
Joint pain is a common problem worldwide, making it hard to move and feel uncomfortable. Many things can cause joint pain, but a vitamin deficiency is often overlooked. A lack of a specific vitamin can lead to tiredness, weakness, and joint pain.
A vitamin B12 deficiency can seriously affect your health. It’s key for making red blood cells, keeping nerves healthy, and making DNA. Studies have found that not having enough of this vitamin can cause joint pain, among other issues.
Is a vitamin B12 deficiency causing your pain? Discover how this essential nutrient provides amazing support for your orthopedic health.
Key Takeaways
- Joint pain can be caused by a deficiency in certain vitamins.
- Vitamin B12 plays a critical role in making red blood cells and keeping nerves healthy.
- A lack of vitamin B12 can lead to tiredness, weakness, and joint pain.
- Understanding the link between vitamin deficiency and joint pain can help in diagnosis and treatment.
- Addressing a vitamin deficiency can potentially alleviate joint pain symptoms.
The Relationship Between Vitamins and Joint Health

Vitamins are key to keeping our joints healthy. Vitamin B12 is very important. Not having enough vitamin B12 can cause joint pain and stiffness.
How Vitamins Support Joint Function
Vitamins and minerals help our joints stay healthy. Vitamin B12 helps make red blood cells. These cells carry oxygen to our joints.
This oxygen is vital for joint health. It helps prevent anemia, which can make joints weak and tired.
The Impact of Nutritional Deficiencies on Joints
Not getting enough nutrients, like vitamin B12, hurts our joints. A lack of vitamin B12 means fewer red blood cells. This can cause joint pain and stiffness.
Inflammation Pathways
Vitamin B12 helps control inflammation in our bodies. Without enough, inflammation goes up. This makes joint pain and stiffness worse.
Structural Support Mechanisms
Vitamin B12, along with vitamins D and calcium, keeps joints strong. It helps the tissues and bones around the joints stay healthy. This ensures our joints work right.
As “A lack of vitamin B12 can have far-reaching consequences on our overall health, including our joints.” It’s important to keep vitamin B12 levels up. We can do this with a good diet or supplements to help our joints stay healthy.
Vitamin B12 and Its Critical Role in the Body
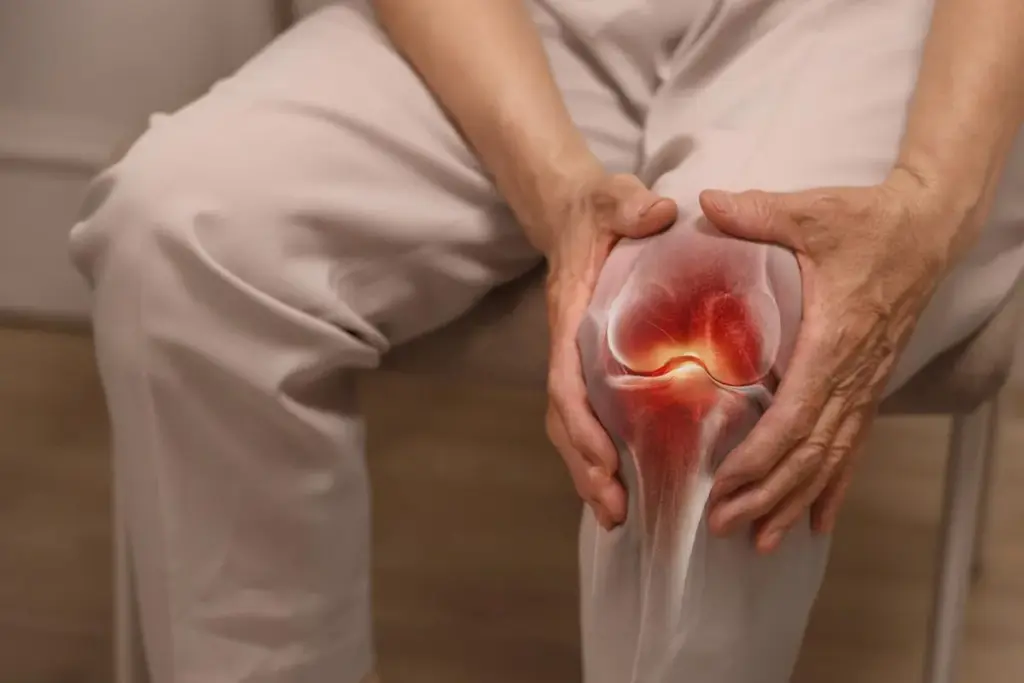
Vitamin B12, or cobalamin, is essential for a healthy diet. It helps with making red blood cells, keeping nerves healthy, and making DNA. This vitamin is water-soluble and plays a key role in our bodies.
What is Cobalamin (Vitamin B12)?
Cobalamin, also known as vitamin B12, is mainly found in animal products. This includes meat, poultry, and dairy. It’s special because it’s made by bacteria, not plants or animals.
Essential Functions of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is important for many functions in our bodies. It helps:
- Make red blood cells to prevent anemia.
- Keep the nervous system healthy by making myelin.
- Help with DNA synthesis, which is key for cell division.
Recommended Dietary Allowance: Adults need 2.4 mcg of vitamin B12 daily. Some doctors suggest more for people with certain health issues.
Recommended Daily Intake by Age Group
The amount of vitamin B12 we need changes with age. Adults should get 2.4 mcg, while pregnant women need 2.6 mcg. Getting the right amount is important for staying healthy.
It’s important to know about vitamin B12’s role and make sure we get enough. This helps keep us healthy and prevents symptoms of deficiency.
How Lacking in Vitamin B12 Affects Your Joints
Vitamin B12 deficiency and joint pain are linked through complex pathways. It’s important to understand this to treat joint pain well.
The Neurological Connection to Joint Pain
Vitamin B12 helps make myelin, a fatty substance around nerve fibers. Without enough B12, myelin can get damaged. This disrupts nerve function and causes pain. This is why people with b12 deficiency disease often feel joint pain.
Inflammatory Responses Due to B12 Deficiency
A deficiency of cobalamin (vitamin B12) can cause inflammation. This inflammation leads to joint pain and stiffness. Chronic inflammation can cause long-term damage and discomfort.
Myelin Sheath Damage and Pain Perception
Vitamin B12 deficiency damages the myelin sheath. This disrupts nerve function and changes how we feel pain. Knowing this helps in finding better treatments for vitamin b12 deficiency cure.
It’s key to treat vitamin B12 deficiency to ease joint pain and improve health. Recognizing signs of deficiency and getting the right treatment can help.
Recognizing Vitamin B12 Deficiency Symptoms
It’s important to know the signs of vitamin B12 deficiency early. This vitamin is key for making red blood cells, nerve health, and DNA. Without enough, you can face health problems, from mild to serious.
Early Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Early signs of vitamin B12 deficiency are subtle. They might include fatigue, weakness, and neurological symptoms like numbness or tingling in your hands and feet. These symptoms can be hard to spot, making it tough to catch vitamin B12 deficiency early.
Advanced Symptoms Affecting Mobility
As vitamin B12 deficiency gets worse, symptoms worsen too. You might feel joint pain and stiffness, muscle weakness, and trouble walking. In severe cases, it can really limit your mobility and quality of life.
Joint-Specific Manifestations
Vitamin B12 deficiency can also affect your joints. It can cause pain and stiffness, mainly in your hands, feet, and knees. Knowing where and how the pain feels is key for diagnosing.
Location and Characteristics of Pain
The pain from vitamin B12 deficiency can be different in intensity and where it is. It’s often a deep, aching pain that lasts. Your knees, hands, and feet are usually hit hard, and the pain can move or get worse with movement.
Associated Symptoms
Joint pain isn’t the only symptom of vitamin B12 deficiency. You might also feel fatigue, neurological symptoms, and digestive issues. These symptoms can show up alone or together and can vary in how bad they are.
Knowing these symptoms can help catch vitamin B12 deficiency early. This can stop long-term damage and improve your health.
Who’s at Risk for B12 Deficiency?
Knowing who is at risk for vitamin B12 deficiency is key. Some people are more likely to get it because of their age, diet, health issues, and medicines.
Age-Related Vulnerability
Older adults face a higher risk of vitamin B12 deficiency. As we get older, our bodies absorb less vitamin B12 from food. This makes supplements or special diets important for them.
Dietary Restrictions
Vegetarians and vegans are also at a higher risk. Vitamin B12 is mostly in animal products. They can use fortified foods or supplements to fill this gap.
Medical Conditions Affecting B12 Absorption
Some health issues, like celiac disease and Crohn’s disease, make it hard to absorb vitamin B12. People with these conditions might need more vitamin B12 or closer watch.
Medications That Deplete Vitamin B12
Some medicines, like proton pump inhibitors and metformin, can block vitamin B12 absorption. Those taking these should talk to their doctor about getting enough vitamin B12.
By knowing these risks, people can take steps to avoid vitamin B12 deficiency. This helps prevent health problems linked to it.
Diagnosing B12 Deficiency Disease
To find out if you have a vitamin B12 deficiency, doctors use several steps. They do blood tests and check your health closely. This way, they can tell if you have this problem and not something else.
Essential Blood Tests and Biomarkers
Blood tests are key in finding out about vitamin B12 deficiency. They look at:
- Serum vitamin B12 levels
- Methylmalonic acid (MMA) levels
- Homocysteine levels
Clinical Assessment Techniques
Doctors also check your health in other ways. They look for signs like:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Neurological symptoms like numbness or tingling
- Pale or yellowish skin
This helps them see how the deficiency affects your health.
Ruling Out Other Causes of Joint Pain
Doctors also make sure it’s not something else causing your joint pain. They do this by:
- Looking at your medical history
- Doing a physical exam
- Running more tests to check for other problems
This way, doctors can find the right treatment for you.
Effective Vitamin B12 Deficiency Cure Options
Vitamin B12 deficiency cure options have grown, giving patients many choices. These include oral supplements, B12 injections, and natural ways to get more B12. The right treatment depends on how bad the deficiency is, the patient’s health, and what they prefer.
Oral Supplementation Protocols
Oral supplements are often the first choice for mild B12 deficiency. They aim to fill up vitamin B12 stores and keep levels right. You can find these supplements in tablets, capsules, and sublingual drops.
B12 Injections: Procedure and Benefits
For serious cases or when oral supplements don’t work, B12 injections are used. These injections put vitamin B12 straight into your blood, skipping your stomach. This is great for people who have trouble absorbing nutrients.
Dietary Interventions for Natural Restoration
Eating more animal products like meat, fish, and dairy can help fix B12 levels naturally. Vegetarians and vegans can use fortified foods and plant-based milk instead.
Recovery Timeline and Expectations
How long it takes to get better from B12 deficiency varies. It depends on how bad the deficiency is and the treatment. Most people start seeing improvements in a few weeks to months. It’s important to keep checking in with your doctor to adjust your treatment as needed.
|
Treatment Method |
Benefits |
Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
|
Oral Supplementation |
Easy to administer, suitable for mild deficiency |
Several weeks to months |
|
B12 Injections |
Bypasses digestive system, effective for severe deficiency |
Few weeks to months |
|
Dietary Interventions |
Natural, promotes overall health |
Variable, depends on dietary adherence |
Other Vitamin Deficiencies That Cause Joint Pain
Other vitamins are key for healthy joints and avoiding pain. A lack of vitamin B12 can cause joint pain. But, other nutritional gaps can also lead to this issue.
Vitamin D Deficiency and Joint Integrity
Vitamin D is vital for strong bones and density. Not having enough vitamin D can cause joint pain and osteoporosis. It’s important to get enough vitamin D through food, supplements, or sunlight.
Vitamin C’s Role in Collagen Formation
Vitamin C helps make collagen, a protein for our skin, bones, and connective tissue. Without enough vitamin C, collagen production drops. This can cause joint pain and less mobility.
Vitamin K and Joint Cartilage Health
Vitamin K helps with bone and cartilage health. Studies show a link between vitamin K deficiency and osteoarthritis and joint pain. It’s key for keeping joints healthy.
Comparing Effects of Different Vitamin Deficiencies
Vitamin B12, vitamin D, vitamin C, and vitamin K deficiencies can all cause joint pain. But, how they affect us is different. Knowing these differences helps in finding the right treatment.
For example, a vitamin D deficiency might need supplements and more sunlight. But, a vitamin B12 deficiency might need diet changes or injections.
In summary, keeping the right levels of vitamins is essential for joint health. A balanced diet and supplements can help avoid joint pain from vitamin deficiencies.
B12 Benefits: Preventing Deficiency and Protecting Joints
Recognizing and preventing vitamin B12 deficiency is crucial for maintaining healthy joints. Vitamin B12 helps the nervous system and makes red blood cells. Both are important for joint health.
Rich Dietary Sources of Vitamin B12
Animal products like meat, poultry, fish, and dairy are full of vitamin B12. People who don’t eat these might need supplements or other sources.
|
Food Source |
Vitamin B12 Content |
|---|---|
|
Salmon |
18.8 mcg per 3 oz serving |
|
Beef Liver |
70.7 mcg per 3 oz serving |
|
Chicken |
0.3 mcg per 3 oz serving |
Strategic Supplementation Approaches
Supplements can help those at risk of B12 deficiency. Oral supplements and B12 shots can boost levels and ease symptoms.
Monitoring Protocols for At-Risk Individuals
Regular checks are vital for those at risk of B12 deficiency. It’s important to know when to test and what signs show B12 levels are up.
Testing Frequency Recommendations
People at risk should get tested every 6-12 months to check their B12 levels.
Signs That Indicate Improved B12 Status
Signs of better B12 levels include more energy, less fatigue, and fewer neurological symptoms.
Conclusion: Maintaining Joint Health Through Optimal Nutrition
Keeping your joints healthy is key to feeling good. Good nutrition is a big part of this. Vitamin B12 is very important for your joints. If you don’t get enough, you might feel pain and stiffness.
Eating foods rich in vitamin B12, like meat, fish, and dairy, helps a lot. If you’re a vegetarian or vegan, taking supplements can also help. Knowing how vitamin B12 affects your joints helps you stay healthy.
Focus on eating well and watch out for vitamin B12 deficiency. This protects your joints and keeps you healthy. Regular checks and changes to your diet or supplements keep your vitamin B12 levels right. This means healthy joints and overall well-being.
FAQ
What are the symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency?
Symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency include fatigue and weakness. You might also feel neurological symptoms, joint pain, and stiffness. These symptoms can get worse and affect how you move, causing pain in your hands, feet, and knees.
How does vitamin B12 deficiency cause joint pain?
Vitamin B12 deficiency can damage the myelin sheath, leading to pain. It can also cause inflammation, which adds to joint pain and stiffness.
Who is at risk for vitamin B12 deficiency?
Older adults, vegetarians, and vegans are at higher risk. People with conditions like celiac disease and Crohn’s disease are also at risk. Some medications, like proton pump inhibitors and metformin, can lower vitamin B12 levels.
How is vitamin B12 deficiency diagnosed?
Diagnosing it involves blood tests and clinical assessment. Blood tests check vitamin B12 levels. Clinical assessment looks for signs of neurological and hematological symptoms.
What are the treatment options for vitamin B12 deficiency?
Treatment includes oral supplements or injections. Oral supplements work for mild cases. For severe cases, injections are often used. Eating more animal products or fortified foods can also help.
Can other vitamin deficiencies cause joint pain?
Yes, other deficiencies can cause joint pain. Vitamin D deficiency is linked to joint pain and osteoporosis. Vitamin C and K are important for joint health.
How can I prevent vitamin B12 deficiency?
To prevent it, eat foods rich in vitamin B12 like animal products. Supplements can help those with dietary restrictions. Regular checks can catch deficiency early.
What is the recommended daily intake of vitamin B12?
Adults need 2.4 mcg of vitamin B12 daily. Some doctors suggest more for certain health conditions.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38294542/





