Did you know that stem cells can fix and grow back damaged tissues? This makes them very important in medical treatments.
Stem cells are special because they can turn into different types of cells. This is key to the body’s healing process. The power of stem cell treatment could change medicine a lot.
Many people are curious about how to get stem cells easily. There are many stem cell procedures being looked into. Knowing how stem cells and treatment work is key to using them to help people.
Key Takeaways
- Stem cells can fix and grow back damaged tissues.
- Stem cell treatment could change medicine a lot.
- Understanding stem cell procedures is important for their use.
- Stem cells can turn into different types of cells.
- The power of stem cells is in their ability to heal and repair the body.
Understanding Stem Cells: The Building Blocks of Regenerative Medicine
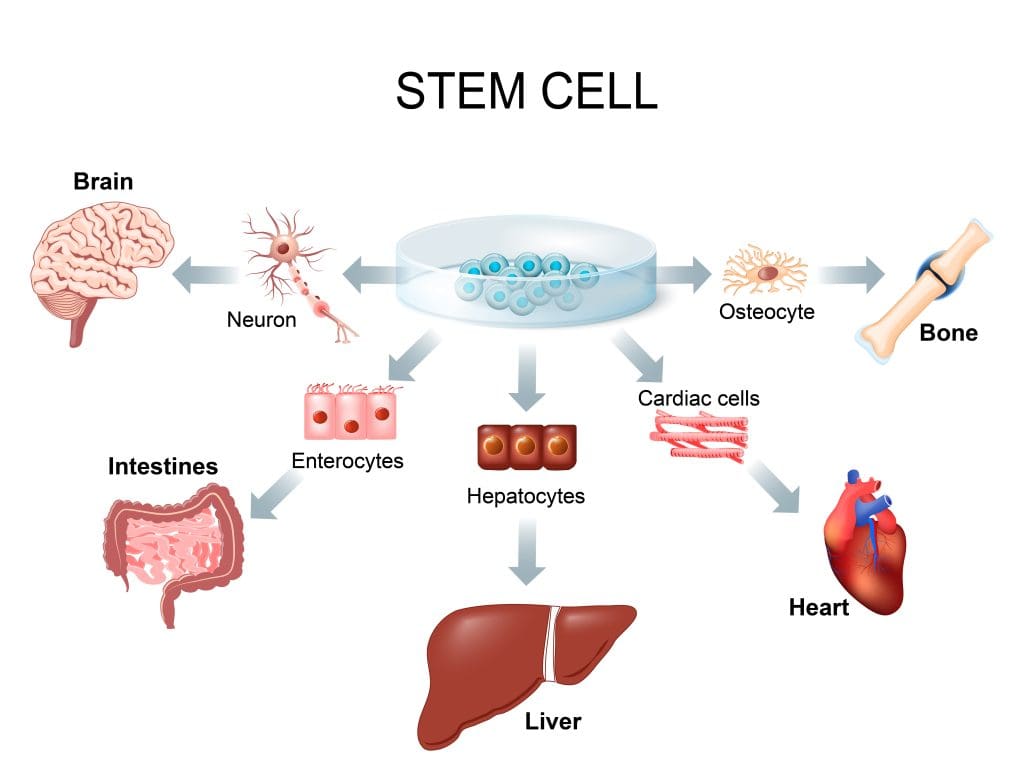
Stem cells are at the core of regenerative medicine. They can turn into different types of cells. This makes them key for fixing or replacing damaged tissues and organs.
What Are Stem Cells and Why Are They Important?
Stem cells are cells that can become many types of cells in our bodies. They are vital for stem cells therapy. This therapy offers new ways to treat many health issues. Their ability to change into specific cells is essential for regenerative medicine stem cells.
Different Types of Stem Cells
There are several kinds of stem cells, each with its own traits and uses. The main kinds are:
- Embryonic stem cells, which come from embryos and can become any cell type.
- Adult stem cells, found in adult bodies, which can turn into different cell types but have less ability than embryonic stem cells.
- Perinatal stem cells, from umbilical cord blood and other tissues, providing a good source of stem cells without the ethical issues of embryonic stem cells.
Knowing the differences between these types is key for finding the right use for them in medicine.
| Type of Stem Cell | Source | Differentiation Ability |
| Embryonic | Embryos | High |
| Adult | Adult tissues | Moderate |
| Perinatal | Umbilical cord blood and perinatal tissues | Moderate to High |
So, what is stem cell? It’s a cell that can become specific cell types. The possibilities of stem cells in medicine are huge. Research is always finding new ways to use stem cells therapy.
Common Sources of Stem Cells in the Human Body
The human body has many sources of stem cells, key for regenerative medicine. These cells can come from different tissues and organs. Each has its own benefits and challenges. Knowing these sources is key for making stem cell treatments work.
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a rich source of stem cells, mainly hematopoietic stem cells. These cells make blood cells and have been used in treatments for years.
“Bone marrow transplantation has been a cornerstone of treatment for various blood disorders, showing the power of stem cells.”
To get stem cells from bone marrow, doctors use aspiration from the hip bone. This method is effective, but it may be painful and invasive for the patient.
Adipose Tissue
Adipose, or fat, tissue is a good alternative source of stem cells. Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) can help heal and have many uses in medicine.
Getting ADSCs usually involves liposuction, which is less painful than bone marrow aspiration. This method may also help shape the body.
Peripheral Blood
Peripheral blood is another source of stem cells, but there are fewer of them than in bone marrow or fat tissue. Peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs) can be made more available with certain medicines.
| Source | Extraction Method | Stem Cell Type |
| Bone Marrow | Aspiration | Hematopoietic |
| Adipose Tissue | Liposuction | Mesenchymal |
| Peripheral Blood | Apheresis | Hematopoietic |
Dental Pulp
Dental pulp, inside teeth, is a new source of stem cells. Dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) can turn into many cell types. This makes them useful for dental and medical healing.
Getting DPSCs is easy and doesn’t hurt much, as it involves taking dental pulp from pulled teeth. This source is great because it’s easy to get and can be used by the person themselves.
In summary, the human body has many stem cell sources, each with its own benefits and uses. Knowing about these sources is key for improving regenerative medicine and making stem cell treatments better.
The Stem Cell Procedure: From Extraction to Application
Understanding the stem cell procedure is key for those looking into regenerative medicine. It includes several steps, from getting stem cells to using them in treatments.
Overview of Collection Methods
Stem cells can come from different places in the body. These include bone marrow, fat tissue, and blood. Each way has its own benefits and fits different patient needs.
- Bone Marrow Aspiration: This traditional method takes stem cells from the bone marrow, usually from the hip.
- Adipose Tissue Extraction: Stem cells are taken from fat tissue through a small liposuction. It’s a good source of cells.
- Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Collection: This method gets stem cells from the blood. It often comes after moving them from other parts of the body.
Processing and Isolation Techniques
After getting stem cells, they go through processing and isolation. This makes them ready for use in treatments. It separates the right cell types and checks if they’re safe and working well.
The steps in processing include:
- Centrifugation to sort cells by density.
- Cell sorting with markers specific to stem cells.
- Culturing cells to grow their numbers and boost their healing power.
Storage and Preservation Options
After processing, stem cells must be stored and kept safe. Freezing them at very low temperatures is a common way. This stops their metabolic processes.
Keeping stem cells in good condition is vital. It ensures they’re healthy and ready for use when needed. This means careful handling and watching for any contamination or damage.
Bone Marrow Aspiration
Bone marrow aspiration is the top choice for getting stem cells. It takes stem cells from the bone marrow, often from the pelvis. This method is key because it gives a lot of stem cells for treatments like stem cell transplants and regenerative medicine.
How Bone Marrow Extraction Works
First, local anesthesia is given to make the process painless. A needle is then put into the bone, usually in the pelvis, to get the bone marrow. This marrow has stem cells that are then cleaned up for use in treatments. The whole thing usually takes about 30 minutes to an hour.
Recovery and Side Effects
After the procedure, some people might feel pain, bruising, or swelling where the needle was. These effects are usually mild and go away in a few days. Serious problems are very rare, making bone marrow aspiration a safe way to get bone marrow stem cells.
- Mild pain or discomfort at the aspiration site
- Bruising or swelling
- Infection (rare)
Effectiveness and Applications
Bone marrow aspiration is used in many medical treatments, including stem cell surgery for bone and blood disorders. The stem cells from this method can turn into different cell types. This makes them very useful for fixing damaged tissues.
The success of bone marrow aspiration in getting stem cells for treatments is proven. As research gets better, the uses of bone marrow-derived stem cells will grow. This will open up new ways to treat many diseases.
Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Extraction
Adipose-derived stem cell extraction is a simple and safe way to get stem cells. It takes stem cells from fat, which is found all over our bodies.
Mini-Liposuction Procedure
This method is easy and safe. It uses a mini-liposuction to take fat from a donor site. This is done under local anesthesia.
The fat is then processed to get the stem cells. “The mini-liposuction procedure is not only effective but also offers the advantage of being less invasive compared to traditional surgical
Advantages Over Other Methods
Adipose-derived stem cell extraction has many benefits. It’s less invasive than bone marrow aspiration, causing less pain and quicker recovery. Also, fat tissue is easy to get to and full of stem cells.
- Minimally invasive procedure
- Quick recovery time
- Abundant source of stem cells
Limitations and Considerations
While it has many benefits, there are also downsides. The quality and amount of stem cells can change based on the patient’s health and age. The extraction method also plays a role.
It’s important for patients to talk to a healthcare expert. They can decide if this method is right for them. Knowing the risks and benefits is key.
Blood-Based Collection Methods: Minimally Invasive Options
Peripheral blood stem cell collection is changing regenerative medicine. It’s a less invasive way to get stem cells. This method is getting more attention because it might be safer than older ways.
Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Collection
This method uses apheresis to separate stem cells from blood. It’s less invasive because it only needs to access the blood through a vein.
Apheresis Procedure Explained
Apheresis is a way to remove certain blood parts. For stem cell collection, it separates stem cells from other blood parts. The process can take hours and might need special drugs to get the stem cells ready.
Who Is a Good Candidate?
Who can get peripheral blood stem cell collection depends on health, the condition, and the therapy needs. Good candidates are those who:
- Need a less invasive stem cell collection method
- Have a condition treatable with peripheral blood stem cells
- Are in good health with enough veins for apheresis
| Candidate Criteria | Description |
| Health Status | Good overall health |
| Venous Access | Adequate venous access for apheresis |
| Therapeutic Needs | Condition treatable with peripheral blood stem cells |
It’s key for those interested to talk to a doctor. They can check if peripheral blood stem cell collection is right for them.
Umbilical Cord Blood Banking: Planning for the Future
Umbilical cord blood banking is about saving stem cells from the umbilical cord after birth. It’s a way to prepare for future medical needs. This method is seen as a smart step towards keeping families healthy.
Collection During Childbirth
Umbilical cord blood is collected right after birth, during the third stage of labor. This happens after the baby is born and the umbilical cord is cut. It’s a safe and painless process for both mom and baby.
The blood is then sent to a lab for processing and storage. Cord blood collection is easy and doesn’t disrupt the birth process. It’s a chance for parents to save stem cells for future medical needs.
Public vs. Private Banking Options
Parents can choose between public and private cord blood banking. Public cord blood banking means donating the blood to a public bank. This way, anyone in need can use it. On the other hand, private cord blood banking keeps the blood for the family’s use only.
- Public banking is free and helps a global registry. It increases the chances of finding a match for patients.
- Private banking costs money upfront and every year. It keeps the blood for the family’s future needs.
Potential Uses and Limitations
Cord blood stem cells can treat serious diseases like cancers and blood disorders. They also have a big role in regenerative medicine. Scientists are studying their use for many diseases.
But, there are some limits. The amount of cord blood might not be enough for adults or some treatments. The quality of the blood and how it’s processed also matter for its future use.
In summary, umbilical cord blood banking is a great way for families to save stem cells. Knowing how it works, the choices available, and its uses can help families plan for the future.
Clinical Trials and Research Programs: Alternative Access Points
Clinical trials on stem cells are key for improving regenerative medicine. They give patients early access to new, potentially life-changing treatments. These studies involve people to check if stem cell treatments work and are safe for different health issues.
Finding and Qualifying for Stem Cell Studies
To join stem cell clinical trials, patients must fit certain criteria. This includes age, medical history, and how severe their condition is. Researchers look for specific participants to get reliable and useful study results.
There are many ways to find stem cell clinical trials:
- ClinicalTrials.gov, a database by the U.S. National Library of Medicine
- Research institutions and universities
- Patient advocacy groups
- Specialized stem cell therapy centers
Benefits and Risks of Participation
Joining stem cell clinical trials has benefits. You get early access to new treatments and help future medical research. But, there are risks too. These include possible side effects or the treatment not working.
It’s important to think about these points and talk to your doctor before deciding.
Resources for Finding Legitimate Trials
To make sure a trial is real, check if it’s listed on trusted databases. Also, look for approval from bodies like the FDA in the U.S.
Also, talking to your doctor or patient advocacy groups can help find reliable info on stem cell studies.
Understanding how to find and join stem cell clinical trials helps advance regenerative medicine. It also gives individuals a chance to contribute to new treatments.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Stem Cell Acquisition
It’s important for both patients and doctors to know about stem cell laws and ethics. This field is growing fast, with new findings all the time.
FDA Regulations in the United States
The FDA is key in controlling stem cell treatments in the U.S. FDA guidelines make sure treatments are safe and work well. They require strict testing and checks.
The FDA’s rules help keep patients safe from bad treatments. They also help good treatments get approved for those who need them.
Approved vs. Experimental Treatments
Knowing the difference between approved stem cell treatments and experimental ones is key. Approved treatments have passed many tests and are safe and effective.
Experimental treatments are being tested in trials to see if they work and are safe. Patients should know the risks and benefits of each.
Avoiding Fraudulent Stem Cell Clinics
More people are interested in stem cell treatments, which has led to fake clinics. Patients need to be careful and do their homework.
- Verify the credentials of the medical professionals involved.
- Check if the clinic is transparent about the risks and benefits of the treatment.
- Be wary of clinics that make exaggerated claims about their treatments.
By staying informed and careful, patients can avoid harmful or useless treatments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Stem Cell Approach for Your Needs
Choosing the right stem cell therapy depends on several factors. These include the condition being treated and your individual health needs. Different stem cell sources, like bone marrow, adipose tissue, and peripheral blood, offer unique benefits and considerations.
When looking into stem cell treatment options, it’s key to think about the source of stem cells. Also, consider the procedure for extracting them and their possible uses. Stem cells therapy has shown promise in treating many conditions. Understanding the available choices is essential for making informed decisions.
By considering these factors and understanding the different stem cell treatment options, individuals can make informed choices about their care. Whether through bone marrow aspiration, adipose-derived stem cell extraction, or other methods, selecting the most appropriate stem cell approach is vital for achieving the best possible outcomes.
FAQ
What are stem cells and why are they important?
Stem cells can turn into different types of cells. They are key in regenerative medicine. They help fix or replace damaged tissues.
What is stem cell therapy?
Stem cell therapy uses stem cells to fix or replace damaged cells. It’s a part of regenerative medicine.
Where are stem cells located in the human body?
You can find stem cells in many places. This includes bone marrow, fat tissue, blood, and dental pulp.
How is stem cell therapy done?
First, stem cells are taken from a source. Then, they are processed and isolated. After that, they are applied to the area needing repair, usually through injection.
What is bone marrow aspiration?
Bone marrow aspiration takes stem cells from the bone marrow. It’s often done from the hip bone for therapy or transplantation.
What are the advantages of adipose-derived stem cell extraction?
Taking stem cells from fat tissue is simpler and less invasive. It might have fewer side effects than bone marrow aspiration.
How are peripheral blood stem cells collected?
Peripheral blood stem cells are collected through apheresis. This process draws blood, separates stem cells, and returns the rest to the body.
What is umbilical cord blood banking?
Umbilical cord blood banking stores blood from the umbilical cord after birth. It’s rich in stem cells for future medical use.
How can I find and qualify for stem cell clinical trials?
Look for stem cell clinical trials on ClinicalTrials.gov. Talk to your healthcare provider. Make sure you meet the trial’s criteria.
How can I avoid fraudulent stem cell clinics?
Research the clinic’s credentials and check for FDA approval. Be wary of clinics making false claims.
What is regenerative medicine using stem cells?
Regenerative medicine uses stem cells to repair or replace damaged tissues. It offers new ways to treat various conditions.
What are the potentials uses of cord blood stem cells?
Cord blood stem cells can treat blood disorders and immune system diseases. Research is ongoing for more uses.
What is the difference between public and private umbilical cord blood banking?
Public banking donates cord blood for anyone in need. Private banking keeps it for the family’s use only.


































