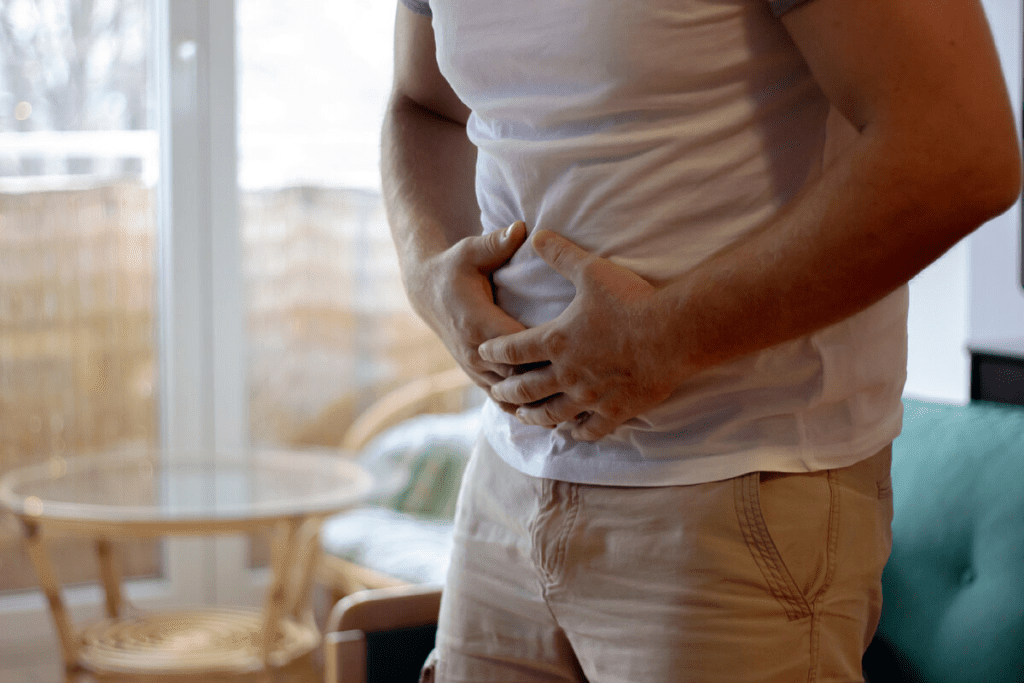
A hyperthermic syndrome is a serious condition where your body temperature gets too high. It happens when your body can’t cool down properly. This usually means your body temperature is over 104 °F (40 °C).
This is different from a fever, which is the body’s way to fight off infection. Hyperthermia is when your body temperature goes up too much because of things like too much heat or certain medicines.
It’s important to know the signs of heat-related illness. This helps stop hyperthermic syndrome from getting worse and becoming a serious problem.
Key Takeaways
- Hyperthermic syndrome is a life-threatening condition caused by impaired body temperature regulation.
- It is distinct from fever and is often triggered by external factors.
- Understanding the risks and symptoms is vital for prevention and timely medical intervention.
- Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent serious complications.
- Awareness and prevention are key to managing heat-related illnesses.
The Science Behind Elevated Body Temperature
Keeping the body at the right temperature is a complex task. It involves many physiological processes that can sometimes go wrong. This leads to higher body temperatures.
The body keeps its temperature in balance. It produces and loses heat in a delicate dance.
Normal Thermoregulation Processes
The hypothalamus, often called the body’s thermostat, controls temperature. It manages metabolic heat production and heat loss. This keeps the body at a normal temperature of about 98.6 °F (37 °C).
When the body gets too hot, the hypothalamus makes us sweat. If it gets too cold, it makes us shiver.
Keeping the body temperature right is all about balance. Metabolic heat production comes from the body’s activities and the environment.
When Temperature Control Mechanisms Fail
Hyperthermia happens when the body can’t cool down. It’s different from fever, which is a controlled response to infection. Malignant hyperthermia shows how serious it can be.
When the body can’t control its temperature, it can get very sick. Knowing the difference between fever and hyperthermia is key. Fever is a response to infection, while hyperthermia is an uncontrolled rise in temperature.
Many things can cause the body to lose temperature control. This includes the environment, too much exercise, and some medical conditions or medicines.
Understanding Hyperthermic Syndrome and Its Impact
Hyperthermic syndrome, including various heat-related illnesses, is a growing concern worldwide. It has severe health implications. This condition encompasses a spectrum of illnesses, including heatstroke, heat exhaustion, heat edema, heat syncope, and heat cramps. Each has distinct symptoms and severity levels.
Definition and Epidemiology
Hyperthermia is when the body temperature goes too high because it can’t cool down. The spread of hyperthermic syndrome is complex. It depends on many factors like the environment, how active someone is, and their health.
Hyperthermia causes nearly half a million deaths worldwide each year. This shows how big of a health problem it is globally.
Also points out that some groups are more at risk. The elderly and young children can’t cool down as well as others.
Distinguishing Hyperthermia from Fever
It’s important to know the difference between hyperthermia and fever. Fever is a body temperature rise due to infection or inflammation. Hyperthermia is when the body can’t get rid of heat.
- Fever is usually treated with medicine and by fixing the cause.
- Hyperthermia needs quick cooling and supportive care.
Global Health Burden
The global health impact of hyperthermic syndrome is huge. It causes a lot of sickness and death from heat-related illnesses. Several factors add to this problem:
- Climate change makes temperatures rise and heatwaves happen more often.
- More people living in cities makes it hotter because of the urban heat island effect.
- Some groups don’t know how to prevent it or protect themselves.
It’s key to understand hyperthermic syndrome and its effects. This knowledge helps create better ways to prevent and treat it. It’s important to lessen its global health burden.
Five Major Types of Heat-Related Illnesses
It’s important to know about the different heat-related illnesses. They range from mild to severe and can hit anyone, no matter their age or health. Knowing the symptoms is key to getting the right care, which is vital during heatwaves.
Heatstroke: Life-Threatening Emergency
Heatstroke is the most serious heat-related illness. It happens when the body can’t cool itself down. The body temperature goes up fast, and sweat stops working. Getting medical help right away is critical because heatstroke can cause brain damage, organ failure, and even death.
Heat Exhaustion: Warning Before Crisis
Heat exhaustion is a less severe form of heat-related illness. It can turn into heatstroke if not treated. Symptoms include heavy sweating, pale skin, fast and weak pulse, nausea or vomiting, and dizziness or fainting.
Quick treatment involves cooling the body and drinking plenty of fluids. If not treated, heat exhaustion can turn into heatstroke.
Heat Syncope and Heat Edema
Heat syncope, or fainting, happens when someone is in high heat for too long. It’s a sign of a more serious heat-related illness. Heat edema is swelling in the feet, ankles, and hands from too much heat.
While not as serious, these signs show the body is stressed by the heat.
Heat Cramps: Muscular Manifestations
Heat cramps are muscle spasms that happen during intense exercise in hot weather. They’re linked to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Drinking enough water and replacing lost electrolytes are important for preventing and treating heat cramps.
These cramps can be very painful but are usually not life-threatening.
In summary, knowing the different heat-related illnesses is key to getting the right care. By understanding the symptoms and severity, we can prevent and treat these conditions effectively.
Key Risk Factors for Developing Hyperthermia
Several key risk factors contribute to the development of hyperthermia, a potentially life-threatening condition. Understanding these factors is essential for prevention and effective management.
Environmental Contributors
High ambient temperatures and humidity are significant environmental contributors to hyperthermia. Heatwaves are dangerous, as they can quickly raise body temperature. The urban heat island effect makes built-up areas warmer than rural areas, increasing the risk.
“As temperatures and humidity rise, the body’s cooling ability is impaired, raising the risk of hyperthermia,” health experts say.
Physical Activity and Dehydration
Strenuous physical activity in hot environments can lead to hyperthermia. Dehydration, from not drinking enough or sweating too much, also raises the risk. Metabolic heat production during intense exercise can overwhelm the body’s cooling mechanisms.
- Exertional heat illness is common among athletes and those who work outdoors.
- Drinking enough water is key to preventing dehydration and heat-related illnesses.
- Getting used to hot environments can help lower the risk of hyperthermia.
Medical Predispositions
Certain medical conditions can make people more likely to get hyperthermia. Neurological disorders, like neuroleptic malignant syndrome, and conditions that affect sweat glands can make it hard for the body to regulate temperature.
People with a history of malignant hyperthermia or serotonin syndrome are also at higher risk.
Medication and Substance Interactions
Some medications and substances can mess with the body’s temperature control, raising the risk of hyperthermia. This includes certain antipsychotics, stimulants, and recreational drugs.
“The risk of hyperthermia is heightened when certain medications are used with other substances that affect body temperature regulation.”
Emergency Management and Treatment Protocols
It’s key to know how to handle hyperthermia to save lives. This condition happens when the body can’t cool itself down. It needs quick and proper treatment.
Recognition of Warning Signs
Spotting hyperthermia early is critical. Look for high body temperature, confusion, and dry, flushed skin. Other signs are headache, dizziness, and nausea.
Immediate Cooling Interventions
Cooling down fast is key in treating hyperthermia. Here are some ways to do it:
- Moving the patient to a cooler place
- Removing extra clothes
- Using cool water or ice packs
- Using cooling blankets or devices
These steps help lower the body’s temperature quickly.
Medical Support Measures
Medical help is also vital. This includes:
- Drinking fluids to fight dehydration
- Keeping an eye on vital signs
- Using oxygen if needed
- Handling any complications
Prevention Strategies
Preventing hyperthermia is just as important. Stay hydrated, avoid hard work in the heat, and wear the right clothes. Also, public awareness helps teach people about hyperthermia risks.
Conclusion: The Critical Importance of Hyperthermia Awareness
Hyperthermic syndrome is a serious condition that needs quick action. It’s important to know the difference between hyperthermia and fever. Hyperthermia is when your body temperature goes up too high without warning.
Healthcare teams can make a big difference by spreading the word about hyperthermia. Places like LivHospital lead the way in teaching about this. They show how important it is to learn about hyperthermia to stay safe.
FAQ’s:
What is the difference between hyperthermia and fever?
Hyperthermia happens when the body can’t cool itself down. This causes the body temperature to go up. Fever, on the other hand, is when the body’s temperature goes up as a response to infection or inflammation.
What are the symptoms of heatstroke, a severe form of hyperthermia?
Heatstroke symptoms include a body temperature over 103 °F (39.4 °C), confusion, and dry skin. Other signs are a fast pulse and headache. It’s a serious condition that needs immediate medical help.
How does the body regulate its temperature, and what happens when this process fails?
The body keeps its temperature stable through sweating and changing blood vessel size. If it can’t do this, it might get too hot. This can happen because of the weather or certain health issues.
What are the risk factors for developing hyperthermia?
High temperatures and humidity, being active, and not drinking enough water are risks. So are some health problems and certain medicines.
How is hyperthermia treated, and what are the key components of emergency management?
To treat hyperthermia, cool the body down by removing clothes and using cool packs. Drinking cool water is also important. Medical care is key, including watching vital signs and treating any complications.
Can certain medications or substances increase the risk of developing hyperthermia or related conditions like serotonin syndrome or neuroleptic malignant syndrome?
Yes, some medicines or substances can make it harder for the body to cool down. This can lead to hyperthermia or other serious conditions.
What preventive measures can be taken to mitigate the risk of developing hyperthermia?
To avoid hyperthermia, drink plenty of water, stay cool in hot weather, and wear light clothes. Knowing the signs of heat illness is also important.
How does malignant hyperthermia differ from other forms of hyperthermia?
Malignant hyperthermia is a very serious condition. It happens when certain anesthetics are used and causes a fast rise in body temperature. It also includes muscle stiffness and other serious problems.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Extreme Heat. Retrieved fromhttps://www.cdc.gov/disasters/extremeheat/index.html.
- Pryor, T. D., M. D. (2018). Malignant Hyperthermia. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing. Retrieved fromhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459392/.


































