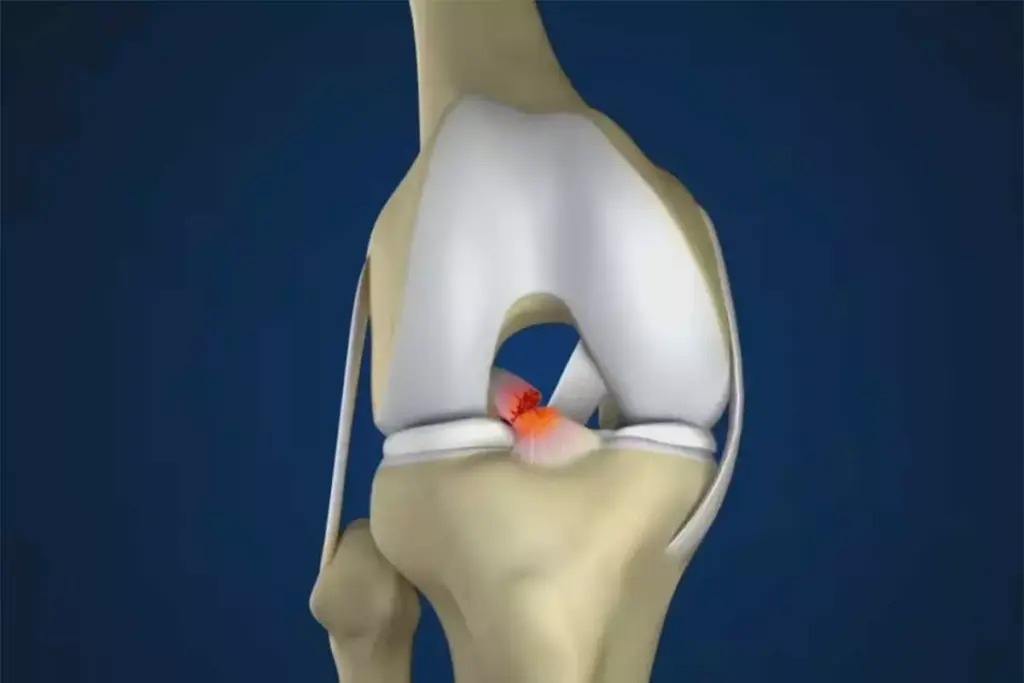
Feeling shoulder discomfort without a clear trauma can be worrying. It can mess up your daily life. Many people face shoulder problems that affect their work, sleep, and how they move.
At our place, we know non-traumatic shoulder pain can come from different things. This includes rotator cuff tendinitis, bursitis, and osteoarthritis. Knowing what causes it is key to fixing it.
Key Takeaways
- Non-traumatic shoulder pain can result from various underlying issues.
- Common causes include rotator cuff tendinitis, bursitis, and osteoarthritis.
- Understanding the causes is key for effective management and treatment.
- Symptoms can include pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
- Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause.
Common Causes of Left Shoulder Pain Without Injury
Many people experience left shoulder pain without injury. This can affect their daily life and quality of life. Finding the cause is key to treating and managing it.
How Non-Traumatic Shoulder Pain Develops
Non-traumatic shoulder pain comes from several sources. Rotator cuff tendinitis is a common cause. It happens when the tendons in the rotator cuff get inflamed or irritated.
As we get older, our tendons and muscles around the shoulder wear out. This makes them more likely to get inflamed. Doing the same movements over and over can make this worse, causing pain and discomfort.
Distinguishing Features from Injury-Related Pain
It’s important to tell non-traumatic shoulder pain from pain caused by injury. Non-traumatic pain builds up slowly and is linked to certain activities. Injury pain, on the other hand, comes on suddenly and is tied to a specific event.
Doctors need to know the difference to treat it right. By figuring out the cause, we can create a plan to ease the pain and help the shoulder work better.
Rotator Cuff Tendinitis: The Primary Culprit
Rotator cuff tendinitis is a main reason for shoulder pain in older adults. It comes from aging and repeated use. We help patients understand their shoulder pain, focusing on rotator cuff tendinitis.
Factors Contributing to Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
Age and repeated use are big risks for rotator cuff tendinitis. As we get older, our tendons wear down. This makes them more likely to get inflamed or damaged. Activities that involve lifting your arms up and down can make this worse.
Studies show that rotator cuff tendinitis happens when tendons get irritated under the shoulder bone. This leads to inflammation or damage. People who do a lot of overhead work are more likely to get it, as seen in a study on chest muscles and rotator cuff injuries.
Symptoms and Progression in Adults Over 40
Symptoms of rotator cuff tendinitis include pain, stiffness, and limited shoulder movement. If not treated, these symptoms can get worse. This can lead to less mobility and more pain.
| Symptom | Description |
| Pain | Pain when moving the shoulder or when lying on the affected side |
| Stiffness | Reduced mobility and stiffness in the shoulder joint |
| Limited Range of Motion | Difficulty in performing overhead activities or rotating the shoulder |
Knowing the causes and symptoms of rotator cuff tendinitis is key to managing it. We stress the need for early diagnosis and treatment to stop it from getting worse.
Secondary Conditions Leading to Shoulder Discomfort
Other medical conditions can also cause shoulder pain. It’s important to know about these to help our patients fully.
Bursitis and Its Relationship with Tendinitis
Shoulder bursitis is when the fluid-filled sacs around the joint get inflamed. It often happens with tendinitis. This can cause pain and swelling without a clear cause. It’s key to treat both bursitis and tendinitis at the same time.
Bursitis symptoms include:
- Localized pain and tenderness
- Swelling and redness around the affected bursa
- Reduced mobility and stiffness in the shoulder
Frozen Shoulder in Women Aged 40-50
Frozen shoulder, or adhesive capsulitis, is more common in women aged 40 to 50. It starts with pain and stiffness that gets worse over time. The exact cause is not known, but it involves inflammation and scarring of the connective tissue.
Frozen shoulder symptoms are:
- Progressive stiffness and pain in the shoulder
- Reduced range of motion, affecting daily activities
- Symptoms that can last for several months to a few years
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Degeneration
Osteoarthritis is when cartilage wears down, causing bone-on-bone pain and limited mobility. It’s common in older adults and can greatly affect their quality of life. Understanding osteoarthritis is key to finding effective treatments.
| Condition | Primary Symptoms | Common Demographics |
| Bursitis | Pain, swelling, reduced mobility | Active individuals, those with repetitive motion injuries |
| Frozen Shoulder | Pain, stiffness, reduced range of motion | Women aged 40-50 |
| Osteoarthritis | Bone-on-bone pain, limited mobility | Older adults |
Knowing about these secondary conditions helps us give better care to our patients. We can meet their unique needs more effectively.
Conclusion: Treatment Options and Prevention Strategies
Knowing why your left shoulder hurts is the first step to feeling better. There are many ways to treat shoulder pain, like physical therapy, medicines, and injections. The right treatment depends on the cause of the pain.
We at our institution are committed to top-notch healthcare for everyone, including international patients. We help our patients understand their treatment choices and how to avoid symptoms from getting worse. This way, we aim to prevent serious problems.
Being proactive about your shoulder health is important. It helps you figure out why you’re in pain. This could be due to rotator cuff tendinitis, shoulder bursitis, or osteoarthritis. Women, in particular, should watch out for shoulder pain, as they are more likely to get frozen shoulder.
Our goal is to stop complications and improve your life. We offer detailed care to find out what’s causing your shoulder pain. This ensures you get the help you need to heal and live well.
FAQ:
What are the common causes of left shoulder pain without injury?
Common causes include rotator cuff tendinitis, bursitis, frozen shoulder, and osteoarthritis. These can happen due to age, repetitive use, or medical conditions.
How does rotator cuff tendinitis cause shoulder pain?
Rotator cuff tendinitis happens when tendons get inflamed. This leads to pain, stiffness, and limited movement. It’s common in adults over 40.
What are the symptoms of shoulder bursitis?
Shoulder bursitis adds to the pain and inflammation. It makes the shoulder more uncomfortable and limits its movement.
Why is frozen shoulder more common in women aged 40-50?
Frozen shoulder is more common in women aged 40-50. It causes stiffness and pain. Hormonal changes and inflammation might play a role.
How does osteoarthritis affect the shoulder?
Osteoarthritis causes cartilage to wear down, leading to bone pain and stiffness. It affects daily activities and quality of life.
What treatment options are available for non-traumatic shoulder pain?
Treatment depends on the cause but includes physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes. Knowing the cause is key to effective treatment.
Can shoulder pain be prevented?
Yes, by taking care of your shoulder health, you can prevent pain. A healthy lifestyle, avoiding strain, and managing conditions are important.
Why is it essential to distinguish non-traumatic pain from injury-related pain?
It’s important to tell the difference between non-traumatic and injury pain. Non-traumatic pain needs a specific treatment plan, focusing on the cause.
What are the risk factors for developing rotator cuff tendinitis?
Risk factors include age and repetitive use. Adults over 40 are more likely to get rotator cuff tendinitis.
References:
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9730650/