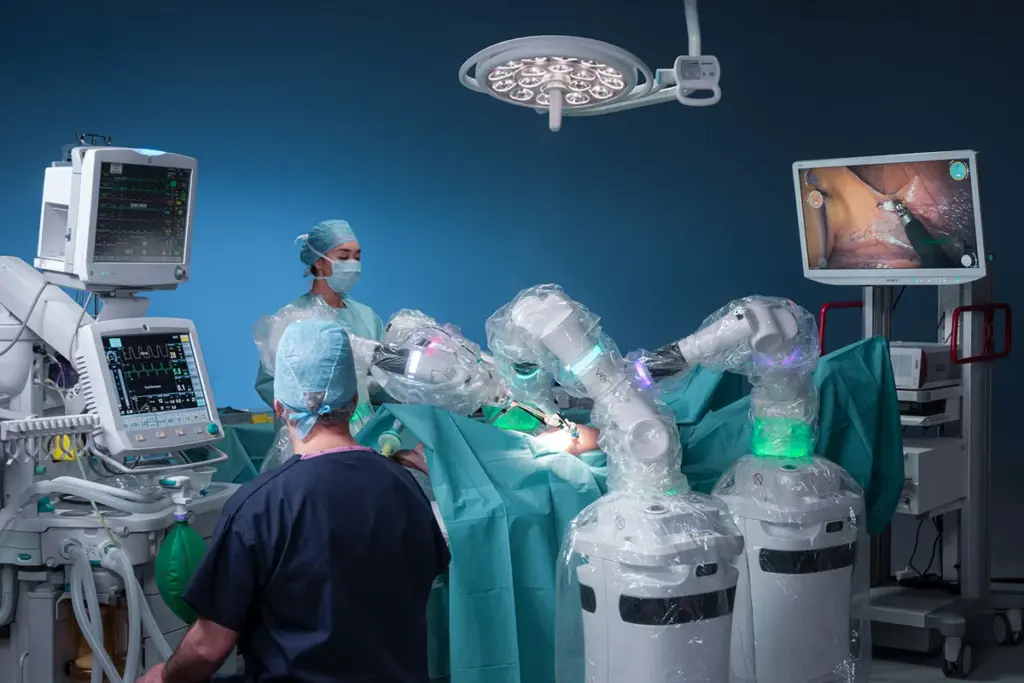
More than 6 million people worldwide have had robot-assisted surgery. This number is growing fast every year. The da Vinci Surgical System is leading this change. It lets surgeons do complex tasks with better precision and less invasion.
Robot-assisted surgery is getting more common in many medical fields. It’s important to know how safe it is. While it has many benefits, there are also safety worries.
Key Takeaways
- The da Vinci Surgical System is the most widely used robotic system.
- Robotic surgery has been applied in various medical specialties.
- The safety of robotic surgery is a growing concern.
- Robot-assisted surgery offers enhanced precision and minimal invasion.
- Understanding the safety profile is critical for its continued use.
What Is Robotic Surgery?
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, lets surgeons do operations with better precision and less invasion. It has changed the medical world by giving surgeons new tools for complex surgeries.
Definition and Core Concepts
Robotic surgery uses robotic systems to help surgeons during operations. These systems have a console for the surgeon, a cart with instruments, and a vision system for clear images. The main idea is to improve the surgeon’s skills, making movements more precise and visuals clearer.
Historical Development of Surgical Robotics
The first robotic system in neurosurgery was the Puma 560 in 1985. After that, big steps were taken, with the da Vinci Surgical System becoming a top choice worldwide. It has helped make robotic surgery popular in many medical areas.
Current Applications in Modern Medicine
Robotic surgery is used in many fields, like urology, gynecology, and general surgery. The da Vinci system is used for surgeries like prostate and uterus removals. Its precision and less invasive nature have made patients’ recovery times better.
|
Medical Specialty |
Common Procedures |
|---|---|
|
Urology |
Prostatectomy, Nephrectomy |
|
Gynecology |
Hysterectomy, Myomectomy |
|
General Surgery |
Cholecystectomy, Hernia Repair |
The Technology Behind Robotic Surgery Systems<
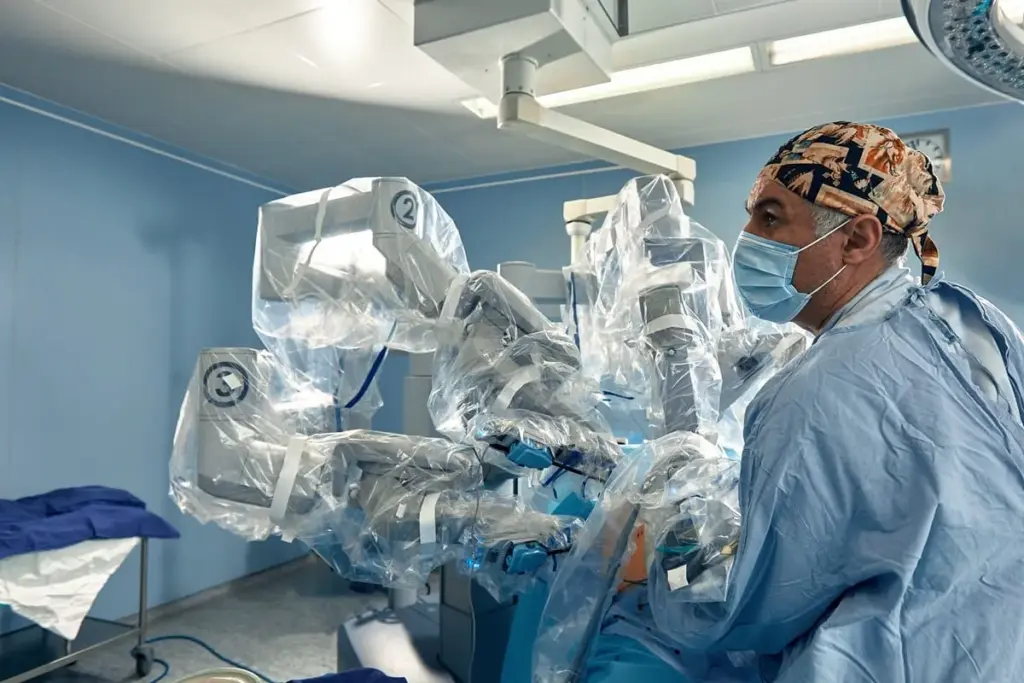
Understanding the tech behind robotic surgery systems is key. They’ve changed surgery, making it more precise and less invasive.
Key Components of Surgical Robots
Surgical robots, like the da Vinci Surgical System, have important parts. These parts help with complex surgeries. They include:
- A robotic tower that houses the robotic arms
- A bedside cart that contains the surgical instruments
- A surgeon console that provides high-definition 3D visualization and precise control
The da Vinci Surgical System is a top example of advanced robotic surgery. It has changed surgery a lot.
How Surgeons Control Robotic Systems
Surgeons use a console to control the robots. This console shows a high-definition 3D view of the surgery site. It has hand controls and foot pedals for precise control.
Technological Safeguards and Fail-Safe Mechanisms
Robotic surgery systems have many safety features. These include:
- Redundant systems to prevent mechanical failure
- Emergency stop mechanisms
- Continuous monitoring by the surgical team
These technological safeguards are vital. They help avoid problems during robot-assisted surgeries.
Common Procedures Using Robotic Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery is changing how surgeries are done. It brings better precision and less invasion. This tech is used in many surgeries, making patients’ recovery times shorter.
Urological Applications
Robotic surgery has made a big difference in urology. It’s great for prostate and kidney surgeries. The tech helps keep more of the surrounding tissues and nerves safe.
Prostatectomy and Kidney Procedures
In urology, robotic surgery is key for prostatectomies and kidney procedures. It lets surgeons do complex tasks with more accuracy. This is thanks to the system’s better vision and control.
Success Rates and Outcomes
Research shows robotic urological surgeries have fewer complications. They also lead to quicker recovery times. Patients often feel less pain and stay in the hospital for less time.
Gynecological Procedures
Robotic surgery is also used in gynecology. It’s used for things like hysterectomies and treating endometriosis. The tech helps surgeons do delicate work with more precision.
General and Thoracic Surgery Applications
Robotic surgery is also used in general and thoracic surgery. It’s used for surgeries like cholecystectomies and lobectomies. This leads to less harm to the patient and better results.
The growth of robotic surgery in these fields will likely lead to even better results for patients. It will help them recover faster and more smoothly.
Is Robotic Surgery Safe? Examining the Evidence
To understand if robotic surgery is safe, we need to look at the data and research. It’s known for its benefits like shorter recovery times and better precision. But, it’s important for both patients and doctors to know about its safety.
Overall Safety Statistics and Complication Rates
Research shows robotic surgery has similar or lower complication rates than traditional surgery. The complication rate for robotic surgeries is about 4-6%. This is lower than many traditional surgeries. Robotic surgery safety is improved by advanced technology and precise control.
Looking at safety statistics, robotic surgery is generally safe when done by skilled surgeons. The data shows a low rate of serious complications. This makes robotic surgery more accepted in many medical fields.
Comparative Safety: Robotic vs. Traditional Surgery
Studies comparing robotic and traditional surgery show robotic surgery often has fewer complications and quicker recovery. The precision of robotic systems can cause less tissue damage and lower infection risks.
But, robotic surgery isn’t risk-free. The technology’s complexity means it needs special training. There’s a learning curve for surgeons to master robotic techniques.
Patient Selection and Safety Considerations
Patient selection is key to robotic surgery safety. The patient’s health, the condition being treated, and the surgeon’s robotic experience are important factors.
Choosing the right patients for robotic surgery helps reduce risks and improve results. This tailored approach is vital for robotic surgery’s ongoing success and safety.
Benefits of Robot-Assisted Surgery
Robot-assisted surgery uses advanced technology to improve surgery. It offers many benefits, making surgery better and outcomes better for patients.
Enhanced Surgical Precision and Visualization
Robot-assisted surgery is known for its precision. It uses high-definition, 3D images for better views. This helps surgeons work on complex areas with more accuracy.
Enhanced visualization and robotic tools allow for precise movements. This leads to better results in delicate surgeries.
Reduced Invasiveness and Smaller Incisions
This surgery is less invasive, meaning smaller cuts than traditional surgery. This leads to less blood loss, lower infection risk, and less scarring. It also makes patients look better after surgery.
Patient Recovery Advantages
Robot-assisted surgery benefits don’t stop after surgery. Patients recover faster, feel less pain, and stay in the hospital less. This is because the surgery is less invasive, causing less damage to the body.
The main benefits of robot-assisted surgery are:
- Enhanced surgical precision and visualization
- Reduced invasiveness with smaller incisions
- Faster patient recovery times and reduced postoperative pain
Potential Risks and Complications of Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery is becoming more common, but it’s important to look at the risks. It has changed many medical procedures for the better. But, knowing its possible downsides is key for doctors and patients.
Technical and Mechanical Malfunctions
One big risk is technical and mechanical problems. Mechanical failures can happen, even though they’re rare. A study in the Journal of Robotic Surgery showed that these failures sometimes turn robotic surgeries into open surgeries.
Surgeon Experience and Learning Curve Issues
The learning curve for surgeons using robots can be very steep. This can lead to problems during surgery. It’s important for surgeons to get a lot of practice and training.
Procedure-Specific Complications
Each surgery has its own risks when done with robots. For example, robotic prostatectomies and robotic hysterectomies have different risks. Knowing these procedure-specific complications helps manage patient expectations and improve results.
Reported Adverse Events
Even though rare, adverse events in robotic surgery do happen. These can be anything from small issues to serious problems that need more treatment. It’s important to track and report these events to make robotic surgery safer.
Regulatory Oversight and Safety Standards
Regulatory bodies are key in making sure robotic surgical systems are safe and work well. They follow many rules and standards to protect patients.
FDA Approval Process for Surgical Robots
The FDA checks robotic surgical systems before they hit the market. They look at the system’s design, tests, and clinical trial data. This makes sure it meets safety standards. The FDA also keeps an eye on how these systems do after they’re approved.
Monitoring and Reporting Systems
Good monitoring and reporting systems are vital. They help spot and fix any safety problems with robotic surgery. The FDA has a database of bad events related to these systems. This helps find trends and areas to get better.
International Safety Standards
There’s a push to make safety standards the same worldwide for robotic surgery. Groups like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) create guidelines. These guidelines help ensure safety is consistent everywhere.
Surgeon Training and Certification Requirements
The safety and success of robotic surgery depend on the training and certification of surgeons. As robotic surgery grows, it’s key to know how surgeons get the skills and certifications they need.
Training Pathways for Robotic Surgeons
Robotic surgeons go through detailed training programs. These programs mix theory and practice. They aim to teach surgeons how to use robotic systems well.
Training includes using robotic simulators, watching live surgeries, and doing supervised cases. This hands-on approach helps surgeons learn and improve.
Hospital Credentialing Standards
Hospital credentialing standards are important for ensuring surgeons are ready for robotic surgery. These standards vary but usually require surgeons to show they can do robotic procedures well. They also need to keep learning and meet certain experience levels.
Credentialing committees check a surgeon’s training, experience, and results. They decide if a surgeon can perform robotic surgeries.
Ongoing Education and Skill Maintenance
Robotic surgeons must keep learning to stay current with new technology and techniques. They attend conferences, workshops, and engage in ongoing professional development. Regular practice and staying informed about robotic surgery advancements are also key.
With a focus on thorough training, certification, and continuous learning, robotic surgery can remain safe and effective for patients.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery is becoming more common, and its financial side is key. We look at costs like equipment, operational, insurance, and the long-term effect on healthcare. This helps us understand its value.
Equipment and Operational Costs
Buying a robotic surgery system costs a lot, from $1 million to $2.5 million. Maintenance and upgrades add to this, with yearly costs of $100,000 to $200,000. Training staff and using disposable tools also add to the costs.
Insurance Coverage and Patient Financial Considerations
Insurance for robotic surgery varies a lot. Many plans cover it, but patients might face big out-of-pocket costs. It’s important for patients to check with their insurance. Hospitals also face financial challenges with robotic surgery.
Long-term Economic Impact on Healthcare Systems
The long-term effects of robotic surgery on healthcare are complex. The initial costs are high, but there could be savings later. These savings come from shorter hospital stays and fewer complications. Yet, ongoing maintenance and training costs might reduce these savings. A detailed analysis is needed to fully understand the costs and benefits.
Latest Research and Innovations in Surgical Robotics
Surgical robotics is getting better thanks to new research and tech. This change is making surgery safer and more precise. It’s helping doctors care for patients better.
Recent Clinical Studies on Safety Outcomes
Studies have looked into how safe robotic surgery is. They found it has fewer problems and quicker healing than old methods. For example, a study in the Journal of Robotic Surgery showed better results for prostate surgery.
Emerging Safety Technologies
New safety tech in surgical robotics includes better sensors and monitoring. These tools aim to make surgery more precise and safe. Next-gen robots might use augmented reality and AI for real-time help.
Next-Generation Robotic Systems
New robotic systems are getting smarter and more capable. They will let doctors do more surgeries without big cuts. Companies like Intuitive Surgical are leading these advancements.
Conclusion: The Future of Robotic Surgery Safety
Robotic surgery is getting better, and we need to keep it safe. New technologies and strict safety rules have made it safer. Now, it’s a good choice for many surgeries.
Next steps in robotic surgery will aim to make it even better. We want it to be more precise and quick to recover from. It should also be used for more types of surgeries.
Improving robotic surgery systems and training doctors will be key. This will help make sure it stays safe and effective. We must keep focusing on quality care and solving the challenges of this new tech.
FAQ
What is robotic surgery?
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, is a minimally invasive method. It uses a robotic system to help with the surgery. A surgeon controls the system from a console, guiding the instruments.
How does robotic surgery work?
The system includes a console, a cart for the patient, and a vision system. The surgeon uses the console to control the instruments on the cart. The vision system gives a clear, 3D view of the area being operated on.
What are the benefits of robotic surgery?
Robotic surgery offers better precision and smaller incisions. This leads to less blood loss, less pain, and quicker recovery times for patients.
Is robotic surgery safe?
Robotic surgery is safe when done by skilled surgeons. It has similar or better safety records compared to traditional surgery.
What are the possible risks and complications of robotic surgery?
Risks include technical issues, learning curve problems, and specific complications like bleeding or infection. These can vary based on the procedure.
How is robotic surgery regulated?
The FDA oversees robotic surgery, approving systems and monitoring safety. Hospitals and surgeons must follow strict guidelines and standards.
What kind of training do robotic surgeons need?
Surgeons need specialized training, including hands-on practice. They must also keep their skills up to date through ongoing education.
Is robotic surgery covered by insurance?
Coverage varies by insurance provider and procedure. It’s best to check with your insurance to see if it’s covered.
What is the cost of robotic surgery?
Costs include equipment and operational expenses, which might be higher than traditional surgery. But, the benefits like quicker recovery times can make it worth it.
What are the latest developments in robotic surgery?
New safety technologies and next-generation systems are emerging. Research is ongoing to improve safety and effectiveness.
How does robotic surgery compare to traditional surgery?
Robotic surgery offers better precision and faster recovery times. But, the choice between it and traditional surgery depends on the procedure and patient needs.
Can robotic surgery be used for complex procedures?
Yes, it can be used for complex procedures like urological, gynecological, and general surgeries. It is safe and effective.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28868166/





