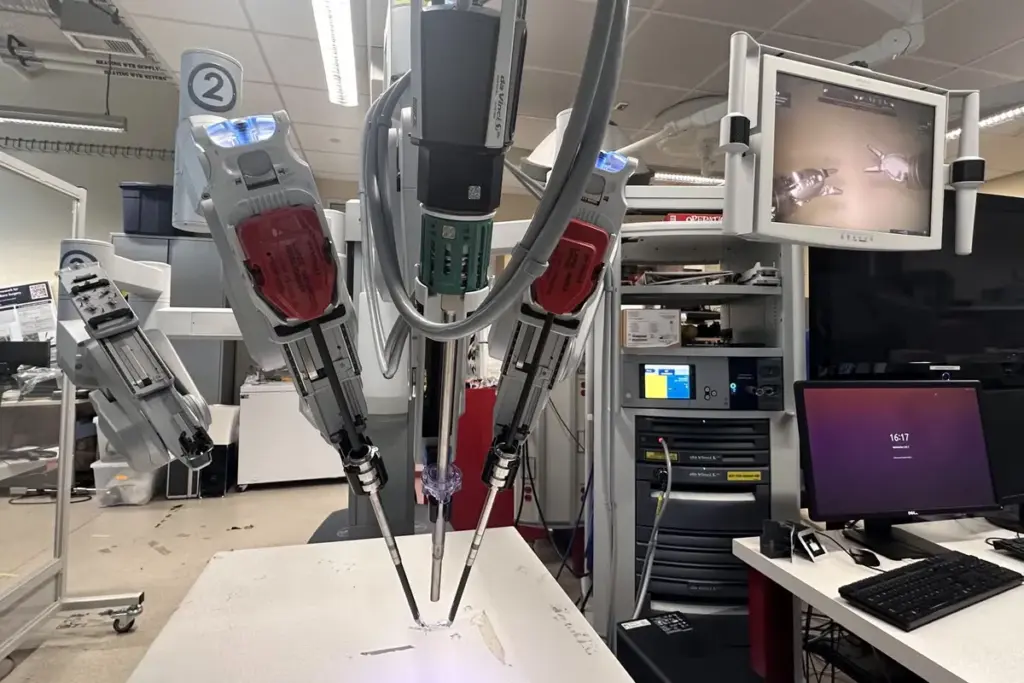

Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, has changed the medical world. It uses a surgical robot for precise, less invasive procedures. This method could mean less damage to tissues and less pain after surgery.
With a robotic surgery machine, surgeons can do operations more accurately. This leads to less scarring and quicker healing times. So, patients might feel less pain and discomfort while they get better.
Key Takeaways
- Robotic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure.
- It can reduce pain, scarring, and recovery time.
- The use of surgical robots enhances precision and control.
- Patients may experience less postoperative pain.
- Faster recovery times are potentially achievable.
Understanding Robotic Surgery: A Modern Surgical Approach
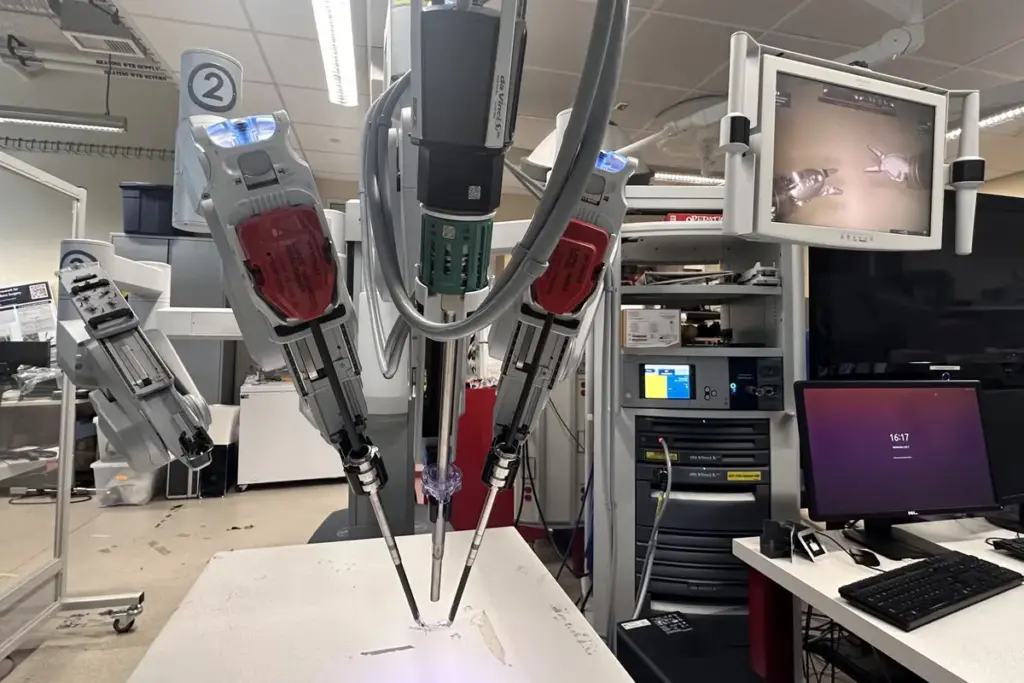

Robotic surgery is changing how we do surgery. It uses advanced tech for better results. This method is known for its precision, less invasion, and faster healing.
What Defines Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery, or robot-assisted surgery, makes complex procedures easier and more accurate. It uses a robotic system controlled by the surgeon. This system has a 3D camera and precise instruments.
Key features of robotic surgery include:
- Enhanced visualization through high-definition 3D imaging
- Increased precision and dexterity
- Minimally invasive, reducing tissue trauma and promoting faster healing
- Improved ergonomics for surgeons, reducing fatigue
Evolution of Surgical Robotics
Robotic surgery has grown a lot since the 1980s. The first system was approved by the FDA in 2000. Since then, tech has improved, making surgery better.
The evolution of surgical robotics has seen big improvements in:
- Visualization and imaging
- Instrument design and functionality
- Surgeon interface and control systems
Common Types of Robotic Surgical Systems
There are many robotic surgical systems, each for different procedures. Some top systems include:
|
System |
Application |
Key Features |
|---|---|---|
|
da Vinci Surgical System |
General surgery, urology, gynecology, cardiothoracic surgery |
High-definition 3D visualization, EndoWrist instruments |
|
Robotic Surgical System XYZ |
Orthopedic surgery, neurosurgery |
Precision instruments, advanced navigation |
Robotic surgery is getting better, with new tech coming. This will lead to more advanced systems and more uses in surgery.
“The future of surgery is robotic. It’s not just about the technology; it’s about improving patient outcomes and enhancing the surgical experience.”
Renowned Surgeon
Pain in Surgery: Traditional vs. Robotic Approaches
It’s important to know how traditional and robotic surgery differ in pain. The method used can greatly affect how much pain a patient feels. This is true both during and after the surgery.
Sources of Pain in Conventional Surgery
Traditional surgery uses big cuts to reach the area needing surgery. This can cause a lot of damage to tissues, leading to pain after surgery. The bigger the cut, the more damage and the longer recovery time.
Tissue trauma and larger incisions are main causes of pain in traditional surgery. The damage causes inflammation and irritation, leading to pain. Also, using tools like retractors can add to the pain.
How Robotic Surgery Differs in Pain Causation
Robotic surgery uses small cuts for its tools and camera. This approach causes less damage to tissues, leading to less pain after surgery. The tools used in robotic surgery are very precise, which helps avoid more damage.
The precision and minimal invasiveness of robotic surgery make it different from traditional surgery in pain. Smaller cuts and less tissue damage mean less pain after surgery.
Comparative Pain Studies and Research Findings
Many studies have looked at pain after traditional and robotic surgery. These studies show robotic surgery often leads to less pain and quicker recovery times.
|
Surgical Approach |
Postoperative Pain Level |
Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
|
Traditional Open Surgery |
High |
Longer |
|
Robotic Surgery |
Lower |
Shorter |
Studies support that robotic surgery can cause less pain and faster recovery. This is because it’s less invasive and precise.
The Patient Experience During Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery can seem scary, but knowing what to expect can help. The experience includes the anesthesia, sensations during surgery, and what happens right after.
Anesthesia in Robotic Procedures
Most patients get general anesthesia for robotic surgery. This keeps them pain-free during the surgery. It’s a key part of the experience, making complex surgeries easier.
An anesthesiologist will give the anesthesia and watch the patient’s vital signs. This ensures the patient’s safety and comfort during the surgery.
Sensations During the Operation
Since patients are under general anesthesia, they don’t feel anything during the surgery. The robotic surgery machine or surgery robot is controlled by the surgeon. This allows for precise and accurate work.
Even though patients are asleep, they might feel pain or discomfort later. This is managed through care after the surgery.
Immediate Post-Operative Experience
After surgery, patients go to the recovery room. They are watched as they wake up from the anesthesia. The robot-assisted surgery method often means less pain and smaller cuts.
- Patients may feel pain or discomfort, which is treated with medication.
- Swelling or bruising can happen but usually goes away on its own.
- Some might feel drowsy or confused from the anesthesia, but this usually goes away in a few hours.
Knowing what to expect during robotic surgery can ease worries. Understanding anesthesia, sensations during surgery, and what happens right after can help patients prepare for their surgery.
Minimally Invasive Nature of Robotic Surgery and Pain Reduction
Robotic surgery is changing how we think about surgery. It makes operations less invasive, which means less pain for patients. This new way of surgery uses robots to make procedures less invasive, helping patients recover faster and feel better.
Smaller Incisions and Reduced Trauma
Robotic surgery uses smaller incisions than old methods. This means less damage to the body. Patients feel less pain and heal quicker because of it.
Precision and Tissue Preservation
Robotic systems are very precise. They allow for meticulous dissection and preservation of tissues. This precision means less damage to healthy tissues, which helps reduce pain after surgery.
Impact on Post-Surgical Pain
The small incisions and precise handling in robotic surgery greatly reduce pain after surgery. Patients often say they feel less pain than those who had traditional surgery. This is because robotic surgery causes less damage to the body.
|
Aspect |
Robotic Surgery |
Traditional Surgery |
|---|---|---|
|
Incision Size |
Smaller |
Larger |
|
Tissue Trauma |
Less |
More |
|
Postoperative Pain |
Reduced |
Higher |
Robotic surgery offers many benefits, including less pain after surgery. It’s a big step forward in surgery. It helps patients make better choices and improves their outcomes.
Post-Operative Pain Management After Robotic Surgery
The success of robotic surgery is not just about the procedure. It’s also about managing pain after surgery. Good pain management is key for a smooth recovery.
Robotic surgery is less invasive than traditional surgery. This means less damage and trauma. But, managing pain after surgery is still very important.
Standard Pain Control Protocols
After robotic surgery, pain control usually involves a mix of methods. This multi-modal approach aims for the best pain relief.
Multi-modal pain management includes medicines and non-medical ways to reduce pain. The goal is to lessen pain and speed up recovery.
Medication Options and Approaches
Medicine is a big part of managing pain after robotic surgery. The right medicine depends on the surgery, the patient’s health, and how much pain they have.
- Opioids: Used for severe pain, but can lead to addiction and side effects.
- NSAIDs: Help with pain and swelling, often used with opioids.
- Acetaminophen: Good for mild to moderate pain, often mixed with other medicines.
|
Medication Type |
Use |
Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
|
Opioids |
Acute pain management |
Morphine, Oxycodone |
|
NSAIDs |
Reducing inflammation and pain |
Ibuprofen, Naproxen |
|
Acetaminophen |
Mild to moderate pain |
Tylenol |
Non-Pharmaceutical Pain Management
There are also non-medical ways to manage pain. These include:
- Physical Therapy: Gentle exercises can help with pain and mobility.
- Relaxation Techniques: Deep breathing, meditation, and guided imagery can reduce stress and pain.
- Cold Therapy: Cold packs on the surgical site can help with swelling and pain.
By using these methods together, healthcare providers can create personalized pain plans. These plans help patients after robotic surgery.
Recovery Timeline and Pain Progression
After robotic surgery, recovery times vary. Pain levels during this time are a big worry for many. Knowing what to expect can ease anxiety and prepare patients for what’s ahead.
First 24-48 Hours After Surgery
The first 24-48 hours after surgery are key. Patients are watched closely for any immediate issues. Pain management is a top priority, with meds given to control pain. It’s normal to feel some pain, discomfort, or numbness at the surgery site.
First Week of Recovery
In the first week, patients start to feel better. Pain levels usually drop, but some discomfort may stay. Gradual mobilization and sticking to a rehab plan help a lot. Patients are told to avoid hard activities and follow a care plan.
Long-Term Pain Resolution
Over time, most patients see a big drop in pain. The minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery means less tissue damage and pain. While recovery times vary, most people feel more comfortable and less in pain as time goes on.
Recovery and pain levels after robotic surgery differ for everyone. Health, procedure complexity, and following care instructions affect recovery speed. Understanding these factors helps patients manage their recovery better.
Common Types of Robotic Surgery and Their Pain Profiles
Robotic surgery has become common, with each type having its own pain management needs. It offers patients less pain and quicker recovery times than traditional surgery. This is thanks to its minimally invasive nature.
Robotic Prostatectomy
Robotic prostatectomy treats prostate cancer by removing the prostate gland. It uses a robotic system for precise dissection and less blood loss. Studies show it leads to less pain and shorter hospital stays than open surgery.
Robotic Hysterectomy
Robotic hysterectomy removes the uterus for conditions like fibroids or prolapse. It uses small incisions, reducing blood loss and pain. Patients often feel less pain and can get back to normal faster than with traditional methods.
Robotic Cardiac Surgery
Robotic cardiac surgery uses robots for heart procedures like valve repair and bypass grafting. It causes less chest trauma, leading to less pain and faster recovery. But, pain management varies due to surgery complexity.
Robotic Gastrointestinal Surgery
Robotic GI surgery includes procedures like colectomies and gastric bypass. It causes less tissue damage, leading to less pain and quicker recovery. Patients often report less discomfort and can get back to normal activities sooner.
|
Type of Robotic Surgery |
Typical Postoperative Pain Level |
Average Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
|
Robotic Prostatectomy |
Mild to Moderate |
2-4 weeks |
|
Robotic Hysterectomy |
Mild |
3-6 weeks |
|
Robotic Cardiac Surgery |
Moderate to Severe |
6-12 weeks |
|
Robotic Gastrointestinal Surgery |
Mild to Moderate |
2-6 weeks |
The pain levels for robotic surgery vary by procedure and location. Knowing these differences helps manage patient expectations and pain management plans.
Patient Testimonials: Real Experiences with Robotic Surgery Pain
Patients who have had robotic surgery share their stories. These stories show both the good and the bad sides of this surgery. They help us understand what to expect when it comes to pain after robotic surgery.
Success Stories and Positive Experiences
Many patients say they had minimally invasive surgeries with less post-operative pain. For example, a patient who had robotic prostatectomy said they felt only mild pain during recovery. They needed very little medicine to manage it.
Another patient, who had robotic hysterectomy, had a quick recovery. She was back to her usual activities in a few weeks. Her pain was much lower than she expected.
Challenging Recovery Accounts
But not everyone’s story is the same. Some patients faced a tougher recovery with higher-than-expected pain levels. For instance, a patient who had robotic cardiac surgery felt some pain. They needed more time to manage their pain.
These different experiences show how important personalized care is. Patients should talk to their doctors about what they expect and worry about.
Factors Affecting Individual Pain Experiences
Several things can affect how much pain someone feels after robotic surgery. These include the type of procedure, the patient’s overall health, and the surgical team’s experience. Knowing these can help set realistic pain expectations and manage it better.
- The complexity and duration of the surgery
- The patient’s pre-existing health conditions
- The skill and experience of the surgical team
By understanding these factors and learning from others, people can prepare for the pain of robotic surgery. They can also work with their doctors to manage it.
Surgeon Perspectives on Pain in Robotic Surgery
Surgeons share their views on pain management in robotic surgery. They play a key role in managing pain and setting patient expectations before, during, and after surgery.
Expert Opinions on Patient Pain Management
Surgeons say managing pain requires a team effort. They believe it starts with talking to patients before surgery. It continues through the surgery and after.
- Pre-surgical counseling to set realistic pain expectations
- Tailored anesthesia plans to minimize discomfort during surgery
- Post-operative pain management protocols that may include a combination of medication and non-pharmaceutical approaches
Surgical Techniques to Minimize Discomfort
Surgeons use many methods to reduce pain during robotic surgery. These include:
- Precision in surgical techniques to reduce tissue trauma
- Utilization of advanced robotic systems that allow for more precise dissections and suturing
- Minimally invasive approaches that result in smaller incisions and less post-operative pain
These methods help surgeons avoid complications and speed up recovery.
Communication About Pain Expectations
Good communication between surgeons and patients is key. Surgeons say it’s important to talk clearly about pain before, during, and after surgery.
Key aspects of communication include:
- Explaining the surgical process and potential sources of pain
- Discussing pain management options and creating a personalized plan
- Providing post-operative care instructions to manage pain effectively at home
By talking openly, surgeons help patients feel ready to handle pain after surgery.
Complications That May Increase Pain in Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery is a minimally invasive method. Yet, it carries risks of complications that can raise pain levels. Although rare, these issues can happen during or after surgery, making pain worse.
Potential Technical Issues
Technical problems during robotic surgery can cause more pain later. Issues like equipment failure or robotic system problems add complexity. Keeping equipment in good shape and training staff well are key to avoiding these problems.
- Equipment failure
- Software glitches
- Inadequate training of surgical staff
Patient-Specific Risk Factors
Some factors can raise the risk of complications in robotic surgery. These include pre-existing medical conditions, obesity, and previous surgeries. Knowing these risks helps manage pain after surgery.
- Pre-existing conditions like diabetes or heart disease
- Previous surgical history
- Obesity and its related health issues
Managing Unexpected Pain Complications
When complications happen, managing pain is crucial. This might mean changing pain medication, trying other pain relief methods, or sometimes needing more surgery.
Handling unexpected pain complications needs a detailed plan. This includes:
- Keeping a close eye on the patient’s health
- Changing treatment plans as needed
- Using both medicine and non-medicine pain relief
Understanding potential complications and how to manage them helps patients prepare for robotic surgery and recovery.
Preparing for Robotic Surgery: Pain Management Planning
Creating a personalized pain management strategy is key for robotic surgery prep. It helps patients manage pain after surgery better. This makes their recovery smoother.
Pre-Surgical Discussions About Pain
Talking about pain before surgery is crucial. Patients should share their pain limits, past pain experiences, and worries. This helps doctors create a pain plan that fits the patient.
These talks also let patients know about pain relief options. This includes medicines and non-medical ways to ease pain. Being informed helps patients make better care choices.
Setting Realistic Expectations
It’s important to set realistic pain expectations. Patients should know some pain is normal after surgery. But, the right plan can manage it well.
Doctors should guide patients on what to expect during recovery. Clear advice helps patients prepare better. This reduces anxiety and improves recovery outcomes.
Creating a Personalized Pain Management Plan
A personalized pain plan considers the patient’s health history, surgery type, and preferences. This ensures pain is managed well. It also lowers the chance of complications and aids in a quicker recovery.
The plan might include different pain relief methods. For example, multimodal analgesia uses various pain medicines. Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or physical therapy can also be suggested to help manage pain.
Future Developments in Robotic Surgery and Pain Reduction
Robotic surgery is on the verge of a new era. Innovations aim to reduce patient discomfort. We can look forward to big steps in robotic surgery and pain management.
Emerging Technologies in Surgical Robotics
The next wave of robotic surgical systems will be more precise and flexible. They will have improved dexterity and better visualization. This means surgeons can do complex tasks with more accuracy.
One exciting development is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in robotic surgery. AI can predict complications and make surgical tasks more precise.
Research Directions in Pain Management
Research is underway to find better ways to manage pain. It’s looking into new pharmacological agents and non-pharmacological interventions. These will help reduce pain after surgery.
There’s also a focus on personalized pain management plans. These plans are made for each patient. They aim to reduce pain and lower the chance of opioid addiction.
Potential Improvements in Patient Comfort
The future of robotic surgery looks bright for patient comfort. Advances in technology and pain management will lead to shorter recovery times and less post-operative pain.
Using enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocols with robotic surgery will also help. These protocols aim to reduce stress and promote faster recovery.
Conclusion
Robotic surgery has changed the medical world. It brings a new way to operate that cuts down on pain and speeds up recovery. This method uses small cuts and advanced tech, making it a great choice for those wanting less pain after surgery.
Robotic surgery has many benefits. It uses smaller cuts, is very precise, and helps save tissue. This means less pain and trauma for patients. For example, robotic prostatectomy and hysterectomy have shown to reduce pain effectively.
Knowing how robotic surgery is different from traditional surgery helps patients choose the right treatment. Good pain management plans, made before surgery, make the experience better. This includes talking about pain and creating a plan just for the patient.
As robotic surgery keeps getting better, patients will see even better results. It’s a great way to reduce pain and speed up recovery. This makes it a good choice for those thinking about surgery.
FAQ
What is robotic surgery?
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, uses a robotic system for surgery. It’s known for its precision and is less invasive.
How does robotic surgery differ from traditional surgery in terms of pain?
Robotic surgery causes less tissue damage and has smaller incisions. This can lead to less pain after surgery.
What types of surgeries are commonly performed using robotic systems?
Robotic surgery is used for many surgeries. These include prostatectomy, hysterectomy, cardiac surgery, and gastrointestinal surgery. Each has its own pain level.
How is pain managed after robotic surgery?
After robotic surgery, pain is managed with standard protocols and medication. Non-pharmaceutical methods are also used to control pain.
What is the typical recovery timeline after robotic surgery?
Recovery starts with pain reduction in 24-48 hours. Pain continues to decrease in the first week. Eventually, pain goes away.
Are there any potential complications that may increase pain during or after robotic surgery?
Yes, complications like technical issues and patient-specific risks can increase pain. Proper care and planning can manage these issues.
How can patients prepare for robotic surgery to minimize pain?
Patients can prepare by discussing pain with their doctor. They should set realistic expectations and create a pain management plan.
What advancements are being made in robotic surgery to reduce pain?
New technologies and research are exploring ways to improve comfort and reduce pain in robotic surgery.
Is robotic surgery painful during the operation?
No, patients are under anesthesia during robotic surgery. They don’t feel pain during the operation.
How does the precision of robotic systems impact pain?
Robotic systems’ precision helps preserve tissue and reduce damage. This leads to less pain after surgery.
Can robotic surgery be used for all types of surgical procedures?
Robotic surgery is versatile but not used for all procedures. Its use depends on the case and the surgeon’s judgment.
Reference
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9314304/





