At Liv Hospital, we know how vital it is to watch over breast health. This is true, even for benign tumors like fibroadenomas. While these tumors are usually safe, there are rare cases where they can turn malignant.
We know that the chance of a benign tumor becoming cancerous is a worry for many. Our doctors stress the need for regular check-ups and catching problems early. This helps manage breast health well.
Understanding the risks of benign breast tumors and how they can turn cancerous helps us treat them better. At Liv Hospital, we offer full care and keep a close eye on our patients. This way, we aim for the best results for them.
Key Takeaways
- Fibroadenomas are generally considered benign tumors.
- Rare instances of malignant transformation can occur.
- Regular monitoring is key for early detection.
- Comprehensive care is vital for managing breast health.
- Liv Hospital provides ongoing monitoring and treatment.
Understanding Benign Breast Tumors
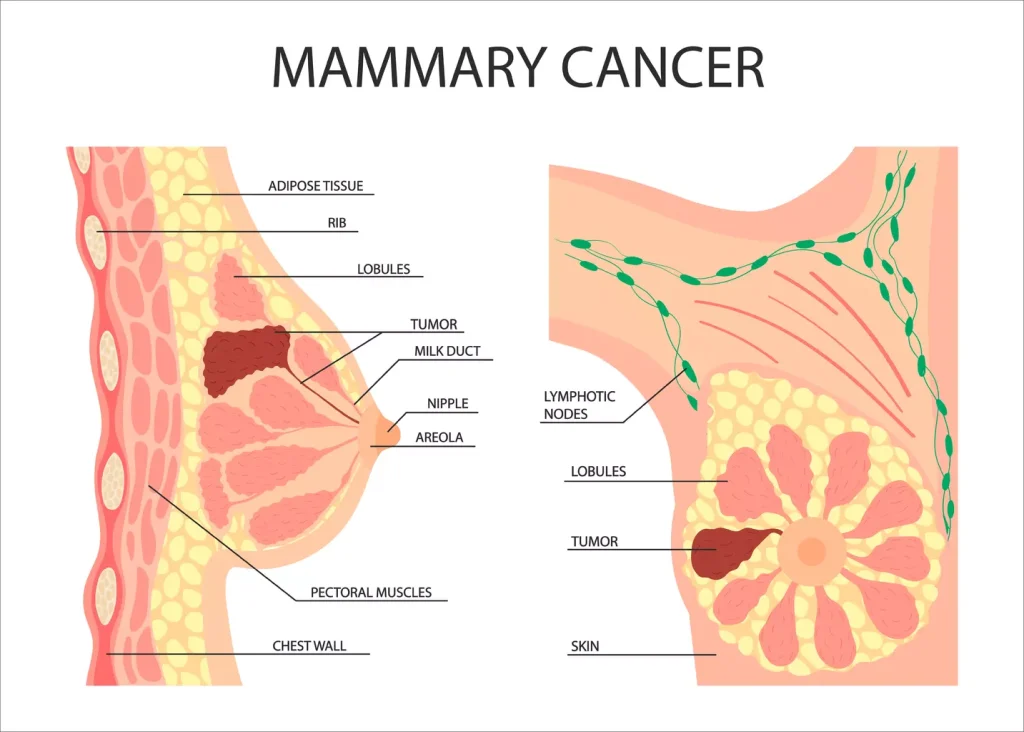
Benign breast tumors are a common worry for many women. Knowing what they are can help ease anxiety and ensure the right care. We’ll look into what benign breast tumors are, their traits, and the most common types.
Definition and Characteristics
Benign breast tumors are non-cancerous growths in the breast tissue. They don’t spread or invade other tissues. Though harmless, they can cause discomfort or worry.
These tumors can be solid or fluid-filled. Their size can vary, from small to several centimeters. Some stay the same, while others grow or change.
Common Types of Benign Breast Tumors
There are several types of benign breast tumors, each with its own features. Fibroadenomas are common and solid and mobile. They often appear in younger women and feel firm and rubbery.
Breast cysts are also common and fluid-filled. They can be simple or complex. Breast cysts can change size and may hurt, mostly before menstruation.
Knowing about these common benign breast tumors is key for diagnosis and care. While they’re usually not a worry, watching them and sometimes treating them is advised.
Fibroadenomas: The Most Common Benign Breast Tumor
Fibroadenomas are the most common benign breast tumors, mainly found in younger women. They are firm, smooth, and moveable. This makes them easy to spot compared to other breast lumps.
Structure and Appearance
Fibroadenomas are solid, non-cancerous tumors that can grow in size. They mix glandular and fibrous tissues, making them firm. On scans, they show up as clear, round shapes.
Doctors say fibroadenomas are common in women of childbearing age. They are often a relief for those worried about breast cancer.
Who Is at Risk for Fibroadenomas
Fibroadenomas mostly affect younger women, in their 20s and 30s. Hormones seem to play a part in their growth, as they can grow during hormonal changes like pregnancy. Though their cause is not fully known, they are not linked to breast cancer.
Diagnosis Methods
Doctors use a few ways to diagnose fibroadenomas. Ultrasound is often used because it can tell fibroadenomas apart from other lumps. Sometimes, a biopsy is needed to confirm the diagnosis and check for cancer.
Being told you have a breast tumor can be scary. But fibroadenomas are usually benign and don’t often turn cancerous. Regular checks and accurate diagnosis help manage these tumors well.
Breast Cysts: Fluid-Filled Sacs
Fluid-filled sacs, or breast cysts, are common in women. They are fluid-filled sacs in the breast tissue. Many women worry about them. We’ll look at how they form, their traits, and the types of cysts.
Formation and Characteristics
Breast cysts happen when glands and ducts in the breast get bigger and fill with fluid. Hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle often cause this. These cysts can be tender or painful, mostly before menstruation.
Characteristics of Breast Cysts: They are usually not cancerous, can be one or many, and differ in size. Some women feel mild discomfort, while others have severe pain.
Simple vs. Complex Cysts
Breast cysts are divided into simple and complex based on ultrasound. Simple cysts are just fluid and have a smooth wall. Complex cysts have solid parts or a thick wall.
| Cyst Type | Characteristics | Cancer Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Cysts | Fluid-filled, smooth wall | Generally not associated with increased cancer risk |
| Complex Cysts | Contain solid components or thick wall | May require further evaluation due to a slightly higher risk of malignancy |
Women with breast cysts often worry if they can turn cancerous. Simple cysts usually don’t raise cancer risk. But, complex cysts might need more checking.
Knowing about breast cysts is key to handling breast health worries. We’ll look at more benign breast conditions next.
Other Types of Benign Breast Conditions
There are many conditions that can affect the breast, aside from the well-known tumors. It’s important for women to know about these to stay healthy.
Intraductal Papillomas
Intraductal papillomas are small, non-cancerous tumors in the milk ducts. They are usually under 2 cm and can cause nipple discharge. This discharge might be bloody, clear, or sticky.
These growths are often found near the nipple but can also appear in other parts of the breast. While they are not cancerous, they can slightly increase the risk of breast cancer.
- Typically present with nipple discharge
- Can be associated with a palpable lump
- Diagnosed through imaging and biopsy
Sclerosing Adenosis
Sclerosing adenosis can look like cancer on mammograms. It involves the growth of small breast lobules. This can cause distortion that may look concerning on imaging studies.
Even though sclerosing adenosis is benign, it’s important to tell it apart from cancer. This is done through thorough diagnostic evaluation, including biopsy.
Key characteristics include:
- Often appears as a suspicious lesion on mammography
- May require biopsy for definitive diagnosis
- Not associated with an increased risk of breast cancer
Radial Scars
Radial scars are benign lesions that can look like cancer on imaging. They are usually small and can be seen during mammography.
Radial scars are not linked to an increased risk of breast cancer. But, their look can mean more tests are needed to rule out cancer.
- Appear as architectural distortion on mammograms
- May require surgical excision for diagnosis
- Typically benign, but can be associated with other high-risk lesions
Knowing about these benign breast conditions is key for accurate diagnosis and care. Even though they are not cancerous, some may need more checks to keep the breast healthy.
Can a Benign Tumor Turn Cancerous? Understanding Malignant Transformation
The change from a benign tumor to a malignant one is a complex topic. We will look into the biological changes that happen during this transformation. We will also talk about how likely it is for this to occur.
The Process of Malignant Transformation
Malignant transformation is when normal cells or benign tumor cells become like cancer cells. This happens through genetic and epigenetic changes. These changes lead to uncontrolled growth and the ability to spread to other tissues.
Many factors can cause a benign tumor to become malignant. These include genetic predispositions, environmental factors, and hormonal influences. For example, some genetic mutations can raise the risk of a benign tumor becoming malignant. Knowing these factors is key to managing benign tumors.
Statistical Likelihood
The chance of a benign tumor becoming cancerous varies by tumor type. For example, fibroadenomas, a common benign breast tumor, rarely become malignant. On the other hand, some types of atypical hyperplasia have a higher risk.
Research shows that the risk of cancer in benign breast lesions is generally low. But, it’s important to get accurate diagnoses and regular check-ups. This helps catch any signs of cancer early.
By understanding how a benign tumor can turn malignant and the likelihood of this happening, we can make better choices. This is true for both patients and healthcare providers when dealing with benign breast tumors.
How Fast Can Breast Lumps Appear and Change
Breast lumps can change quickly or slowly. It’s important to watch for any changes. They can be caused by hormones, benign tumors, or other reasons.
Typical Growth Patterns
Breast lumps grow at different rates. For example, fibroadenomas, which are common benign tumors, grow slowly. Some lumps stay the same size or even get smaller.
Knowing how lumps grow can help spot problems early. Here are some important points:
- Slow-growing lumps: These are often benign and may not need treatment right away.
- Rapidly growing lumps: These could be serious and need more investigation.
- Stable lumps: It’s best to keep an eye on lumps that don’t change.
| Growth Pattern | Possible Causes | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Slow Growth | Benign tumors like fibroadenomas | Regular monitoring |
| Rapid Growth | Potential malignancy or cysts | Medical evaluation and possibly biopsy |
| No Change | Stable benign conditions | Continued observation |
Warning Signs of Rapid Changes
Knowing the signs of quick changes in breast lumps is key. Look out for:
- Increase in size: A noticeable growth in a short time.
- Change in shape or texture: Becoming irregular or hard.
- Pain or discomfort: New or worsening pain with the lump.
- Skin changes: Dimpling, redness, or other skin changes over the lump.
If you see any of these signs, see a healthcare professional right away. They can evaluate and advise you.
Risk Factors for Malignant Transformation
Several factors can turn a benign breast tumor into cancer. These include genetics, hormones, and the environment. Knowing these factors helps us spot who might be at higher risk.
Genetic Predispositions
Genetics play a big role in the risk of a benign tumor turning cancerous. If you have a family history of breast cancer, you’re at higher risk. Certain genes, like BRCA1 and BRCA2, also increase this risk.
Genetic tests can find these genes. If you have a family history of breast cancer, getting tested is a good idea. It helps with early monitoring and care.
Hormonal Influences
Hormones also affect the risk of a tumor turning cancerous. Estrogen and progesterone can make breast tissue grow, which might lead to tumors. Things like early puberty, late menopause, and hormone therapy can raise your risk.
- Early menarche (before age 12)
- Late menopause (after age 55)
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- Use of oral contraceptives
Knowing how hormones work can help us understand your risk better. This helps us plan how to watch your tumor more closely.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors also play a part. Radiation, like from X-rays, is a big risk, mainly if you got it when you were young. Drinking alcohol and being overweight also raise your risk.
“Exposure to radiation, specially at a young age, is a known risk factor for breast cancer. Minimizing radiation exposure and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are key to reducing risk.”
By knowing and dealing with these risk factors, we can keep an eye on benign tumors. This helps lower the chance of them becoming cancerous.
Diagnostic Approaches for Breast Tumors
Healthcare professionals use many ways to find out if a breast tumor is benign or malignant. Knowing this is key to picking the right treatment.
Clinical Examination
The first step is a clinical exam. A doctor checks the tumor by touch and sight.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging is next. It includes mammograms, ultrasound, and MRI. These methods give clear pictures of the breast tissue.
Biopsy Procedures
Biopsy takes a tumor sample for lab tests. There are fine-needle and core needle biopsies.
Genetic Testing
Genetic tests look for cancer-causing genes. This helps figure out risk and treatment plans.
| Diagnostic Approach | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Examination | Initial assessment through palpation and visual examination | Non-invasive, quick assessment |
| Imaging Techniques | Includes mammography, ultrasound, and MRI | Provides detailed images of breast tissue |
| Biopsy Procedures | Involves taking a tissue sample for pathological examination | Definitive diagnosis of tumor nature |
| Genetic Testing | Identifies genetic mutations predisposing to breast cancer | Assesses risk, guides treatment planning |
To sum up, finding out about breast tumors needs a few steps. These include clinical exams, imaging, biopsies, and genetic tests. Knowing about these methods helps patients understand their journey better.
Monitoring and Management Strategies
Managing benign breast tumors involves regular screening, considering tumor removal, and creating personalized care plans. At Liv Hospital, we focus on a multi-faceted approach for the best patient outcomes.
Regular Screening Protocols
Regular screening is key in managing benign breast tumors. We suggest annual mammograms and ultrasounds for those with a history of benign tumors or risk factors. This helps catch any changes early, allowing for quick action if needed.
Screening Frequency Guidelines:
| Risk Category | Recommended Screening Frequency |
|---|---|
| Low Risk | Every 2-3 years |
| Moderate Risk | Annually |
| High Risk | Every 6-12 months |
When to Consider Removal
Not every benign breast tumor needs to be removed. But, some may require surgery. This includes tumors that are big, growing, or causing pain, or those with unusual features on scans or biopsies. We talk to each patient about the risks and benefits of removal to decide the best option.
Liv Hospital’s Approach to Tumor Monitoring
At Liv Hospital, our tumor monitoring is focused on the patient. We use the latest imaging and work closely with patients to create personalized plans. Our aim is to reassure and support while catching any changes quickly.
We combine advanced medical care with caring support to help patients make informed health choices. Regular check-ups and open talks are part of our monitoring plan.
Treatment Options for Benign Breast Tumors
Treatment for benign breast tumors depends on the tumor type and what the patient wants. We will look at the different ways to treat these tumors. This ensures patients get the best care for their needs.
Watchful Waiting
Many women start with watchful waiting for benign breast tumors. This means regular checks and scans to see if the tumor grows or changes. Watchful waiting is often suggested for small tumors that don’t cause pain.
Surgical Interventions
If the tumor is big, hurts, or looks suspicious, surgery might be needed. Surgery can give a clear diagnosis and ease symptoms. The choice to have surgery is a big decision, made after talking it over with a doctor.
- Lumpectomy: Removing the tumor and some tissue around it.
- Excisional biopsy: Taking out the tumor for a diagnosis.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
For some benign tumors, less invasive methods are available. These include:
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the tumor to shrink it.
- Vacuum-assisted biopsy: A device that removes the tumor.
These methods usually mean less recovery time and fewer side effects.
Post-Treatment Monitoring
After treatment, keeping an eye on things is key. Follow-up visits and scans are important. They help catch any new problems early. Each person’s care plan is based on their treatment and health.
Dealing with benign breast tumors can be scary. We promise to give full care and support during treatment.
Conclusion: Managing Concerns About Breast Tumors
Understanding benign breast tumors and their risks is key. At Liv Hospital, we help patients every step of the way. We offer expert care and keep a close eye on their health.
Dealing with breast tumors needs a full plan. This includes regular checks, quick diagnosis, and the right treatment. Knowing the risks and acting early can ease worries and help patients make smart choices.
Our team at Liv Hospital is dedicated to top-notch healthcare. We offer full support to international patients. We focus on each patient’s needs, giving them the care and advice they need.
We aim to help patients feel confident about their breast tumor concerns. Our goal is to create a caring space. Here, patients can get the help they need to tackle their health worries.
Can a benign tumor in the breast turn cancerous?
Benign breast tumors are not cancerous. But, there’s a small chance they could turn cancerous. We look at the changes that can happen and how likely it is.
How fast can breast lumps appear?
Breast lumps can grow at different rates. We talk about how they usually grow and when you should see a doctor.
Can fibroadenomas turn into cancer?
Fibroadenomas are usually not precancerous. But, knowing more about them can help ease worries.
Can breast cysts become cancerous?
Simple breast cysts are not linked to cancer risk. But, complex cysts might need more checks. We explain the difference between simple and complex cysts.
What are the risk factors for malignant transformation in benign breast tumors?
Genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors can increase the risk. Knowing these can help spot higher risk patients.
How are breast tumors diagnosed?
Accurate diagnosis is key. We cover how doctors use exams, imaging, biopsies, and genetic tests to diagnose.
What are the treatment options for benign breast tumors?
Treatment choices depend on the tumor type and patient wishes. We talk about options like watching, surgery, and less invasive methods.
How are benign breast tumors monitored?
Keeping an eye on benign tumors is important. We discuss regular checks and when to consider removing the tumor.
Can intraductal papillomas become cancerous?
Intraductal papillomas are usually benign but raise cancer risk. We explore their characteristics and importance.
What is the likelihood of a benign breast tumor becoming malignant?
The chance of a benign tumor turning cancerous varies. It depends on the tumor type and individual risk. We discuss the transformation process and risks.




































