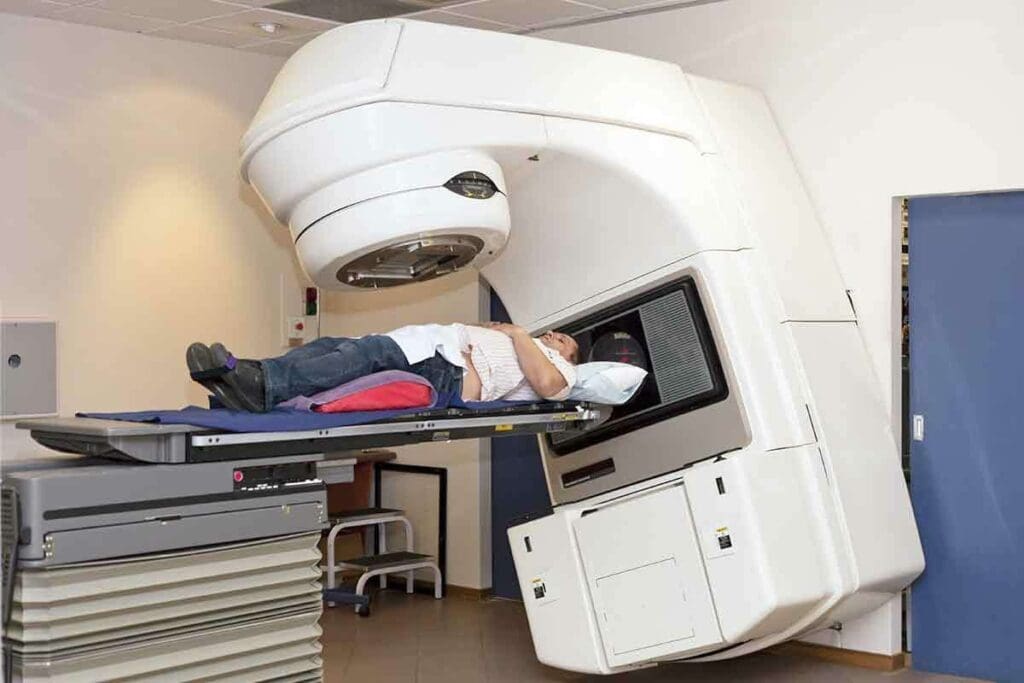
Knowing how often you get beam radiation therapy is key for cancer patients. At Liv Hospital, patients get expert advice on radiation therapy and learn what to expect during treatment.
Most patients get external radiation treatments every day, five days a week. This goes on for 2 to 10 weeks. How long it lasts depends on the cancer type and stage.
Liv Hospital’s top experts use the latest tech to hit tumors right on target. This ensures patients get the top care possible.
Key Takeaways
- Beam radiation therapy is a common cancer treatment.
- Treatment frequency is typically once daily, five days a week.
- Duration varies from 2 to 10 weeks, depending on cancer type and stage.
- Advanced technologies are used to target tumors effectively.
- Liv Hospital provides patient-focused expertise and care.
Understanding Beam Radiation Therapy
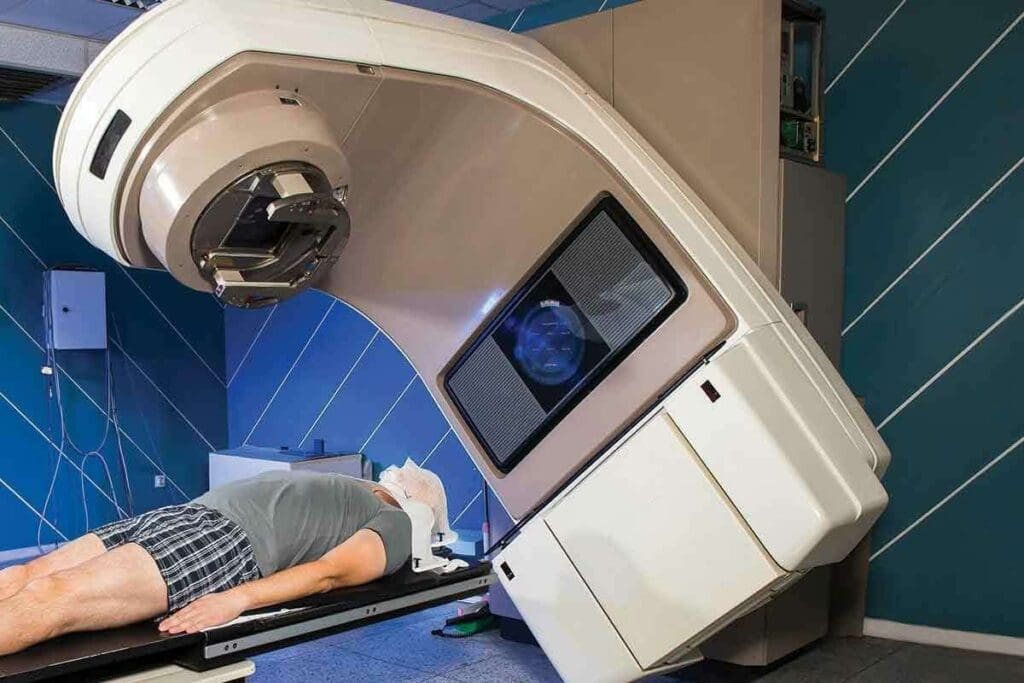
External-beam radiation therapy (EBRT) is a treatment that sends radiation beams to specific body areas with cancer. It’s very good at hitting cancer cells without harming nearby healthy tissues.
What Is External-Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)?
EBRT is a non-invasive treatment that uses a machine to send high-energy radiation beams to cancer sites. The precision of EBRT allows for the delivery of a high dose of radiation directly to the tumor, reducing the risk of damage to nearby healthy cells.
The process starts with a simulation session. Here, the radiation oncologist defines the treatment area and finds the best angle for the radiation beams. This approach ensures the radiation goes straight to the tumor.
How Radiation Beams Target Cancer Cells
Radiation beams in EBRT aim to damage the DNA of cancer cells, stopping them from reproducing and leading to cell death. The beams are carefully calibrated to match the size and shape of the tumor, ensuring effective treatment.
The technology behind EBRT has improved a lot. Now, machines can send radiation beams from different angles. This adapts to the tumor’s shape and size.
| Key Features of EBRT | Benefits |
| Precision in targeting cancer cells | Minimizes damage to surrounding healthy tissues |
| Non-invasive treatment | Reduces risk of complications and promotes faster recovery |
| Personalized treatment planning | Ensures optimal radiation dose delivery to the tumor site |
Types of Beam Radiation Used in Cancer Treatment

Beam radiation therapy is key in cancer treatment, with many options available. It uses different types of radiation beams to target tumors. The choice of beam type depends on the tumor’s location, size, and the patient’s health.
Photon Beam Radiation Therapy
Photon beam radiation therapy is the most common type. It uses high-energy photons to kill or slow cancer cells. These photons come from a machine called a linear accelerator.
Advantages of Photon Beam Radiation Therapy:
- Widely available in cancer treatment centers
- Effective for treating a variety of cancer types
- Can be precisely targeted to minimize damage to surrounding healthy tissues
Proton Beam Radiation Therapy
Proton beam radiation therapy uses protons to kill cancer cells. Protons are positively charged particles that focus their energy on the tumor. This reduces damage to nearby tissues.
“Proton therapy is beneficial for tumors in the brain, spine, or near vital organs, where precision is key.”
Other Specialized External Radiation Technologies
There are other specialized external radiation technologies. These include:
- Electron Beam Radiation Therapy: Uses electrons for superficial tumors or areas not deeply seated.
- Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT): A photon beam therapy that shapes the radiation beam to fit the tumor’s contours.
- Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT): Delivers high doses of radiation to small, well-defined tumors in a few fractions.
Each technology has its own benefits and applications. The choice depends on the individual case and the cancer treatment plan.
How Often Do You Get Beam Radiation Treatments?
Knowing how often to get beam radiation therapy is key for cancer patients. The treatment schedule changes based on the cancer type, stage, and where it is.
Standard Five-Day Weekly Schedule
Most people get external beam radiation therapy once a day, from Monday to Friday. This schedule helps deliver a steady dose of radiation. It also lets healthy cells recover between treatments.
Factors That Determine Treatment Frequency
Several things affect how often you get radiation treatments. These include:
- The type and stage of cancer
- The size and location of the tumor
- The overall health of the patient
- The specific goals of the treatment (curative vs. palliative)
Alternative Scheduling Options
In some cases, doctors might suggest different schedules. For example, hypofractionated radiation therapy gives larger doses in fewer sessions. The choice depends on the patient’s health and the tumor’s characteristics.
Treatment Frequency for Different Cancer Types
| Cancer Type | Typical Treatment Frequency | Total Number of Sessions |
| Breast Cancer | Once daily, Monday to Friday | 15-30 sessions |
| Prostate Cancer | Once daily, Monday to Friday | 20-40 sessions |
| Lung Cancer | Once daily, Monday to Friday | 30-35 sessions |
The table shows typical treatment schedules for different cancers. Remember, these are general guidelines. Your actual treatment plan will depend on your unique needs.
Duration of External Radiation Therapy Courses
The time needed for external radiation therapy changes a lot. It depends on the cancer type and stage. The National Cancer Institute says each patient gets a plan that fits their needs.
Short-Course vs. Long-Course Treatment Plans
Radiation therapy comes in two main types: short-course and long-course. Short-course radiation therapy uses high doses for a short time. It’s for cancers that grow fast or are advanced.
Long-course radiation therapy uses smaller doses over a longer time. It’s for cancers that grow slower. This plan helps reduce side effects. The choice depends on the cancer, its size, and the patient’s health.
How Cancer Type Affects Treatment Duration
The type of cancer greatly affects how long radiation therapy lasts. For example, breast cancer and prostate cancer need different times. This is because of the cancer’s biology and treatment goals.
“The duration of radiation therapy is highly individualized and depends on the specific characteristics of the patient’s cancer.”
Average Number of Radiation Sessions by Cancer Type
The number of radiation sessions also varies by cancer type. For example:
- Breast Cancer: Usually 15-25 sessions
- Prostate Cancer: Often 20-40 sessions
- Lung Cancer: Can be 10-30 sessions
Knowing these differences helps patients prepare for their treatment. It also helps them understand what to expect.
What Happens During a Beam Radiation Session
A beam radiation session is a precise procedure to target tumors with radiation. Before starting, patients have a planning scan to locate the treatment area. This ensures the radiation beams hit the cancer cells right on.
Pre-Treatment Preparation
Getting ready for beam radiation therapy is a key step. It involves several important actions:
- Patients lie on a treatment table and may use immobilization devices to stay in place.
- The radiation therapist uses the planning scan to set up the radiation beams.
- Patients are told how to breathe and stay calm during the treatment.
Precision is key in beam radiation therapy. A leading oncologist says, “The goal is to give the tumor the highest dose of radiation while protecting healthy tissues.”
“The advances in radiation therapy have significantly improved patient outcomes, allowing for more precise targeting of tumors.”
The Actual Radiation Delivery Process
The radiation delivery is painless and quick, lasting just a few minutes. The radiation therapist leaves the room, and the machine sends beams from different angles. The patient is watched remotely to ensure safety and treatment accuracy.
The radiation delivery aims to be efficient and comfortable for the patient. The use of advanced technology allows for precise high doses of radiation.
Post-Session Procedures
After the treatment, the therapist helps the patient off the table. Patients can usually go about their day, but might be told to rest.
Post-session steps include:
- Checking for any immediate side effects.
- Guiding patients on managing side effects at home.
- Scheduling the next treatment session.
As treatment goes on, patients see their radiation oncologist regularly. This is to check how well the treatment is working and to address any worries.
Preparing for Your External Radiotherapy Journey
Starting external radiotherapy can feel scary, but with the right steps, it can be easier. The process includes several important parts, from the first meeting to the actual treatment. Knowing these steps can make a big difference in how you feel.
Initial Consultation and Planning
The first step is a 1- to 2-hour meeting with a doctor or nurse. They talk about the treatment’s benefits, possible side effects, and how to take care of yourself. This meeting is key for setting clear expectations and answering any questions you might have.
Simulation and Treatment Mapping
After the first meeting, you’ll go through a simulation process. This step maps out the area to be treated to make sure the radiation is delivered exactly right. Accurate treatment mapping is key for the therapy’s success and protecting healthy tissues.
In the simulation, you’ll lie on a table, and CT scans will pinpoint the target area. Immobilization devices might be used to keep you in the right position during treatment.
Practical Tips for Managing Daily Treatments
Handling daily radiation treatments needs some planning and changes in your daily life. Here are some helpful tips:
- Eat healthy to manage side effects and aid in recovery.
- Drink plenty of water to help your body handle the treatment.
- Organize your day around your treatment schedule, making sure to rest when needed.
Keeping a record of your treatments and any side effects is also a good idea. This info is very useful for your healthcare team to adjust your treatment plan if needed.
| Preparation Step | Description | Importance |
| Initial Consultation | Meeting with a healthcare provider to discuss treatment | High |
| Simulation | Mapping out the treatment area | High |
| Lifestyle Adjustments | Managing diet, hydration, and rest | Medium |
Advanced Technology in Beam Radiation Therapy
Beam radiation therapy has seen big changes, thanks to new technologies. These advancements help make treatments more precise. This means radiation can hit the tumor right on target, while keeping healthy tissues safe.
Imaging Technologies Used for Precision
Advanced imaging is key to precise beam radiation therapy. Tools like 3-D conformal radiation therapy, Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT), and Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) use high-tech images to aim at tumors.
IGRT, for example, combines CT scans, MRI, or PET scans with radiation therapy. This mix lets doctors watch the tumor’s position in real-time. They can make adjustments to ensure the radiation hits the right spot.
Immobilization Devices and Their Purpose
Immobilization devices are vital for keeping patients steady during treatment. They help reduce movement, making the treatment more precise.
- Molds and casts are used to keep specific body parts in place.
- Body frames help keep the patient’s position steady.
- Breathing control devices manage breathing, helping with tumors in the chest or belly.
How Pinpoint Radiation Treatment Is Achieved
Pinpoint radiation treatment combines advanced imaging, detailed planning, and immobilization devices. Here’s how it works:
- Imaging and simulation pinpoint the tumor’s exact spot.
- Special software creates a treatment plan tailored for each patient.
- Immobilization devices keep the patient in the right position.
- Real-time imaging checks if the treatment is on target.
| Technology | Description | Benefit |
| 3-D Conformal Radiation Therapy | Delivers radiation beams from multiple angles to match the tumor’s shape. | Reduces damage to surrounding healthy tissue. |
| IMRT | Modulates the intensity of radiation beams. | Enhances precision in delivering radiation to complex tumor shapes. |
| IGRT | Uses imaging to guide radiation therapy. | Improves accuracy by adjusting for tumor movement during treatment. |
Side Effects to Expect During and After Treatment
It’s important for patients to know about the side effects of beam radiation therapy. This treatment is good at targeting cancer cells but can affect the body in different ways. Side effects can happen during treatment and sometimes after it’s over.
Common Short-Term Side Effects
Short-term side effects happen during or right after treatment. They can change based on where the treatment is given. Here are some common ones:
- Fatigue: Feeling very tired, which can be helped by resting a lot.
- Skin Changes: The skin in the treated area might get red, irritated, or dry, like a sunburn.
- Hair Loss: Hair loss in the treated area is usually temporary.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These are more common if the treatment area is near the stomach or abdomen.
Potential Long-Term Side Effects
Some side effects can last for months or even years after treatment ends. These long-term side effects include:
- Fibrosis: Scarring that can make tissues stiff and limit movement.
- Secondary Cancers: Rarely, radiation therapy can raise the risk of getting secondary cancers.
- Infertility: Radiation can affect fertility, depending on the area treated and the dose.
- Organ Damage: Radiation can damage organs in or near the treated area.
Managing Radiation Side Effects Effectively
It’s key to manage radiation side effects to improve comfort and treatment success. Ways to manage side effects include:
- Maintaining Good Nutrition: Eating well helps the body heal.
- Skin Care: Keeping the treated skin clean and moisturized.
- Rest and Relaxation: Getting enough rest and doing things that reduce stress.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers to watch for and handle side effects.
By knowing about the side effects of beam radiation therapy and using good management strategies, patients can handle their treatment better.
Special Considerations for Different EBRT Regimens
Different EBRT regimens, like hypofractionation and accelerated fractionation, are chosen based on cancer type and goals. These plans offer benefits tailored to the patient and tumor characteristics.
Hypofractionated Radiation Therapy
Hypofractionated radiation therapy gives higher doses in fewer fractions than usual. It’s often used for tough-to-treat tumors or when a strong effect is needed.
Benefits of Hypofractionation:
- Less time in treatment
- May control tumors better
- Helps patients with busy schedules
A study found hypofractionation works well in some cancers, improving results and patient comfort.
Accelerated Radiation Treatment
Accelerated radiation treatment gives the total dose in a shorter time than usual. It’s great for fast-growing tumors.
Key Considerations:
- More intense dose
- May fight tumors better
- Needs careful planning to avoid side effects
| Treatment Regimen | Fractionation Schedule | Typical Use |
| Conventional | 1.8-2 Gy/fraction, 5 days/week | Most cancer types |
| Hypofractionated | Higher dose/fraction, fewer fractions | Tumors with low α/β ratio |
| Accelerated | Same total dose, shorter overall time | Tumors with high proliferation rates |
Can You Receive Radiation Treatment More Than Once?
Getting radiation treatment more than once is possible, depending on several factors. These include the first dose, cancer type, and overall health.
Factors Influencing Repeat Treatment:
- Recurrence of cancer in the same area
- New primary cancer in a different location
- Assessment of cumulative radiation dose to critical organs
In some cases, reirradiation is considered when benefits outweigh risks. Advanced technologies and careful planning help avoid complications.
Conclusion: Navigating Your Radiation Treatment Journey
Understanding beam radiation therapy is key for patients. We’ve covered the basics of external-beam radiation therapy. This includes its types, how often you’ll get treatment, and possible side effects.
Knowing about photon and proton beam radiation therapy helps patients understand their treatment plans. The length of your treatment depends on your cancer type and goals.
To navigate radiation treatment, you need to know the process, side effects, and available technologies. With this knowledge, you can make informed choices. You can also work closely with your healthcare team for the best results.
Starting your radiation treatment journey? Being informed is essential. Knowing what to expect helps you take an active role in your care. This way, you can face the process with confidence.
FAQ
What is beam radiation therapy?
Beam radiation therapy, also known as external-beam radiation therapy (EBRT), is a cancer treatment. It uses high-energy radiation beams to target and destroy cancer cells.
How often do you get radiation treatments?
Radiation treatment frequency varies by cancer type and stage, and patient needs. Treatments are usually given daily, Monday through Friday, for weeks.
What are the different types of beam radiation therapy?
There are several types, including photon and proton beam radiation therapy. Other technologies like intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) are also used.
How long is radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy duration varies by cancer type and patient needs. It can last from a few days to weeks or months.
Can you receive radiation treatment more than once?
Yes, in some cases, patients can receive radiation treatment more than once. This depends on the cancer type and specific circumstances.
What happens during a beam radiation therapy session?
During a session, the patient lies on a table. The radiation therapist positions the machine to deliver the precise dose to the tumor site.
How is beam radiation therapy tailored to individual patient needs?
Treatment planning tailors beam radiation therapy to each patient. It involves imaging tests, simulation, and mapping to determine the best radiation dose and schedule.
What are the common side effects of beam radiation therapy?
Common side effects include fatigue, skin reactions, and changes in bowel or bladder habits. These depend on the tumor location.
How can the side effects of beam radiation therapy be managed?
Side effects can be managed with medications, lifestyle changes, and supportive care. This includes skin care and nutritional counseling.
What is hypofractionated radiation therapy?
Hypofractionated radiation therapy delivers higher doses in fewer sessions than traditional therapy.
What is external radiotherapy?
External radiotherapy, also known as external-beam radiation therapy (EBRT), uses high-energy beams from outside the body to target and destroy cancer cells.
How many rounds of radiation are normal?
The number of radiation therapy rounds varies by cancer type and stage, and the patient’s needs. It can range from a few sessions to several weeks or months.
References
- National Cancer Institute. (2018). External Beam Radiation Therapy for Cancer. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/types/radiation-therapy/external-beam

































