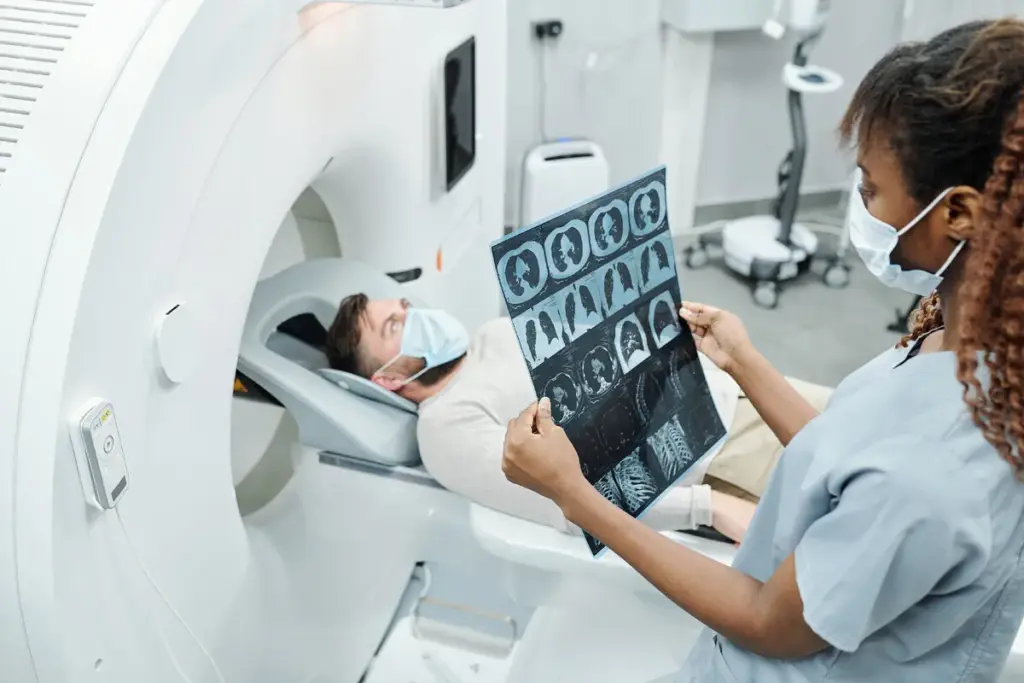
Early detection of lung cancer is key to successful treatment. PET scans are now a key tool for checking lung nodules. They help doctors figure out if these nodules are cancerous. Identifying a lung nodule early is vital. Learn how amazing technology provides a perfect and fast diagnosis for your peace of mind.
Studies have found that PET scans are very good at spotting cancerous pulmonary nodules. They have a high sensitivity of 94-96% and a specificity of 78-86%. This means PET scans can find most cancerous nodules accurately, with few false alarms.
Understanding the effectiveness of PET scans is essential for both doctors and patients. This knowledge helps in getting a clear diagnosis.
Key Takeaways
- PET scans are highly sensitive in detecting cancerous lung nodules.
- The specificity of PET scans ranges from 78-86%, indicating a relatively low rate of false positives.
- Recent meta-analyses support the effectiveness of PET scans in evaluating pulmonary nodules.
- Accurate diagnosis with PET scans can lead to timely treatment for lung cancer.
- Understanding the limitations of PET scans is important for both doctors and patients.
Understanding Lung Nodules
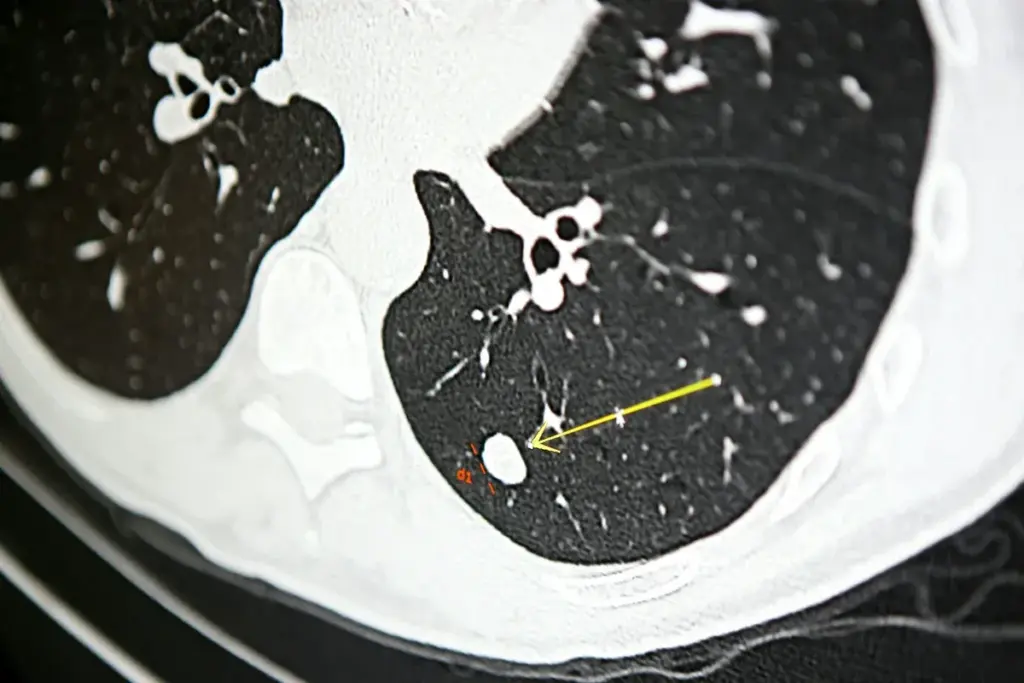
Lung nodules are abnormal growths found in the lung tissue. They are often seen during chest imaging. Knowing if they are benign or malignant is key to managing them.
What is a Lung Nodule?
A lung nodule is a small, rounded mass in the lung. It can be seen on X-rays, CT scans, or PET scans. These nodules are usually under 3 cm and can appear in one or both lungs.
Common Causes of Lung Nodules
Lung nodules can come from different sources:
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can cause nodules in the lungs.
- Inflammatory conditions: Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or sarcoidosis can lead to lung nodules.
- Benign tumors: Non-cancerous growths such as hamartomas or adenomas.
- Malignant tumors: Cancerous nodules, including primary lung cancer or metastases from other cancers.
Risk Factors for Malignant Nodules
Some factors make a lung nodule more likely to be cancerous:
- Smoking history: Smoking is a big risk factor for lung cancer.
- Age: The risk of cancer goes up with age, after 50.
- Family history: A family history of lung cancer or other cancers can increase risk.
- Exposure to carcinogens: Exposure to substances like asbestos or radon.
Knowing about these risk factors and causes is vital for managing lung nodules. Tests like PET scans are often used to figure out what they are.
The Basics of PET Scan Technology
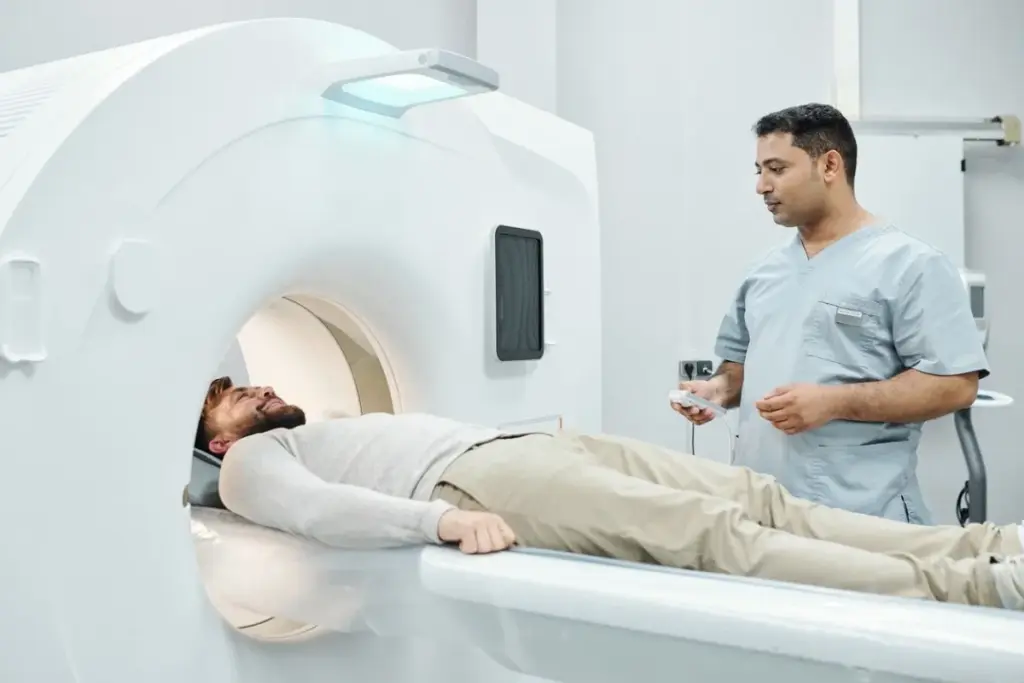
PET scan technology is all about finding metabolic changes in tissues. This is key for spotting cancerous lung nodules.
PET scans use a special sugar called Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) to see how active body tissues are. Cancer cells eat more FDG because they are more active. This makes them show up clearly on the scan.
How PET Scans Work
The scan starts with FDG being injected into the patient. As cells take in FDG, the PET scanner picks up the radiation. This creates detailed images of how active the body’s tissues are.
PET scans are special because they show how tissues work, not just what they look like. This is why they’re great for finding cancerous nodules.
FDG-PET/CT Explained
FDG-PET/CT combines PET scans with CT scans. This gives both how tissues work and their structure in one go. It makes finding lung nodules more accurate.
Combining PET and CT allows for precise localization of active tissues. This is key for diagnosing and understanding cancer.
Difference Between PET and Other Imaging Techniques
PET scans are different from CT or MRI scans. While CT and MRI show what tissues look like, PET scans show how active they are. This makes PET scans especially effective in detecting cancerous lung nodules.
Other scans might not tell the difference between harmless and cancerous nodules. PET scans can spot nodules that are very active, which means they’re likely cancer.
Accuracy of PET Scans in Detecting Cancerous Nodules
PET scans are very good at telling the difference between harmless and cancerous lung nodules. This is key for choosing the right treatment and easing patient worries.
Sensitivity Rates
PET scans can spot malignant lung nodules with a high success rate, from 94% to 96%. This means they can find 94 to 96 out of 100 cancerous nodules. Their skill comes from spotting the increased metabolic activity in cancerous tumors.
Specificity Rates
PET scans are also good at identifying harmless nodules, with a range of 78% to 86%. This means they can correctly say 78 to 86 out of 100 harmless nodules are not cancer. While not as high as their sensitivity, these rates are important for their overall accuracy.
Interpreting PET Scan Results
Understanding PET scan results needs a deep look at the scan’s data, like the standardized uptake value (SUV). A high SUV often means a tumor is likely. But, other factors like the patient’s history and the nodule’s details are also important for a correct diagnosis.
Doctors must watch out for false positives, which can happen with inflammation or infections. So, a detailed review of the scan results is needed to make sure the right treatment is chosen for the patient.
Limitations of PET Scans for Lung Nodule Evaluation
<SEP-14418_image_4>
PET scans are useful for checking lung nodules, but they have some limits. Knowing these limits helps doctors make better choices and give accurate results.
False Positive Results
PET scans can sometimes show cancer where there isn’t any. This is called a false positive result. It happens when something like an infection or inflammation makes a nodule look like cancer.
Infectious diseases can make this problem worse. In places where infections are common, PET scans might show false positives more often. This is because infections also make cells use more sugar, just like cancer does.
Reduced Specificity in Regions with Prevalent Infectious Diseases
In areas with lots of infections, PET scans aren’t as reliable. Studies show that in these places, the scans might only be right 40-66% of the time. This means more people might get extra tests or treatments that aren’t needed.
Size Limitations for Small Nodules
PET scans also struggle with small nodules. They can’t always tell if a nodule is small enough to be cancer. This is because the scans can’t see very small details well. So, small nodules might be misdiagnosed as cancer or not cancer.
Doctors need to know these limits to understand PET scan results. This helps them make the best choices for their patients.
Common Causes of False Positives in PET Scans
PET scans are great at finding cancer, but they can sometimes show false positives. False positives happen when a scan says there’s cancer when there isn’t. Knowing why this happens helps doctors give the right treatment.
Infectious Diseases
Infections can make PET scans show false positives. When the body fights an infection, it uses more glucose. This looks like cancer on a PET scan. Pneumonia, tuberculosis, and abscesses are common culprits.
Granulomatous Diseases
Granulomatous diseases, like sarcoidosis, can also cause false positives. These diseases cause inflammation, which increases glucose use. This makes it hard to tell if it’s cancer or not, as it affects many parts of the body.
Inflammatory Conditions
Inflammatory conditions, like rheumatoid arthritis, can also lead to false positives. Inflammation makes the body use more glucose, which PET scans pick up. It’s important to look at the whole picture when reading these scans.
In summary, PET scans are very useful for finding cancer, but it’s key to understand why they might show false positives. By looking at the patient’s overall health, doctors can make better choices.
The Role of PET Scans in Nodule Management
<SEP-14418_image_5>
PET scans are key in managing lung nodules. They help in the first check, keeping an eye on changes, and planning treatment.
Initial Assessment Protocol
PET scans check lung nodules’ activity. This tells doctors if a nodule might be cancerous or not.
Follow-up Monitoring Guidelines
For nodules not treated right away, PET scans track changes. They watch how active the nodule stays to see if it could turn cancerous.
Treatment Planning Applications
PET scans give important info for treatment plans. They show how far the disease has spread and what treatment is best.
|
Management Stage |
PET Scan Role |
Clinical Benefit |
|---|---|---|
|
Initial Assessment |
Determine metabolic activity |
Identify potentially malignant nodules |
|
Follow-up Monitoring |
Track changes in metabolic activity |
Assess risk of malignancy over time |
|
Treatment Planning |
Determine extent of disease |
Guide treatment strategy |
Clinical Impact of PET Scans on Treatment Decisions
PET scans have a big impact on how we treat lung nodules. They give detailed info about the nodules’ metabolism. This helps doctors make better choices for treatment.
Reduction in Nontherapeutic Resections
PET scans help cut down on surgeries that aren’t needed. Research shows they can reduce these surgeries by 17-20%. This is good because it lowers the risks of surgery and makes patients healthier.
Improved Staging Accuracy
PET scans also make cancer staging more accurate. Knowing the cancer’s stage is key to choosing the right treatment. PET scans help doctors tailor treatments to each patient’s needs.
Treatment Optimization
PET scans help doctors pick the best treatment. They show how active the nodules are metabolically. This helps decide if surgery, chemo, radiation, or a mix is best.
|
Clinical Benefit |
Description |
Impact |
|---|---|---|
|
Reduction in Nontherapeutic Resections |
Decrease in unnecessary surgeries due to accurate diagnosis |
17-20% reduction |
|
Improved Staging Accuracy |
Enhanced precision in determining cancer stage |
Better treatment planning |
|
Treatment Optimization |
Tailored treatment strategies based on nodule metabolism |
Improved patient outcomes |
In conclusion, PET scans have a big impact on treating lung nodules. They lead to better diagnoses, fewer surgeries, and more effective treatments. As medicine keeps improving, PET scans will play an even bigger role in lung nodule management.
Comparing PET Scans to Other Diagnostic Methods
<SEP-14418_image_6>
Many imaging techniques are used to diagnose lung nodules. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses. Knowing these differences helps choose the best diagnostic path.
CT Scans for Nodule Detection
CT scans are the top choice for finding lung nodules. They give clear images that spot small nodules and describe their details.
Advantages of CT scans include:
- High sensitivity for detecting small nodules
- Detailed information about nodule size, shape, and location
- Ability to monitor changes in nodule size over time
MRI Applications
MRI is not usually the first choice for lung nodule checks. But, it’s useful in certain cases.
MRI is useful for:
- Evaluating nodules in patients who cannot undergo CT scans with contrast
- Assessing mediastinal invasion or chest wall involvement
- Providing additional information in complex cases
Biopsy Procedures
Imaging like PET and CT scans give important clues. But, biopsies are the best way to confirm lung nodule diagnoses.
Types of biopsy procedures include:
- Needle biopsy (percutaneous)
- Bronchoscopic biopsy
- Surgical biopsy
Here’s a comparison of the diagnostic methods discussed:
|
Diagnostic Method |
Sensitivity |
Specificity |
Primary Use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
PET Scan |
High |
Moderate |
Metabolic activity assessment |
|
CT Scan |
Very High |
High |
Nodule detection and monitoring |
|
MRI |
Moderate |
High |
Soft tissue characterization |
|
Biopsy |
Very High |
Very High |
Definitive diagnosis |
When a Lung Nodule Requires Further Investigation Beyond PET
PET scans are key in checking lung nodules. But, some details might need more looking into. Size, how fast it grows, and the patient’s risk factors are important. They help decide if more tests are needed.
Size Thresholds for Concern
The size of a lung nodule matters a lot. Nodules bigger than 8-10 mm need a closer look. Nodules over 10 mm are more likely to be cancerous. So, they need more checking.
|
Nodule Size (mm) |
Risk of Malignancy |
Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
|
< 6 |
Low |
Monitoring |
|
6-10 |
Moderate |
PET Scan or Follow-up CT |
|
> 10 |
High |
Biopsy or Further Investigation |
Growth Patterns Indicating Malignancy
How fast a lung nodule grows is also important. Nodules that grow quickly or change size a lot might be cancer. Regular CT scans can track these changes.
Risk Factors Necessitating Additional Testing
Some things about a patient can raise the chance of cancer in a lung nodule. For example, smoking, being around harmful substances, or having a family history of lung cancer. In these cases, more tests than just PET scans might be needed.
For those at high risk, regular checks and aggressive tests are often advised. This could mean more CT scans, biopsies, or other tests.
The Patient Experience During a PET Scan for Lung Nodule Evaluation
When patients prepare for a PET scan to check lung nodules, knowing what to expect can ease their worries. A PET scan is a detailed test that shows how lung nodules work. It helps doctors figure out the best treatment.
Preparation Requirements
Before a PET scan, patients must follow certain steps to get good results. Fasting for 4-6 hours before the scan is key to avoid sugar messing with the test. They might also need to skip hard workouts and some medicines that could mess up the scan.
Here’s what you need to do:
- Avoid food and drink (except water) for 4-6 hours before the scan
- Don’t do hard exercise on the day of the scan
- Tell your doctor about all your medicines, including diabetes ones
- Take off jewelry and wear loose, comfy clothes
What to Expect During the Procedure
During the PET scan, you’ll lie on a table that moves into a big, ring-shaped scanner. The scan is painless and non-invasive, lasting about 30-60 minutes. You must stay very quiet to get clear pictures.
Many patients find the PET scan easy. They say the staff made them feel calm, and the scan was quicker than they thought. This is what many people say after their PET scans for lung nodules.
“The PET scan experience was more comfortable than I anticipated. The team explained everything clearly, making the process less intimidating.”
A patient undergoing PET scan evaluation
Post-Scan Care
After the scan, you can usually go back to your normal day unless your doctor says not to. It’s good to drink lots of water to get rid of the tracer. Some people might feel a bit tired or taste something metallic, but these feelings usually go away.
|
Post-Scan Care Instructions |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Hydration |
Drink plenty of water to help eliminate the tracer |
|
Activity Level |
Resume normal activities unless advised differently |
|
Monitoring |
Keep an eye out for any odd side effects and tell your doctor |
Familiarity with the PET scan process can help alleviate patient anxiety. Even though it might seem scary, it’s a key tool for doctors to diagnose and treat lung nodules.
Advanced PET Techniques for Improved Nodule Characterization
<SEP-14418_image_7>
Advanced PET techniques are changing how we look at lung nodules. These new methods help doctors get better at diagnosing and treating them. This is key for better patient care.
Dual-Time-Point Imaging
Dual-time-point imaging takes PET scans at two times after the radiotracer is given. It helps tell if a nodule is cancerous or not. Malignant nodules show more uptake on later scans, while benign ones might not change much.
Novel Radiotracers Beyond FDG
Even though FDG is common, scientists are looking at other radiotracers. Novel radiotracers like FLT and FES might give more detailed info about nodules.
Artificial Intelligence Integration in Image Analysis
Artificial intelligence (AI) is making PET scans better. AI helps measure radiotracer uptake and spot small changes. It also predicts if a nodule might be cancerous.
These new PET methods are big steps forward in lung nodule diagnosis. With dual-time-point imaging, new radiotracers, and AI, doctors can make more accurate diagnoses. This leads to better care for patients.
Cost and Insurance Considerations for PET Scans
Understanding the cost of PET scans is key for those diagnosed with lung nodules. The price can change a lot. This depends on where you are, who you see, and the technology used.
Average Costs in the United States
In the U.S., PET scans can cost between $1,000 and $5,000 or more. This price range varies with the scan’s complexity and the facility. For example, a PET/CT scan, which adds CT imaging, is usually pricier.
Insurance Coverage Criteria
Insurance for PET scans differs by provider. Most cover them for cancer patients or those suspected of having cancer. You’ll often need pre-approval and meet certain criteria, like nodule size or growth patterns.
It’s important to talk to your insurance about what’s covered and any costs you might face.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
PET scans might seem expensive at first. But they can save money in the long run. They help make accurate diagnoses and avoid unnecessary surgeries or treatments. This can cut down healthcare costs.
For instance, a PET scan might show a lung nodule is harmless. This could mean no biopsy or surgery. It saves money and reduces risks for the patient.
Multidisciplinary Approach to Lung Nodule Assessment
For lung nodules, a team effort is key. This team approach means patients get the best care. It brings together many medical experts.
Tumor Board Process
The tumor board is a big part of this team effort. It’s where doctors like radiologists and oncologists get together. They talk about patient cases and plan treatments.
“The tumor board brings together experts from different disciplines to provide a complete view of the patient’s condition, leading to more informed treatment decisions.”
Liv Hospital Oncologist
This teamwork makes diagnoses more accurate. It also leads to better treatment results. This is because many viewpoints are considered.
Integrating Multiple Diagnostic Modalities
Using many tests is important for lung nodule checks. Tests like PET scans and CT scans help. So do MRI and biopsies. They give a full picture of the nodule.
|
Diagnostic Modality |
Primary Use |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
PET Scan |
Assessing metabolic activity |
Helps identify cancerous nodules |
|
CT Scan |
Detailed structural imaging |
Provides precise measurements and characteristics of nodules |
|
Biopsy |
Tissue sampling |
Confirms diagnosis through histological examination |
Liv Hospital’s Approach to Lung Nodule Evaluation
Liv Hospital focuses on the patient first. They use a team of experts and the latest tech. This way, patients get care that’s both effective and tailored to them.
The hospital’s tumor board looks at tough cases often. They make sure treatments are based on the latest research and expert advice.
Conclusion: The Future of PET Scanning for Lung Nodule Evaluation
PET scanning has changed how we look at lung nodules in cancer care. It gives us key details for diagnosing and planning treatments. But, it’s not perfect, with some false positives and size limits.
New tech and methods in PET scanning are on the horizon. We’re talking about better imaging, new tracers, and AI in analyzing images. These could make PET scans even more accurate, helping patients more.
PET scans will keep being a big deal in checking lung nodules. Places like Liv Hospital show how working together can improve care. With these advancements, PET scans will play a bigger role in fighting cancer.
FAQ
What is a lung nodule?
A lung nodule is a small growth on the lung, usually under 3 centimeters. It can be harmless or cancerous. Often, it’s found by accident during tests for other reasons.
How accurate are PET scans in detecting cancerous lung nodules?
PET scans are very good at finding cancerous lung nodules, with a 94-96% success rate. But, they can also show false positives, with a 78-86% chance of this happening.
What are the common causes of false positives in PET scans?
False positives in PET scans can come from infections, diseases like tuberculosis, and inflammation. These conditions can make the scan show activity that looks like cancer.
Can a PET scan differentiate between benign and malignant thyroid nodules?
PET scans can spot thyroid nodules that might be cancerous by showing increased activity. However, to confirm findings, additional tests such as a biopsy may be necessary.
How do PET scans compare to CT scans in evaluating lung nodules?
PET scans show how active lung nodules are, while CT scans show their shape and size. PET scans are better at telling if a nodule is cancerous by looking at its activity.
What is the role of PET scans in managing lung nodules?
PET scans are key in checking, watching, and planning treatment for lung nodules. They help find cancerous nodules, track changes, and guide treatment plans.
Are PET scans covered by insurance for lung nodule evaluation?
Insurance for PET scans for lung nodules varies. Usually, it’s covered if there’s a high chance of cancer or if CT scans are unclear.
What are the limitations of PET scans in evaluating small lung nodules?
PET scans have trouble with very small lung nodules, under 8-10 mm. This is because they can miss small details and sometimes show false negatives.
How does Liv Hospital approach lung nodule evaluation?
Liv Hospital uses a team effort to check lung nodules. They utilize a combination of PET scans, CT scans, and biopsies to provide comprehensive care.
What is the significance of dual-time-point imaging in PET scans?
Dual-time-point imaging takes PET scans at two times after FDG injection. It can make PET scans more accurate by showing how FDG uptake changes over time, helping tell if a nodule is cancerous.
Can PET scans be used to monitor treatment response in lung cancer?
Yes, PET scans can track how lung cancer responds to treatment. They look at how the tumor’s activity changes. This helps doctors make better treatment choices and care for patients.
References
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Accuracy of PET in diagnosing lung nodules. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3186439/
- NCBI. PET/CT for lung nodule evaluation: clinical outcomes. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4315183/
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). PET scans and immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. https://www.cancer.gov/news-events/cancer-currents-blog/2023/pet-scans-immunotherapy-nsclc
- UpToDate. Diagnosis of lung cancer: clinical criteria and ancillary tests. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/diagnosis-of-lung-cancer-clinical-criteria-and-ancillary-tests
- News Medical. PET scan indications and limitations. https://www.news-medical.net/health/PET-Scan-Indications-and-Limitations.aspx