As we get older, our joints wear out, leading to osteoarthritis. Studies show that height loss accelerates after 60, which can be linked to joint degeneration and the possible need for replacements. Joint replacement surgery helps those with severe pain and trouble moving.
The average age for knee replacement is usually 65-70 years. But, it depends on your health, lifestyle, and if you have osteoarthritis. Knowing about the knee replacement age and what affects it helps you make a big medical choice.
Key Takeaways
- The average age for undergoing knee replacement surgery is typically between 65-70 years.
- Factors such as overall health and lifestyle can influence the need for knee replacement.
- Osteoarthritis is a common condition leading to the need for joint replacement surgery.
- Age-related height loss accelerates after age 60, potentially indicating the need for joint replacement.
- Understanding the factors that influence knee replacement age can aid in medical decision-making.
Understanding Joint Replacement Surgery
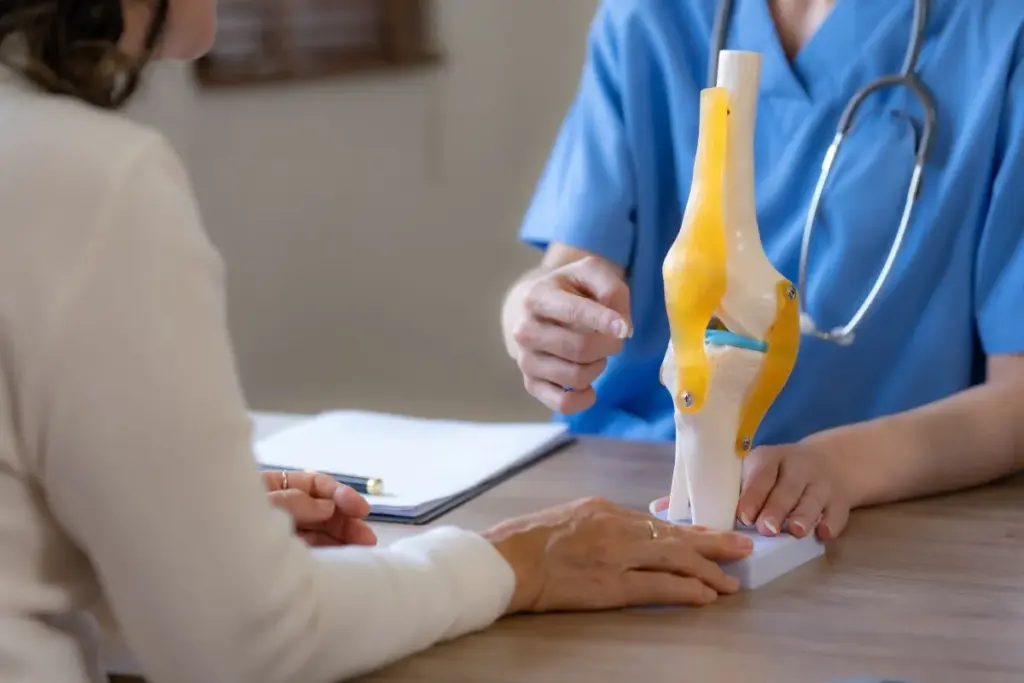
Joint replacement surgery has changed a lot, giving hope to people all over the world. This surgery, also known as arthroplasty, replaces a damaged or arthritic joint with an artificial one. It’s often done on hips and knees, but can also be done on shoulders, elbows, and ankles.
Types of Joint Replacements
There are different types of joint replacement surgeries, each for a specific joint and condition. The most common types are:
- Total joint replacement, where the whole joint is replaced.
- Partial joint replacement, where only the damaged part is replaced.
- Revision joint replacement, a complex procedure to replace a previous artificial joint.
Each type has its own use and benefits. The choice depends on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s advice.
Common Reasons People Need Joint Replacements
People usually need joint replacement surgery when other treatments don’t work. Common reasons include:
- Osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease.
- Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder that causes joint inflammation.
- Post-traumatic arthritis, resulting from severe injuries.
- Other conditions like avascular necrosis and certain bone deformities.
These conditions can make everyday activities hard, affecting a person’s quality of life.
Evolution of Joint Replacement Procedures
Joint replacement surgery has seen big improvements over time. Modern techniques and materials have made joint replacements last longer and work better. Some key advancements are:
- Improved implant materials and designs that last longer and wear less.
- Minimally invasive surgical techniques that help patients recover faster.
- Computer-assisted and robotic surgery for more accurate implant placement.
These improvements have made joint replacement surgeries better. They’ve also made it possible for younger and more active people to get the surgery.
The Average Age for Knee Replacement Surgery
To find the average age for knee replacement surgery, we look at different factors. Knee replacement, or arthroplasty, is a surgery to fix the knee joint. It’s mainly for osteoarthritis and when other treatments don’t work.
Statistical Data on Knee Replacement Age
Studies say the average age for knee replacement is about 65 years. But, this can change based on health, condition severity, and lifestyle.
Most knee replacements happen to people between 60 and 80. But, more younger people are getting the surgery. This is because of better surgery methods and older adults staying active.
Changing Trends in Patient Demographics
More young people are getting knee replacements, often from sports injuries or early osteoarthritis. Older adults are also getting surgery, wanting to stay active and healthy.
This means the average age for knee replacement is getting more varied. Obesity, genetics, and past knee injuries are making people need surgery at different ages.
Geographic and Demographic Variations
Where you live and who you are can affect when you get knee replacement surgery. Places with more obesity see younger people getting surgery. Lifestyle and genetics also play a part in when you might need surgery.
Knowing these differences helps doctors and patients make better choices. It’s key for healthcare to be more personalized.
When Should You Get a Knee Replacement?
Deciding on knee replacement surgery is a big choice. It’s important to know the signs that show you might need it. We’ll help you understand what to look for.
Key Indicators for Knee Replacement Necessity
There are clear signs that might mean you need surgery. These include:
- Chronic knee pain that makes daily tasks hard
- Loss of knee function or mobility
- When other treatments don’t help the pain
- Visible deformity or instability in the knee
If you see these signs, talking to an orthopedic specialist is key. They can check if surgery is needed.
Pain Severity and Mobility Assessment
How bad your knee pain is and how well you can move are important. We use special tools to see how pain and mobility affect your life.
We use pain scales to measure pain and functional tests to check mobility. These help us see how much pain and mobility issues affect your life.
Conservative Treatments to Try First
Before surgery, we suggest trying other treatments. These include:
- Physical therapy to strengthen and stretch the knee
- Medicines like anti-inflammatory drugs or pain relievers
- Changes in lifestyle, like losing weight and doing low-impact exercises
- Corticosteroid injections to reduce swelling
These treatments can help a lot. They might even make surgery unnecessary.
Timing Considerations for Optimal Outcomes
When you have surgery matters a lot. We look at your health, how bad the damage is, and how well you can recover.
Choosing the right time can lead to better results. It can also lower the risk of problems and make you happier with the outcome. We help find the best time for surgery based on your situation.
When is Knee Replacement Necessary?
Deciding on knee replacement surgery involves a detailed look at the patient’s health and life quality. We check many things to see if surgery is the best choice.
Medical Criteria for Surgery Candidacy
To qualify for knee replacement, patients must have tried other treatments without relief. Medical criteria include severe knee damage, often from osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or trauma. We use imaging and clinical checks to see the damage.
“The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons says knee replacement is needed when pain and mobility issues are severe, even with conservative treatments.” This rule helps us decide if surgery is needed.
Quality of Life Considerations
How knee problems affect a patient’s life is key. We look at how pain impacts daily tasks, mobility, and happiness. For many, not being able to do everyday things without pain means surgery might be needed.
Risk-Benefit Analysis for Different Age Groups
When thinking about knee replacement, we weigh risks and benefits by age. Younger patients worry about future implant wear and tear. Older patients focus on surgery’s risks versus the benefits of better mobility and less pain.
A risk-benefit analysis helps us make personalized recommendations. This ensures knee replacement surgery is the right choice for each patient.
“Knee replacement surgery can greatly improve life for those with severe knee damage. It’s a choice that needs careful thought of medical and personal factors.”
By looking at these factors, we can figure out when knee replacement surgery is needed. It’s likely to greatly benefit the patient.
How Long Do Knee Replacements Last?
Many patients wonder how long their knee replacement will last. This depends on several things. The life of a knee replacement is influenced by the patient, the implant type, and post-surgery care.
Average Lifespan of Modern Knee Implants
Modern knee implants are much more durable. They can last between 15 to 20 years, sometimes longer. Studies show that the average life of a knee implant is about 17 years.
Factors Affecting Knee Replacement Longevity
Several factors can affect how long a knee replacement lasts. These include:
- Patient Age: Younger patients may wear out implants faster because they are more active.
- Implant Type: The material and design of the implant greatly affect its life span.
- Surgical Technique: The surgeon’s skill and method can impact the implant’s longevity.
- Patient Weight and Activity Level: Being overweight or very active can stress the implant more.
Activity Level Impact on Implant Durability
The activity level after surgery can greatly affect the implant’s durability. While some activity is good for joint mobility, high-impact activities can wear it down faster.
We suggest talking to your surgeon about your activity plans. This can help understand how it might affect your knee replacement.
Maintenance Practices for Extending Implant Life
Proper care can extend the life of a knee replacement. This includes:
- Keeping a healthy weight to reduce stress on the implant.
- Doing low-impact exercises to keep the joint mobile without wearing it down too fast.
- Going to regular check-ups with the surgeon to monitor the implant’s condition.
By understanding these factors and taking proactive steps, patients can make their knee replacement last longer. This can improve their quality of life.
Knee Replacement Surgery in Younger Patients
Knee replacement surgery is becoming more common among younger people. This is due to sports injuries, genetic issues, and lifestyle choices. It’s important to understand the needs and outcomes for this group.
Special Considerations for Patients Under 50
Younger patients face unique challenges with knee replacement surgery. They are more active and live longer, so their implants must last a long time.
When considering knee replacement for the young, we must think about several things:
- The best implant material for durability and compatibility.
- The surgical technique to reduce recovery time and improve results.
- Rehab strategies that fit the patient’s age and activity level.
Knee Replacement at Age 40: What to Expect
Patients getting knee replacement at 40 have specific expectations. Many are active in their jobs, family, or sports.
Choosing knee replacement at 40 requires careful thought. It’s about the impact on their lifestyle, the chance of needing more surgery, and weighing surgery’s benefits against its risks.
Here’s a table summarizing key points for knee replacement at different ages:
|
Age Group |
Key Considerations |
Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
|
Under 40 |
High activity level, possible future revision |
Significant pain relief, better mobility |
|
40-50 |
Activity level vs. implant longevity |
Improved life quality, chance for continued activity |
|
50+ |
Lower activity, longer implant life |
Enhanced mobility, less pain |
Long-term Implications for Younger Recipients
Younger patients need to think about the long-term effects of knee replacement. They may outlive their implants, needing more surgeries.
Revision surgery is a big deal. It’s more complex than the first surgery. We must talk about future surgeries and how to make the first implant last longer.
By understanding these points and working with healthcare providers, younger patients can make better choices. They can prepare for the long-term effects of knee replacement surgery.
Symptoms of Knee Replacement Wearing Out
Knee replacement implants can last a long time, but they can wear out. It’s important to know the signs of wear to get medical help early. As we get older or keep up with our daily lives, our knee replacements can start to show signs of wear.
Early Warning Signs of Implant Failure
Knowing the early signs of implant failure is key. These signs include:
- Pain or stiffness in the knee, which gets worse after rest or at night.
- Swelling or redness around the knee, which could mean inflammation or infection.
- A feeling of instability or the knee “giving way.”
These symptoms don’t always mean the implant has failed. But they are signs you should see your doctor.
Progressive Symptoms to Monitor
As the knee replacement wears out more, symptoms can get worse. It’s important to watch for:
- Increasing pain during activities or at rest.
- Decreased mobility or stiffness that makes daily activities hard.
- Noise from the implant, like clicking or grinding, which means it’s wearing down.
Watching these symptoms helps your doctor figure out what to do next.
When to Consult Your Doctor About Implant Issues
If you notice any of these symptoms, see your doctor right away. They can check your knee replacement by:
- Physical examination to look for pain, swelling, or instability.
- Imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs to see how the implant is doing.
Knowing the signs of knee replacement wear is important for your quality of life. By spotting early signs and watching for worsening symptoms, you can work with your doctor to manage any problems.
Knee Replacement Success Rates and Outcomes
It’s important to know how well knee replacement surgery works. This surgery has greatly improved the lives of millions around the world.
Statistical Success Rates in the United States
In the U.S., knee replacement surgery is very successful. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons says over 90% of patients see big improvements. This means more than 9 out of 10 patients feel better and live better lives.
Thanks to better surgery methods, new implants, and care after surgery, fewer problems happen. More patients are happy with their results.
Patient Satisfaction Metrics
How happy patients are after surgery is key to measuring success. Many studies show most patients are very happy with their knee replacements. What makes them happy includes:
- Pain Relief: Feeling less pain in the knee.
- Improved Mobility: Being able to do more things every day.
- Quality of Care: Good experiences with doctors and care after surgery.
More than 85% of patients say they’re very happy with their surgery. They feel less pain and can do more things.
Functional Improvement Expectations
The main goal of knee replacement surgery is to help patients move better and feel better. Most people can walk better, climb stairs, and do light activities again.
It’s important for patients to know what to expect after surgery. While surgery can make a big difference, results can vary. This depends on health, age, and how bad the knee was before surgery.
Talking to a doctor about what to expect can help. This way, patients can get the best results from their surgery.
Knee Replacement Recovery Timeline
After knee replacement surgery, patients go through different recovery phases. These phases include initial healing and full rehabilitation. Knowing about these phases helps manage expectations and improve the recovery process.
Short-term Recovery Expectations
The first few weeks after surgery are key. Patients often feel pain, swelling, and can’t move much. It’s important to follow a care plan that includes managing pain, physical therapy, and slowly getting back to moving.
Key aspects of short-term recovery include:
- Managing pain and swelling through medication and rest
- Engaging in gentle exercises to maintain range of motion
- Gradually increasing mobility with the help of physical therapy
Long-term Rehabilitation Process
The long-term phase can last several months. It focuses on getting stronger, improving function, and fully recovering. This part involves more intense physical therapy to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
Patients are encouraged to be patient and persistent, as full recovery can take time.
Returning to Normal Activities
Getting back to normal activities is a big step. Most can start with light activities in 6-8 weeks. But, it may take 3-6 months to fully recover and do strenuous activities. Always follow your surgeon’s advice on when to start driving, working, or exercising again.
Age-Related Recovery Differences
Age can affect recovery, with older patients facing a longer and harder time. This is because of less muscle, bone density, and health. But, with the right care and rehab, many older patients can get back to their old level of function.
We make rehab plans based on each patient’s age, health, and goals.
Hip Replacement: Age and Longevity Considerations
When thinking about hip replacement, knowing the average age and how long the implant lasts is key. This surgery is a reliable fix for those with hip pain and trouble moving. This is often due to osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or hip fractures.
Average Age for Hip Replacement Surgery
The typical age for hip replacement surgery is between 65 to 70 years old. But, it’s not just for this age group. Younger people with severe hip damage or older folks with health issues can also get it.
Studies show more young people are getting hip replacements. This is because implants last longer and lifestyles have changed.
Lifespan of Hip Implants
Hip implants have gotten better, lasting 20 to 25 years or more. This depends on the patient’s age, how active they are, and the type of implant.
We’ll look at what affects how long hip implants last. We’ll also compare this to knee replacements.
Comparing Hip and Knee Replacement Outcomes
Hip and knee replacements are both successful surgeries. But, their results can vary. This depends on the patient, the implant, and aftercare.
|
Characteristics |
Hip Replacement |
Knee Replacement |
|---|---|---|
|
Average Age |
65-70 years |
65-70 years |
|
Implant Lifespan |
20-25 years |
15-20 years |
|
Common Complications |
Dislocation, infection |
Infection, loosening |
The table shows both surgeries have similarities and differences. This includes how long the implants last and common problems.
Other Joint Replacements: Shoulder, Ankle, and Elbow
Knee and hip replacements are common, but shoulders, ankles, and elbows can also get new parts. These surgeries help people with severe joint damage or disease. They improve quality of life.
Each joint replacement is tailored to the patient’s needs. It’s important to know about demographics, durability, and special considerations. This helps both patients and doctors.
Age Demographics for Different Joint Replacements
The age for joint replacement varies by joint. Shoulder replacements often happen in older adults. This is due to osteoarthritis or rotator cuff tears.
Ankle replacements are less common. They’re for those with severe arthritis who haven’t found relief with other treatments. Elbow replacements are for patients with rheumatoid arthritis or trauma.
Here are some key age demographics for different joint replacements:
- Shoulder Replacement: Typically occurs in individuals aged 60 and above.
- Ankle Replacement: Commonly performed on patients between 50 and 70 years old.
- Elbow Replacement: Can be performed across a wider age range, depending on the underlying condition.
Durability Expectations by Joint Type
Joint replacement durability varies by joint, materials, and patient factors. Modern implants are made to last long. But, patient activity, health, and conditions can affect their lifespan.
For example:
- Shoulder Replacements: Can last 15-20 years or more with proper care.
- Ankle Replacements: Have shown significant improvement in durability, with some lasting over 15 years.
- Elbow Replacements: The lifespan can vary, but many modern implants are designed to last for decades.
Specialized Considerations for Upper Extremity Replacements
Upper extremity replacements need special care. This is because of the joints’ complex anatomy and function. Bone quality, soft tissue, and patient expectations are key to success.
Doctors must choose the right implant and technique for each patient. Rehabilitation is also critical. It helps patients regain strength and mobility.
Technological Advances Improving Joint Replacement Longevity
New technologies are changing joint replacement surgery for the better. We’re seeing big improvements in materials, design, and surgery methods. These changes are making joint replacements last longer and work better.
Modern Materials and Design Improvements
New materials and designs are key to longer-lasting joint replacements. Implants now use advanced ceramics, titanium alloys, and special polyethylene. These materials help implants last longer, break less often, and work better with the body.
Key advancements include:
- Enhanced surface coatings to promote osseointegration
- Improved bearing surfaces to reduce wear
- Modular designs for easier revision surgeries
These design changes help implants last longer. They also make patients’ outcomes better by reducing the need for more surgeries.
Robotic-Assisted Joint Replacement Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery is a big step forward in joint replacement. It offers more precision, better alignment, and soft tissue balance. Robots give surgeons real-time data and 3D images for better planning and execution.
|
Benefits of Robotic-Assisted Surgery |
Traditional Surgery |
Robotic-Assisted Surgery |
|---|---|---|
|
Precision |
Limited by human error |
Enhanced precision with robotic assistance |
|
Recovery Time |
Variable, often longer |
Generally shorter due to less tissue damage |
|
Implant Longevity |
Dependent on surgical technique |
Improved longevity due to precise alignment |
Future Innovations in Joint Replacement Technology
The future of joint replacement looks bright, with new materials, techniques, and technologies on the horizon. We’re seeing more personalized implants, 3D printing, and artificial intelligence in planning surgeries.
As these technologies get better, we’ll see even more improvements in joint replacement surgeries. This will make patients’ lives better around the world.
Conclusion
Joint replacement surgery is a big step that can really improve life for those with severe joint damage or arthritis. Knowing the average age for this surgery and how long the implants last is key. It helps people make better choices.
Knee replacement surgery is very common, with most patients around 65 years old. But, thanks to new tech, this age is going down. Modern knee implants can last 15 to 20 years or more. This depends on how active the patient is and how well they take care of the implant.
In short, while age matters, it’s not the only thing that counts for joint replacement success. A full look at joint replacement must include the latest tech, patient needs, and how to recover after surgery. By looking at all these, people can choose the best treatment and get the best results.
FAQ
What is the average age for knee replacement surgery?
Most people getting knee replacement surgery are between 50 and 80 years old. But, we’re seeing more younger patients. This is because surgery and implants have gotten better.
How long do knee replacements typically last?
Knee replacements can last 15 to 20 years or more. This depends on how active you are, your weight, and your health. New materials and techniques are making implants last longer.
What are the signs that my knee replacement is wearing out?
Signs include more pain, stiffness, swelling, and less movement. If you notice these, talk to your doctor. They can check your implant.
Can younger patients undergo knee replacement surgery?
Yes, younger people can get knee replacements. But, it’s usually for those with severe damage or arthritis. Younger patients get special implants for better results.
How long does it take to recover from knee replacement surgery?
Recovery time varies, but most are back to normal in 3 to 6 months. First, you manage pain and swelling. Then, you work on getting strong and moving well again.
What are the success rates for knee replacement surgery?
Over 90% of patients see big improvements in pain and function. Most are very happy with their results, saying their life is better after surgery.
Are there any age-related differences in knee replacement recovery?
Older patients might take a bit longer to recover. This is because of less muscle and bone. But, with the right care, many older patients do very well.
Can I undergo knee replacement surgery if I have other health conditions?
It depends on your health and conditions. We look at your overall health to decide if surgery is right for you.
What advancements are being made in knee replacement technology?
New materials, designs, and robotic surgery are improving knee replacements. These changes aim to make implants last longer and work better, and to speed up recovery.
How do I know if I need a knee replacement or just conservative treatment?
You’ll need surgery if other treatments don’t help. We check your symptoms, damage, and health to choose the best treatment.
What is the average lifespan of a hip replacement?
Hip replacements usually last 15 to 20 years or more. Your activity, weight, and health can affect how long it lasts.
Are there differences in outcomes between hip and knee replacements?
Both have high success rates, but results can vary. Hip and knee surgeries can both greatly improve your life. But, the specifics of each surgery and recovery can differ.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29546996/





