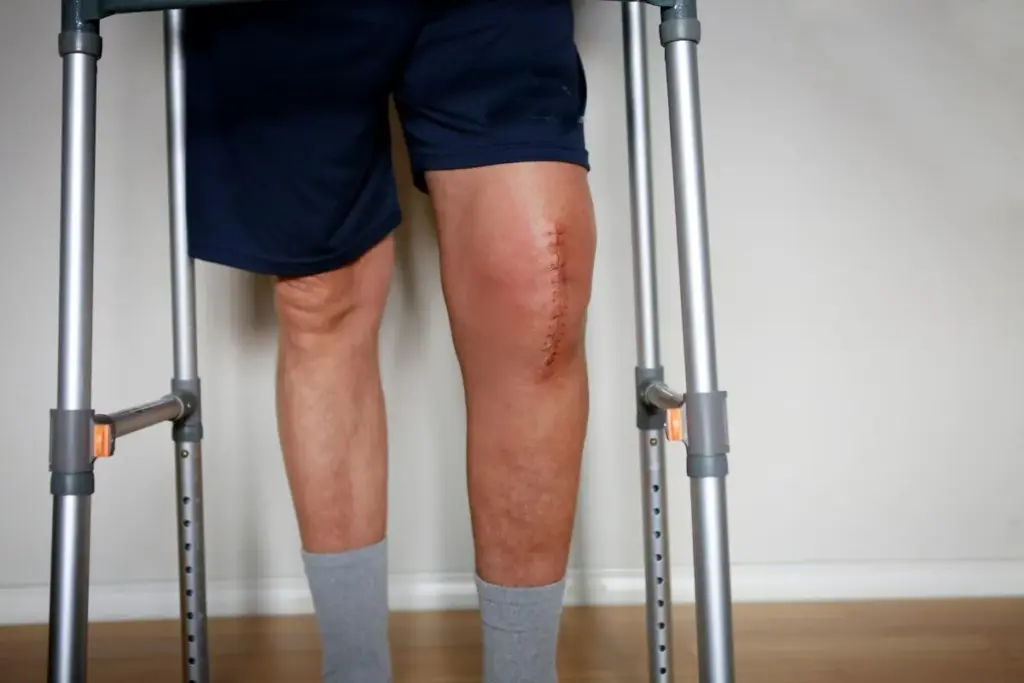
Getting a total knee replacement can be scary, with many questions about pain and getting better. We aim to give you a clear picture of what’s ahead. This will help you feel more confident about your decision. Knee surgery is a powerful fix for chronic injuries. Learn the essential and healthy steps of knee surgery for an amazing and fast recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the pain associated with knee replacement
- Exploring the recovery process after total knee replacement
- Factors influencing the outcome of knee replacement surgery
- Preparing for a successful knee replacement experience
- What to expect during the rehabilitation phase
Understanding Joint Replacement Surgery
Joint replacement surgery is a big step for those considering it. It’s also known as arthroplasty. This surgery replaces a damaged or arthritic joint with an artificial one. It’s often done on knees, hips, shoulders, and ankles.
Types of Joint Replacements
There are many types of joint replacement surgeries. Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most common. It replaces the knee joint with artificial parts. Other surgeries include hip, shoulder, and ankle replacements, each for a specific joint and condition.
The right type of surgery depends on the patient’s condition, age, and lifestyle. For example, younger patients might need more durable materials. Older patients might prefer less invasive methods. Knowing these options helps patients make better choices.
Why Joint Replacements Are Performed
Joint replacement surgery helps those with severe joint pain and damaged or arthritic joints. It’s often for osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or injuries. The surgery can greatly reduce pain and improve mobility.
It’s usually considered when other treatments like medication or physical therapy don’t work. An orthopedic surgeon will assess the patient’s condition and suggest the best surgery.
Modern Surgical Techniques That Minimize Pain
New surgical techniques have made joint replacement surgery less painful. Minimally invasive surgery uses smaller cuts, causing less damage and faster recovery. Computer-assisted surgery and robotic-assisted surgery also improve precision and reduce risks.
Modern pain management, like regional anesthesia and multi-modal pain management, also helps. These methods make surgery more comfortable for patients. Thanks to these advancements, joint replacement surgery is now more appealing to many.
The Reality of Pain in Knee Surgery
Pain after knee surgery is different for everyone. Their experiences with joint pain and surgery vary greatly.
Pain Perception Varies by Individual
Many things affect how we feel pain, like our genes, our mind state, and past pain experiences. This means two people having the same knee surgery can feel pain differently.
It’s key to understand this to manage pain well. We make sure each patient’s pain journey is unique. We adjust our pain management plans for each person.
Factors That Influence Pain Levels
Several things can change how much pain we feel after knee surgery. These include:
- The overall health of the patient
- The presence of any comorbid conditions
- The surgical technique used
- The effectiveness of the pain management plan implemented
|
Factor |
Influence on Pain |
|---|---|
|
Patient’s Overall Health |
Patients with fewer comorbidities tend to have less pain |
|
Surgical Technique |
Minimally invasive techniques can reduce pain |
|
Pain Management Plan |
A well-tailored plan can significantly reduce pain levels |
Setting Realistic Expectations
Before surgery, it’s important to set realistic expectations. We help our patients understand what pain and recovery from TKR (Total Knee Replacement) will be like.
Knowing what affects pain and having a good pain plan helps patients recover better. Our aim is to prepare and support our patients fully during their recovery.
Pre-Surgery Pain vs. Post-Surgery Pain
It’s important to know the difference between pain before and after surgery for knee replacement. This helps patients understand what to expect during recovery.
Chronic Pain Before Surgery
Many patients have been in pain for a long time before surgery. This pain can really affect their life, not just their knee. Chronic pain often comes from conditions like osteoarthritis or injuries. Talking to a doctor about pain levels is key to knowing how it might affect surgery and recovery.
Acute Surgical Pain
Acute pain is what you feel during and right after surgery. Thanks to new techniques and anesthesia, this pain is much less than before. Using nerve blocks can really help reduce pain during and after surgery. Advanced pain management makes recovery more comfortable.
Pain Improvement Timeline
How fast pain gets better after surgery varies for everyone. Most people start feeling better in a few weeks to months. Big improvements are common within the first few months. Here’s a table showing what to expect:
|
Timeframe |
Expected Pain Level |
Recovery Milestones |
|---|---|---|
|
First 2 weeks |
High |
Initial healing, pain management |
|
2-6 weeks |
Moderate |
Increased mobility, physical therapy |
|
3-6 months |
Low to minimal |
Significant improvement in function and pain |
Knowing the difference in pain before and after surgery helps patients prepare. It’s vital to follow doctor’s advice for a smooth recovery.
Preparing Mentally and Physically for Joint Replacement Pain
Getting ready for joint replacement surgery is a big step. It involves getting your body and mind ready. Knowing how to prepare for knee replacement surgery is key.
Pre-Surgery Conditioning Exercises
Doing exercises before surgery can make recovery easier. Strengthening muscles around the knee is important. This includes exercises like straight leg raises and squats.
It’s important to talk to your doctor or physical therapist about your exercises. They can help make a plan just for you. Also, staying active with walking or swimming can help your body get ready for surgery.
Psychological Preparation Techniques
Mental preparation is as important as physical. Practices like meditation and deep breathing can help with anxiety. Having a positive mindset and understanding what to expect can make a big difference.
Learning about the surgery and recovery can help. Knowing what to expect can reduce fears and worries.
Setting Up Your Home for Recovery
Getting your home ready for recovery is important. Make a comfortable area and have assistive devices ready. Having a support system and planning meals can make recovery easier.
Understanding the surgery, like knee ligament repair or knee cartilage restoration, helps set realistic goals. A well-prepared home makes the recovery smoother and faster.
Pain Management During Joint Replacement Surgery
Joint replacement surgery needs a good pain management plan. This plan helps reduce pain and improves recovery. It’s key for patient comfort and a smooth recovery.
Types of Anesthesia Used
Several anesthetics can be used during joint replacement surgery. These include general, regional, and local anesthesia. The choice depends on the patient’s health, the surgery type, and the surgeon’s choice.
- General Anesthesia: Makes the patient unconscious, used for complex surgeries.
- Regional Anesthesia: Numbs a larger area, like below the waist, for knee and hip surgeries.
- Local Anesthesia: Numbs a small area where surgery is done.
Regional Pain Blocks
Regional pain blocks are a form of regional anesthesia. They involve injecting medication into nerves to block pain. These blocks work well for total knee replacement and other lower limb surgeries.
- Femoral Nerve Block: Used for knee surgery, numbs the front thigh.
- Sciatic Nerve Block: Numbs the back leg, often used with femoral nerve block.
Intraoperative Medication Protocols
Intraoperative medication protocols use various drugs during surgery. These help manage pain and inflammation. They include:
- Opioids: Strong pain relievers, used carefully due to addiction risk.
- Non-opioid analgesics: Like acetaminophen or NSAIDs, reduce pain and inflammation.
- Anti-inflammatory medications: Reduce swelling and pain.
By using these strategies, we can greatly improve the surgical experience. This is for patients having knee surgery or other joint replacement procedures.
Immediate Post-Operative Pain Experience
After knee replacement surgery, the first 24-48 hours are key. They set the stage for your recovery. Everyone’s pain experience is different, but knowing what to expect can help.
First 24-48 Hours After Surgery
The first 24-48 hours after total knee arthroplasty are the toughest. This is when your body starts to heal from the operation of knee. You might feel pain, swelling, and have trouble moving.
Managing pain well during this time is vital for a good recovery. Your healthcare team will use different methods to help you feel better.
Hospital Pain Management Strategies
Hospitals use many pain management strategies to help patients after surgery. These include:
- Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pumps
- Regional anesthesia
- Oral pain medications
- Non-pharmacological interventions like ice therapy
Your healthcare team will help find the best pain management plan for you.
What to Expect When Waking Up
Waking up after knee replacement surgery can be confusing. You might feel drowsy or confused because of the anesthesia. You may also start to feel pain or discomfort as the anesthesia fades.
Telling your healthcare providers about your pain is important. They can adjust your pain management plan to help you feel better.
Pain During the First Week of Recovery
Understanding what to expect in terms of pain after joint replacement surgery is key. The first week is when your body starts to heal. Managing pain well is important for a smooth recovery.
Transitioning to Oral Pain Medications
Patients start with IV pain management after surgery. Then, they move to oral pain meds. This step helps them manage pain at home. It’s important to follow the medication schedule to control pain well.
Physical Therapy and Pain
Physical therapy is key in recovery, helping patients get stronger and move better. While it might hurt a bit, the benefits are worth it. Your physical therapist will create a plan that fits your needs and doesn’t hurt too much.
- Gentle exercises to improve range of motion
- Strengthening exercises to support the new joint
- Functional activities to enhance daily living skills
Normal vs. Concerning Pain Patterns
It’s important to know the difference between normal and concerning pain. Some pain is okay after surgery, but other signs might mean trouble. Always watch your pain and tell your doctor if it’s unusual or bad.
|
Pain Characteristic |
Normal |
Concerning |
|---|---|---|
|
Intensity |
Mild to moderate, manageable with medication |
Severe, unrelenting despite medication |
|
Pattern |
Gradually improving |
Worsening or unchanging |
Being informed and proactive helps you get through the first week of recovery. Your healthcare team is there to help you every step of the way.
Managing Pain During Weeks 2-6 After Knee Replacement
Understanding how to manage pain after knee replacement surgery is key. As you get better, your pain might change. You’ll need to adjust how you handle it.
Rehabilitation Milestones and Associated Pain
In weeks 2-6, you’ll see big improvements in how you move and get stronger. But, some steps in your rehab might hurt a bit more. It’s vital to talk to your doctor about managing this pain.
Some milestones you might hit include:
- Increasing knee flexion and extension
- Strengthening the quadriceps and hamstring muscles
- Improving balance and proprioception
Each milestone can bring different kinds of pain. Knowing what to expect helps you prepare and manage your pain better.
Weaning Off Pain Medications
As you heal, it’s important to stop taking pain meds. This helps avoid side effects and keeps you from getting too used to them. Always follow your doctor’s advice on this. They’ll help you slowly stop taking pain meds as your pain goes down.
Here’s a basic plan for stopping pain meds:
- Slowly cut down on pain meds over days or weeks
- Switch to over-the-counter meds when your pain is less
- Try other ways to manage pain, like physical therapy
Non-Pharmaceutical Pain Management
There are many ways to manage pain without meds. These methods not only help with pain but also make you feel better overall. Activities like physical therapy, acupuncture, and relaxation exercises can really help. Trying these can make your recovery better.
Some good non-med ways to manage pain include:
|
Technique |
Description |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Physical Therapy |
Guided exercises to improve mobility and strength |
Reduces pain, improves function |
|
Acupuncture |
Insertion of fine needles into specific points |
Relieves pain, promotes healing |
|
Relaxation Techniques |
Meditation, deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation |
Reduces stress, alleviates pain |
Long-Term Pain Expectations (3-12 Months)
After knee replacement surgery, patients often wonder about long-term pain. It’s important to know how pain changes over time. This helps us understand the recovery journey better.
Residual Pain and Discomfort
Some pain or discomfort is normal after surgery. But, it usually gets better as the knee heals and gets stronger. Following a rehabilitation program closely can help reduce discomfort.
- Adhering to physical therapy exercises
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce knee stress
- Using appropriate pain management strategies
Activity-Related Pain
Pain from activities is common, mainly from movements that stress the knee. It’s important to know the difference between normal pain and pain that might mean a problem.
Common activities that may cause pain include:
- Bending or kneeling
- Climbing stairs
- Engaging in high-impact activities
When Full Recovery Can Be Expected
Full recovery from knee replacement surgery can take 3 to 12 months. Most see big improvements in 3 to 6 months. But, getting back to normal activities fully can take up to a year.
Factors influencing recovery time include:
- The patient’s overall health and age
- Adherence to the rehabilitation program
- Presence of any complications
Total Knee Arthroplasty: Specific Pain Considerations
Total knee arthroplasty can help patients regain mobility and reduce chronic knee pain. It’s important to understand the pain aspects of this surgery. This knowledge helps manage expectations and ensures a smooth recovery.
Unique Aspects of Knee Replacement Pain
Knee replacement pain is different from other joint replacement surgeries. The knee’s complexity, with its ligaments and soft tissues, leads to unique pain. Patients often feel pain from the surgical incision, swelling, and the body’s reaction to the implant.
Several factors affect knee replacement pain, including:
- The surgery’s extent and technique
- The patient’s health and pre-existing pain
- Any complications during or after surgery
Kneeling and Bending Discomfort
Kneeling and bending can be tough after total knee arthroplasty. The discomfort comes from the changed knee joint mechanics and healing tissues. Patients should slowly start these activities as advised by their healthcare provider to avoid pain.
Rehabilitation is key in reducing discomfort from kneeling and bending. Physical therapy helps regain strength and flexibility. This makes these activities easier without much pain.
Weather-Related Pain After Knee Replacement
Some patients feel pain due to weather changes after knee replacement. The exact cause is unknown, but changes in atmospheric pressure might affect the joint or tissues. Keeping a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can help manage these effects.
“I’ve had patients tell me that they can feel weather changes, even after their knee replacement. While we don’t fully understand it, it shows how complex our bodies are and how much we have to learn about our environment.”
Knowing about these pain considerations helps patients prepare for their recovery. By working with their healthcare team, patients can create a plan to manage pain. This ensures the best outcomes from their total knee arthroplasty.
Comparing Pain Across Different Joint Replacements
When thinking about joint replacement surgery, knowing about pain is key. Patients wonder about pain and recovery. The joint being replaced matters a lot.
Hip Replacement vs. Knee Replacement Pain
Hip and knee replacements are common. But, the pain after surgery can be different. Usually, hip replacement patients feel less pain at first than knee replacement patients.
A study showed knee replacement patients need more pain meds early on.
Shoulder and Ankle Replacement Pain Profiles
Shoulder and ankle replacements are less common but important. Shoulder patients often feel more pain because of the joint’s complexity. Ankle replacement can lead to longer recovery due to the ankle’s weight-bearing role.
Which Joint Replacements Tend to Be Most Painful
Knee replacement surgery is often seen as more painful short-term. This is because of the knee’s complexity and the need for a lot of rehab.
“Knee replacement surgery is a big deal. While pain can be managed, patients need to be ready for a tough rehab,” said a top orthopedic surgeon.
Knowing these differences helps patients get ready for surgery and recovery. By comparing pain, we can better manage expectations and improve care.
When Pain Indicates a Problem
It’s important to know the difference between normal pain after surgery and pain that means something is wrong. Some pain is okay, but other signs can mean serious issues that need quick help.
Signs of Infection
Infection is a big worry after joint replacement surgery. Look out for these signs:
- Redness and swelling around the surgical site
- Increased pain or tenderness
- Warmth or redness around the incision
- Fever or chills
- Drainage or pus from the wound
If you see any of these, call your surgeon right away.
Implant Complications
Implant problems are rare but can happen. They might include:
- Loosening of the implant
- Wear and tear on the implant components
- Dislocation of the implant
- Fracture around the implant
Look out for ongoing pain, feeling unstable, or a grinding feeling in your joint.
When to Contact Your Surgeon
If you notice anything odd or really bad, reach out to your surgeon. This includes:
- Severe pain not helped by medicine
- Sudden swelling or shape changes
- Can’t move the joint
- Signs of infection as mentioned earlier
Keep an eye on your symptoms and talk to your doctor about them. This helps catch any problems early.
|
Symptom |
Possible Cause |
Action |
|---|---|---|
|
Increased pain or redness |
Infection or implant complication |
Contact surgeon |
|
Fever or chills |
Infection |
Seek immediate medical attention |
|
Instability or grinding sensation |
Implant complication |
Schedule a consultation with your surgeon |
Conclusion
Understanding pain after joint replacement surgery, like knee replacement, is key. It helps set realistic goals and makes recovery smoother. We’ve looked at how to manage pain during and after these surgeries.
Good pain management starts before surgery. Exercises and mental prep are important. During surgery, the right anesthesia and pain blocks help a lot. After, a mix of meds and physical therapy is used.
Pain levels vary for everyone getting knee surgery. Health, chronic pain, and surgery method all play parts. Knowing this and working with doctors helps manage pain better.
Even though knee surgery can hurt, new methods make it easier. Being informed and ready helps patients face their recovery with confidence.
FAQ
How painful is a total knee replacement?
The pain from a total knee replacement can vary. Modern pain management has made it less painful. Some discomfort is expected, but it’s not as bad as it used to be.
What are the most common pain management strategies after joint replacement surgery?
After joint replacement surgery, doctors use several pain management methods. These include oral pain meds, regional blocks, and intraoperative meds. Non-pharmaceutical methods like physical therapy and relaxation exercises are also recommended.
How long does pain last after knee replacement surgery?
Pain after knee replacement surgery follows a timeline. The initial pain usually goes away in a few weeks. Some people may feel pain or discomfort for months after.
Is it normal to experience kneeling and bending discomfort after knee replacement?
Yes, it’s common to feel discomfort when kneeling or bending after knee replacement. This pain usually gets better as the knee heals and mobility improves.
Can weather changes affect pain after knee replacement?
Some people say weather changes can make their pain worse after knee replacement. The exact reason is not clear, but changes in atmospheric pressure might play a role.
How does pain from knee replacement compare to other joint replacements?
Pain levels vary with different joint replacements. Knee replacements are generally moderately painful. Hip replacements tend to be less painful. Shoulder and ankle replacements have different pain levels.
When should I contact my surgeon about pain after joint replacement?
Contact your surgeon if you notice signs of infection like increased redness, swelling, or fever. Also, if you have concerns about implant complications, such as unusual sounds or instability.
What are the signs of infection after joint replacement surgery?
Signs of infection include increased pain, redness, swelling, warmth, or drainage around the surgical site. Fever or chills are also signs. If you notice any of these, seek medical help right away.
How can I prepare mentally and physically for joint replacement pain?
To prepare for joint replacement pain, start with pre-surgery exercises and mental preparation. Also, make your home comfortable for recovery. Talk to your healthcare provider about these steps.
What are the rehabilitation milestones after knee replacement, and how do they relate to pain?
Rehabilitation milestones include improving range of motion, strengthening muscles, and increasing mobility. As you reach these milestones, your pain should decrease.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12096998/





