Knowing about a brain tumor is key to finding the right treatment. A biopsy is a test where a sample of tumor tissue is taken for lab tests.
At Liv Hospital, we know how important tests like biopsies are for cancer diagnosis. Our team helps you understand every step, making sure you feel supported and informed.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the procedure and safety of a brain tumor biopsy is vital.
- A biopsy is a key tool for figuring out what kind of brain tumor you have.
- The recovery time can vary based on many factors.
- Tests like spine CT scans can spot metastatic osseous lesions.
- Liv Hospital offers full support and guidance during diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Brain Tumors and the Need for Biopsy
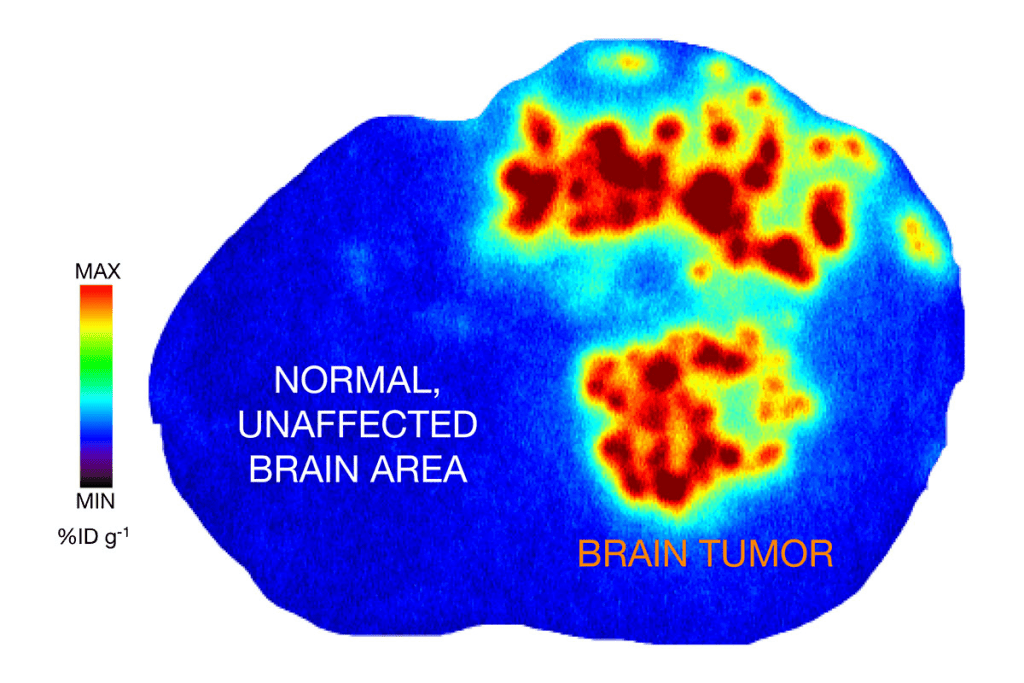
It’s key to know about brain tumors to find the right treatment. There are two main types: benign and malignant. Knowing which one you have helps decide how to treat it.
Types of Brain Tumors
Brain tumors come from different brain cells. Gliomas start from glial cells, and meningiomas from the brain’s protective membranes. The type of tumor is based on its cell origin and behavior.
| Tumor Type | Origin | Malignancy |
| Gliomas | Glial cells | Can be benign or malignant |
| Meningiomas | Meninges | Usually benign |
| Medulloblastomas | Cerebellum | Malignant |
Why Diagnostic Confirmation is Essential
Getting a biopsy is vital to know what kind of tumor you have. It involves looking at a tumor sample to find out its type and grade. Accurate diagnosis helps plan the best treatment, like surgery or chemotherapy.
A bone scan can check if cancer has spread to bones. But it doesn’t diagnose brain tumors. Yet, it helps in planning treatment by showing if cancer has spread.
When a Brain Tumor Biopsy is Recommended
A biopsy is usually needed when scans show a tumor that needs more study. The decision to do a biopsy depends on the tumor’s location, size, and type.
Knowing the tumor type helps doctors create a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
What is a Brain Tumor Biopsy?
A brain tumor biopsy is a medical test where a tumor sample is taken for detailed study. This helps find out the tumor’s type and how serious it is. It’s key for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Definition and Purpose
A brain tumor biopsy removes a small piece of tumor tissue for study. The main goal is to figure out the type and grade of the tumor. This info is vital for choosing the right treatment.
Doctors look at the tumor tissue to see if it’s benign or malignant and how aggressive it is. Knowing this helps create a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
Different Types of Brain Biopsies
There are several brain biopsy types, each with its own use and method. The main ones are:
- Stereotactic Biopsy: A minimally invasive method that uses a three-dimensional system to find the tumor.
- Open Biopsy: Done during surgery, where a part of the tumor is removed for study.
- Endoscopic Biopsy: Uses an endoscope to see the tumor and take a sample.
Each biopsy type has its benefits and is chosen based on the tumor’s location, size, and the patient’s health.
Pre-Biopsy Preparation: What Patients Need to Know
The time before a brain tumor biopsy is very important. It includes medical checks and personal steps to get ready. We know this time can be scary, but being ready can help a lot.
Medical Evaluations and Tests
Before the biopsy, you’ll have many tests. These help doctors know about your health and the tumor. You might have imaging tests like MRI or CT scans to see the tumor’s size and where it is.
You might also have blood tests. These check for bleeding problems or other issues that could affect the biopsy. We make sure all tests are done to keep you safe and help the biopsy go well.
Medication Adjustments
Some medicines can make the biopsy riskier or not work right. Tell us about all your medicines, including blood thinners and supplements. We might change or stop some to keep you safe during the biopsy.
Fasting Requirements
You might need to not eat for a while before the biopsy, if you’re getting general anesthesia. We’ll tell you exactly how long to fast and what else to do to get ready.
Mental Preparation
Having a brain tumor biopsy can be tough on your mind. It’s good to understand what will happen and ask questions. Talking to our team and getting support from loved ones can also help.
By following these steps, you can help make the biopsy safe and successful. We’re here to give you the best care and support every step of the way.
The Brain Tumor Biopsy Procedure: Step by Step
We will guide you through the step-by-step process of a brain tumor biopsy. This complex medical procedure involves several critical steps, from preparation to the examination of the tissue sample.
Anesthesia Administration
The first step in the brain tumor biopsy procedure is the administration of anesthesia. To ensure patient comfort and safety, the type of anesthesia used is carefully selected based on the patient’s overall health and the specifics of the tumor location.
General anesthesia is commonly used for brain tumor biopsies, as it ensures the patient remains unconscious and pain-free during the procedure. The anesthesiologist will closely monitor the patient’s vital signs throughout the process.
Surgical Techniques
Once the anesthesia has taken effect, the surgical team proceeds with the biopsy. The surgical technique used can vary depending on the tumor’s location and size.
- Stereotactic biopsy: This technique uses a three-dimensional coordinate system to precisely locate the tumor, allowing for a more targeted approach with minimal invasion.
- Open biopsy: In some cases, an open biopsy may be performed, which involves surgically opening the skull to access the tumor directly.
Duration of the Procedure
The duration of a brain tumor biopsy procedure can vary, typically ranging from 1 to 3 hours, depending on the complexity of the case and the surgical technique employed.
As one neurosurgeon noted,
“The key to a successful biopsy is not just in the surgical skill, but also in the meticulous planning and coordination among the medical team.”
What Happens to the Tissue Sample
After the tissue sample is obtained, it is sent to the pathology laboratory for examination. The pathologists will analyze the sample to determine the type of tumor and its grade.
| Tissue Sample Analysis | Description |
| Histopathological Examination | The tissue sample is examined under a microscope to identify the tumor type and grade. |
| Molecular Testing | Additional tests may be conducted to identify specific genetic markers or mutations. |
By understanding the step-by-step process of a brain tumor biopsy, patients can better prepare themselves for the procedure and what to expect during recovery.
Safety and Risks of Brain Tumor Biopsies
Brain tumor biopsies are invasive medical procedures. They carry risks and complications. It’s important for patients to know these to make informed decisions.
Common Complications
Common issues include bleeding, infection, and brain swelling. These can be managed with medical care. Sometimes, they need extra treatment.
Table: Common Complications and Their Management
| Complication | Management Approach |
| Bleeding | Monitoring, medication, or additional surgery |
| Infection | Antibiotics, hospitalization for observation |
| Swelling | Corticosteroids, close monitoring |
Rare but Serious Risks
Rare risks include damage to brain tissue and anesthesia reactions. These risks are low but highlight the need for skilled professionals.
Safety Measures During the Procedure
Several safety steps are taken during biopsies. Advanced imaging guides the needle. Vital signs are closely monitored. A skilled team is present.
Risk Factors That May Increase Complications
Some factors increase the risk of complications. These include tumor location, size, and patient health. Previous brain surgeries also play a role. Knowing these helps plan the procedure.
Understanding risks helps patients and doctors ensure a safe biopsy. This teamwork is key to the best outcome.
Recovery After a Brain Tumor Biopsy
The recovery time after a brain tumor biopsy is key for healing and avoiding problems. We know this time can be tough, but with the right help, patients can get through it better.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
Right after the biopsy, patients go to a recovery room. There, doctors watch their health closely. We make sure patients are comfy and fix any quick issues fast. It’s important to watch for and handle any problems right away.
Hospital Stay Duration
How long a patient stays in the hospital varies. It depends on their health and the biopsy details. Usually, patients stay at least 24 hours for observation. We check how each patient is doing to decide when it’s time to go home.
Managing Pain and Discomfort
Handling pain is a big part of caring for patients after a biopsy. We use medicines and other methods to keep pain under control. We also tell patients how to handle pain at home, like using pain meds and resting.
Good pain care helps patients feel better and get back to normal faster.
Activity Restrictions
After leaving the hospital, patients need to follow certain rules to stay safe. We tell them to avoid hard work, heavy lifting, and bending. As they get better, they can start doing more things again, with their doctor’s okay.
By sticking to these rules and advice, patients can have an easier recovery. Our team is here to support and care for them every step of the way.
Understanding Biopsy Results
The biopsy results give important information about the brain tumor. They help decide what to do next. Patients and doctors wait for these results together.
Timeframe for Results
It usually takes a few days to a couple of weeks to get the biopsy results. How long it takes depends on the test’s complexity and the lab’s work. Waiting can make patients anxious.
Interpreting Pathology Reports
Pathology reports detail what the biopsy found. They tell the type and grade of the tumor. This info is key for treatment planning.
Key components of a pathology report include:
- Type of Tumor: Whether it’s benign or malignant.
- Tumor Grade: How aggressive the tumor is.
- Margins: If all tumor tissue was removed.
What Different Diagnoses Mean
Biopsy results can show different types of brain tumors. Each type affects treatment and outlook. For example, glioblastoma is aggressive, while meningioma might be benign and curable.
Understanding the diagnosis is key for:
- Determining Prognosis: Knowing the recovery or disease progression outlook.
- Planning Treatment: Choosing the best treatment options.
- Clinical Trials: Finding out if you can join trials.
Next Steps Based on Results
After getting the biopsy results, the healthcare team will talk about them. They’ll discuss further tests, treatment options, and follow-up care.
Treatment options vary based on the diagnosis. They can include:
| Treatment Option | Description | Applicability |
| Surgery | Removing as much of the tumor as possible. | Works for many brain tumors. |
| Radiation Therapy | Killing tumor cells with high-energy rays. | Used for malignant or inoperable tumors. |
| Chemotherapy | Drugs to kill tumor cells. | Can be used alone or with other treatments. |
Getting and understanding biopsy results is a big step in managing brain tumors. It helps patients and families make informed decisions about their care.
Advanced Imaging and Diagnostic Methods Used Alongside Brain Tumor Biopsies
Diagnosing brain tumors has gotten better with new imaging methods and traditional biopsies. These advanced imaging tools give important details about the tumor and the tissue around it. They help doctors diagnose and plan treatments.
MRI and CT Scan Integration
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans are key tools in diagnosing brain tumors. MRI shows soft tissue details, helping find the tumor’s size and location. CT scans show the tumor’s density and if it has calcium.
Using MRI and CT scans with biopsy results makes diagnosis more accurate. For example, MRI can guide the biopsy needle to the right spot in the tumor. This increases the chance of getting a good tissue sample.
Functional MRI Applications
Functional MRI (fMRI) is a special MRI that looks at brain activity by tracking blood flow changes. It’s great for seeing how the tumor affects brain areas important for movement or language.
fMRI helps surgeons plan the safest way to remove the tumor. It helps avoid damaging important brain functions. Knowing how the tumor affects brain activity helps doctors plan better treatments.
PET Scans and Nuclear Medicine
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans are another advanced tool used with biopsies to check brain tumors. PET scans use tiny amounts of radioactive tracers to see how active the tumor is.
PET scans can tell the difference between a tumor coming back and damage from radiation therapy. This is key for choosing the right treatment.
Molecular and Genetic Testing of Samples
Molecular and genetic testing of biopsy samples is also key in diagnosing brain tumors. These tests find specific genetic changes or markers in the tumor. They give clues about how the tumor might behave and how it might react to certain treatments.
These tests help doctors classify tumors more accurately and plan treatments that fit each patient. Knowing the tumor’s genetic makeup helps doctors choose the best treatments. This can lead to better outcomes for patients.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Brain Tumor Biopsies
Understanding a brain tumor biopsy is key for patients to make smart choices about their care. We’ve looked at the whole process, from getting ready to recovering, and why tests are important for diagnosis and treatment.
A brain tumor biopsy is a key tool for doctors to understand the tumor. It helps decide the best treatment. Knowing the risks helps patients plan their care better. Tests like MRI and CT scans help doctors get a clear picture of the tumor.
It’s very important to make informed choices about your health, even with serious conditions like brain tumors or bone cancer. Tests like bone scans are used to help diagnose these conditions. We urge patients to talk openly with their doctors, asking all the questions they have.
This way, patients can take charge of their health. They can use all the available tests and treatments to manage their condition well.
FAQ
What is a bone scan, and how is it used in cancer diagnosis?
A bone scan is a test that uses a small amount of radioactive material. It helps find bone diseases, like cancer. The material goes into the bloodstream and sticks to active bones, like cancer spots. This helps us find where cancer might have spread.
Does uptake on a bone scan mean cancer?
Not always. A bone scan can show different things, like cancer, arthritis, or broken bones. We look at other tests, like CT scans or MRI, to figure out what’s causing the abnormal spots.
What does cancer look like on a bone scan?
Cancer shows up as “hot spots” on a bone scan. These are areas where the bone is very active. But, not all hot spots are cancer. We need to look at other tests to be sure.
Can a bone scan detect bone cancer?
Yes, a bone scan can find bone cancer. We use it with other tests to see if cancer is in the bones and how far it has spread.
How does a bone scan differ from a CT scan?
A bone scan shows how active the bones are. A CT scan shows the bones’ structure. We often use both to understand bone health and find cancer or other problems.
What is the role of a brain tumor biopsy in diagnosis and treatment planning?
A brain tumor biopsy is a test where we remove a piece of tumor tissue. This helps us know what kind of tumor it is and how serious it is. This information helps us plan the best treatment.
What are the risks associated with a brain tumor biopsy?
Like any surgery, a brain tumor biopsy has risks. These include bleeding, infection, and problems with the brain. We do our best to make sure these risks are low and keep you safe.
How do I prepare for a brain tumor biopsy?
To get ready for a biopsy, you’ll need to have some medical tests and maybe change your medications. You might need to fast before the procedure. We also help you get ready mentally to feel more at ease.
What happens during a brain tumor biopsy procedure?
During the biopsy, we make sure you’re comfortable with anesthesia. Then, we carefully remove a piece of tumor tissue. We look at it under a microscope to find out what kind of tumor it is.
How do I recover from a brain tumor biopsy?
After the biopsy, we tell you how to take care of yourself. This includes managing pain and knowing what activities to avoid. We also watch for any problems and support you as you recover.
Referneces
- Miller, J. J., & Zadeh, G. (2019). Brain tumor biopsy: Techniques, risks, and outcomes. Neurosurgery Clinics of North America, 30(2), 135-145.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30930935/
- NHS. (2023). Brain biopsy. NHS.uk.https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/brain-biopsy/



































