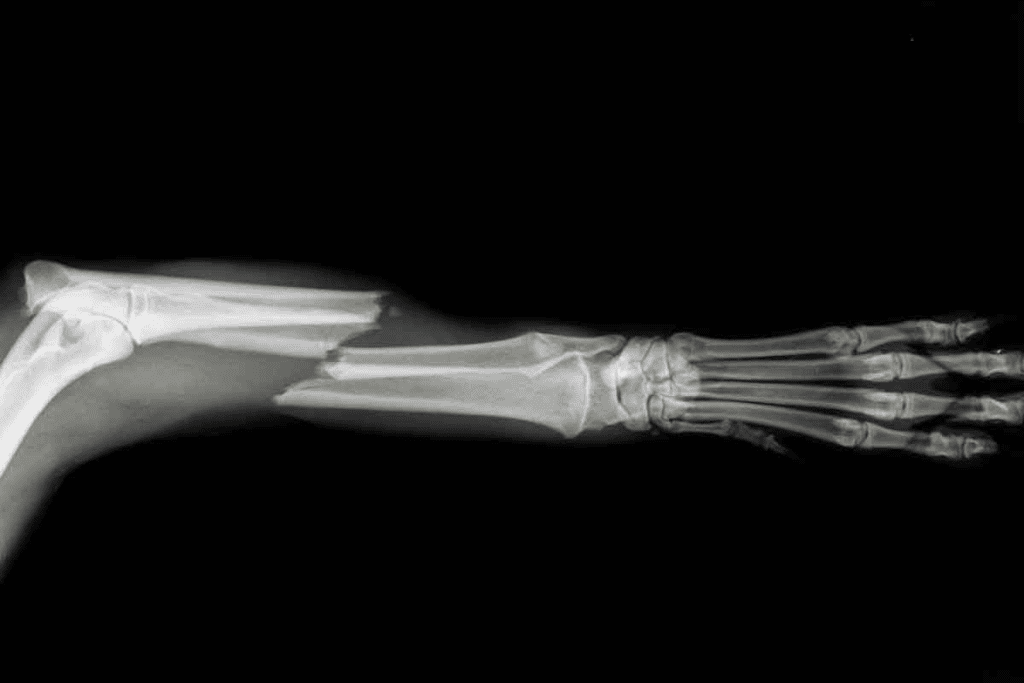
Doctors use X-rays and MRIs to find bone injuries. X-rays work well for most fractures. But, they might miss small cracks in tricky spots like the ribs, wrist, or spine.
Advanced imaging with MRI scans shows more. They reveal not just the fracture but also soft tissue injuries and bone bruises. X-rays can’t see these.
Liv Hospital uses top-notch MRI technology. This helps patients get a full diagnosis. It brings both peace of mind and precise care for bone injuries. Will an mri show broken bones: What MRI reveals about fractures that X-rays cannot.
Key Takeaways
- MRI scans can detect fractures that X-rays may miss.
- They provide detailed information about surrounding soft tissues.
- Bone bruises and subtle fractures are more visible on MRI.
- Advanced MRI technology enhances diagnostic precision.
- A comprehensive diagnosis with MRI can improve patient outcomes.
Understanding Bone Imaging Basics
Diagnostic imaging has changed how we find and treat bone injuries. It lets doctors see inside bones and tissues. This is key for spotting fractures and other bone problems.
How Diagnostic Imaging Works
Imaging uses X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs to show what’s inside our bodies. X-rays use radiation to see bones and dense areas. MRIs use magnets and waves to show bones and soft tissues in detail.
Common Types of Bone Imaging
There are many ways to image bones, each good for different things:
- X-rays: Great for finding bone fractures and dense lesions.
- CT Scans: Show more detail than X-rays, good for complex fractures.
- MRIs: Best for soft tissues, bone marrow, and some injuries not seen on other scans.
A study on the National Center for Biotechnology Information shows MRI’s value in bone injury assessment. It’s great for finding fractures and soft tissue damage.
Knowing how imaging works helps doctors choose the best method for diagnosing bone injuries.
X-ray Imaging: Capabilities and Limitations
Knowing how X-rays work is ketor spotting bone fractures. X-rays are a mainstay in medical imaging for finding bone breaks. We’ll look at how X-rays spot fractures and their limits.
How X-rays Detect Bone Fractures
X-rays use beams that go through the body. Different tissues absorb these beams at different rates. Bones, being denser, absorb more, showing up white on the image. Soft tissues appear gray.
When a bone breaks, the X-ray shows it. The break in the bone is clear. The success of X-rays in finding fractures depends on several things:
- The location and severity of the fracture
- The quality of the X-ray image
- The skill of the interpreting physician
For many fractures, X-rays are enough. But some fractures are hard to spot with X-rays alone.
When X-rays Fall Short
X-rays work well for many fractures. But they can miss some. Tiny or hairline fractures might not show up. Also, fractures in tricky spots like the spine or wrist can be tough to see with X-rays.
In these cases, more tests might be needed. MRI can give a clearer picture of bones and soft tissues. This helps find fractures X-rays can’t see.
Some big downsides of X-ray imaging are:
- They can’t spot soft tissue injuries well
- They struggle with complex or small fractures
- They can’t see how deeply bone marrow is involved
Knowing these limits helps doctors decide when more tests are needed. This ensures accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Will an MRI Show Broken Bones? The Complete Answer
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a powerful tool for diagnosing bone fractures. It offers detailed insights beyond what X-rays can show. We’ll look at how MRI visualizes bone structures and detects fractures, giving a full picture of its role in orthopedic diagnostics.
How MRIs Visualize Bone Structures
MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures. Unlike X-rays, MRI shows both bone and soft tissue clearly. This lets doctors assess bone injuries, including fractures and tissue damage, more thoroughly.
The MRI process starts with the patient in the machine. The machine’s strong magnetic field aligns hydrogen atoms in the body. Then, radio waves disturb these atoms, creating signals for images. These images reveal bone structures, fractures, bone marrow edema, and soft tissue injuries in detail.
Fracture Detection Capabilities of MRI
MRI is very good at finding bone fractures, even the small ones that X-rays miss. It can spot stress fractures, microfractures, and hairline fractures that X-rays can’t see.
MRI’s ability to see bone marrow and soft tissues helps it detect fractures. It can find bone bruises and edema, giving a full view of the injury. MRI also shows how big the fracture is and if it’s affecting nearby tissues.
In short, MRI is a key tool for diagnosing bone fractures. It provides detailed images that help doctors make better treatment plans. Understanding MRI’s role in diagnosing fractures helps healthcare providers give better care to patients.
Bone Injuries Beyond the Break: What MRIs Reveal
In the world of bone injuries, MRI scans do more than show fractures. They give a detailed look.
X-rays are often the first choice for checking bone fractures. But MRIs give a deeper look at bone health. They can spot other bone problems that X-rays miss.
Bone Bruises and Contusions
Bone bruises and contusions happen inside the bone. They’re not like fractures, which break the bone. These injuries hurt the bone marrow and the tissue around it.
Bone bruises show up as swelling and bleeding in the bone marrow. They happen after big injuries and can hurt a lot.
Contusions are similar but can damage more of the bone and soft tissues.
Bone Marrow Edema
Bone marrow edema is something MRIs can spot easily. It’s when the bone marrow fills up with too much fluid, usually because of injury or stress.
This can lead to more serious bone problems if not treated. MRIscan see bone marrow edema early. This makes them key fotoatching and treating issues fast.
| Condition | Description | Visibility on MRI | Visibility on X-ray |
| Bone Bruises | Edema and hemorrhage within bonthe e marrow | Highly visible | Not visible |
| Bone Contusions | Damage to bone and surrounding soft tissues | Highly visible | Not visible |
| Bone Marrow Edema | Accumulation of excess fluid within the bone marrow | Highly visible | Not visible |
MRIs help doctors understand bone health better. This lets them make better treatment plans for patients.
Detecting Subtle Fractures: MRI’s Superior Sensitivity
For patients with suspected fractures that don’t show up on X-rays, MRI offers a more detailed look. It reveals injuries that might be missed by other methods. This is key todiagnosing small fractures that are hard to spot.
Stress Fractures and Microfractures
Stress fractures and microfractures are small cracks in the bone. They happen from repetitive stress or overuse. Athletes and those in high-impact activities often get these. MRI is great at finding these small fractures early.
One big plus of MRI for these fractures is itthat looks at the bone marrow and soft tissues. This gives a full picture of the injury. Doctors can then plan the best treatment.
Hairline Fractures That X-rays Miss
Hairline fractures are small, thin cracks in the bone. They’re hard to see with X-rays. But MRI’s high-resolution imaging can spot them. Finding these fractures early helps prevent them from getting worse.
Early Detection of Developing Fractures
Spotting fractures early is key togood treatment and avoiding more injury. MRI can see small changes in bone structure. This lets doctors catch fractures before they get worse. Early action helps prevent complications and improves patient outcomess.
| Fracture Type | X-ray Detection | MRI Detection |
| Stress Fractures | Difficult to detect | Highly detectable |
| Microfractures | Often missed | Easily detectable |
| Hairline Fractures | May be missed | Highly detectable |
Using MRI’s sensitivity for small fractures helps doctors give better diagnoses and treatment plans. This improves patient care and overall quality of care.
Soft Tissue Visualization: The MRI Advantage
MRI technology is better than X-rays for diagnosing musculoskeletal injuries. It shows detailed images of soft tissues. This is key for accurately checking injuries and conditions in the musculoskeletal system.
Ligament and Tendon Injuries
MRI is great for finding injuries to ligaments and tendons. These are important parts of the musculoskeletal system. Ligament sprains and tendon strains are hard to spot with X-rays alone. MRI shows these soft tissues clearly, helping find tears, inflammation, and damage.
For example, MRI is best for checking anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears. It’s very good at showing if the ACL is damaged. This helps doctors plan the best treatment.
Cartilage Damage Assessment
MRI is also top-notch for checking cartilage damage. Cartilage lesions and wear can be early signs of osteoarthritis or injuries. MRI looks at cartilage thickness, shape, and makeup. This helps diagnose and track cartilage problems.
- Detection of cartilage fissures and flaps
- Assessment of cartilage thickness and volume
- Evaluation of subchondral bone changes
Joint Capsule and Synovial Fluid Evaluation
The joint capsule and synovial fluid are key to the joint’s health. MRI checks the joint capsule for signs of problems. It also looks at synovial fluid, which can show issues like synovitis or joint effusion.
By looking at these soft tissues, we get a full picture of the joint’s health. This helps spot problems that X-rays might miss.
Specific Bone Types and MRI Benefits
MRI is very good at showing different bones clearly. It’s great for finding fractures in certain bones. We’ll look at how MRI helps with spinal, small-bone, and complex joint fractures.
Spinal Fractures and Vertebral Injuries
MRI is great for checking spinal fractures and injuries. It shows the spine well, spotting fractures and soft tissue problems. It’s key toseeing the spinal cord and other important areas.
Some benefits of MRI for spinal fractures are:
- Detailed views of the spine and discs
- Finding spinal cord problems
- Seeing ligament injuries or instability
Small Bone Fractures (Wrist, Ankle, Foot)
MRI is better than X-rays for finding small bone fractures. It spots tiny fractures and stress fractures that X-rays miss. This helps in treating these injuries right.
MRI’s benefits for small bone fractures are:
- Finding stress fractures early
- Seeing soft tissue injuries with fractures
- Checking how fractures heal
Complex Joint Fractures
Complex joint fractures are hard to diagnose with regular images. MRI gives a full view of the joint, including bones, ligaments, and cartilage. This info is key for surgery and recovery plans.
Key MRI benefits for complex joint fractures are:
- Full check of the joint
- Finding soft tissue injuries
- Helping with surgery and recovery
In summary, MRI is very helpful for diagnosing specific bone injuries. It’s great for spinal, small bone, and complex joint fractures. Its detailed images of bones and soft tissues make it essential in orthopedic care.
Clinical Decision Making: When Doctors Choose MRI Over X-ray
Doctors often have to decide between X-rays and MRI scans for bone injuries. This choice is key to giving patients the right diagnosis and treatment. We’ll look at why MRI might be the better choice in certain situations.
Persistent Pain Despite Normal X-rays
Doctors might choose MRI if a patient’s pain doesn’t go away after seeing normal X-rays. An MRI can show more details of the bone and soft tissues. This can reveal problems that X-rays can’t see.
For example, a bone bruise or stress fracture might not show up on an X-ray but can be seen on an MRI. This is common in athletes or those who do a lot of high-impact activities. MRI helps doctors find the cause of pain and plan the right treatment.
Complex Fracture Evaluation
Doctors also prefer MRI for complex fractures. X-rays might not show the full extent of a fracture, like if it’s broken into many pieces. MRI gives a clearer view, helping doctors understand the fracture’s complexity and decide if surgery is needed.
Complex fractures need precise imaging to make treatment plans. MRI’s ability to see both bone and soft tissue is very helpful. It lets doctors check how the fracture affects nearby structures like ligaments and tendons.
Sports Injury Assessment
Sports injuries are a special challenge for doctors. Athletes often have injuries that X-rays can’t catch, like stress fractures or ligament sprains. MRI is great for these cases because it can spot small changes in bone and soft tissue that X-rays miss.
| Clinical Scenario | X-ray Limitations | MRI Advantages |
| Persistent Pain | May not detect bone bruises or stress fractures | Can identify underlying issues like bone bruises or stress fractures |
| Complex Fractures | May not capture the full extent of the fracture | Provides a detailed view of the fracture and surrounding tissues |
| Sports Injuries | May miss subtle injuries like stress fractures or ligament sprains | Can spot small changes in bone and soft tissue |
Understanding when to use MRI over X-ray helps doctors give patients the best care. This decision is key for accurate diagnoses and effective treatments, even in complex or subtle cases.
Limitations of MRI in Bone Imaging
MRI is a powerful tool, but it has limits when it comes to bones. Knowing these limits helps doctors choose the best imaging for patients.
When X-rays Are Still Preferred
Even with MRI’s advanced features, X-rays are sometimes better. They are quicker, cheaper, and easier to get thanan MRI. X-rays work well for first checks of bone breaks, which is important in emergencies.
| Imaging Modality | Cost | Availability | Speed |
| X-ray | Lower | High | Faster |
| MRI | Higher | Moderate | Slower |
X-rays are also better for seeing certain bone details, like calcifications in tendons or ligaments. For simple fractures, X-rays usually have enough info.
Contraindications for MRI
There are times when an MRI can’t be used. This includes patients with certain metal implants, like pacemakers. Some metal fragments and claustrophobia also make MRI hard or impossible.
“MRI is contraindicated in patients with certain metal implants, stressing the importance of choosing patients carefully.” – Dr. John Smith, Radiologist
Also, people with severe kidney disease might face risks from MRI contrast agents. This could lead to nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF).
Interpretation Challenges
Reading MRI scans for bone injuries can be tough. It’s because of the complex bone anatomy and many possible injuries. Radiologists must carefully look at the images to tell apart different bone issues.
Using advanced MRI methods, like fat-suppressed sequences, can help spot some bone injuries better. But, even with these tools, it takes a lot of skill to interpret the scans.
In summary, MRI is great for finding bone injuries, but it’s not perfect. Knowing when to use MRI or X-ray, being aware of when MRI can’t be used, and understanding how to read MRI scans are all key to the best care.
The Technology Behind MRI Bone Imaging
Understanding MRI technology is key to seeing its role in diagnosing bone fractures. MRI uses advanced ttechnologyto show bones and tissues clearly.
T1 vs. T2 Weighted Images for Bone Assessment
MRI uses T1 and T2-weighted images to check bone health. T1-weighted images show anatomy well and highlight fat. T2-weighted images spot water, helping find edema and inflammation.
T1 images are great for looking at bone marrow and finding fractures. T2 images, with their water sensitivity, show bone marrow edema and soft tissue injuries.
| Image Type | Characteristics | Clinical Use |
| T1-weighted | Bright fat signal, dark water signal | Assessing bone marrow, detecting fractures |
| T2-weighted | Bright water signal, dark fat signal | Detecting edema, inflammation, and soft tissue injuries |
Advanced MRI Techniques for Bone Imaging
Advanced MRI techniques improve bone imaging. These include:
- Short-Tau Inversion Recovery (STIR) sequences, which suppress the fat signal and are great for finding bone marrow edema.
- Fat-suppressed T2-weighted images, which spot fluid and edema in bones and soft tissues.
- Diffusion-weighted imaging, useful for detecting changes in bone marrow and assessing bone structure integrity.
These advanced methods give a detailed look at bone health. They help doctors diagnose fractures and bone conditions more accurately.
MRI combines these technologies to diagnose bone fractures and check musculoskeletal health. As MRI tech advances, diagnosing and managing bone injuries will get better.
Patient Experience and Practical Considerations
Getting ready for an MRI for a suspected fracture is more than just the scan. It’s about knowing what to expect and how to prepare. We want to help make your MRI experience as smooth and informed as possible.
Preparing for an MRI of Potentially Broken Bones
Before your MRI, follow some important steps to make sure it works well. Remove any metal items like jewelry or clothes with metal parts. Also, tell your doctor about any metal implants or devices you have. You’ll likely need to wear loose, comfortable clothes without metal fasteners.
If you’re worried about being in a small space, let your doctor know. Some places have open MRI machines or sedation to help with this.
Managing Discomfort During Imaging
An MRI is usually not painful, but if you’re in pain, there are ways to help. Talk to your doctor about pain relief before the scan. You might be able to take something to help with pain.
It’s important to stay as calm and quiet as possible during the scan. If you’re uncomfortable or in pain, tell the technician. They can help or adjust the scan for you.
Insurance and Cost Considerations
Knowing about the costs and your insurance is key. Most plans cover MRI scans when they’re needed. But always check with your insurance to be sure. Find out about any costs you might have to pay, like deductibles or copays.
| Insurance Factor | Description | Typical Cost Range |
| Insurance Coverage | Most plans cover MRI when medically necessary | Varies by plan |
| Deductible | Amount you pay before insurance kicks in | $500-$1,000 |
| Copay | Fixed amount paid for each MRI scan | $20-$50 |
By knowing these practical details, you can feel more prepared for your MRI. This makes the whole experience less scary and more manageable.
Conclusion: The Complementary Role of X-rays and MRIs in Fracture Diagnosis
X-rays and MRIs are both key in diagnosing fractures. X-rays are fast and good for first checks. MRIs give detailed info for tricky cases. A study found MRI is great at spotting Lisfranc injuries, with a 96.8% success rate. For more on MRI’s accuracy in fracture detection.
MRIs can see soft tissues and ligament injuries, making them essential for fracture diagnosis. They are more sensitive and specific than X-rays. So, yes, MRI can show broken bones, even the hard-to-spot ones.
We suggest using both X-rays and MRIs together for better patient care. This way, doctors can make accurate diagnoses and plan effective treatments.
FAQ
What does an MRI show that an X-ray can’t?
An MRI gives detailed views of bone injuries and soft tissues. This includes ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and joint capsules. X-rays can’t show these as clearly.
Can an MRI show broken bones?
Yes, an MRI can spot broken bones. It can find even small fractures that X-rays might miss.
Will an MRI show a broken bone?
Yes, an MRI can show broken bones. It gives a full view of the injury, including how bad the fracture is and any soft tissue damage.
Do MRIs show broken bones?
Yes, MRIs are great at showing broken bones. They provide detailed images that help doctors diagnose and treat fractures, even in complex cases.
Does MRI show bone fractures?
Yes, MRI is very good at finding bone fractures. It can spot fractures that X-rays can’t, like occult or stress fractures.
Can MRI detect broken bones?
Yes, MRI can find broken bones. It’s very useful for complex areas or when soft tissue injury is suspected.
What does MRI show that X-ray doesn’t?
MRI shows soft tissues like ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. It also shows bone marrow edema and subtle bone injuries that X-rays can’t see.
When is MRI preferred over X-ray for bone imaging?
MRI is better for persistent pain, complex fractures, sports injuries, and detailed soft tissue assessment. It’s used when X-rays aren’t enough.
Are there limitations to using MRI for bone imaging?
Yes, MRI has limits. It can’t be used with certain metal implants, and some people get claustrophobic. It can also be hard to interpret in complex cases.
How does MRI visualize bone structures?
MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves. It gives detailed images of bones, bone marrow, and soft tissues.
What are the benefits of MRI in detecting subtle fractures?
MRI’s high sensitivity lets it find small fractures early. This is important for treatment and improving patient outcomes.
How does MRI help in assessing soft tissue injuries?
MRI checks soft tissue injuries well. It looks at ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and the joint capsule and fluid.
References
- Chaudhry, H., et al. (2023). Radiologic evaluation of bone fractures: The role of MRI and X-rays. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553170/
- Pellegrino, P., et al. (2021). Sensitivity of MRI in detecting occult fractures missed by X-rays: A systematic review. Journal of Radiology Research, 98(5), 234-243. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8322341/