Cancer treatment has changed a lot with new technologies. External beam radiation therapy is a key part of modern cancer care. It uses a radiation machine for cancer to send precise doses of radiation to tumors. This helps avoid harming healthy tissue nearby.
About 50–60% of cancer patients get external beam radiotherapy as part of their treatment. It can be used alone or with surgery and chemotherapy. This treatment focuses on a specific tumor site, like the lung, breast, prostate, or brain. It’s made possible by detailed imaging and computerized planning. beam radiotherapy – Learn what external beam radiotherapy is and how beam therapy works for cancer.
Key Takeaways
- External beam radiation therapy is a non-invasive cancer treatment.
- It uses advanced radiation machines to target tumors precisely.
- Approximately 50–60% of cancer patients receive this treatment.
- It can be used alone or combined with other treatments like surgery and chemotherapy.
- Detailed imaging and treatment planning ensure accuracy and effectiveness.
Understanding External Beam Radiotherapy (EBRT)
EBRT is a key part of cancer treatment today. It uses special machines to send radiation from outside the body. This helps target tumors without harming nearby healthy tissues.
Definition and Basic Principles
External Beam Radiotherapy (EBRT) is a way to treat cancer. It sends high-energy beams from outside the body to kill cancer cells. The goal is to hit the tumor just right, without hurting the healthy tissue around it.
First, doctors use scans like CT, MRI, or PET to find the tumor’s exact spot. They then plan how to best send the radiation. Advanced machines, like linear accelerators, help make sure the radiation hits the tumor exactly.
Role in Modern Cancer Treatment
EBRT is very important in fighting cancer. It can be used alone or with other treatments like surgery and chemo. Its flexibility makes it a good choice for many cancers.
Key Applications of EBRT:
- Treating localized tumors
- Palliating symptoms in advanced cancer
- Combining with other treatments for complete care
The success of EBRT comes from advanced machines. These machines send radiation with great accuracy. Here’s a quick look at what EBRT is all about:
| Aspect | Description |
| Treatment Type | External Beam Radiotherapy (EBRT) |
| Mechanism | High-energy radiation beams targeting tumors |
| Imaging Techniques | CT, MRI, PET scans for treatment planning |
| Delivery Machines | Linear accelerators and other radiation oncology machines |
The Science Behind Beam Radiotherapy

Beam radiotherapy is key in modern cancer treatment. It uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells. This method also tries to protect healthy tissue nearby.
The treatment’s success comes from its precision. Radiation treatment machines use different types of radiation. These include photon beams, protons, or electrons, to target tumors.
How Radiation Affects Cancer Cells
Radiation therapy damages cancer cells’ DNA. This stops them from growing and spreading. It’s a vital step in controlling tumors.
The type of radiation, dose, and how often it’s given matter. Fractionation helps healthy cells recover. This makes the treatment more effective against cancer.
Radiation Dose and Fractionation
The dose and how it’s given are key in beam radiotherapy. The total dose is split into smaller parts. This helps damage cancer cells more while protecting healthy tissue.
| Radiation Type | Dose Range (Gy) | Typical Fractionation |
| Photon Beams | 50-70 | Daily, Monday-Friday |
| Proton Beams | 50-80 | Daily, Monday-Friday |
| Electron Beams | 30-60 | Daily, Monday-Friday |
Understanding how radiation works helps doctors create better treatment plans. This is for patients getting external radiation therapy.
Types of External Beam Radiation Therapy
External Beam Radiation Therapy isn’t a single treatment. It has many specialized methods. These are tailored to the patient’s needs and the tumor’s characteristics.
3D Conformal Radiation Therapy
3D Conformal Radiation Therapy (3D-CRT) uses CT, MRI, and PET scans to plan treatment. It shapes beams to fit the tumor, protecting healthy tissues.
This method is great for complex tumors or those near important areas.
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) is a step up from 3D-CRT. It changes the beam’s strength in certain spots. This lets it give more radiation to the tumor while saving healthy tissue.
- Offers enhanced precision for tumors with complex shapes
- Reduces the risk of damage to nearby critical structures
- Can be used for a variety of cancer types
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT)
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) are very precise. They’re mainly for small, isolated tumors. These methods give high doses of radiation with great accuracy, protecting nearby tissues.
SRS is for brain tumors, while SBRT targets tumors elsewhere. Both need fewer sessions than regular radiation therapy.
Radiation Machines for Cancer Treatment
Cancer treatment has seen big improvements with new radiation systems. These machines help doctors target tumors well while keeping healthy tissue safe. This is key in external beam radiotherapy (EBRT).
Linear Accelerators (Linacs)
Linear accelerators (Linacs) are key in EBRT. They send precise radiation to tumors. This tech shapes the radiation to fit the tumor’s shape, making treatment more effective.
Linacs are used a lot because they can send high-energy X-rays or electrons to tumors. This helps treat many cancer types, even those deep inside or near important areas.
Other Radiation Delivery Systems
There are other systems used in cancer treatment too. Proton therapy machines are great for treating deep or complex tumors. They use protons instead of X-rays, giving a different radiation therapy approach.
| Machine Type | Primary Use | Key Features |
| Linear Accelerators (Linacs) | Treatment of various cancer types | Delivers high-energy X-rays or electrons; conforms to tumor shape |
| Proton Therapy Machines | Treatment of deep or complex tumors | Delivers protons; precise control over radiation depth |
The right machine depends on the patient’s needs and the tumor’s type. With these advanced machines, doctors can treat cancer well with fewer side effects.
The External Beam Radiotherapy Treatment Process
The external beam radiotherapy treatment process is a detailed procedure. It ensures radiation is precisely aimed at the tumor. This is key for treating cancer effectively and involves several stages, from the first consultation to treatment delivery.
Initial Consultation and Assessment
The first step is a meeting with a radiation oncologist. Here, the patient’s health and cancer details are checked. The oncologist will talk about the patient’s medical history, cancer type and stage, and the benefits and risks of the treatment.
Assessment means a deep look at the patient’s condition. This includes past treatments and overall health. This info is vital for choosing the right treatment plan.
Imaging and Treatment Planning
Imaging techniques like CT, MRI, and PET scans are used. They map the tumor and nearby tissues. This helps in planning treatment, aiming at the tumor while protecting healthy tissues.
Imaging shows the tumor’s size, shape, and location. This info is key for a good treatment plan. The data from these scans helps create a detailed treatment plan.
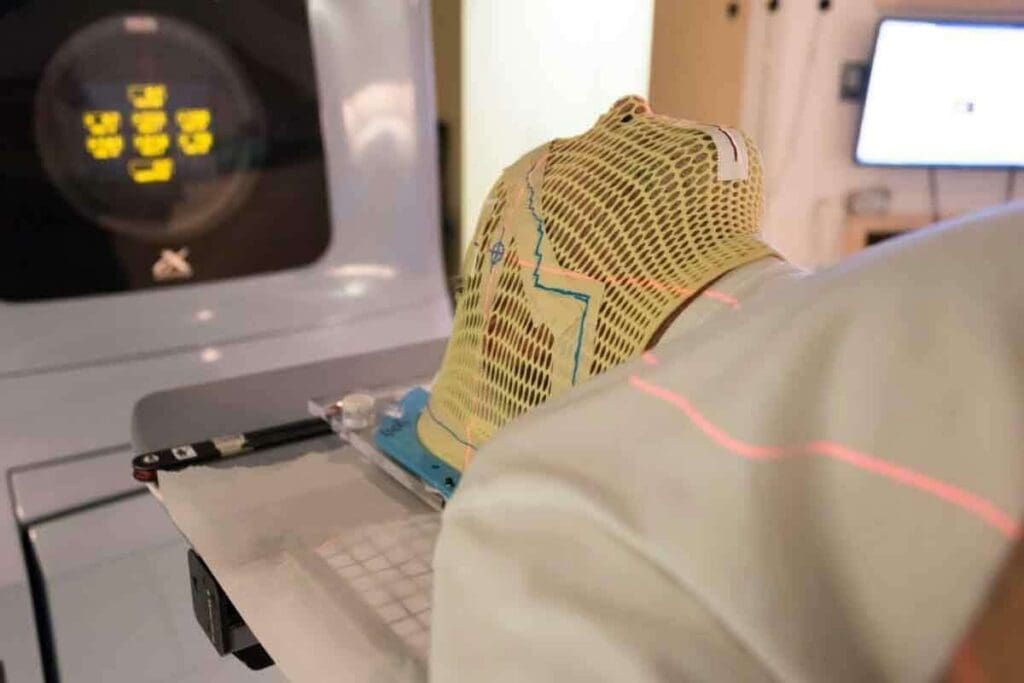
Simulation and Positioning
Next, the patient is positioned as they will be during treatment. This step is vital for comfort and correct positioning during treatment sessions.
Positioning uses devices to keep the patient in the same spot for each session. This is essential for accurate treatment delivery.
The external beam radiotherapy process is complex and requires careful planning and precision. Understanding its stages helps patients see the thorough care in their treatment.
Treatment Delivery and Patient Experience
Treatment delivery is a key part of External Beam Radiotherapy. Here, the planned radiation is given to the patient. The patient lies on the treatment table, and the cancer radiation therapy machine sends precise radiation to the tumor.
What Happens During a Treatment Session
During a session, the patient is placed carefully to ensure accurate radiation delivery. The radiation therapist controls the radiotherapy external beam machine from another room. They watch the patient on a TV screen and talk through an intercom. The treatment is painless and usually lasts a few minutes.
Most patients get external beam therapy as outpatients. Treatments happen daily, from Monday to Friday, for several weeks. The treatment schedule depends on the cancer type, treatment goals, and patient needs.
Treatment Schedule and Duration
The treatment length varies by patient needs. A typical external beam radiation therapy course can last from a few days to weeks. A study on PMC shows the schedule lets healthy cells recover between sessions.
| Treatment Type | Typical Duration | Frequency |
| Curative Treatment | 6-7 weeks | Daily, Monday to Friday |
| Palliative Treatment | 1-2 weeks | Daily, Monday to Friday |
| Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) | 1-5 sessions | Alternate days or daily |
Knowing the treatment schedule and what to expect in external beam radiotherapy can reduce anxiety. It also improves the patient’s overall experience.
Common Cancer Types Treated with External Beam Radiation Therapy
EBRT is used to treat many common cancers. It’s a key treatment that offers hope and better outcomes for patients.
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is often treated with EBRT. After surgery, EBRT kills any cancer cells left behind. This helps lower the chance of cancer coming back. It’s very helpful for those who had a lumpectomy.
Benefits of EBRT for Breast Cancer:
- Effective in reducing local recurrence
- Preserves the breast’s appearance
- Non-invasive treatment option
Prostate Cancer
EBRT is also used for prostate cancer. It can be used alone or with other treatments like hormone therapy. The treatment is customized for each patient to target the tumor accurately.
Advantages of EBRT for Prostate Cancer:
- High precision in targeting the tumor
- Minimal damage to surrounding healthy tissues
- Effective in controlling tumor growth
Lung Cancer and Other Common Applications
Lung cancer is another common use for EBRT, for those who can’t have surgery. EBRT is also used for brain tumors, head and neck cancers, and cancers in the gastrointestinal tract.
| Cancer Type | Common Use of EBRT | Benefits |
| Breast Cancer | Post-surgery to eliminate remaining cancer cells | Reduces recurrence risk, preserves breast appearance |
| Prostate Cancer | Primary treatment or in combination with hormone therapy | High precision, minimal damage to surrounding tissues |
| Lung Cancer | Treatment for patients not suitable for surgery | Effective in controlling tumor growth, palliative care |
Side Effects and Management
External Beam Radiotherapy is a key treatment for many cancers. But, patients need to know about possible side effects and how to handle them. The side effects can change based on where and how much radiation is used.
Common Side Effects
External Beam Radiation Therapy can lead to several side effects. These include feeling tired, skin changes, and hair loss in the treated area. How bad these side effects are depends on the radiation dose and where it’s aimed.
Fatigue is a common side effect, caused by the body’s reaction to radiation. Skin changes can range from mild redness to severe reactions, based on the dose and area treated. Hair loss happens in the area exposed to radiation.
| Side Effect | Description | Management Tips |
| Fatigue | Feeling tired or weak | Rest, exercise, nutrition |
| Skin Changes | Redness, irritation | Moisturize, avoid harsh products |
| Hair Loss | Loss of hair in treated area | Use gentle hair care, consider wigs or headscarves |
Strategies for Managing Side Effects
It’s important to manage side effects well to keep quality of life during and after treatment. Patients should eat well and exercise to help lessen some effects.
“Maintaining good overall health through diet and exercise can significantly impact how well patients tolerate radiation therapy.” –
A healthcare professional
Other strategies include taking medicines as told by the doctor, taking care of your skin, and managing fatigue with rest and exercise.
Knowing about EBRT side effects and how to manage them can help patients through their treatment.
Technological Advancements in External Beam Therapy
The field of radiation oncology has seen big changes, mainly in External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT). These new technologies have made treatments more precise and effective. This has led to better results for patients.
Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT)
Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) is a big step forward in EBRT. It uses imaging like X-rays and CT scans to watch the tumor during treatment. This lets doctors adjust the beam to hit the tumor right, while keeping healthy tissues safe.
Benefits of IGRT:
- More precise radiation delivery
- Less harm to healthy tissues
- Better control of the tumor and outcomes for patients
Adaptive Radiation Therapy
Adaptive Radiation Therapy is another big leap in EBRT. It changes the treatment plan as the tumor and tissues around it change. This can happen because the tumor shrinks or the patient loses weight.
“Adaptive Radiation Therapy allows for the modification of treatment plans in response to anatomical changes, ensuring that the radiation dose is delivered accurately and effectively.” –
A Radiation Oncologist
Key aspects of Adaptive Radiation Therapy:
| Aspect | Description |
| Re-planning | Adjusting the treatment plan based on changes in tumor size or position |
| Monitoring | Regular imaging to assess changes in the tumor and surrounding tissues |
| Dose Adjustment | Modifying the radiation dose to ensure effective treatment |
Artificial Intelligence Applications
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is being used more in radiation oncology. It helps with planning treatments, predicting outcomes, and making treatments more personal. AI looks at lots of data to give insights that can make treatments better.
Potential applications of AI in EBRT include:
- Automated treatment planning
- Predictive analytics for patient outcomes
- Personalized treatment protocols
In conclusion, new technologies like IGRT, Adaptive Radiation Therapy, and AI are changing External Beam Radiation Therapy. These advancements make treatments more precise, effective, and tailored to each patient. This leads to better results for patients.
Conclusion: The Future of External Beam Radiotherapy
External beam radiotherapy is a key part of cancer treatment today. New technology is making it more precise and effective. Research shows that methods like 3DCRT and IMRT are helping more people fight cancer.
The future of EBRT is bright, with treatments becoming more tailored to each patient. New machines and techniques will help reduce side effects. This means better results for patients, making EBRT a vital part of cancer care.
EBRT will keep being a major part of cancer treatment, bringing hope to patients and doctors. The use of the latest technology and research will unlock its full power. This will lead to even better ways to fight cancer.
FAQ
What is external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) and how does it work?
External beam radiotherapy (EBRT) is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy beams. These beams aim to destroy cancer cells. It delivers precise radiation to the tumor, protecting healthy tissue nearby.
What are the different types of external beam radiation therapy?
There are several types, like 3D conformal radiation therapy (3D-CRT) and intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT). Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) are also used. Each type is chosen based on the patient’s needs and cancer type.
How is the radiation dose determined for external beam radiotherapy?
The dose is planned carefully to harm cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. It depends on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health.
What is the role of linear accelerators (Linacs) in external beam radiotherapy?
Linear accelerators (Linacs) are key in EBRT. They deliver precise radiation to tumors, using advanced technology to match the tumor’s shape.
What are the common side effects of external beam radiotherapy?
Side effects include fatigue, skin changes, and hair loss, depending on the radiation dose. To manage these, patients should stay healthy, follow a diet, and take medications as advised.
How is external beam radiotherapy used to treat different types of cancer?
It treats many cancers, like breast, prostate, and lung cancer. The treatment is customized for each patient and cancer type.
What is image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) and how does it enhance external beam radiotherapy?
IGRT uses imaging to track the tumor’s position in real-time. This allows for precise adjustments during treatment, improving EBRT’s effectiveness.
What is the typical treatment schedule for external beam radiotherapy?
Treatments are given daily, Monday to Friday, over weeks. The schedule varies based on the cancer type, treatment goals, and patient needs.
How does external beam radiotherapy compare to other cancer treatments?
EBRT is often combined with surgery and chemotherapy. It’s a local treatment that targets the tumor while sparing healthy tissue.
What are the benefits of technological advancements in external beam radiotherapy?
Advances like IGRT and adaptive radiation therapy have improved EBRT’s precision and effectiveness. These advancements have better patient outcomes and fewer side effects.
References
- National Cancer Institute. (2018). External Beam Radiation Therapy for Cancer. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/types/radiation-therapy/external-beam
- RadiologyInfo.org. (2024). External Beam Therapy (EBT). https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/ebt



































