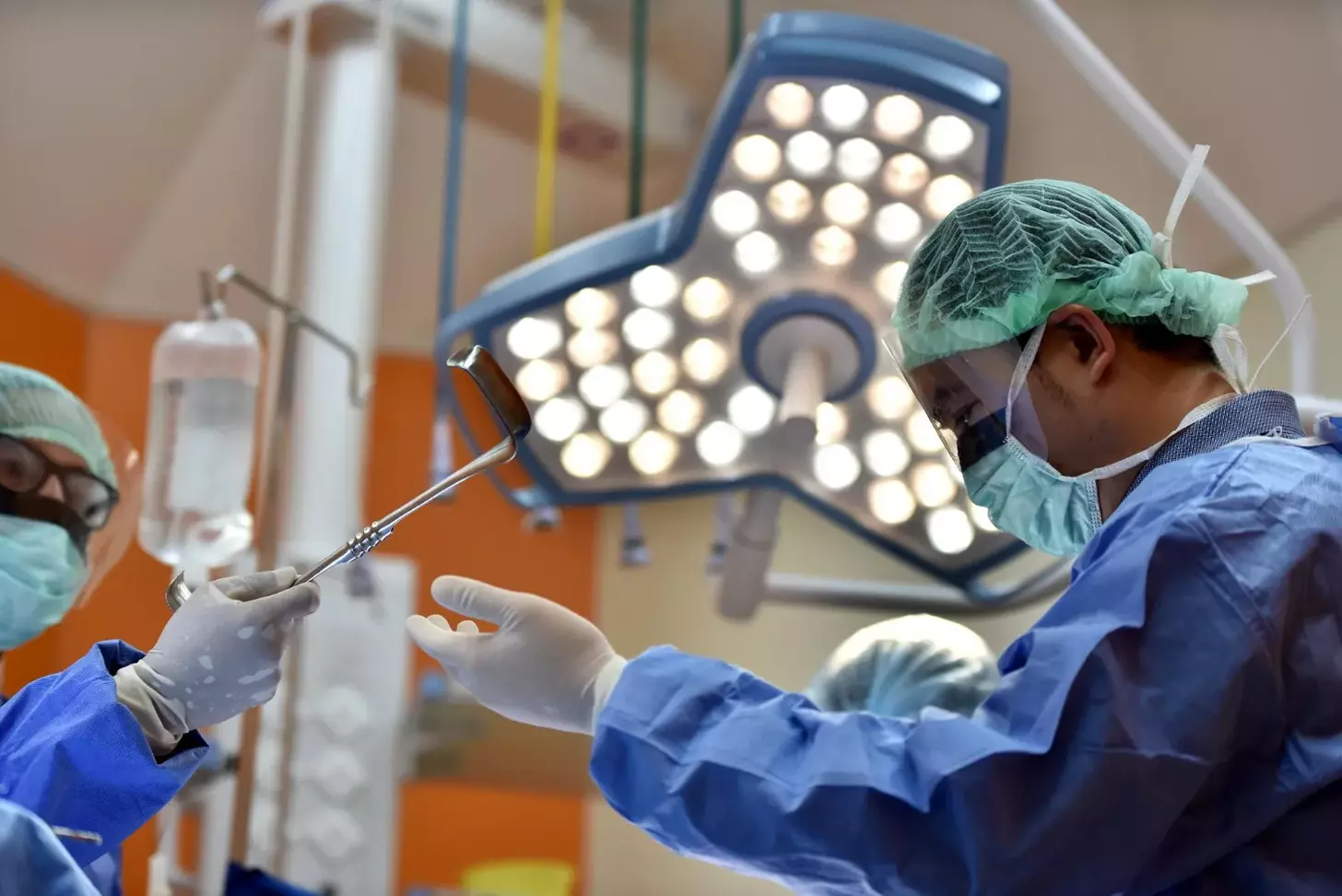
Getting a brain tumor diagnosis can feel scary. But knowing your treatment options is key. At Liv Hospital, we focus on you, following the best global practices. We help you figure out if removing a brain tumor is safe.
New ways in brain cancer surgery have made treatments better. We use cutting-edge methods to treat you more effectively. For example, removing benign brain tumors can succeed 90-95% of the time if the whole tumor is taken out.
Every patient is different, and surgery’s success depends on many things. The tumor’s spot, size, and type matter a lot. Our team is dedicated to giving you care that fits you, supporting you every step of the way.
Key Takeaways
- Advances in surgical techniques have improved brain tumor removal success rates.
- Benign brain tumor removal can have a success rate of 90-95% with full resection.
- The feasibility of surgery depends on tumor location, size, and type.
- Liv Hospital provides patient-centered care and adheres to international best practices.
- Personalized treatment plans are developed based on individual patient needs.
Understanding Brain Tumors and Their Classification
Brain tumors are divided into two main types: benign and malignant. This division is key for making treatment decisions. Tumors can grow slowly or quickly, and some can be very dangerous.
Types of Brain Tumors: Benign vs. Malignant
Benign tumors grow slowly and don’t spread to other tissues. But, they can cause problems because of where they are. Malignant tumors, on the other hand, grow fast, spread, and can be deadly. We sort tumors by where they come from, how fast they grow, and other traits.
Key differences between benign and malignant brain tumors include:
- Growth rate: Benign tumors grow slowly, while malignant tumors grow rapidly.
- Invasion: Benign tumors typically do not invade surrounding brain tissue, whereas malignant tumors often do.
- Metastasis: Benign tumors do not metastasize, but some malignant tumors can spread to other parts of the brain or spine.
Common Symptoms and Diagnostic Approaches
Symptoms of brain tumors vary a lot. They can include headaches, seizures, and changes in thinking. Doctors use CT scans and MRI to find tumors. Sometimes, they take a sample of the tumor for more information.
For example, a silent brain tumor might not show symptoms until it’s big. This shows why we need good ways to find tumors early.
Initial Assessment for Treatment Options
When we first look at a brain tumor, we check its type, size, and where it is. We also look at the patient’s overall health. This helps us choose the best treatment, like surgery or radiation.
Knowing how to classify and understand brain tumors is key for picking the right treatment. We use tests and check-ups to make a plan that fits each patient’s needs.
The Science of Cerebral Tumor Surgery
The science of cerebral tumor surgery is advancing fast. New techniques and technologies are being developed to improve treatment. This means better outcomes for patients with brain tumors, giving them hope for successful treatment.
Historical Development of Neurosurgical Techniques
Neurosurgery has made huge strides over the years. Advances in technology, imaging, and understanding of the brain have driven this progress. “The development of neurosurgical techniques is a story of continuous innovation,” says a leading neurosurgeon.
Brain surgery used to be very risky with low success rates. But, modern imaging like MRI and CT scans has changed that. Now, surgeons can accurately locate and assess brain tumors, leading to more precise and effective surgeries.
Modern Surgical Approaches for Brain Masses
Today, there are many advanced surgical options for brain masses. These include traditional open craniotomy, minimally invasive techniques, and awake brain surgery. Each method has its benefits and is chosen based on the tumor and patient’s health.
A recent study found that advanced technologies like intraoperative MRI and navigation systems have greatly improved brain tumor surgery. These tools help surgeons remove tumors more effectively while protecting surrounding brain tissue.
The Surgical Decision-Making Process
Choosing the right surgery for a cerebral tumor is complex. It involves looking at the tumor’s location, size, and type, as well as the patient’s health and medical history. Neurosurgeons work with other healthcare professionals to create a treatment plan that balances risks and benefits.
As neurosurgery advances, the decision-making process is getting more detailed. By combining clinical knowledge with the latest technology, we can offer patients the best possible outcomes and improve their quality of life.
When Can a Brain Tumor Be Removed?
Deciding to remove a brain tumor is complex. It depends on several key factors. We know that the thought of brain surgery can be scary. But knowing what makes a tumor operable can help.
Factors Determining Operability
The chance to remove a brain tumor depends on its type, location, size, and how it grows. Tumors that are benign and well-defined are generally more likely to be removed successfully. But malignant tumors or those that spread out in the brain may be harder to remove.
A study in the neurosurgery journal says,
“The location and size of the tumor are critical factors in determining the feasibility of surgical removal.”
This shows how important it is to check the tumor before surgery. It helps plan the best treatment.
Critical Role of Tumor Location
The location of a brain tumor is very important. Tumors near important brain areas, like those controlling speech or movement, may not be operable. But tumors in easier-to-reach areas might be operable.
- Tumors near critical brain structures may need special surgery.
- Advanced imaging and navigation technologies help surgeons remove tumors more precisely.
Size and Growth Pattern Considerations
The size and growth of a brain tumor also matter. Large or fast-growing tumors may need quick action. But small, slow-growing tumors might be watched or treated differently.
| Tumor Characteristic | Operability Consideration |
|---|---|
| Size | Large tumors may be more challenging to remove completely. |
| Growth Pattern | Rapidly growing tumors may necessitate urgent surgical intervention. |
We know each patient is different. The choice to have brain tumor removal surgery is made carefully. It considers the tumor’s details and the patient’s health.
Understanding Inoperable Brain Tumors
It’s important for patients and doctors to understand inoperable brain tumors. These tumors can’t be safely removed by surgery. Their location, size, or other factors make them inoperable. This affects how they are treated.
Defining “Inoperable” Brain Masses
An “inoperable” brain tumor is one that can’t be safely removed. Doctors decide this based on the tumor’s location and the patient’s health. Tumors near important brain areas are often inoperable.
High-Risk Locations in the Brain
Some brain areas are too risky for surgery. Tumors in these spots, like the brainstem, are big challenges. Surgeons must weigh the risks and benefits of surgery here.
Some high-risk spots include:
- The brainstem, which controls vital functions like breathing and heart rate.
- Motor control areas, where damage could lead to big neurological problems.
- Areas for speech and language processing.
Partial Removal Considerations
Partial removal might be an option for some tumors. This is when removing the whole tumor is too risky. The goal is to shrink the tumor, ease symptoms, and make other treatments work better.
A leading neurosurgeon says, “The decision to perform partial removal requires careful consideration of the benefits and risks.” We help patients decide the best option for them.
After partial removal, treatments like radiation or chemotherapy might follow. This combo can help patients with inoperable tumors.
Success Rates of Brain Tumor Removal
Brain tumor removal success rates change a lot based on the tumor’s type and details. It’s key for patients and doctors to know these rates to choose the best treatment.
Benign Tumor Removal Success
Removing benign brain tumors works well, with 90-95% of patients seeing good results. These tumors are clear and simple to take out. Their success comes from being non-cancerous and fully removable.
Malignant Tumor Removal Outcomes
Removing malignant tumors is harder and depends on many things. Like where the tumor is, how big it is, and its grade. Surgery can remove a lot of the tumor, but success rates are lower than for benign tumors. After surgery, treatments like radiation and chemotherapy help get rid of any left-over cells.
Glioblastoma: Surgical Impact on Survival
Glioblastoma is a tough malignant brain tumor. Surgery can help, but survival chances are not great. Below is a table showing survival rates for glioblastoma patients after surgery.
| Time Post-Surgery | Median Survival Rate | Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Year | 50% | 30-70% |
| 2 Years | 20% | 10-30% |
| 5 Years | 5% | 2-10% |
Every patient is different, and surgery success depends on many factors. Our team works hard to give full care and support during treatment.
Brain Surgery Tumor Removal Techniques
Today, neurosurgeons have many ways to remove brain tumors. Each method is chosen based on the tumor’s size, location, and type. The patient’s health also plays a big role.
Traditional Open Craniotomy
Open craniotomy is a common method. It involves removing part of the skull to reach the tumor. This way, the tumor can be seen and removed directly. Its main benefits are:
- Direct access to the tumor
- Ability to remove large or complex tumors
- Established technique with a high success rate
But, it also has risks like infection, bleeding, and damage to brain tissue.
Minimally Invasive Approaches
Minimally invasive methods, like endoscopic surgery, are alternatives. They use smaller cuts and disturb less brain tissue. The advantages are:
- Smaller scars
- Less post-operative pain
- Shorter recovery times
These methods work well for tumors near the brain’s surface or in easy-to-reach areas.
Awake Brain Surgery for Functional Preservation
Awake brain surgery is used for tumors in key brain areas. The patient stays awake during the surgery. This lets the team watch brain function live. This method helps:
- Maximize tumor removal
- Minimize damage to critical brain areas
- Preserve important brain functions
This surgery needs a team of experts, including neurosurgeons, anesthesiologists, and neuropsychologists.
Advanced Technologies in Brain Tumor Resection
Advanced technologies are changing how brain tumors are removed. They bring new hope to patients everywhere. These new tools make brain tumor surgery more precise and effective.
Intraoperative MRI and Navigation Systems
Intraoperative MRI lets surgeons see the tumor in real-time during surgery. This helps them check how much of the tumor they’ve removed and make changes if needed. Navigation systems help find the tumor and important brain areas, making the surgery safer and more effective.
Benefits of Intraoperative MRI: It helps remove as much of the tumor as possible while protecting the brain.
Fluorescence-Guided Surgery
Fluorescence-guided surgery uses special dyes that make tumors glow. This makes it easier to see and remove the tumor. It also helps avoid damaging healthy brain tissue.
Advantages of Fluorescence-Guided Surgery: It helps see the tumor’s edges better, leading to more complete removals.
Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy
Laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT) uses laser heat to kill tumor cells. It’s great for tumors in hard-to-reach or sensitive brain areas.
Key Benefits of LITT: It’s a less invasive option than open surgery, which can lead to faster recovery and fewer brain problems.
The Brain Mass Removal Process
Understanding the brain mass removal process is key for patients and doctors. This complex procedure has several important steps. Each step is vital for the best results.
Preoperative Preparation and Planning
Before surgery, detailed preparation is vital. We do a full check-up, including MRI or CT scans. This helps us plan the surgery and manage risks.
Patients also have tests to check their health. We talk about what to expect and any worries they have.
The Surgical Procedure Step-by-Step
The surgery for removing brain mass is very detailed. We start by giving anesthesia for comfort. Then, we make a scalp incision and remove a part of the skull.
With advanced tools, we find and remove the tumor. We aim to take out as much as we can without harming the brain.
Immediate Post-Surgical Care
After surgery, we watch the patient in the ICU. We focus on pain management, infection prevention, and swelling control.
We check the patient’s brain function and recovery. We adjust the care plan to help them heal well.
Recovery After Brain Tumor Removal Surgery
Recovering from brain tumor surgery is a long journey. It includes time in the hospital, rehabilitation, and managing side effects. We know this time is very important for patients and they need a lot of support.
Hospital Recovery Timeline
The time spent in the hospital after surgery varies. It depends on the surgery’s complexity and the patient’s health. Usually, patients stay for a few days to a week.
In the hospital, we watch the patient’s brain function closely. We manage their pain and look for any complications. The medical team also teaches them about caring for themselves after surgery and starting their rehabilitation.
| Day | Typical Activities | Care Focus |
|---|---|---|
| 1-2 | Rest, initial mobility | Pain management, neurological monitoring |
| 3-5 | Physical therapy begins, increased mobility | Wound care, complication surveillance |
| 6-7 | Discharge planning, patient education | Rehabilitation planning, medication management |
Long-term Rehabilitation Needs
After leaving the hospital, the recovery journey continues. This part is key for getting stronger, improving thinking, and adjusting to surgery changes.
Rehabilitation may include:
- Physical therapy to improve mobility and balance
- Occupational therapy to regain daily living skills
- Speech therapy if there are difficulties with speech or swallowing
- Cognitive rehabilitation to address memory or concentration issues
Managing Potencial Side Effects
Handling side effects is a big part of recovery. Common ones are tiredness, headaches, and brain changes. We help patients manage these with medicine, lifestyle changes, and therapy.
It’s important for patients and their caregivers to know about possible side effects. They should talk to their healthcare team if they have any worries.
Breakthrough Treatments for Inoperable Brain Tumors
New medical technologies are changing how we treat inoperable brain tumors. These advances give hope to patients who once had few options. We’re seeing big improvements in treatments, making life better for these patients.
Radiation Therapy Advancements
Radiation therapy is key in fighting brain tumors. New methods like Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) and Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) are more precise. They deliver strong doses right to the tumor, protecting healthy tissue.
These new methods lead to better results and fewer side effects. This makes radiation therapy a better choice for patients with inoperable brain tumors.
Targeted Chemotherapy Approaches
Targeted chemotherapy is another big step forward. It attacks cancer cells directly, leaving normal cells alone. This reduces side effects and boosts treatment success.
Drugs like Bevacizumab are showing great promise. They slow tumor growth and improve patient outcomes. Researchers are working on even better targeted therapies.
Dual-Target CAR T Cell Therapies
CAR T cell therapy is a new hope for cancer, including brain tumors. Dual-target CAR T cell therapies target two proteins on cancer cells. This makes the therapy more effective and less likely to fail.
Early trials are showing promising results. Some patients have seen big reductions in tumors. While more research is needed, dual-target CAR T cell therapies could be a game-changer.
These new treatments are changing brain tumor care. They offer hope and better outcomes for patients. As research keeps advancing, we’ll see even more innovative treatments for these patients.
Conclusion: Navigating Brain Tumor Treatment Decisions
Choosing a treatment for brain tumors is tough for both patients and doctors. It’s key to know the different treatments and what they mean. We’ve looked into brain tumors, how they’re classified, diagnosed, and treated.
When picking a treatment, it’s important to think about the good and bad sides. Things like where the tumor is, how big it is, and how fast it grows matter a lot. We talked about different surgeries, like open craniotomy and newer, less invasive methods. We also mentioned using advanced tools like intraoperative MRI and fluorescence-guided surgery.
It’s important for patients to make choices based on good information. We think patients should know a lot about their condition and the treatment choices. Doctors and healthcare teams work with patients to help them through treatment. This way, patients can make the best decisions for their care.
What is cerebral tumor surgery?
Cerebral tumor surgery is a complex procedure. It involves removing a tumor from the brain. This surgery requires great skill to ensure the best results for patients.
Can all brain tumors be removed surgically?
No, not all brain tumors can be removed surgically. Whether surgery is possible depends on the tumor’s location, size, and type.
What are the success rates for benign tumor removal?
The success rate for removing benign tumors is high, around 90-95%. This makes surgery a good option for many patients with benign brain tumors.
What are inoperable brain tumors?
Inoperable brain tumors are those that can’t be safely removed surgically. This is due to their location, size, or other factors. Treatment options include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or other alternatives.
What are the different surgical techniques used for brain tumor removal?
Different techniques are used for brain tumor removal. These include traditional open craniotomy, minimally invasive approaches, and awake brain surgery. Each has its own benefits and considerations.
What is intraoperative MRI, and how is it used in brain tumor surgery?
Intraoperative MRI is a technology used during surgery. It provides real-time imaging to help surgeons remove tumors more accurately.
What is the recovery process like after brain tumor removal surgery?
Recovery after brain tumor surgery varies. It includes a hospital stay and long-term rehabilitation. Patients also need to be monitored for side effects.
Are there breakthrough treatments being developed for inoperable brain tumors?
Yes, new treatments are being developed for inoperable brain tumors. These include advancements in radiation therapy, targeted chemotherapy, and CAR T cell therapies.
How is the decision made to remove a brain tumor surgically?
Deciding to remove a brain tumor surgically involves many factors. These include the tumor’s location, size, and type, as well as the patient’s health and medical history.
What is the role of neurosurgeons in brain tumor treatment?
Neurosurgeons are key in treating brain tumors. They perform surgeries to remove tumors and relieve symptoms.
Can brain tumor surgery be performed using minimally invasive techniques?
Yes, some brain tumor surgeries use minimally invasive techniques. This can lead to less tissue damage and faster recovery.
What are the possible side effects of brain tumor removal surgery?
Side effects of brain tumor surgery can include neurological deficits, seizures, and cognitive changes. It’s important to monitor and support patients during recovery




































