
More than 26 million people worldwide face heart failure. This condition is very deadly. But, artificial hearts might help. They could make people live longer and feel better.
We look into how this new tech can help. It might make life longer and better for those with heart failure. Our team provides high-quality medical care that prioritizes patient needs and outcomes. We support patients from all over the world.
Key Takeaways
- Artificial hearts offer a promising solution for individuals with severe heart failure.
- Improved survival rates and quality of life are associated with artificial heart treatment.
- Advanced medical treatments and support are available for international patients.
- Cardiovascular health is key to overall well-being.
- Heart transplant and treatment options are getting better with new tech.
The Evolution of Artificial Hearts
The journey of artificial hearts from ideas to real medical tools shows our creativity and progress in medicine. These devices have grown from simple designs to complex systems that keep people alive. This change is a big part of medical history.
Early Developments and Pioneering Research
At first, scientists aimed to make a device that could replace the heart, either partly or fully. They made big steps in materials science, mechanical engineering, and biomedicine. The work of early researchers set the stage for future breakthroughs.
The idea of a mechanical heart started in the 1960s. This was when research into artificial heart technology really began. The first challenges were finding materials safe for the body and making a device that worked like the real heart.
The First Successful Artificial Heart Implantation
The first time an artificial heart was successfully put in a person was a big deal. It showed that artificial heart tech could work. This success opened doors for more research and use in treating heart failure.
The journey of artificial hearts is ongoing. Scientists keep working to make these devices last longer, work better, and improve life for patients. As medical technology gets better, we’ll see even more new things in this field.
Understanding Heart Failure and the Need for Mechanical Intervention
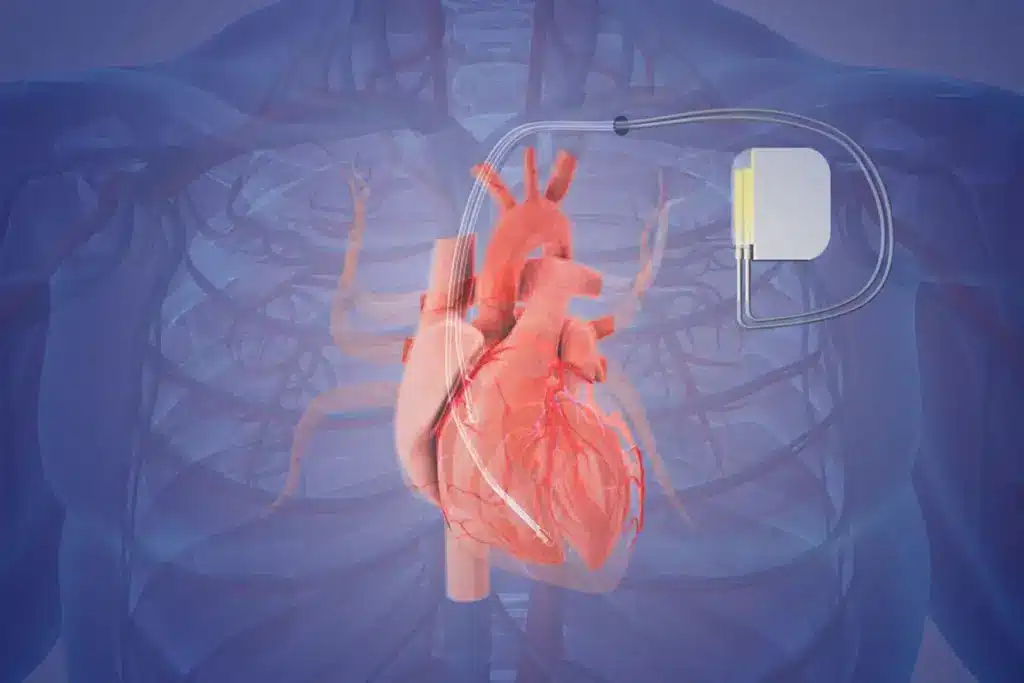
Heart failure is when the heart can’t pump enough blood. It’s a big problem, causing illness and death for millions. It really hurts cardiovascular health.
Many things can cause heart failure. These include heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and problems with heart valves. Knowing these causes helps us find better heart failure treatment plans.
Common Causes of Severe Heart Failure
Severe heart failure often comes from heart damage or too much work for the heart. The main causes are:
- Coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attacks and damage the heart muscle.
- Hypertension, or high blood pressure, which makes the heart work harder.
- Diabetes, which can harm the heart muscle and lead to heart failure.
- Heart valve problems, such as stenosis or regurgitation, which can make the heart less efficient.
As heart failure gets worse, it can really hurt your life and increase death risk.
When Traditional Treatments Fail
Traditional heart failure treatments include medicines, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery. But for many, these treatments don’t work well enough.
“For patients with advanced heart failure, mechanical intervention such as ventricular assist devices (VADs) or heart transplantation becomes necessary to improve survival and quality of life.”
When usual treatments don’t work, heart transplant or a ventricular assist device might be needed. These options can greatly improve life and survival chances.
|
Treatment Option |
Description |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Medications |
Drugs to manage symptoms and slow disease progression. |
Improved symptoms, slowed disease progression. |
|
Ventricular Assist Device (VAD) |
A mechanical pump that supports the heart’s function. |
Improved heart function, enhanced survival. |
|
Heart Transplant |
Surgical replacement of the diseased heart with a healthy donor heart. |
Significantly improved survival and quality of life. |
As we keep improving cardiovascular health care, using VADs and heart transplants is more important for managing heart failure.
How Artificial Heart Technology Works
Understanding artificial heart technology is key to seeing its impact on heart failure patients. Artificial hearts are complex, needing advanced mechanical parts and design. They work to pump blood like a real heart.
Mechanical Components and Design Principles
An artificial heart has pumps, valves, and sensors. These parts work together to pump blood. The design aims for a device that’s effective, durable, and fits well with the body.
Designing artificial hearts is tough. They must last a long time without breaking down. Advanced materials and making techniques help make them better and more reliable.
Power Sources and Operational Systems
Artificial hearts need power to work. This can come from inside or outside the body. Inside power, like batteries, makes moving easier. But outside power can lead to infections.
The systems that control artificial hearts are complex. They watch how the device works and change as needed. These systems can be set by hand or work on their own. They also give updates to patients and doctors, helping everyone involved.
Types of Artificial Heart Systems Available Today
Today, we have many artificial heart systems, each with its own benefits. They help patients with severe heart failure. These systems aim to improve their life quality and survival chances.
Total Artificial Hearts (TAH)
Total Artificial Hearts replace the whole heart when both ventricles are badly damaged. They are for patients waiting for a transplant or not suited for a ventricular assist device.
Key Features of TAH:
- Complete replacement of the heart
- Used for patients with severe biventricular failure
- Can be a bridge to heart transplantation
Ventricular Assist Devices (VADs)
Ventricular Assist Devices are mechanical pumps that help the heart pump blood better. They support one or both ventricles, based on the patient’s condition.
Types of VADs:
- Left Ventricular Assist Devices (LVADs)
- Right Ventricular Assist Devices (RVADs)
- Biventricular Assist Devices (BiVADs)
Emerging Technologies in Heart Replacement
The field of artificial hearts is growing fast, with new technologies on the horizon. These include:
- Biological heart substitutes
- 3D-printed hearts
- Advanced materials for better biocompatibility
These new ideas aim to make artificial hearts work better, last longer, and be more compatible with patients. They could change how we treat heart failure.
The Artificial Heart Experience: Patient Selection and Eligibility
The path to getting an artificial heart starts with checking if a patient is eligible. This involves looking at many factors to see if a patient can get an artificial heart transplant.
Medical Criteria for Candidacy
To qualify for an artificial heart, patients must meet certain medical standards. These include:
- Advanced Heart Failure: Patients usually have severe heart failure that other treatments can’t fix.
- Medical History: We look at the patient’s medical history to see if it could impact the success of the transplant.
- Current Health Status: We check the patient’s current health to see if there are any risks or complications.
We examine these factors to see if a patient is right for an artificial heart. Our goal is to make sure the patient will benefit from the transplant and have a better life.
Psychological and Support System Requirements
Being mentally ready and having a strong support system are also key for artificial heart patients. We look at:
- Psychological Evaluation: We do a deep psychological check to see if the patient is ready for the transplant and care after.
- Support System: Having a caring family or caregiver is vital for the patient’s recovery and ongoing care.
By looking at both medical and mental health, we find the best candidates for an artificial heart transplant.
Our team works closely with patients and their families to make sure they’re ready for what’s next. This way, we aim for the best results for those getting an artificial heart.
Comparing Artificial Hearts to Natural Hearts
Artificial hearts and natural hearts share some similarities but also have key differences. These differences highlight the progress and challenges in heart technology. Understanding these points is vital for better patient care and future advancements.
Functional Differences and Similarities
Artificial hearts aim to copy the natural heart’s function but do so differently. A natural heart is a muscle that pumps blood. An artificial heart is a machine that does the same job.
Some functional differences include:
- Power source: Natural hearts use the body’s energy, while artificial hearts need batteries or electrical connections.
- Pumping method: Natural hearts use muscle contractions, while artificial hearts use mechanical pumps.
- Adaptability: Natural hearts adjust their rate based on the body’s needs. Artificial hearts are getting better but have limits.
Despite these differences, there are similarities in their functions:
- Both aim to keep blood flowing and tissues oxygenated.
- They both strive for consistent blood flow to meet the body’s needs.
Limitations of Current Technology
Artificial hearts have come a long way but face several challenges. These include needing external power, the risk of mechanical failure, and possible complications like infection or blood clots.
Some key limitations of current artificial heart technology are:
- Need for external power, which can limit mobility and require frequent charging or replacement.
- Risk of mechanical failure, which can be dangerous and needs constant monitoring.
- Possible complications like infection, blood clots, or device failure, which require careful management.
Overcoming these challenges is essential for improving artificial heart technology. This will help patients live better lives and increase the technology’s benefits.
Can an Artificial Heart Extend Life Expectancy?
The question of whether an artificial heart can extend life expectancy is complex. We must look at survival statistics, clinical outcomes, and the quality of life for patients.
Survival Statistics and Clinical Outcomes
Clinical trials show artificial hearts can greatly improve survival for those with severe heart failure. Studies indicate patients with an artificial heart have a better survival rate than those without.
Survival rates are a major focus of research. Many studies show artificial hearts lead to better short-term and sometimes long-term survival.
Quality of Life Considerations
The quality of life for patients with an artificial heart is key. These devices can extend life but require big lifestyle changes. Patients must live with a device that needs regular care and checks.
Despite these challenges, many patients see their quality of life improve. They have more energy and fewer heart failure symptoms. Being able to do daily tasks without severe limits boosts patient satisfaction.
- Regular monitoring and maintenance are key.
- Lifestyle adjustments are needed but can improve well-being.
- Patient support systems are vital for quality of life.
Understanding survival statistics and quality of life helps us see how artificial hearts extend life and improve outcomes.
Success Stories: Living with an Artificial Heart
For many, an artificial heart is more than a device; it’s a second chance at life. Each person’s journey with an artificial heart is unique. It’s filled with challenges and triumphs.
Notable Cases and Patient Testimonials
There are many inspiring stories of patients with artificial hearts. One patient got a total artificial heart (TAH) and lived for years. They enjoyed time with family and experienced milestones they thought were lost forever.
“Receiving an artificial heart was a turning point in my life,” said a patient. “It gave me the chance to reconnect with loved ones and pursue activities I thought I’d have to give up.”
These stories show the medical success of artificial hearts. They also highlight the impact on patients’ quality of life.
Long-term Survivors and Their Experiences
Long-term survivors of artificial heart implantation share common themes. They talk about the importance of support systems and ongoing medical care. They also talk about adapting to a new lifestyle.
|
Aspect of Life |
Pre-Implantation |
Post-Implantation |
|---|---|---|
|
Physical Activity |
Limited due to heart failure |
Increased mobility and ability to perform daily tasks |
|
Social Interaction |
Often isolated due to health concerns |
Re-engagement with family and friends, participation in social activities |
|
Medical Care |
Frequent hospital visits, medication management |
Ongoing monitoring, device maintenance, and follow-up care |
The table shows the big changes in a patient’s life after getting an artificial heart. It shows how the technology can extend and improve life.
As we keep improving artificial heart technology, the stories of long-term survivors will inspire and inform us. They will help the medical community and the public.
The future of artificial hearts holds much promise. Research is ongoing to make devices last longer, reduce complications, and improve patient outcomes.
The Surgical Journey: Implanting an Artificial Heart
Getting an artificial heart transplant is a big change. It starts with a detailed surgical journey. A team of experts works together to help patients get better.
Pre-Operative Preparation
Before surgery, patients get checked to see if they’re a good fit for an artificial heart. They have tests like echocardiograms and blood work. These help doctors understand the heart’s condition and the patient’s health.
Key steps in pre-operative preparation include:
- Medical history review and physical examination
- Cardiac imaging and diagnostic tests
- Consultations with cardiologists, surgeons, and other specialists
- Education on the procedure, risks, and post-operative care
The Implantation Procedure
The surgery to put in an artificial heart is very complex. It involves removing the old heart and putting in the new one. The team must connect the artificial heart to the blood vessels carefully.
The surgical team must carefully connect the artificial heart to the patient’s blood vessels, ensuring proper fit and function.
A leading cardiac surgeon says, “The success of an artificial heart transplant depends on careful surgery and aftercare.”
“The implantation of an artificial heart is a significant milestone in the treatment of heart failure, giving new hope to patients with few options.”
Immediate Post-Operative Care
After surgery, patients are watched closely in the ICU. They are managed for pain, infection, and the artificial heart’s function. This care is vital for recovery.
Critical aspects of post-operative care include:
- Monitoring vital signs and device performance
- Administering medications to prevent rejection and infection
- Providing nutritional support and rehabilitation
- Educating patients and families on device management and lifestyle adjustments
As patients get better, they move to a regular room and then home. Follow-up care is key to check on the device and the patient’s health.
Life After Receiving an Artificial Heart
Getting an artificial heart is just the start. It opens a new chapter in life. People who get this surgery must learn to live differently.
Daily Maintenance Requirements
Keeping an artificial heart working right is a big job. It needs a lot of care every day. Here’s what’s involved:
- Checking the device’s power and making sure it’s charged
- Looking for any problems or wear
- Keeping the area where the device connects clean to avoid infection
- Going to regular check-ups with the doctor
Table: Daily Maintenance Tasks for Artificial Heart Patients
Lifestyle Adjustments and Limitations
Life with an artificial heart means big changes. It gives a second chance but has its limits. People must:
- Stay away from heavy lifting and hard work
- Watch out for things that could hurt the device
- Take a power source and tools when traveling
- Plan their day to fit in device care
It’s key to know these changes and limits to live well with an artificial heart. Following the care routine and adjusting to life helps people enjoy a better life.
|
Task |
Frequency |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
|
Device Check |
Daily |
Ensure proper functioning |
|
Driveline Site Care |
Daily |
Prevent infection |
|
Power Source Monitoring |
Continuous |
Avoid power loss |
Risks and Complications Associated with Artificial Hearts
Artificial hearts have made great strides, but they come with risks. Patients face medical and psychological challenges. It’s important for both patients and doctors to know about these risks.
Medical Complications
Patients with artificial hearts can face several health issues. Infection is a big worry, as it is with any medical device. Keeping the device clean and well-maintained can help prevent infections.
Bleeding is another risk, due to the blood thinners needed. Finding the right balance to prevent clots and bleeding is tricky. Doctors must manage this carefully.
Device malfunction is rare but serious. Thanks to new technology, artificial hearts are more reliable. But, they can fail. Regular checks and upkeep are key to avoiding this.
Psychological and Social Challenges
Living with an artificial heart also brings psychological and social hurdles. Anxiety and depression are common. Adjusting to life with a mechanical heart is tough.
The ongoing need for care and the device’s limitations can affect a patient’s life and social life. Support from loved ones and healthcare is essential. It helps patients deal with these challenges.
The social stigma of having a mechanical heart can also be a big issue. It can hurt a patient’s self-esteem and make it hard to connect with others. Counseling and support groups can help a lot.
By understanding these risks and challenges, we can support patients better. This can improve their lives and outcomes.
The Future of Artificial Heart Technology
Artificial heart technology is set to change how we treat heart failure. The field is growing fast, with new devices and better patient results.
Current Research and Innovations
Scientists are working on new materials and designs for artificial hearts. They aim to make them last longer and work better. Using biocompatible materials is key to avoiding complications and improving health outcomes. Also, making devices smaller and more portable is helping patients move around more easily.
Studies show that 3D printing could make artificial heart parts that fit each patient perfectly. This tech can create complex shapes that match individual needs. It might also cut down on recovery time.
“The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into artificial heart technology is expected to play a significant role in its future development, enabling more precise control and monitoring of device function.”
Cardiac Surgeon
Potential Breakthroughs on the Horizon
Several exciting breakthroughs are coming up in artificial heart tech. These include:
- The creation of fully implantable artificial hearts that don’t need external power or drivelines. This could lower infection risks and boost patient mobility.
- Improvements in battery technology for longer battery life and more efficient charging.
- The use of artificial intelligence to make devices work better and keep a closer eye on patients.
|
Breakthrough |
Description |
Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
|
Fully Implantable Artificial Hearts |
Devices that are completely implanted within the body, eliminating the need for external components. |
Reduced risk of infection, improved patient mobility. |
|
Advanced Battery Technology |
Batteries with longer life and more efficient charging systems. |
Enhanced patient freedom, reduced need for frequent recharging. |
|
AI Integration |
Artificial intelligence systems that monitor and adjust device function in real-time. |
Improved device performance, enhanced patient safety. |
As research keeps moving forward, we’ll see big improvements in artificial heart tech. This will greatly help patients with heart failure.
Conclusion: Weighing the Promise and Reality of Artificial Hearts
Looking at artificial heart technology today, we see a big chance to change how we treat heart failure. These devices could bring new hope to those with few treatment options.
Artificial hearts promise to help people live longer and better lives, even with severe heart failure. The real world of artificial hearts is growing, with many types now available. This shows how far we’ve come.
Devices like total artificial hearts and ventricular assist devices are helping patients. New technologies are making even more progress. We can look forward to better artificial hearts in the future.
The future of artificial hearts is full of hope and possibility. We must keep working to make these devices better for patients. This means exploring their benefits and challenges carefully.
FAQ
What is an artificial heart?
An artificial heart is a mechanical device. It replaces a failing heart. It pumps blood throughout the body.
How does an artificial heart work?
Artificial hearts use pumps and valves to mimic a heartbeat. They run on batteries or external drivers.
What are the types of artificial heart systems available?
There are total artificial hearts (TAH) and ventricular assist devices (VADs). New technologies are also emerging.
Who is eligible for an artificial heart transplant?
Doctors check if you’re eligible based on heart failure severity and mental readiness. Having a strong support system is key.
Can an artificial heart extend life expectancy?
Yes, artificial hearts can improve survival rates and quality of life. They help those with severe heart failure.
What are the risks and complications associated with artificial hearts?
Risks include infections and device malfunctions. There are also psychological and social challenges. Careful management is needed.
How is an artificial heart implanted?
The implantation is a complex surgery. It requires careful preparation, precise implantation, and post-operative care.
What lifestyle adjustments are required after receiving an artificial heart?
You’ll need to make big lifestyle changes. This includes daily maintenance, monitoring, and adapting to device limits.
What is the future of artificial heart technology?
Research and innovations are ongoing. They aim to improve device function, patient outcomes, and quality of life. Exciting breakthroughs are expected.
How does a ventricular assist device (VAD) work?
A VAD helps the heart pump blood. It improves cardiac output and reduces heart failure symptoms.
What is the difference between a total artificial heart and a ventricular assist device?
A total artificial heart replaces the whole heart. A VAD supports the existing heart, boosting its pumping function.
Who invented the artificial heart?
Many researchers and scientists have worked on the artificial heart over decades. Pioneers have made significant milestones
.
Reference
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15173740/





