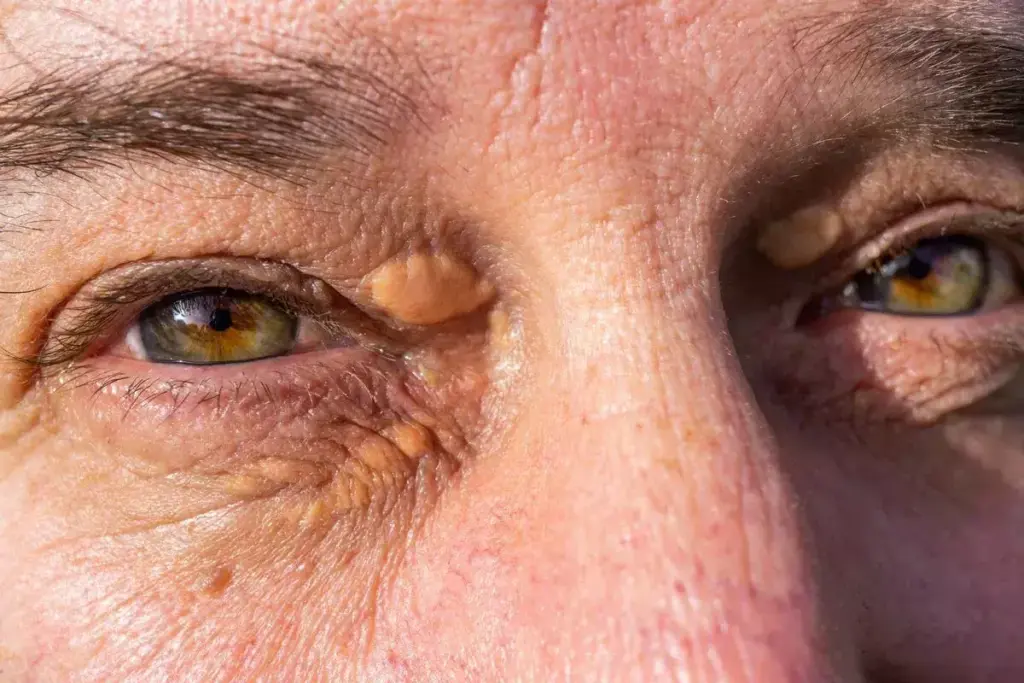
Eruptive xanthomatosis is a rare skin condition linked to high triglycerides. It often shows up in people with uncontrolled diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Knowing its causes, symptoms, and how it’s diagnosed is key.
What Causes Eruptive Xanthomatosis?
Eruptive xanthomatosis happens when high triglycerides leak into the skin. This is due to severe hypertriglyceridemia. It’s often seen in those with uncontrolled diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
A study found that high triglycerides are a big part of eruptive xanthomatosis. This shows how important it is to manage lipids and metabolic health.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The symptoms of eruptive xanthomatosis include small, yellowish-red bumps with red halos. These bumps usually appear on the arms, legs, buttocks, and back. They are a key sign of the condition and can be painful for those affected.
Spotting these symptoms early is important. Seeing these skin lesions should lead to a check-up. This helps figure out the lipid and metabolic health.
Diagnosis Process
To diagnose eruptive xanthomatosis, doctors use a mix of looking at the skin and lab tests. A fasting lipid panel is key to check lipid levels. The diagnosis is confirmed by the skin lesions and high triglycerides.
| Diagnostic Criteria | Description |
| Clinical Examination | Assessment of characteristic skin lesions |
| Fasting Lipid Panel | Evaluation of serum triglyceride levels |
| Metabolic Health Assessment | Evaluation for underlying conditions like diabetes |
The diagnostic process helps identify eruptive xanthomatosis. It also sheds light on the metabolic issues that need attention.
Treatment Options for Eruptive Xanthomatosis

Managing eruptive xanthomatosis needs a plan that tackles symptoms and causes. This plan includes medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and managing metabolic conditions.
Medical Interventions
Plasmapheresis is very effective for severe hypertriglyceridemia. It quickly lowers triglycerides and clears skin lesions. Statins and fibrates are also key in managing dyslipidemia linked to eruptive xanthomatosis.
A study on eruptive xanthomas shows managing lipid levels is vital. Lipid-lowering drugs control the condition and stop more skin eruptions.
| Medical Intervention | Description | Benefits |
| Plasmapheresis | Process of removing plasma from the blood to reduce triglyceride levels | Rapid reduction in triglycerides, resolution of skin lesions |
| Lipid-lowering medications (Statins, Fibrates) | Medications that help lower lipid levels in the blood | Effective in managing dyslipidemia, reducing the occurrence of eruptive xanthomatosis |
Lifestyle and Dietary Modifications
A low-fat diet is key in managing eruptive xanthomatosis. Lowering fat intake controls lipid levels and stops skin eruptions. Regular exercise and a healthy weight also help manage lipids.
Managing Underlying Conditions
It’s important to manage conditions like diabetes and hyperlipidemia. Controlling these with medication, diet, and lifestyle changes reduces skin lesions.
By tackling the causes and using a full treatment plan, people with eruptive xanthomatosis can manage their condition and live better.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into eruptive xanthomatosis, a skin condition linked to high cholesterol. It shows up as xanthomata. Knowing its causes, symptoms, and treatments is key to managing it.
Effective care involves medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and regular checks on cholesterol levels. This helps manage the skin problems caused by high cholesterol. It also improves overall health.
Our talk has shown the need for a complete treatment plan for EX. This approach helps healthcare teams give the best care. It leads to better health and quality of life for those with this condition.
FAQ:
What is eruptive xanthomatosis?
Eruptive xanthomatosis is a skin condition. It shows up as small, yellowish-red bumps. These bumps are often linked to high blood triglycerides and cholesterol.
What causes eruptive xanthomatosis?
It’s caused by severe high triglycerides in the blood. This is often seen in people with uncontrolled diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
What are the symptoms of eruptive xanthomatosis?
Symptoms include small, yellowish-red skin lesions. These lesions have a red halo around them. They usually appear on the arms, buttocks, and back.
How is eruptive xanthomatosis diagnosed?
Doctors use a mix of clinical checks and lab tests to diagnose it. A fasting lipid panel helps check the blood’s lipid levels.
What are the treatment options for eruptive xanthomatosis?
Treatments include plasmapheresis and lipid-lowering drugs. Changing your diet to low-fat is also recommended.
Can eruptive xanthomatosis be managed with lifestyle changes alone?
Lifestyle changes are important. But, managing it often needs medical treatments too. This is to tackle the underlying metabolic issues.
What is the role of plasmapheresis in treating eruptive xanthomatosis?
Plasmapheresis is a key treatment for severe high triglycerides. It quickly lowers triglyceride levels and clears up skin lesions.
Are there any specific dietary recommendations for managing eruptive xanthomatosis?
Yes, a low-fat diet is advised. It helps control lipid levels and manage the condition.
How does managing underlying metabolic conditions help in treating eruptive xanthomatosis?
Controlling diabetes and metabolic syndrome is key. It helps manage lipid levels and prevent the condition from coming back.
What is the importance of a complete treatment plan for eruptive xanthomatosis?
A complete treatment plan is vital. It tackles symptoms and underlying causes. This is essential for managing the condition and improving patient outcomes.
Is eruptive xanthomatosis associated with high cholesterol?
Yes, it’s often linked to high triglycerides and cholesterol in the blood.
Can eruptive xanthomatosis be a sign of an underlying metabolic issue?
Yes, it can be a sign of metabolic issues like uncontrolled diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
REFERENCES:
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11927605/























