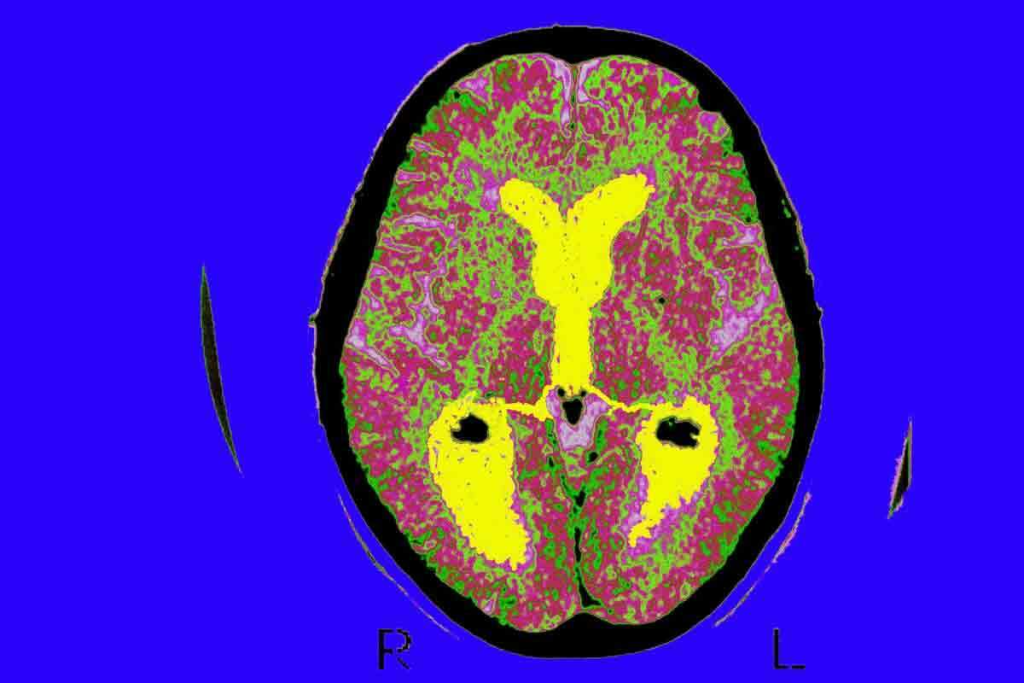
Diagnosing brain tumors needs precise imaging to find the best treatment. At Liv Hospital, we use top-notch imaging tech for accurate diagnoses. For brain tumor detection, CT scans and MRI are both useful. But MRI is better because it’s more sensitive to soft tissue issues.
The Tisch Brain Tumor Center says MRI is the best for brain tumor imaging. It finds 60% of tumors, while CT scans find 50%. MRI is great for seeing soft tissues, blood vessels, and tumors, making it the top choice for finding brain tumors.
Key Takeaways
- MRI is more sensitive to soft tissue abnormalities, making it ideal for brain tumor detection.
- CT scans are better suited for detecting acute conditions like brain hemorrhages and fractures.
- MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safer option for repeated imaging.
- The choice between MRI and CT scans depends on the specific diagnostic needs.
- Advanced imaging technologies like those at Liv Hospital improve diagnostic accuracy.
Understanding Brain Imaging Technologies
Brain imaging technologies have grown a lot, helping doctors diagnose better. We’ve seen big steps forward in Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
The Evolution of Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging has changed neurology a lot. It gives us detailed views of the brain’s structure and how it works. CT scans came out in the 1970s, showing the brain’s cross-sections. MRI started in the 1980s, giving better images without using radiation.
These technologies keep getting better. Now, we have things like functional MRI (fMRI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). They help us see brain activity and the brain’s white matter.
Basic Principles of CT Scanning
CT scanning uses X-rays to make detailed images of the brain. It works by moving an X-ray source and detectors around the head. This captures data to make images. CT scans are fast and good for finding emergencies like bleeding or breaks.
Basic Principles of MRI Technology
MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to make images without radiation. This makes MRI safer for people needing many scans or who can’t handle radiation, like kids and pregnant women. MRI is great for seeing soft tissue, like brain tumors.
Knowing how CT and MRI work helps us understand their strengths and weaknesses. By using these tools, we can make better diagnoses and treatment plans for brain tumors and other brain issues.
Brain CT Scan or MRI: Key Differences in Technology
CT scans and MRI use different technologies. This affects how well they can find brain tumors. Let’s look at how these differences play out.
How CT Scans Generate Images
CT scans use X-rays to make images. They rotate an X-ray source and detectors around the body. This captures detailed cross-sectional images. CT scans are great for emergencies because they’re fast and easy to get.
How MRI Creates Detailed Brain Images
MRI uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to make images. It’s safer because it doesn’t use ionizing radiation. MRI shows soft tissues better, which is key for finding and understanding brain tumors.
Radiation Exposure Considerations
CT scans use radiation, which is a big deal for some patients. This includes kids and pregnant women. MRI, on the other hand, doesn’t use radiation. This makes MRI safer for those worried about radiation.
| Imaging Modality | Radiation Exposure | Soft Tissue Contrast | Speed and Availability |
| CT Scan | Yes | Limited | High |
| MRI | No | Excellent | Moderate |
For more on choosing between CT scans and MRI for brain tumors.
Diagnostic Capabilities for Brain Tumor Detection
Understanding MRI and CT scans is key to finding brain tumors. We’ll look at how these tools compare in finding tumors. We’ll see their strengths and weaknesses.
Detection Rates: Statistical Comparison
Research shows MRI finds brain tumors in about 60% of cases. CT scans find them in about 50%. This is a big difference, mainly for small or deep tumors. MRI’s better soft tissue contrast helps it spot some tumors better.
Here’s a comparison of detection rates:
| Imaging Modality | Detection Rate |
| MRI | 60% |
| CT Scan | 50% |
Types of Brain Tumors Better Visualized by CT
Even though MRI is better, CT scans have their own strengths. They’re great for finding tumors with calcium or a lot of bleeding. CT scans are also faster and easier to get in emergencies.
Types of Brain Tumors Better Visualized by MRI
MRI’s detailed soft tissue images are a big plus. It’s best for spotting small or complex tumors. Tumors near the brainstem or optic nerves are clearer on MRI.
In summary, MRI and CT scans both have their uses in finding brain tumors. But,RI’s better diagnostic skills make it the top choice for many cases. This is true, mainly for tumors needing detailed soft tissue images.
Soft Tissue Contrast: Why It Matters for Tumor Identification
Soft tissue contrast is key for spotting and understanding brain tumors. It helps doctors tell different soft tissues apart in the brain. This is vital for treating brain tumors rigcorrectlyRI’s Superior Soft Tissue Resolution
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) beats Computed Tomography (CT) scans in showing soft tissues. MRI can spot tiny differences in soft tissues. This makes MRI a top choice for brain tumor care.
We use MRI to get clear pictures of brain tumors. This helps us make accurate diagnoses and plans. MRIs’ sharp images let us see how far tumors spread and where they are in relation to other parts of the brain.
“MRI has revolutionized the field of neuro-oncology by providing unparalleled soft tissue contrast, which is critical for the accurate diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors.”
CT’s Limitations in Soft Tissue Differentiation
CT scans are good for quick checks and some types of lesions. But they’re not as good as MRI for seeing soft tissues. This can make diagnoses less accurate.
| Imaging Modality | Soft Tissue Contrast | Diagnostic Accuracy for Brain Tumors |
| MRI | High | High |
| CT | Low | Moderate |
Impact on Diagnostic Accuracy
MRI’s better soft tissue contrast really helps in making accurate diagnoses. It lets doctors spot and understand brain tumors better. This leads to better treatment plans.
MRI’s edge in soft tissue detail is huge for some brain tumors that CT scans can’t see. This makes MRI a key tool in brain tumor diagnosis.
Speed and Accessibility Factors in Emergency Situations
In emergency cases, how fast and easy imaging is matters a lot. Doctors need to act quickly to help patients. This can mean the difference between life and death.
CT Scan Advantages in Acute Settings
CT scans are often the first choice in emergencies. They are quick and easy to get. This is key when every second counts.
Key benefits of CT scans in emergency settings include:
- Rapid image acquisition
- Wide availability in emergency departments
- Ability to quickly assess acute injuries or conditions
When Time is Critical: Hemorrhage and Trauma Assessment
For suspected hemorrhage or head trauma, CT scans are a big help. They spot bleeding and fractures fast. This helps doctors act fast.
The importance of timely diagnosis cannot be overstated. In trauma, every second is precious. CT scans’ quick images are a big plus.
Availability and Cost Considerations
MRI is better for soft tissue, but it’s not always available or affordable. CT scans are cheaper and easier to get. This makes them better for first checks in emergencies.
| Imaging Modality | Typical Scan Time | Availability in Emergency Departments | Relative Cost |
| CT Scan | Minutes | High | Lower |
| MRI | 15-90 minutes | Moderate to Low | Higher |
The table shows that CT scans are fast, easy to get, and cheaper. This makes them a top pick for many emergency cases.
Difference Between CT vs MRI Brain Imaging for Tumor Characterization
Both CT and MRI are key in understanding brain tumors. They help figure out what the tumor is made of and how big it is. This info is key tochoosing the right treatment.
CT scans and MRI give us a full picture of brain tumors. CT scans are great at finding calcifications in tumors. This is important for some brain tumor types.
CT’s Strength in Detecting Calcification
CT scans are top-notch at spotting calcifications because they’re very sensitive to calcium. This is vital for tumors like oligodendrogliomas, which often have calcifications. Knowing the differences between CT and MRI helps doctors pick the best imaging for each case.
MRI’s Advantage in Tissue Characterization
MRI is better at showing the soft parts of brain tumors. It gives detailed information on the tumor’s shape and how it fits with the brain. This is key for planning surgery and checking how well the tumor responds to treatment.
MRI’s clear view of soft tissues helps doctors tell different tissues apart. This is important for figuring out the tumor’s type and how aggressive it is.
Bone Structure vs. Soft Tissue Visualization
CT scans are better at showing bones and finding calcifications. But MRI is better at seeing soft tissues. This means doctors often use both to get a full picture of the tumor.
In short, CT and MRI each have their own strengths in studying brain tumors. Knowing these strengths helps doctors choose the best way to diagnose each patient.
Patient-Specific Considerations When Choosing Imaging Methods
Choosing between a CT scan and an MRI for brain tumors depends on the patient. We look at several factors, like what each scan can’t do and the patient’s background.
Contraindications for MRI
MRI isn’t for everyone, mainly those with metal implants. People with pacemakers or certain clips can’t have an MRI because of the strong magnetic fields. Also, those who are claustrophobic might struggle with the MRI’s closed space.
Contraindications for CT Scans
CT scans use radiation, which is a problem for some. Pregnant women should avoid them unless really needed. Kids are also at risk because they’re more sensitive to radiation. People with kidney issues might face problems with CT scan contrast agents.
Special Populations: Children, the Elderly, and Pregnant Patients
For kids, MRI is better because it doesn’t use radiation. But young ones might need sedation. Older patients with health issues or metal implants might lean towards MRI. Pregnant women should choose MRI over CT scans if possible.
The table below highlights key points for choosing between CT scans and MRI for brain tumors:
| Patient Group | CT Scan Considerations | MRI Considerations |
| Pregnant Women | Not recommended due to radiation exposure | Preferred due to lack of radiation |
| Children | Use with caution; minimize radiation dose | Preferred; consider the need for sedation |
| Patients with Metal Implants | Generally safe | May be contraindicated depending on implant type |
| Elderly Patients | Consider kidney function for contrast use | Consider the presence of metal implants |
Choosing between CT scans and MRI for brain tumors depends on the patient’s needs. Healthcare providers must weigh the benefits against the risks. This way, they can make the best choice for each patient.
The Role of Contrast Agents in Brain Tumor Imaging
In neuroimaging, contrast agents are key to showing brain tumors on CT and MRI scans. They help doctors see the tumor’s details better. This makes it easier to tell where the tumor starts and ends.
CT Contrast Agents: Benefits and Risks
CT contrast agents, made of iodine, make certain body parts, like brain tumors, stand out. They help doctors get a clearer picture and see how blood flows to the tumor. But, they can cause allergic reactions and kidney problems.
It’s important to think about these risks and benefits before using CT contrast agents. This is true, even more so for patients with allergies or kidney issues.
MRI Contrast Agents: Benefits and Risks
MRI contrast agents, made of gadolinium, work the same way as CT agents but for MRI scans. They help doctors see brain tumors in more detail. They are mostly safe but can cause problems in people with severe kidney disease.
Doctors should consider a patient’s kidney health and risk of allergies when choosing MRI contrast agents.
Enhancement Patterns in Brain Tumors
The way a tumor looks after contrast is very telling. Different tumors show up differently on scans. For example, some might look the same all over, while others might have spots or rings.
Knowing these patterns helps doctors and radiologists make better plans for treatment.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Brain Tumor Detection
Choosing between a brain CT scan or andI depends on several things. These include what you need to diagnose, how safe it is for the patient, and the situation. We’ve looked at what each imaging method can do well and its limitations in finding brain tumors.
MRI is often the better choice because it shows soft tissues clearly and doesn’t use radiation. This makes it great for detailed brain scans. But CT scans are useful in emergencies or when an MRI can’t be used. They quickly check for things like bleeding or injuries.
When deciding between an MRI and a CT scan for brain tumors, consider the situation and the patient. MRI is better for seeing soft tissues, but CT scans are fast and reliable in urgent cases. The best choice should be made with a doctor’s advice, considering the patient’s specific needs.
FAQ
What is the main difference between a CT scan and an MRI for brain imaging?
CT scans use X-rays to create images. MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves. MRI is safer because it doesn’t use radiation.
Which imaging modality is preferred for detecting brain tumors?
MRI is best for finding brain tumors. It shows soft tissue details clearly. This helps doctors diagnose and plan treatment better.
Are CT scans or MRI better for emergencies involving brain injuries?
CT scans are better for emergencies. They’re quick and can spot injuries like hemorrhages or trauma fast.
Can MRI detect all types of brain tumors?
MRI is great for finding subtle or complex tumors. But it depends on the tumor type and location.
What are the advantages of using MRI over CT scans for brain tumor characterization?
MRI shows soft tissue details well. This isto to understandingnding tumors. It’s very useful in neuro-oncology.
Are there any patient-specific factors that influence the choice between CT and MRI for brain imaging?
Yes, many factors matter. Things like pregnancy or being a child often mean MRI is safer. MRI avoids radiation.
What role do contrast agents play in brain tumor imaging?
Contrast agents make tumors stand out on scans. The right agent depends on the scan type and tumor.
Is MRI completely safe for all patients?
MRI is mostly safe. But, somemetal implants or pacemakers can be a problem. Always check before an MRI.
How does the choice between CT and MRI impact diagnostic accuracy for brain tumors?
Choosing between CT and MRI affects how accurate diagnoses are. MRI’s clear images are key for accurate treatment plans.
Can both CT scans and MRI be used together for brain tumor diagnosis?
Yes, they can work together. CT scans spot calcifications, while MRI shows soft tissue details. Together, they give a full picture of the tumor.
What is the difference between a brain CT scan and an MRI in terms of radiation exposure?
CT scans use X-rays and radiation. MRI doesn’t use radiation. MRI is safer for repeated scans or sensitive patients.
Which is better for detecting brain tumors, a CT scan or an MRI?
MRI is better for finding brain tumors. It shows soft tissues clearly without radiation.
What are the limitations of CT scans in soft tissue differentiation for brain tumor detection?
CT scans struggle to tell soft tissues apart. This makes it hard to spot some tumors or know how big they are.
How do CT scans and MRI compare in terms of speed and accessibility for brain imaging?
CT scans are faster and easier to get to. They’re great for emergencies because of this.
References
- Kaller, M. O. (2023). Contrast Agent Toxicity. StatPearls.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537159/




































