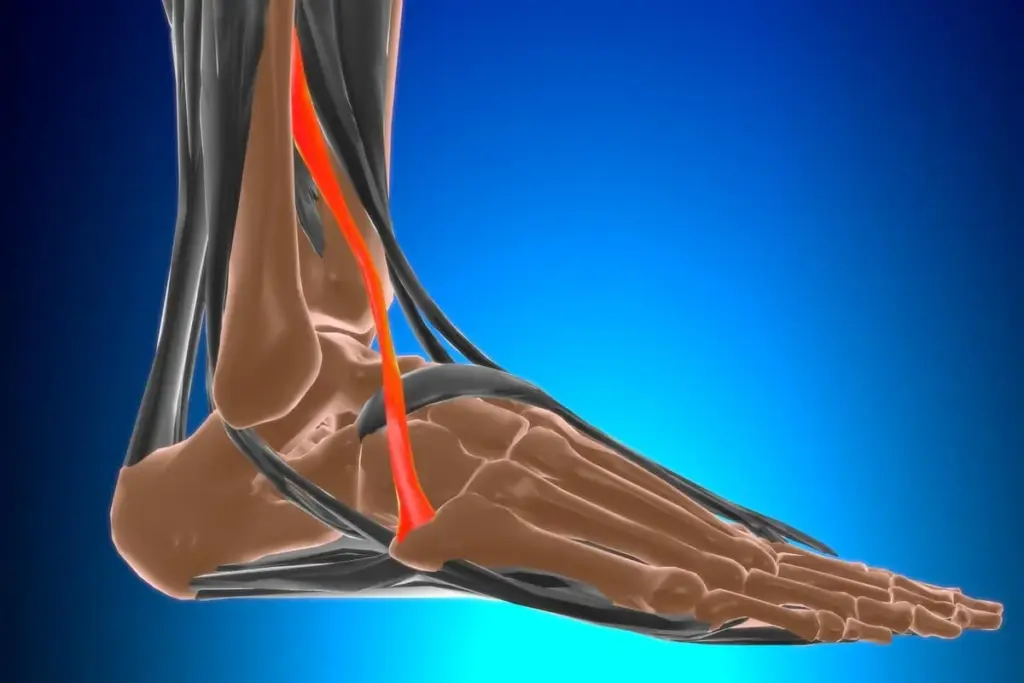
Knowing about ankle anatomy is key to understanding foot and ankle health. The anterior tibiotalar ligament is a big part of this. It helps keep the ankle stable.
This ligament is hidden deep in the medial ankle. It’s part of the deltoid ligament complex. It stops the ankle from moving too much, helping us do daily tasks. Knowing how it works helps us see the impact of injuries and the need for right treatment.
Key Takeaways
- The anterior tibiotalar ligament is vital for ankle stability.
- It’s a deep part of the deltoid ligament complex.
- Knowing its anatomy is key for right diagnosis and healing.
- Injuries to this ligament can really affect ankle health.
- Learning about talar ligaments helps with better ankle care.
Anatomy and Location of the Anterior Tibiotalar Ligament
The anterior tibiotalar ligament is key to the deltoid ligament complex in the ankle. We’ll look at its anatomy, including its structure, attachments, and variations.
This ligament is a big part of the deltoid ligament complex, found on the medial side of the ankle. It links the medial malleolus to the talus’s front part. This connection is vital for ankle stability.
Structure and Attachments
The anterior tibiotalar ligament is thin and short. It’s part of the deltoid ligament, working with others like the tibionavicular ligament to stabilize the ankle.
Its attachments are key to its function. It starts at the medial malleolus and ends at the talus.
Anatomical Variations and Prevalence
There are notable anatomical variations in the anterior tibiotalar ligament. About ten percent of people don’t have this ligament.
Knowing these variations is vital for diagnosing and treating ankle issues.
Function and Biomechanical Role
The anterior tibiotalar ligament is key for keeping the ankle stable during different movements. It’s a big part of the deltoid ligament complex. This makes it very important for the ankle’s biomechanics.
Stabilization of the Ankle Joint
The anterior tibiotalar ligament helps keep the ankle stable on the inside. It works with other ligaments to stop too much movement. It’s very important for keeping the ankle joint strong, during movements like lifting the foot up and rolling it inward.
Medical experts say, “The deltoid ligament complex, which includes the anterior tibiotalar ligament, is key for ankle stability.” This shows how important the ligament is for the ankle’s function.
Control of Eversion and Rotation
The anterior tibiotalar ligament also helps control how the ankle moves. It stops too much rolling outward, which helps protect the ankle from getting hurt. It also helps control rotation, keeping the ankle moving right and preventing bad movements.
This ligament works with other parts of the ankle to give it full support. Its role is closely tied to the ankle’s biomechanics. This makes it a critical part for keeping the ankle moving right and preventing injuries.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into the anatomy, function, and importance of the anterior tibiotalar ligament. It’s a key part of the medial ankle complex. This ligament, also known as the talotibial ligament, helps support the medial ankle and keeps the ankle stable.
The anterior tibiotalar ligament works with other ligaments to control the ankle’s movement. It helps in controlling eversion and rotation. Knowing about its structure and attachments is key for diagnosing and treating ankle problems.
Understanding the role of the anterior tibiotalar ligament in ankle stability helps healthcare professionals. They can better diagnose and manage ankle injuries. This leads to better outcomes for patients. The tibiotalar ligament is essential for the ankle’s health, and its proper function is vital.
FAQ
What is the anterior tibiotalar ligament, and where is it located?
The anterior tibiotalar ligament is a key part of the ankle. It connects the medial malleolus to the talus’s front part. It’s important for keeping the ankle stable.
What is the function of the anterior tibiotalar ligament in ankle stability?
This ligament helps control the ankle’s movement. It stops the ankle from turning outward and rotating. It works with other parts of the deltoid ligament to keep the ankle stable.
Is the anterior tibiotalar ligament present in everyone?
No, about ten percent of people don’t have this ligament. Knowing this helps doctors make accurate diagnoses.
How does the anterior tibiotalar ligament relate to the deltoid ligament complex?
It’s part of the deltoid ligament complex. Along with other ligaments, it helps stabilize the ankle. This is important for ankle health.
What happens if the anterior tibiotalar ligament is injured?
An injury can cause ankle instability. This is more noticeable during movements that involve turning and rotating. It’s important to diagnose and treat this injury properly.
How does understanding the anterior tibiotalar ligament improve patient outcomes?
Knowing about this ligament helps doctors diagnose and treat ankle injuries better. This leads to better care for patients.
What is the significance of the tibionavicular ligament in relation to the anterior tibiotalar ligament?
The tibionavicular ligament works with the anterior tibiotalar ligament to stabilize the ankle. Understanding how they work together is key to ankle health.
How does the anterior tibiotalar ligament contribute to medial ankle support?
It provides essential support by controlling the ankle’s movement. This helps keep the ankle stable and prevents injuries.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2855022/