At Liv Hospital, we understand the importance of accurate diagnosis in neurological care. Neuro scans are key in finding brain issues like tumors, blood vessel problems, and stroke. They also help spot inflammation, injuries, and abnormal brain growth.
Choosing the right brain scan is vital for personalized care. We help our patients understand what scans show. We also guide them on whether they or a loved one should get a neurological scan.
Key Takeaways
- Brain scans diagnose various brain-related conditions, including tumors and vascular malformations.
- Different types of brain scans are used depending on the suspected condition.
- A neurological scan can help identify the cause of neurological symptoms.
- Liv Hospital provides complete guidance on choosing the right brain scan.
- Accurate diagnosis through brain scans is key for effective treatment planning.
The Science Behind Brain Imaging: What Brain Scans Actually Show
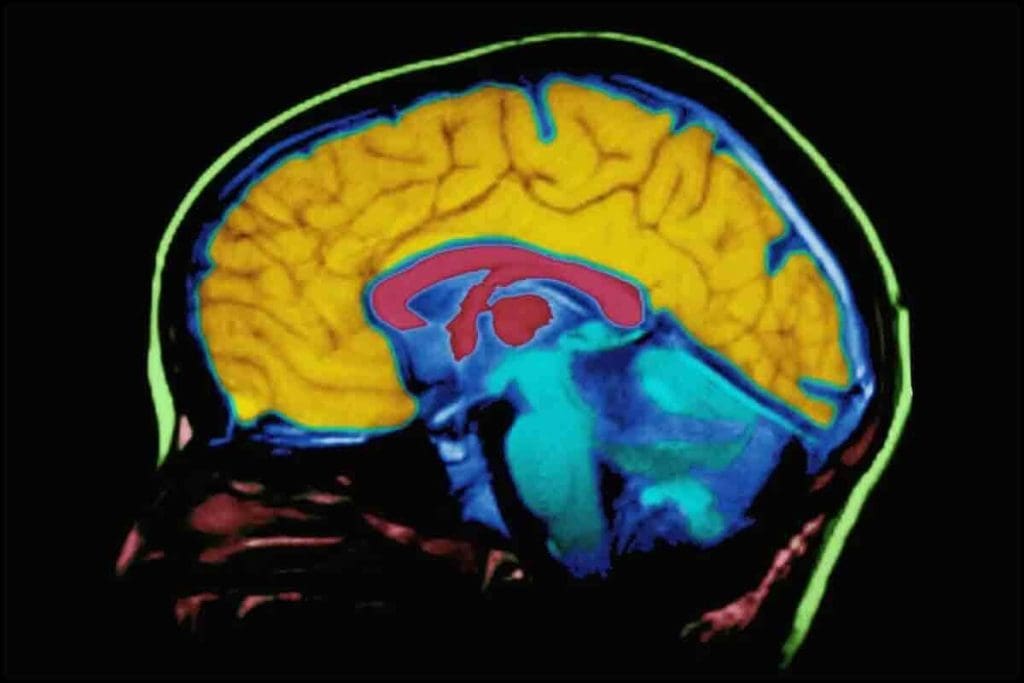
Brain imaging has changed neurology a lot. It lets doctors see the brain’s structure and function clearly. We use different brain imaging methods to find and treat brain problems. New tech has made diagnosing better.
How Neurologists Visualize Brain Structure and Function
Doctors use brain scans to see the brain’s details. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans show the brain’s shape. Functional MRI (fMRI) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans show how the brain works. These images help find problems and plan treatments.
A study found MRI scans can spot up to 30% of brain tumors early. This shows how important these scans are for catching problems early.
Recent Advances in Neurological Imaging Technology
Recently, brain imaging tech has gotten a lot better. This helps us find and treat brain issues better. Some big improvements include:
- High-resolution imaging: Now we can see small problems and changes in the brain better.
- Functional imaging: fMRI and PET scans show how the brain works and reacts.
- Advanced image analysis: New software helps understand complex brain scan data.
These changes have made diagnosing more accurate and treatments better. As brain imaging tech keeps getting better, we’ll see even more precise ways to help patients.
Common Types of Neuro Scans and Their Diagnostic Capabilities
Neuro scans have different uses, so picking the right one is important. They help diagnose and treat brain issues. Knowing the types helps doctors care for patients better.
Structural vs. Functional Brain Imaging Techniques
Neuro scans fall into two main groups: structural and functional. Structural scans show the brain’s layout. Functional scans reveal how the brain works.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) scans are for structural views. They spot problems like tumors or injuries.
PET (Positron Emission Tomography) and SPECT (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography) scans look at brain activity. They help find issues like epilepsy and track neurodegenerative diseases.
Selecting the Appropriate Scan for Different Neurological Conditions
Choosing the right scan depends on the condition.
| Condition | Recommended Scan | Diagnostic Capability |
| Tumors, Injuries | MRI | Detailed structural imaging |
| Stroke, Trauma | CT | Rapid evaluation of brain abnormalities |
| Epilepsy, Seizure Disorders | EEG, PET | Measuring electrical activity and brain function |
Healthcare professionals need to know about neuro scans to make good choices. The right scan, whether for structure or function, gives important insights into the brain.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Detailed Brain Structure Assessment
MRI technology lets us see the brain in amazing detail. It helps find many neurological problems. This method is safe and key to checking how the brain works and looks.
We use MRI scans to look at the brain’s shape and find issues that other methods miss. MRI’s clear images are key for spotting tumors, injuries, and swelling.
Standard MRI vs. Functional MRI (fMRI)
There are two main MRI scans for brain checks: Standard MRI and Functional MRI (fMRI). Standard MRI shows detailed brain pictures, helping spot shape problems. fMRI, on the other hand, tracks brain activity by watching blood flow changes. It shows how the brain works.
fMRI is great for seeing which brain parts do what. For example, it can show which areas handle speech, movement, or memory. This info is vital for planning brain surgeries and understanding brain functions.
| Feature | Standard MRI | Functional MRI (fMRI) |
| Purpose | Anatomical imaging | Functional imaging |
| Application | Diagnosing structural abnormalities | Mapping brain activity |
| Information Provided | Detailed images of brain structures | Insights into brain function and activity |
What MRI Brain Scans Reveal About Tumors, Injuries, and Swelling
MRI brain scans are top-notch for finding and understanding tumors, injuries, and swelling. They give vital details about size, location, and type. This info is key for making treatment plans.
For instance, MRI can tell different brain tumors apart, like gliomas or meningiomas. It also checks injury extent and swelling levels.
Computed Tomography (CT): Rapid Evaluation of Brain Abnormalities
CT scans are key in emergency neurology. They quickly check for brain problems. This makes them very important in caring for the brain.
CT scans are fast and easy to get. This is great for urgent cases like stroke or brain injury. They can spot problems quickly.
When CT Scans Are Preferred Over Other Imaging Methods
There are times when CT scans are better than other methods. These include:
- Emergency situations where speed is critical
- Patients with metal implants or pacemakers, for whom Man RI might not be suitable
- Cases where detailed bone structure imaging is required
The American College of Radiology says, “CT scans are often the first choice in acute neurological emergencies. This is because they are quick and easy to get.”
Emergency Applications in Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injury
For stroke or brain injury, quick diagnosis is key. CT scans help by showing what’s happening right away.
| Condition | CT Scan Findings | Clinical Implication |
| Ischemic Stroke | Early signs of ischemia or normal | Guides thrombolytic therapy decision |
| Hemorrhagic Stroke | Presence of blood in the rain parenchyma or spaces | Contraindicates thrombolytic therapy; may require surgical intervention |
| Traumatic Brain Injury | Skull fractures, hemorrhage, or edema | Assesses need for surgical intervention or monitoring |
A study in the Journal of Neuroimaging says, “CT is the main imaging tool in acute stroke. This is because it’s everywhere and fast.”
We use CT scans to quickly and accurately diagnose brain issues. This is vital in emergency brain care. The info from CT scans helps doctors decide the best treatment.
Metabolic Brain Imaging: PET and SPECT Scans
Understanding brain metabolism is key to diagnosing and treating neurological disorders. PET and SPECT scans are vital in this process. They help us see brain activity and blood flow, giving insights into various neurological conditions.
Visualizing Brain Activity and Blood Flow
PET and SPECT scans are advanced tools for assessing brain function. Unlike MRI and CT scans, they focus on brain metabolism. This lets us see how the brain works in detail.
PET scans use a radioactive tracer that active brain cells absorb. The tracer emits positrons, which the PET scanner detects. This creates a map of brain activity. It’s very useful for diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease, where some brain areas may show less activity.
SPECT scans also use a radioactive tracer but detect single photons. They help evaluate blood flow to the brain. This can show areas with less blood flow, which might indicate stroke or dementia.
Applications in Dementia, Alzheimer’s, and Cognitive Decline
PET and SPECT scans are key in diagnosing and managing dementia and Alzheimer’s. They help us understand cognitive decline by looking at brain activity and blood flow.
“The use of PET and SPECT scans in diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias has revolutionized our understanding of these conditions and has opened up new avenues for research and treatment.”
” An expert opinion
A comparison of PET and SPECT scans in various neurological conditions is provided in the table below:
| Imaging Technique | Primary Use | Key Benefits |
| PET Scan | Assessing brain activity | Early detection of Alzheimer’s, tumor identification |
| SPECT Scan | Evaluating blood flow | Diagnosing stroke, assessing dementia |
PET and SPECT scans are essential for diagnosing and managing neurological disorders. They give insights into brain metabolism and function. This helps healthcare providers make accurate diagnoses and develop effective treatment plans.
EEG and QEEG: Measuring Real-Time Brain Electrical Activity
Electroencephalography (EEG) and Quantitative EEG (QEEG) are key tools for checking the brain’s electrical activity. They are very important in neurology, helping with epilepsy and seizure disorders.
Monitoring Brain Function for Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders
EEG is a main tool for finding and monitoring epilepsy. It shows the brain’s electrical activity. This helps doctors spot odd patterns that might mean seizures.
“EEG is the cornerstone in the diagnosis of epilepsy,” it shows brain problems directly.
To use an EEG, electrodes are put on the scalp to catch brain signals. These signals are then looked at for any odd patterns. For epilepsy, an EEG helps figure out the type of seizure and what treatment to use.
Quantitative EEG Applications in Treatment Monitoring
QEEG goes beyond EEG by analyzing brain activity in numbers. This makes it easier to see how well treatments work for brain problems. QEEG helps doctors change treatments based on real data.
In epilepsy, QEEG watches how brain activity changes over time. This shows how well a treatment is working. This info is key to better patient care.
“The use of QEEG in clinical practice has opened new avenues for personalized medicine in neurology, enabling more precise and effective treatment strategies.”
EEG and QEEG help doctors give better care to patients with epilepsy and other seizure disorders. These tools are key to improving neurological care.
Who Should Get a Neurological Scan? Medical Indications and Referrals
Deciding to get a neurological scan depends on certain medical signs and symptoms. These scans are key in finding and treating brain problems.
Common Symptoms That Warrant Brain Imaging
Some symptoms mean you might need a neurological scan. These include:
- Headaches: If you have headaches often or they’re very bad, it could mean something serious needs to be checked.
- Seizures: If you have seizures, a scan is needed to find out why.
- Changes in Vision or Cognitive Function: If your vision gets blurry, you forget things, or it’s hard to focus, a scan might be needed.
Specific Conditions Requiring Different Types of Brain Scans
Each brain condition needs a specific scan for the right diagnosis. For example:
| Condition | Recommended Scan |
| Stroke | CT Scan or MRI |
| Tumors | MRI or PET Scan |
| Epilepsy | EEG or MRI |
When Preventive Brain Screening Is (and Isn’t) Recommended
Preventive brain scans aren’t usually needed for people who don’t have symptoms. But, if you have a family history of brain problems or are at high risk, it might be a good idea. For those with past brain issues, regular scans can help.
“Regular neurological check-ups can help in early detection and prevention of neurological disorders.”
Neurological Association Guidelines
In summary, knowing who needs a neurological scan involves looking at medical signs and symptoms. By picking the right people for scans, we can better diagnose and treat brain issues.
Where to Get a Brain Scan: Finding the Right Facility
Finding the right place for a brain scan is key to a correct diagnosis and treatment plan. The facility you choose can greatly affect the scan’s quality and your care.
Hospital vs. Outpatient Imaging Centers
Choosing between a hospital and an outpatient imaging center is a big decision for a neuro scan. Hospitals are better for complex cases and emergencies. They have many specialists and equipment ready.
Outpatient centers, though, offer a calmer setting and quicker service. They’re great for routine brain scanning tests. But, for serious issues or emergencies, a hospital is safer.
What to Look for in a Neurological Imaging Facility
When picking a neurological imaging facility, look at a few things. Make sure it has modern, well-kept equipment and skilled staff. Also, check if it’s accredited and has a good reputation.
- Check if the facility is accredited by a recognized accrediting organization.
- Look for reviews and ask for referrals from healthcare professionals or friends who have undergone similar procedures.
- Ensure that the facility uses up-to-date technology and follows best practices for patient care and safety.
Insurance Coverage and Cost Considerations for Brain Scans
It’s important to know about your insurance coverage and the costs of a brain scan. Prices vary, and insurance plans differ in what they cover.
Before the scan, talk to your insurance about what’s covered and what you’ll pay. Also, compare prices at different places. But, be careful of very low prices that might mean lower quality care.
Conclusion: The Evolving Role of Brain Imaging in Neurological Care
Brain imaging has changed how we care for the brain, making diagnosis and treatment better. We’ve looked at MRI, CT, PET, and EEG scans. Each one gives us special views of the brain’s structure and how it works.
Brain scans are key in finding and treating brain problems. They help spot issues like tumors, injuries, dementia, and Alzheimer’s. With the right scan, doctors can create better treatment plans. This helps patients live better lives.
As brain imaging tech gets better, we’ll see even more precise diagnoses and treatments. Brain scans are vital in today’s medicine. Their role in helping the brain will keep growing.
Knowing about brain imaging helps patients and doctors make better choices. This teamwork leads to better health for everyone.
FAQ
What is a brain scan, and how does it work?
A brain scan is a test that shows the brain’s structure and function. It uses MRI or CT scans. We use these scans to find and track neurological conditions.
What do brain scans show?
Brain scans can show many things. They can find tumors, injuries, and changes in brain activity. We use them to diagnose and manage conditions like stroke and dementia.
Who should get a neurological scan?
We suggest scans for people with symptoms like seizures or dizziness. Also, those with a history of neurological issues should consider it. Your doctor will decide if you need a scan.
What is the difference between a CT scan and an MRI?
CT scans use X-rays to quickly check for brain problems. MRI scans use magnetic fields for detailed images. We often use CT scans in emergencies. MRI scans are better for finding tumors and multiple sclerosis.
What is functional MRI (fMRI), and how is it used?
Functional MRI (fMRI) tracks brain activity by looking at blood flow changes. We use it to see how different parts of the brain work. This is important for understanding movement and speech.
Can brain scans diagnose dementia and Alzheimer’s disease?
Yes, PET and SPECT scans can help diagnose dementia and Alzheimer’s. They show brain activity and blood flow. We also use them to see how the disease is progressing and how treatments are working.
How do I prepare for a brain scan?
Preparation for a brain scan depends on the type. You might need to remove metal objects or avoid certain medicines. Your doctor or imaging center will tell you what to do.
Where can I get a brain scan?
You can get a brain scan at hospitals or outpatient imaging centers. Choose a place with skilled staff and modern equipment.
Will my insurance cover the cost of a brain scan?
Insurance coverage for brain scans varies. Check with your provider to see what’s covered and what you might have to pay out of pocket.
How long does it take to get the results of a brain scan?
The time to get scan results varies. It depends on the scan type and the facility. We usually provide results within a few hours or days. Your doctor will talk to you about them.
Are there any risks associated with brain scans?
Most brain scans are safe. But some might involve risks like radiation or allergic reactions. We take steps to keep you safe during the scan.
References
- Riahi, F. (2024). Comparison of PET/CT and PET/MRI in central nervous system tumors. Frontiers in Neuroscience.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11411248/




































