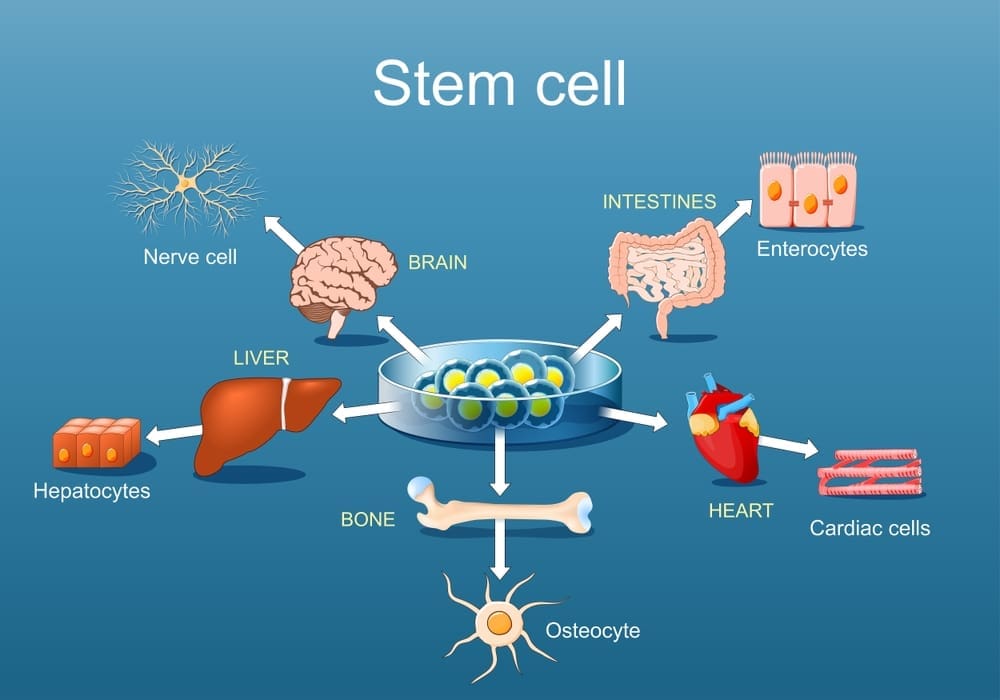
The human body has stem cells, a special type of cell. They are key in development and repair. The National Institutes of Health says stem cells can renew themselves and change into different cell types.
These cells are found in almost all body tissues. They help keep tissues healthy and fix damaged ones.
Key Takeaways
- Stem cells can renew themselves and turn into different cell types.
- They are found in almost all body tissues.
- Stem cells are vital for keeping tissues healthy and fixing damaged ones.
- Learning about stem cell therapy can help find new treatments for diseases.
- Stem cells are a key part of the body’s repair and development.
Understanding Stem Cells: The Body’s Master Cells
At the heart of human biology are stem cells, known for their amazing ability to heal. These cells can turn into many different types of cells in our body. They act like an internal repair system.
Stem cells can self-renew and differentiate into specialized cells. This makes them key for keeping tissues healthy and fixing damaged ones.
Unique Properties of Stem Cells
Stem cells stand out because of their special traits. They can also turn into different cell types when needed.
- Ability to self-renew
- Capacity to differentiate into multiple cell types
- Potential for long-term division
Self-Renewal and Differentiation Capabilities
Stem cells can keep their numbers up through self-renewal. They can also turn into specialized cells like nerve or muscle cells. This is vital for cellular regeneration and regenerative medicine.
| Property | Description |
| Self-Renewal | Ability to divide and renew themselves |
| Differentiation | Capacity to become specialized cell types |
| Long-Term Division | Potential to divide over extended periods |
Experts say stem cells are vital for understanding how we develop and for finding new treatments. This shows how important they are in both science and medicine.
What Are Stem Cells? A Comprehensive Definition
Stem cells can renew themselves and turn into many different cell types. This makes them very important for stem cell research and could help in new treatments.
Stem cells are special because of their power. Embryonic stem cells can become any cell in the body. On the other hand, adult stem cells can only turn into a few types of cells.
The Science Behind Cellular Potency
Cellular potency is about how well a cell can change into different types. It’s all about the genes and how they work. This lets stem cells stay the same or turn into special cells.
- Pluripotent stem cells can become all three germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm.
- Multipotent stem cells can turn into several cell types, but only within certain groups.
- Unipotent stem cells can only turn into one type of cell.
How Stem Cells Differ From Other Cell Types
Stem cells are different from other cells because they can renew themselves and change into many types. Unlike other cells, they can adapt to different needs. This is why they’re so useful for stem cell therapy and fixing damaged tissues.
Induced pluripotent stem cells are made from adult cells. They’re a good choice because they avoid some of the ethical issues of embryonic stem cell research.
Bone Marrow: The Primary Stem Cell Factory
The human body’s bone marrow is a key factory for making stem cells. These cells are vital for many medical treatments. It produces hematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells, which help treat different diseases.
Hematopoietic Stem Cells Production
Hematopoietic stem cells create blood cells like red and white blood cells, and platelets. They are essential for stem cell transplants. These transplants help treat blood disorders like leukemia and lymphoma.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Bone Marrow
Mesenchymal stem cells can turn into different cell types, like bone and muscle cells. Their ability to change makes them useful for stem cell therapy. This is important in regenerative medicine.
Bone Marrow Transplants and Their Significance
Bone marrow transplants save lives for many with blood cancers and other diseases. The process replaces bad stem cells with good ones. This lets the body make healthy blood cells again. Groups like the Canadian Blood Services help by matching donors with those needing transplants.
In summary, bone marrow is key for making stem cells used in medicine. It produces hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cells. These are vital for stem cell therapies. Bone marrow transplants are lifesaving, showing how important bone marrow is.
Adipose Tissue as a Rich Source of Stem Cells
Adipose tissue is now seen as a valuable source of stem cells for medical treatments. It has a lot of stem cells, making it great for regenerative medicine.
Fat-Derived Stem Cells: Extraction and Properties
Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) come from fat tissue through liposuction. This method removes fat, which is then processed to get the stem cells. ADSCs can turn into different cell types, like fat cells and bone cells. This makes them useful for many treatments.
Advantages of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells
ADSCs are easy to get and are plentiful, unlike other sources like bone marrow. They also have immunomodulatory properties, which helps them not be rejected by the body. Their role in repairing and regenerating tissues is a key area of research.
| Characteristics | Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) | Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells (BMSCs) |
| Source | Adipose Tissue | Bone Marrow |
| Ease of Extraction | High | Moderate |
| Differentiative Potentia | High | High |
| Immunomodulatory Properties | Yes | Yes |
Current Research and Applications
Research on ADSCs is looking into treating many conditions, like osteoarthritis, cardiovascular diseases, and tissue injuries. Clinical trials are underway to check if ADSC-based treatments are safe and work well. Their ability to help regenerate tissues and their use in personalized medicine make them exciting for research.
Stem Cells in the Brain: Neurogenesis and Neural Stem Cells
Recent studies have found stem cells in the brain. This challenges the idea that the adult brain can’t make new neurons. This discovery is key to understanding brain growth and the chance for neural repair.
Locations of Neural Stem Cells
Neural stem cells are mainly in two brain areas: the subventricular zone (SVZ) and the hippocampus. The SVZ is near the ventricles, and the hippocampus is key for memory. These spots can make new neurons all our lives, a process called neurogenesis.
Implications for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neural stem cells in the brain could help treat neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Scientists are exploring stem cell therapy to use these cells’ healing power. They hope to fix or replace damaged brain tissue, stopping or reversing disease.
Learning about neural stem cells and their role in neurogenesis is a growing field. As research continues, it could lead to new treatments that use the brain’s own repair abilities.
Umbilical Cord Blood: A Valuable Stem Cell Source
Umbilical cord blood is a key source of stem cells. It offers new ways to treat medical conditions. The blood left in the umbilical cord after birth is full of stem cells. These stem cells can turn into different types of blood cells.
Collection and Storage Procedures
Getting cord blood is easy and doesn’t hurt. It’s done by clamping and cutting the umbilical cord after birth. Then, blood is taken from the cord. To keep the stem cells safe, the blood is frozen at very low temperatures.
Clinical Applications of Cord Blood Stem Cells
Cord blood stem cells help treat blood disorders like leukemia and lymphoma. Scientists are also exploring their use in treating cerebral palsy and type 1 diabetes. This could lead to new treatments in regenerative medicine.
Public vs. Private Banking Considerations
Parents can choose to store their baby’s cord blood in public or private banks. Public banks make the blood available to anyone. Private banks keep it for the family’s use. The choice depends on the family’s medical history and personal wishes.
| Banking Type | Cost | Accessibility |
| Public Banking | Free | Available for anyone |
| Private Banking | Initial fee + annual storage | Reserved for family’s use |
Skin and Hair Follicles: Accessible Stem Cell Reservoirs
Skin and hair follicles are more than just outer parts of our body. They contain stem cells that are key for our health and could help in new treatments. These stem cells are important for healing wounds, making new skin, and improving looks.
Epidermal Stem Cells and Skin Regeneration
Epidermal stem cells are vital for keeping our skin healthy. They help replace the outer skin layer constantly. These cells live in special places in the skin and hair follicles, ready to grow and change when needed.
These stem cells do many things for our skin:
- They fix damaged skin by turning into different cell types.
- They keep our skin’s barrier strong.
- They help slow down skin aging.
Hair Follicle Stem Cells and Their Potential
Hair follicle stem cells are found in the skin too. They live in the hair follicle’s bulge area. These cells are key for growing new hair and can turn into different skin cells.
Potential uses of these stem cells include:
- Helping with skin problems through regenerative medicine.
- Improving wound healing with tissue engineering.
- Creating new hair growth treatments.
Applications in Wound Healing and Aesthetics
Stem cells in skin and hair follicles are great for healing wounds and improving looks. Scientists are studying how to use these cells for better treatments.
For example, epidermal stem cells can make skin for burns or severe injuries. Hair follicle stem cells might help with hair loss and better skin texture.
In summary, the stem cells in skin and hair follicles are very useful. They offer new ways to help our health and beauty, making them exciting for future research.
Embryonic Stem Cells vs. Adult Stem Cells
It’s important to know the differences between embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells. These differences help us move forward in stem cell research and therapy. Each type has its own uses, benefits, and ethical issues.
Ethical Considerations in Embryonic Stem Cell Research
Embryonic stem cell research is a topic of big debate. This is because these cells come from embryos, which are very young. People disagree on whether it’s right to use embryos for research.
On the other hand, adult stem cells come from grown-ups. They don’t raise the same ethical questions as embryonic stem cells.
Scientific Advantages and Limitations of Each Type
Embryonic stem cells can turn into any cell type in the body. This makes them very useful for research and treatments. But, they can sometimes grow into tumors, which is a big problem.
Adult stem cells are safer and more acceptable from an ethical standpoint. But, they can’t change into as many types of cells as embryonic stem cells. They might also be harder to find and grow.
Regulatory Framework in the United States
In the United States, there are rules for stem cell research. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) sets some of these rules. The NIH funds research using certain types of stem cells, like those from embryos not needed for reproduction.
Researchers must follow these rules to get funding and do their work legally.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells: The Revolutionary Alternative
Scientists have found a way to turn adult cells into a special kind called induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). This is a big deal in stem cell biology. It lets researchers make these cells without using embryonic stem cells, which solves some big ethical problems.
The Process of Cellular Reprogramming
Reprogramming adult cells into pluripotent ones is a cool process. It involves adding special genes to cells like skin or blood cells.
Advantages Over Traditional Stem Cell Sources
iPSCs have some great benefits. They can come from a patient’s own cells, which means less chance of rejection. Also, they can be made in big numbers, which is good for treatments.
Current Research Breakthroughs
Studies are showing iPSCs can help with many diseases. For example, they can fix damaged heart tissue in animals. They’re also being looked at for making personalized treatments and disease models.
Stem Cell Therapy: Applications and Success Rates
Stem cell therapy is a new hope for many medical conditions. It’s a big step in regenerative medicine. As research grows, more treatments are getting approved.
Stem cell therapy covers a wide range. It includes FDA-approved treatments and experimental therapies in trials.
FDA-Approved Treatments vs. Experimental Therapies
FDA-approved treatments have been tested well. They are safe and work. For example, they help with some blood disorders. Experimental therapies are being tested for many diseases and injuries.
Common Conditions Treated with Stem Cells
Stem cell therapy helps with many conditions. These include:
- Blood disorders like leukemia and lymphoma
- Orthopedic conditions such as osteoarthritis
- Autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis
- Cardiovascular diseases
More research is needed to find new uses for stem cells.
Cost Considerations and Insurance Coverage
The cost of stem cell therapy varies. It depends on the treatment, condition, and location. Insurance coverage also varies. Some plans cover FDA-approved treatments, but not all.
Patients should talk to their doctors and insurance about costs and coverage. This helps understand what’s available.
Conclusion: The Future of Stem Cell Research and Therapy
The future of stem cell research is very promising. It could lead to new ways to understand human biology and treat diseases. As scientists learn more about stem cells, we might see big advances in medicine.
Stem cell therapy could change medicine a lot. It might help people with diseases that were thought to be untreatable. This could bring new hope to many patients.
Stem cell research is moving forward fast. We can expect to see new treatments and better care for patients. Scientists are working hard to understand stem cells better and find new ways to use them.
As regenerative medicine grows, we’ll see new uses for stem cell therapy. This could lead to even more ways to help people. The future looks bright for stem cell research and therapy.
FAQ
What is the future of stem cell research and therapy?
The future looks bright for stem cell research and therapy. We might see new treatments for diseases. We’ll learn more about stem cells and how they work. And, we could see big steps in regenerative medicine.
Are there any FDA-approved stem cell therapies?
Yes, there are some FDA-approved treatments. These include stem cell transplants for blood disorders and cancers. There are also some experimental treatments in trials
Can stem cells be used for cosmetic applications?
Yes, stem cells from fat are being looked at for beauty treatments. They might help with skin and hair.
What is the role of bone marrow in stem cell production?
Bone marrow is key for making blood cells and other types of cells. It has stem cells that can turn into bone, cartilage, and fat cells.
How are stem cells extracted from adipose tissue?
First, we take fat through liposuction. Then, we break it down and spin it to get the stem cells. These cells are then grown in a lab.
What are the applications of stem cell therapy?
Stem cell therapy can help with blood disorders, some cancers, and degenerative diseases. It also has a role in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
What is induced pluripotent stem cell therapy?
This therapy turns adult cells into a special state. It’s like a reset button. This way, we can use these cells for treatments without needing embryonic stem cells.
What is the difference between embryonic and adult stem cells?
Embryonic stem cells can turn into any cell type. Adult stem cells can only turn into certain types of cells.
Where are stem cells found in the body?
You can find stem cells in many places. This includes bone marrow, liver, fat, brain, skin, and hair follicles. Each place has its own special role.
What are stem cells?
Stem cells are the body’s master cells. They can grow and change into different cell types. This helps the body fix itself.























