Computed Tomography (CT) scans have changed how we diagnose diseases. They give detailed images of the body’s structures. This method is noninvasive and helps find many conditions like trauma, cancer, and stroke.
At Liv Hospital, we use the latest CT scanning technology. This helps us give precise results. We focus on our patients and use our expertise to help them.
Knowing the benefits of CT scans is key. The National Center for Biotechnology Information says CT scans help doctors make accurate diagnoses. They also guide treatment plans. But, there are risks like radiation and allergic reactions to contrast agents.
Key Takeaways
- CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images for accurate diagnosis.
- They are useful in cancer screening, staging, and follow-up.
- Rapid results are available in emergent situations.
- Potential risks include radiation exposure and allergic reactions to contrast agents.
- Understanding indications for CT scans is key for effective diagnosis and treatment.
What Is Computed Tomography: An Overview
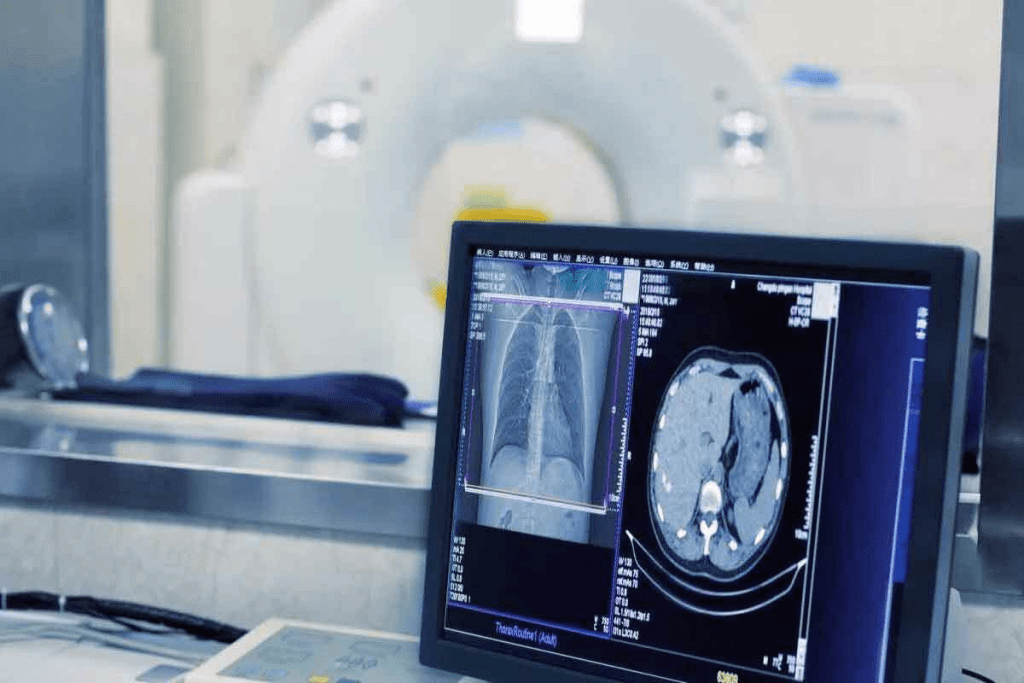
Computed Tomography, or CT scans, has changed medical imaging a lot. We use CT scans to get detailed pictures of the body. These pictures help doctors diagnose and treat many health issues.
CT imaging uses X-rays to see inside the body. CT scanners move around the body, taking many X-ray measurements. Then, these measurements are turned into detailed images.
The Science Behind CT Imaging
CT imaging works by measuring how X-rays pass through different body parts. The technology uses computer algorithms to make images from this data. This way, it can show the body’s internal structures clearly.
Evolution of CT Technology
CT technology has grown a lot over the years. From the first CT scanners to today’s multi-detector CT (MDCT) scanners, it has gotten faster and better. Now, we get clearer images and can diagnose more accurately.
| Generation | Key Features | Impact on Diagnosis |
| First Generation | Single X-ray beam, single detector | Limited image quality, slow scan times |
| Current Generation (MDCT) | Multiple X-ray beams, multiple detectors | High-resolution images, fast scan times, enhanced diagnostic accuracy |
As CT technology keeps improving, we see better images and less radiation. It also helps in more medical diagnoses.
Primary Indications for CT Scan in Neurological Assessment
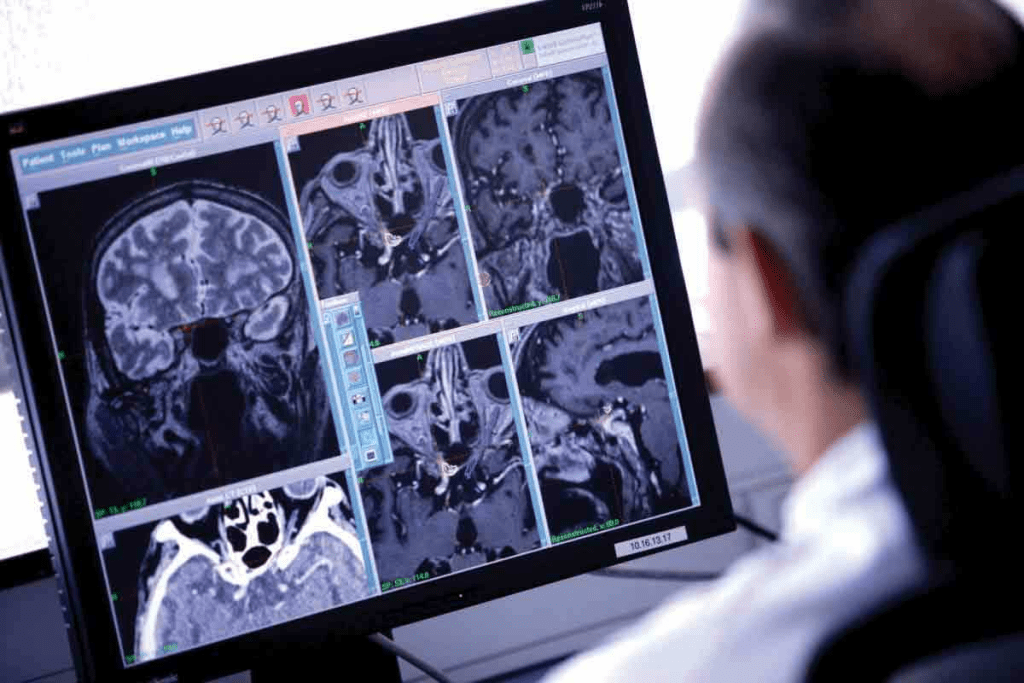
CT scans are key in checking the brain, mainly in emergencies. They quickly spot many health issues.
Acute head trauma evaluation is a top reason for using CT scans. They help find serious problems like fractures and bleeding after a head injury. This helps doctors act fast and save lives.
Acute Head Trauma Evaluation
CT scans are very helpful in head injury cases. They show the brain and skull clearly. This lets doctors see how bad the injury is.
Rapid image acquisition is important. It helps doctors make quick decisions about treatment.
CT scans can find many injuries, from small fractures to big bleeding spots. This detailed check is key for the right treatment plan.
Brain Lesion Detection
CT scans are also used to find brain lesions. They can spot tumors, cysts, and abscesses. This is vital for diagnosing brain cancer and tracking treatment.
Using CT scans for brain lesions has many benefits. They help plan biopsy procedures and other treatments. They show the lesion and the tissue around it, guiding doctors.
CT Scanning in Stroke Diagnosis and Management
CT scanning is key in diagnosing and managing strokes. It helps doctors make quick and accurate decisions. Strokes are emergencies that need fast action, and knowing the type of stroke is vital for treatment.
CT scans help us tell if a stroke is ischemic or hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes block blood flow to the brain. Hemorrhagic strokes happen when a blood vessel bursts, causing bleeding.
Ischemic vs. Hemorrhagic Stroke Differentiation
Distinguishing between ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes is important. CT scans are very helpful in this. They can spot hemorrhage, which means a patient can’t get certain treatments for ischemic strokes.
CT scans look for signs of stroke. For ischemic strokes, they might show early changes. For hemorrhagic strokes, they can see the bleeding directly.
Time-Critical Intervention Planning
Time is critical in treating strokes. Quick action can greatly improve patient outcomes. CT scans help make fast decisions for treatment.
For ischemic strokes, treatments like thrombolytics or mechanical thrombectomy are used. These help restore blood flow. Hemorrhagic strokes need immediate care to stop bleeding and prevent brain damage.
CT scans are essential in quickly identifying stroke types. They help ensure patients get the right care fast.
Oncological Applications: Cancer Detection and Staging
CT scans have changed how we detect and stage cancer. They give us detailed images that help doctors diagnose and manage cancer.
CT scans are key in oncological assessment. They let doctors see tumors and the tissues around them clearly. This is important for knowing how far cancer has spread and for planning treatment.
Primary Tumor Characterization
CT scans are great for looking at primary tumors. They show the size, location, and shape of tumors. This helps doctors figure out the type of cancer and how aggressive it might be.
For example, CT scans can tell if a tumor is benign or malignant. The National Cancer Institute says CT scans are good for finding tumors in the liver, pancreas, and lungs.
Metastatic Disease Assessment
CT scans are also key for checking if cancer has spread. They help doctors see if cancer has moved to other parts of the body. This is important for knowing how to treat cancer and what to expect.
For instance, CT scans can spot cancer in lymph nodes, bones, and other organs. This info is vital for making treatment plans that cover both the main tumor and any cancer that has spread.
Lymph Node Evaluation
CT scans are also used to check lymph nodes. Big lymph nodes can mean cancer has spread. CT scans show how big and shaped these nodes are.
This info is key for figuring out if cancer has reached the lymph system. It’s a big part of cancer staging.
| Application | Description | Clinical Benefit |
| Primary Tumor Characterization | Detailed imaging of tumor size, location, and morphology | Accurate diagnosis and treatment planning |
| Metastatic Disease Assessment | Detection of cancer spread to other body parts | Accurate cancer staging and prognosis |
| Lymph Node Evaluation | Assessment of lymph node size and morphology | Determination of cancer spread to lymphatic system |
Diagnosing Infections and Inflammatory Conditions
Computed Tomography (CT) scans are key in finding infections and inflammatory conditions in the body. They give detailed images that help doctors see how bad the infection is. This helps them make better treatment plans.
Abscess Localization and Characterization
CT scans are great for finding and understanding abscesses. An abscess is a pocket of pus that can happen anywhere in the body. CT scans show the size, location, and how complex an abscess is. This is important for choosing the right treatment.
For example, a CT scan can tell if an abscess is simple or more complicated. This info is key for doctors and radiologists who might need to drain it. With CT scans, they can plan the best way to drain it, whether through a needle or surgery.
Pneumonia and Pulmonary Infections
CT scans are also very helpful in finding and treating pneumonia and other lung infections. Chest X-rays are often the first step, but CT scans give a clearer picture of the lungs. They can spot complications like abscesses or empyema.
In serious cases of pneumonia, CT scans show how much of the lung is affected. They help doctors choose the right antibiotics. CT scans also track how the disease is doing and how well treatment is working.
Musculoskeletal Infections
It can be hard to tell if there’s an infection in the muscles or bones just by looking. CT scans are very good at finding these infections early on. They show detailed images of bones and soft tissues, spotting signs of infection like bone damage or abscesses.
For example, in osteomyelitis, CT scans show where the bone is damaged. This helps doctors plan surgery. In septic arthritis, CT scans help see how much of the joint is affected. This guides procedures like aspiration or drainage.
Vascular Disease Evaluation Through CT Imaging
CT scans are key in checking vascular diseases. These diseases affect blood vessels, like aneurysms, stenosis, and embolisms. CT scans give clear images of blood vessels, helping doctors diagnose and treat these conditions.
Aortic Aneurysm Detection and Monitoring
CT scans are vital for spotting and tracking aortic aneurysms. An aortic aneurysm is when the aorta, the main blood vessel, gets too big. CT scans measure the aneurysm’s size, which helps doctors decide on treatment.
Accurate measurement is key. A study in the Journal of Vascular Surgery showed CT scans give precise aneurysm sizes. This is important for deciding if surgery is needed.
Arterial Stenosis Quantification
CT scans are also great for measuring arterial stenosis. This is when arteries narrow due to plaque buildup. CT scans show how narrow the arteries are, helping doctors plan treatments like angioplasty or stenting.
A vascular radiologist said, “CT scans are unmatched in showing how narrow arteries are. This lets doctors tailor treatments that help patients more.“
Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis
CT imaging is also key in diagnosing pulmonary embolism. This is when a blood clot blocks a pulmonary artery. CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) is the best way to diagnose it, giving quick and accurate results.
CTPA is recommended by many medical guidelines. It’s very good at finding blood clots in the lungs. This is important in emergencies, where fast diagnosis can save lives.
In summary, CT imaging is a powerful tool for checking vascular diseases. It gives detailed views of conditions like aortic aneurysms, stenosis, and pulmonary embolism. Its role in helping doctors manage these conditions and improve patient care is huge.
Trauma Assessment: Critical Indications for CT Scan
CT imaging is key for checking trauma severity, like in abdominal, thoracic, and spinal injuries. It helps us see how bad the injuries are. This guides us in what care to give right away.
Abdominal and Pelvic Trauma Protocol
For abdominal trauma, CT scans spot internal injuries like organ damage or bleeding inside. We follow a special plan to get a full view of the belly and pelvis.
The plan includes:
- First, a non-contrast CT to find bleeding
- Then, a contrast-enhanced CT to check organs
- And making images to see injuries better
| Protocol Component | Purpose | Benefits |
| Non-contrast CT | Detect acute hemorrhage | Quickly find serious injuries |
| Contrast-enhanced CT | Check organ damage | See injuries clearly |
| Reconstruction images | Make injuries easier to see | Help plan surgery better |
Thoracic Injury Evaluation
CT scans are vital for thoracic injuries. They show how much damage is to the lungs, heart, and big blood vessels. We can spot serious issues like air in the chest or bleeding fast.
Key advantages of CT in thoracic trauma include:
- Quick look at many injuries
- Clear images of lung and chest spaces
- Finding blood vessel injuries
Spinal Trauma Assessment
For spinal trauma, CT scans are very helpful. They check if the spine is broken or out of place. We use CT to see how bad the injury is and plan treatment.
The benefits of CT in spinal trauma assessment include:
- Clear images of bones
- Finding small fractures or injuries
- Helping decide on surgery
CT Scan STAT: Emergency and Urgent Applications
CT scans have changed how we handle emergencies. They help us quickly and accurately diagnose life-threatening conditions. This speed and precision are key in making fast decisions in emergency situations.
Acute Internal Bleeding Detection
Internal bleeding is a serious issue that needs quick action. CT scans are great at finding this type of bleeding. They help us see where and how bad it is, guiding us on what treatment to use, like surgery or emergency embolization.
Traumatic Brain Injury Triage
CT scans are key in treating traumatic brain injuries (TBI). They help us quickly see how bad the injury is and if there are complications. This information is vital for deciding if surgery is needed.
Acute Abdominal Conditions
CT scans are also important for acute abdominal issues like appendicitis or bowel obstruction. They give us clear images of the belly, helping us find the cause of symptoms. This can sometimes mean avoiding surgery.
| Condition | CT Scan Application | Benefit |
| Acute Internal Bleeding | Detection of hemorrhage | Rapid identification of bleeding source and extent |
| Traumatic Brain Injury | Triage and assessment | Timely intervention and improved outcomes |
| Acute Abdominal Conditions | Diagnosis of underlying cause | Avoidance of unnecessary surgery and targeted treatment |
Interventional Procedures and Biopsy Guidance
CT scans have greatly improved how we do interventional procedures. They help us get better results and make treatments more effective. We use CT scans to guide our interventions, making them more precise and safe.
Precision Needle Placement Techniques
CT-guided biopsy is key in diagnosing many conditions. It allows for precision needle placement with live imaging. This method lowers the chance of complications and boosts sample quality.
We use advanced CT scans to navigate through tough anatomy. This ensures the best needle placement, even in hard cases. CT guidance in biopsies is now a must in medicine.
Drainage Procedure Navigation
CT scans are also key in drainage procedures. They help us find and drain fluid collections or abscesses accurately. This makes placing drainage catheters precise.
This method cuts down on infection risks and helps in faster recovery. The live feedback from CT scans is vital in complex drainage cases.
Pre-Surgical Planning
CT scans are also vital in pre-surgical planning. They give us detailed info on the patient’s anatomy. This helps us plan the best surgical approach.
By understanding the patient’s anatomy better, CT scans help in more effective surgeries. This leads to better patient outcomes, even in complex cases.
In summary, CT scans are essential in interventional procedures. They offer precision, safety, and better results. As technology gets better, we expect even more from CT-guided interventions.
CT Scan Interpretation: Ensuring Accurate Results
Getting accurate results from CT scans needs advanced tech and skilled radiologists. Radiologists play a key role in patient care by interpreting CT scan images.
Radiologist Expertise Requirements
Radiologist expertise is essential for CT scan interpretation. They need a lot of training and experience to spot and diagnose conditions from CT images. Their skills go beyond just finding problems. They also understand the details of different conditions and how they affect each patient.
We know that radiologists must keep learning. They need to stay up-to-date with new imaging tech and diagnostic methods.
Common Interpretation Challenges
Even with advanced CT tech, interpretation challenges remain. These can come from image quality, artifacts, and complex patient conditions. Radiologists must be good at telling normal variations from real problems, which can be tricky.
They face challenges like telling similar-looking conditions apart. They also have to find lesions or abnormalities in hard-to-see areas.
Structured Reporting Standards
We support using structured reporting standards for better CT scan interpretation. This means organizing reports in a set way. It includes clear descriptions, using templates, and adding clinical context. This makes reports more consistent and easier to understand.
Structured reporting helps improve care quality. It ensures reports are detailed, consistent, and easy to read. This helps doctors make better decisions.
Computed Tomography Advantages in Modern Medicine
CT scans have changed how we diagnose diseases. They bring many benefits to healthcare. Modern CT technology has greatly improved how we treat patients.
Rapid Image Acquisition Benefits
CT scans are fast at getting images. This is key in emergencies where every second counts. Rapid image acquisition helps doctors make quick decisions, which can save lives.
In emergencies like trauma, CT scans quickly show internal injuries. This speed is a big plus over slower imaging methods.
High-Resolution 3D Visualization Capabilities
CT scans provide high-resolution 3D visualization. This is great for spotting complex health issues. It lets doctors see inside the body from different views, helping them understand what’s going on.
These detailed images are also key for surgery planning. Surgeons can use them to plan their approach, which can lower surgery risks.
Comprehensive Tissue Differentiation
CT scans can tell different tissues apart. This is vital for finding problems like tumors or inflammation. Comprehensive tissue differentiation helps doctors diagnose more accurately.
By spotting different tissues, CT scans help find diseases early. Early detection is key for effective treatment and better patient results.
Accessibility and Widespread Availability
CT scanners are found in many hospitals worldwide. This widespread availability makes CT scans a common choice for diagnosis. They are more accessible than some other advanced imaging tools.
CT scans’ availability means patients get quick care without long waits or travel. This is a big plus for fair healthcare access.
Disadvantages of CT Scan: Risks and Limitations
CT scans are very useful in medical diagnosis but have some risks and limitations. It’s important to know these drawbacks to make sure we use them wisely in healthcare.
Ionizing Radiation Exposure Concerns
One big worry with CT scans is the radiation they use. They need more radiation than X-rays to show detailed images. This has raised concerns about long-term risks, like cancer.
But, the benefits of CT scans often outweigh the risks. This is true in emergencies or when diagnosing serious conditions. It’s key to only use them when needed and try to use less radiation, mainly for kids and young adults.
- The risk of radiation-induced cancer is a concern, mainly for children and young adults.
- Trying to lower radiation doses while keeping image quality is a goal.
- Looking into other imaging methods like MRI or ultrasound is considered when possible.
Contrast Medium Reactions and Contraindications
Using contrast media in CT scans can cause problems in some patients. These can range from mild allergic reactions to severe, life-threatening anaphylaxis. Also, some contrast agents are not safe for people with kidney disease or at risk of kidney problems.
We check if contrast media is really needed and look at the patient’s risk before using it. Patients with allergies or kidney issues need extra care and might need other imaging methods instead.
- Before the scan, we check kidney function and allergy history.
- People with severe kidney disease might need other imaging methods.
- It’s important to watch for any bad reactions during and after the scan.
Technical Limitations and Artifacts
Even with the latest technology, CT scans have limits and can have artifacts that affect image quality. These can include beam hardening, scatter, or motion artifacts that can hide important details or lead to wrong interpretations.
We try to reduce these problems by preparing patients well, teaching them to hold their breath, and using advanced algorithms. But, some patients might not get clear images because of artifacts.
Cost and Healthcare Resource Considerations
CT scans are expensive and use a lot of resources. The cost of buying and keeping scanners, plus the need for trained staff, adds up. This can be hard on healthcare systems, even more so in places with less resources.
We need to weigh the benefits of CT scans against their cost. Looking for cheaper alternatives when we can is important. Trying to make CT scans more efficient and reduce unnecessary use can help save money.
- High cost of CT scanners and maintenance.
- Need for specialized training for operators.
- Potential for overuse and unnecessary scans.
In conclusion, CT scans are very useful but have big downsides. Understanding these can help us use them better and reduce their risks.
Conclusion: Balancing Benefits and Risks of CT Imaging
CT scans are key in modern medicine, helping doctors diagnose and treat many conditions. They offer quick images, detailed 3D views, and can show different tissues clearly. This makes them very important for healthcare.
But, CT scans also have downsides like radiation exposure and reactions to contrast media. To use CT scans safely, doctors must weigh their benefits against the risks. This means choosing the right patients, using the least amount of radiation needed, and making sure the scan will help the patient.
Healthcare providers can make better choices by understanding the pros and cons of CT scans. As technology gets better, we might see CT scans that are safer and just as good at finding problems.
FAQ
What are the primary indications for a CT scan?
CT scans are used for many medical conditions. These include acute head trauma, stroke diagnosis, and cancer detection. They also help in diagnosing infections, evaluating vascular diseases, and assessing trauma.
How does CT scan technology work?
CT scans use X-rays and computer technology. They produce detailed images of the body’s internal structures.
What are the benefits of using CT scans in medical diagnosis?
CT scans are quick and provide high-resolution images. They help differentiate tissues and are widely available. This makes them a valuable tool for diagnosis.
What are the risks associated with CT scans?
CT scans expose patients to ionizing radiation. There’s also a risk of reactions to contrast mediums. Technical issues and artifacts can occur.
How are CT scans used in oncological applications?
CT scans help in identifying primary tumors and assessing metastatic disease. They evaluate lymph nodes, which is key for cancer detection and staging.
Can CT scans diagnose infections and inflammatory conditions?
Yes, CT scans can diagnose infections and inflammatory conditions. This includes abscesses, pneumonia, and musculoskeletal infections.
How are CT scans used in vascular disease evaluation?
CT scans detect and monitor aortic aneurysms and quantify arterial stenosis. They diagnose pulmonary embolism, aiding in vascular disease evaluation.
What is the role of CT scans in trauma assessment?
CT scans are critical in assessing abdominal and pelvic trauma. They evaluate thoracic and spinal injuries, helping to identify injury extent.
How are CT scans used in interventional procedures?
CT scans guide biopsy procedures and precision needle placement. They aid in pre-surgical planning, improving intervention accuracy.
What are the challenges in interpreting CT scans?
Interpreting CT scans requires radiologist expertise. Challenges include distinguishing between conditions and managing artifacts.
How can the risks associated with CT scans be minimized?
To minimize risks, reduce radiation exposure and use alternative imaging when possible. Carefully select patients for CT scans.
What are the advantages of CT scans over other imaging modalities?
CT scans offer rapid image acquisition and high-resolution imaging. They can visualize a wide range of tissues and structures.
References
- Dieckmeyer, M., et al. (2023). Computed Tomography of the Head: A Systematic Review. PMC (PubMed Central). https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10449676/



































