We know how critical accurate diagnosis is in healthcare. A CT scan of neck soft tissue with contrast offers detailed views of the neck’s soft tissues and more. It’s a key tool for spotting neck issues.
This tool is great for checking neck masses, infections, and vascular problems. It makes soft tissue and blood vessels stand out, helping doctors plan better treatments.
Key Takeaways
- Detailed visualization of soft tissues, blood vessels, and bones is achieved through contrast-enhanced CT scans.
- Patient preparation includes not eating solid foods for 4 hours before the injection.
- A creatinine level check is required for patients over 50 years of age.
- Patients on metformin must stop taking it for 48 hours after the CT scan.
- The CT scan table has a patient weight limit of 400 pounds.
What Is a CT Scan of Neck Soft Tissue with Contrast?

Contrast-enhanced CT scans have changed how we diagnose and treat neck soft tissue issues. A CT scan of the neck’s soft tissues with contrast uses x-rays and a contrast agent. It creates detailed images of the neck’s soft tissues, lymph nodes, and nearby areas.
Definition and Basic Principles
A CT (Computed Tomography) scan is a non-invasive test that uses x-rays to show the body’s inside. It’s great for looking at the neck’s soft tissues. It helps find problems like tumors, infections, or inflammation. The scan works by moving an x-ray emitter and detector around the neck.
How Contrast Enhancement Works
Contrast enhancement uses a contrast agent, usually iodine-based, given through an IV. This agent makes blood vessels, organs, and tissues stand out. It does this by absorbing x-rays differently than the body’s tissues, highlighting important areas.
Types of Contrast Agents Used in Neck Imaging
There are many contrast agents, but iodine-based ones are most common for CT scans. They’re divided by osmolarity (high, low, or iso-osmolar) and chemical structure. For neck scans, low osmolar agents are safer and have fewer side effects.
The main advantages of contrast agents in neck CT scans are:
- They make vascular structures clearer
- They help see soft tissue problems better
- They improve finding lymph node issues
Understanding how contrast-enhanced CT scans work and the contrast agents used helps us see their value. They’re key in diagnosing neck soft tissue conditions.
Key Clinical Applications of Neck Soft Tissue CT
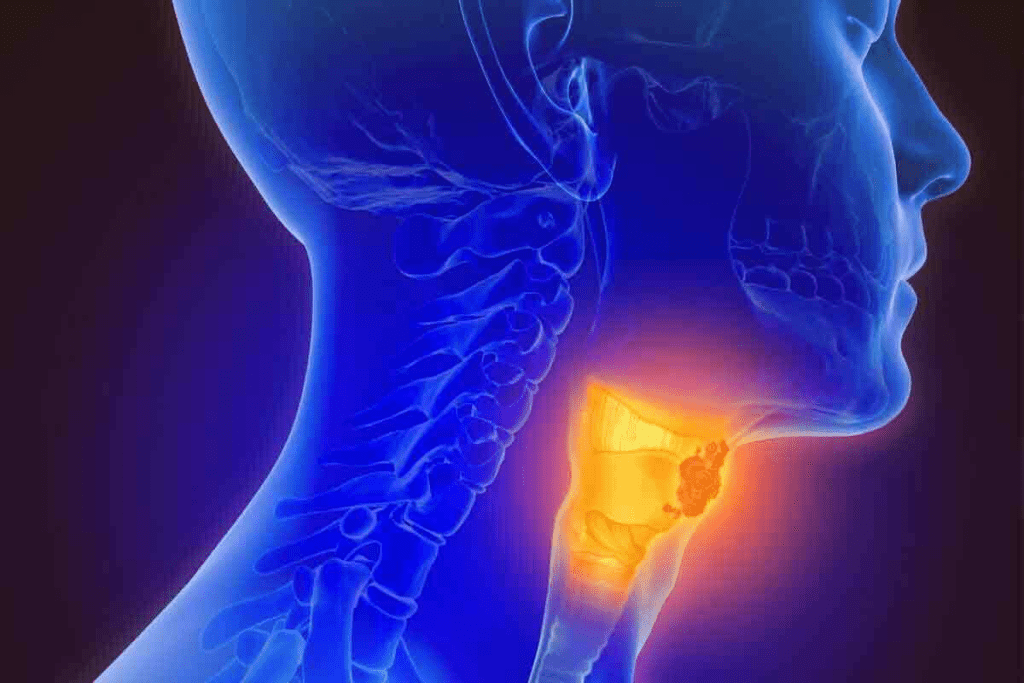
Neck soft tissue CT scans are key for diagnosing many neck conditions. They help doctors see and treat different problems well.
Evaluation of Neck Masses and Abnormalities
These scans are great for checking neck masses and oddities. They show clear images of cysts, tumors, or abscesses. Doctors can then plan the best treatment.
“The use of CT scans in evaluating neck masses has significantly improved diagnostic accuracy and guided treatment decisions,” says a leading radiologist. “It’s a critical tool in our diagnostic arsenal.”
Detection of Inflammatory Conditions
CT scans are also good for spotting neck inflammation. They show swelling, abscesses, or cellulitis. Spotting these early helps start the right treatment fast.
Infection Assessment and Spread Visualization
When infections are suspected, CT scans are key. They show how far the infection has spread. This helps doctors decide if surgery or other treatments are needed.
Vascular Structure Examination
CT scans also check neck blood vessels. They find problems like stenosis, aneurysms, or thrombosis. This helps doctors understand symptoms and plan treatments.
In summary, neck soft tissue CT scans are very useful. They help with many things, from checking masses to looking at blood vessels. Their detailed images are vital in today’s medicine.
CT Scan of Neck Soft Tissue with Contrast: Detailed Procedure
The CT scan for neck soft tissue with contrast has several steps. Knowing these steps can make you feel less anxious.
Patient Positioning and Setup
You’ll lie on the CT scanner table, usually on your back. The radiology team will adjust your position. It’s important to stay very quiet during the scan.
Contrast Administration Process
The contrast agent is given through a vein in your arm. The exact process may vary based on the test. You might feel a pinch or a warm feeling during this.
Breath-Hold Instructions and Scanning Techniques
You’ll be asked to hold your breath during the scan. This helps get clear images. The scan itself is quick, lasting just a few minutes.
Duration and What to Expect During the Scan
The whole process, from start to finish, takes about 15 to 30 minutes. You can talk to the team through an intercom. It’s key to listen to their instructions for the best results.
After the scan, the contrast agent is removed by your kidneys and urine. You can usually go back to your normal activities right away, unless your doctor says not to.
Comprehensive Evaluation of Neck Lymph Nodes
Contrast-enhanced CT scans give us detailed views of neck lymph nodes. This method helps us see the size, shape, and details of lymph nodes. It’s key for spotting and treating conditions like cancer.
Normal vs. Abnormal Lymph Node Appearance
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped parts of our immune system. On a CT scan, normal ones look like small, oval shapes with smooth edges. But, abnormal ones might be bigger, not round, or have a strange texture.
- Normal lymph nodes are usually less than 10 mm in short-axis diameter.
- Abnormal lymph nodes may be larger, with a short-axis diameter exceeding 10 mm.
- Other signs of abnormality include necrosis, calcification, or irregular enhancement.
Lymph Node Mapping and Classification
It’s important to map and classify lymph nodes accurately. This helps in cancer staging and planning treatments. We use the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) system for this.
- Lymph nodes are classified into different levels (I-VI) based on their location in the neck.
- Each level corresponds to a specific group of lymph nodes that drain particular areas of the head and neck.
Cancer Detection and Staging Through Lymph Node Assessment
Checking lymph nodes is key in finding and staging cancer. If lymph nodes are big or look off, it might mean cancer or spread.
Key factors in cancer detection through lymph node assessment include:
- Size and shape of the lymph nodes.
- Presence of necrosis or calcification within the lymph nodes.
- Pattern of enhancement on contrast-enhanced CT scans.
Follow-up Protocols for Abnormal Findings
When a CT scan shows something odd in the neck lymph nodes, we need to keep an eye on it. This helps us adjust treatment plans as needed.
Follow-up protocols may include:
- Repeat CT scans at regular intervals to monitor changes in lymph node size or characteristics.
- Additional imaging modalities, such as PET or MRI to further evaluate the extent of disease.
- Biopsy or fine-needle aspiration to obtain a definitive diagnosis.
Essential Preparation Steps for Your Neck CT Scan
To make sure your neck CT scan goes smoothly, follow some key steps. Getting ready for a medical test can seem tough. But with the right help, you’ll feel more ready and confident.
Pre-Scan Fasting Requirements
One important step is to follow fasting rules before your scan. You might need to not eat for a few hours. It’s very important to listen to your doctor’s fasting instructions, as they can change based on your situation.
Medication Considerations and Adjustments
Some medicines might need to be changed or stopped before your scan. Tell your doctor about all the medicines you’re taking, including vitamins and over-the-counter drugs. This helps your doctor give you the best advice on managing your meds.
Metal and Jewelry Removal Guidelines
You’ll need to take off any metal items, like jewelry or glasses, from your neck. Leaving extra things at home makes getting ready easier. Our team will tell you exactly what to remove.
Communicating Allergies to Your Care Team
If you’re allergic to anything, like contrast agents or iodine, tell your team. We’ll make sure you’re safe during the scan. Our team is ready for different situations and wants to give you the best care.
By following these steps, you can help make your CT scan safe and successful. If you have any questions or worries, talk to your healthcare provider.
CT With Contrast vs. Without Contrast for Neck Imaging
Choosing between a contrast-enhanced CT scan and a non-contrast CT scan for neck imaging depends on several factors. These include the clinical indication and the diagnostic information needed.
Contrast enhancement is key for seeing blood vessels, soft tissues, and certain lesions in the neck. It helps in telling apart different types of tissues and abnormalities. This makes it easier to spot conditions like tumors or abscesses.
Necessity of Contrast Enhancement
Contrast enhancement is needed when we want to look at the vascular structure or find lesions that are hard to see without contrast. For example, in cases of suspected vascular problems or when checking how big a tumor is, contrast-enhanced CT scans give valuable insights.
- Evaluation of vascular structures
- Identification of lesions or tumors
- Assessment of inflammatory conditions
Indications for Non-Contrast Neck CT
Non-contrast CT scans are best when we mainly want to look at calcifications, foreign bodies, or certain types of trauma. They’re also good for patients who can’t have contrast due to allergies or kidney problems.
Common indications for non-contrast neck CT include:
- Assessment of calcifications or foreign bodies
- Trauma evaluation
- Patients with contraindications to contrast
Comparing Image Quality and Diagnostic Value
Contrast-enhanced CT scans usually have better image quality and diagnostic value for soft tissue abnormalities or vascular structures. But non-contrast CT scans have their own benefits, like detecting calcifications or looking at bony structures.
Combined Protocols: Pre and Post-Contrast Imaging
In some cases, we use a combined protocol with both pre-contrast and post-contrast imaging. This method gives a full view by first looking at the area without contrast and then highlighting specific structures or abnormalities with contrast.
We opt for combined protocols when a detailed assessment is needed. This is true for complex cases of cancer or when we need to see how far an infection has spread.
Technical Aspects of Neck Soft Tissue CT Imaging
We use the latest technology in CT scans to get clear images of neck soft tissue. The technical details of these scans are key to making accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
Multiphase Scanning Techniques
Multiphase scanning takes pictures at different times after contrast is given. This method helps see how contrast moves through the body. It gives us important info on neck lesions.
Benefits of Multiphase Scanning:
- Enhanced diagnostic accuracy
- Better characterization of lesions
- Improved assessment of vascular structures
Thin-Slice Reconstructions for Detailed Analysis
Thin-slice reconstructions are vital for a detailed look at the neck’s anatomy. By making images into thin slices, doctors can spot small details and abnormalities.
The importance of thin-slice reconstructions lies in their ability to provide high-resolution images, which are critical for preoperative planning and accurate diagnosis.
Advanced Visualization Methods
Advanced visualization techniques, like 3D reconstructions and multi-planar reformations, boost CT scan’s diagnostic power. These methods give a deeper understanding of the neck’s anatomy and any problems.
Radiation Dose Optimization Strategies
It’s important to keep radiation doses low while keeping image quality high. We adjust scanner settings and use dose modulation techniques to do this.
| Strategy | Description | Benefit |
| Dose Modulation | Adjusts radiation dose based on patient size and anatomy | Reduces unnecessary exposure |
| Low-Dose Protocols | Uses lower radiation doses for certain exams | Minimizes radiation risk |
| Iterative Reconstruction | Improves image quality at lower doses | Enhances diagnostic confidence |
Potential Risks and Managing Side Effects
It’s important to know the risks and side effects of CT scans with contrast for neck soft tissue. These scans are generally safe but can have risks. We need to be aware of these and take steps to reduce them.
Common Contrast Reactions and Their Management
Contrast agents in CT scans can cause reactions in some patients. These reactions can vary from mild to severe.
- Mild reactions might include nausea, vomiting, and itching. These are usually not serious and can be managed with basic care.
- Moderate reactions can have symptoms like hives and facial swelling. These need medical help.
- Severe reactions are rare but can be life-threatening. They need immediate medical care.
Identifying and Addressing Allergic Responses
Allergic reactions to contrast agents can be unpredictable. It’s key for healthcare providers to spot these reactions early and act fast.
- Keep a close eye on patients during and after the scan for any signs of an allergic reaction.
- Have emergency meds and equipment ready.
- Teach patients about the signs of allergic reactions and the need to report them right away.
Radiation Exposure Considerations
CT scans expose patients to ionizing radiation, which can increase cancer risk. But, the benefits of a CT scan often outweigh this risk, mainly when diagnosing serious conditions.
Ways to reduce radiation exposure include:
- Using the least amount of radiation needed.
- Optimizing scanning methods.
- Limiting the scan to only the necessary area.
Post-Procedure Care and Monitoring
After a CT scan with contrast, patients should be watched for any bad reactions. Giving clear instructions after the procedure is also key.
Important parts of post-procedure care include:
- Watching for signs of contrast reaction.
- Making sure the patient is okay before sending them home.
- Providing contact info for any concerns or symptoms after discharge.
By understanding and managing the risks of CT scans of neck soft tissue with contrast, we can make the diagnostic process safer and more effective for patients.
Conclusion: The Critical Role of Contrast-Enhanced CT in Neck Pathology Diagnosis
Contrast-enhanced CT scans are key in diagnosing and treating neck pathologies. They show detailed images of soft tissues, lymph nodes, and blood vessels. This helps doctors accurately diagnose and plan treatments for cancers and vascular diseases.
We’ve looked at how CT scans of the neck with contrast work. We’ve covered their uses, technical aspects, and possible risks. The contrast agents make important structures clearer, helping doctors give better care.
The role of CT scans with contrast in diagnosing neck pathologies is huge. They give doctors the info they need to make treatment plans. As technology improves, so will the role of these scans in healthcare.
FAQ
What is a CT scan of neck soft tissue with contrast?
A CT scan of the neck’s soft tissues with contrast uses X-rays and a special dye. It creates detailed images of the neck’s soft parts, lymph nodes, and nearby areas.
Why is contrast enhancement necessary for neck imaging?
Contrast enhancement helps see blood vessels, soft tissues, and some lesions in the neck. It’s key for accurate diagnosis and treatment plans.
What are the clinical applications of neck soft tissue CT scans?
These scans help check neck masses and abnormalities. They detect inflammation, track infection spread, and look at blood vessels.
How do I prepare for a CT scan of neck soft tissue with contrast?
Before the scan, follow fasting rules and adjust your meds if needed. Remove metal and jewelry and tell the team about any allergies.
What is the difference between a CT scan with contrast and without contrast for neck imaging?
In contrast, scans show blood vessels and soft tissues. Without contrast, they’re better for seeing calcifications or foreign bodies.
What are the possible risks and side effects of a CT scan of neck soft tissue with contrast?
Risks include allergic reactions to the dye, radiation exposure, and other issues. These can be managed with careful care and monitoring.
How are lymph nodes evaluated using a CT scan of neck soft tissue with contrast?
The scan gives detailed lymph node images. Doctors can then check their size, shape, and details. This helps in cancer detection and staging.
What are the technical aspects of neck soft tissue CT imaging?
Technical details include using different scanning phases, thin slices, and advanced views. They also focus on keeping radiation doses low.
How long does a CT scan of neck soft tissue with contrast take?
The scan time varies. It usually needs specific steps, like holding your breath, to get clear images.
What is the role of contrast agents in neck CT scans?
Contrast agents, like iodine-based dyes, are given through an IV. They make blood vessels, organs, and tissues in the neck more visible.
References:
- UCSF Radiology. (2025). Intravenous CT & X-ray Contrast Guidelines. https://radiology.ucsf.edu/patient-care/patient-safety/contrast/iodinated
- Bouchareb, Y., et al. (2024). Technological Advances in SPECT and SPECT/CT Imaging. Diagnostics, 14(7), 1645. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11241697/
- Nakatani, M. (2022). Radiation Exposure and Protection in Computed Tomography Fluoroscopy-Guided Procedures. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 198(1), 15-24. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9527104/


































