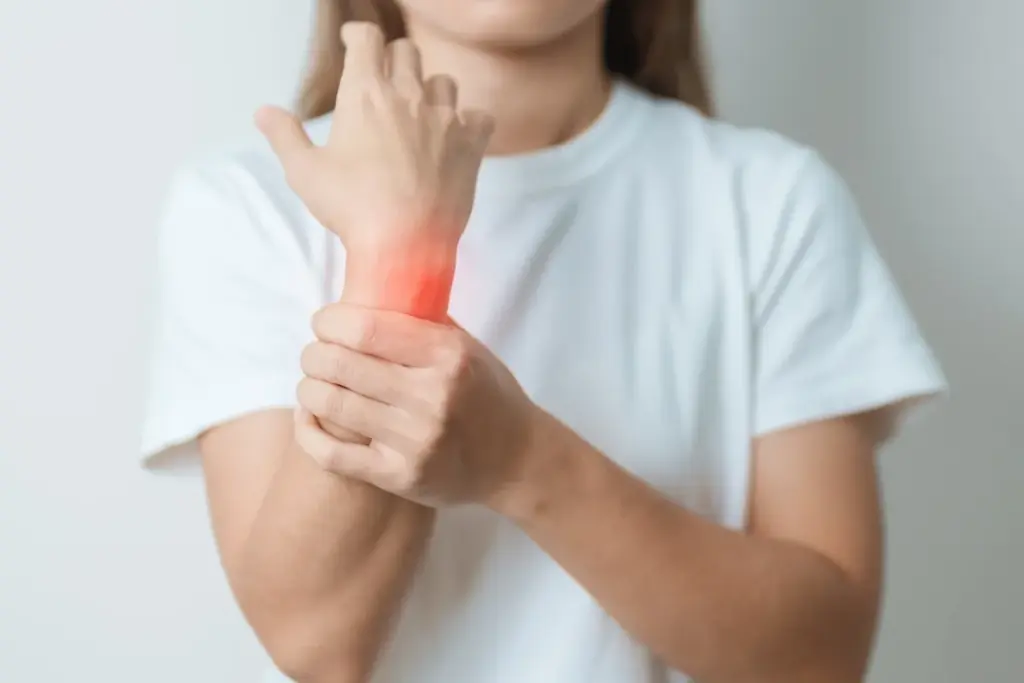

De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a painful condition that affects the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. It causes discomfort and limits thumb mobility. Approximately 1 in 1,000 people are affected by this condition, with women being more likely to develop it than men.
When conservative treatments fail, surgery becomes a viable option to relieve the symptoms. Understanding the duration of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis surgery is key for patients to plan their recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Surgery is often required to relieve symptoms of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis.
- The condition affects approximately 1 in 1,000 people.
- Women are more likely to develop de Quervain’s tenosynovitis than men.
- Conservative treatments are often tried before surgery.
- Understanding surgery duration helps patients plan their recovery.
Understanding de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a common problem in the wrist and thumb. It causes tendon inflammation. People often feel pain and tenderness when making fists, grasping, or turning their wrists.
Definition and Anatomy
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is when the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist get inflamed. It affects the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendons. These tendons help move the thumb. It was named after Swiss surgeon Fritz de Quervain, who first described it.
The wrist has many tendons, nerves, and blood vessels. The tendons in de Quervain’s tenosynovitis are covered by a sheath. When this sheath gets inflamed, it causes pain and discomfort.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis often comes from repetitive motion or strain. This is true for activities that involve gripping, twisting, or lifting. Repetitive strain injuries are common in people who do tasks that require thumb and wrist movement over and over.
Risk factors include:
- Repetitive motion or strain
- Direct injury to the wrist or thumb
- Inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis
- Activities that involve repetitive thumb and wrist movements, like typing or assembly line work
Prevalence and Demographics
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is quite common and affects people of all ages and jobs. It is more common in women, often during pregnancy and after giving birth. It also affects people who do activities that require a lot of wrist and thumb movement.
Knowing who is at risk helps us take steps to prevent it.
Common Symptoms and Diagnosis

Knowing the symptoms of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis is key for early treatment. This condition causes pain and tenderness on the thumb side of the wrist.
Characteristic Signs of de Quervain’s
The symptoms of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis include pain and swelling on the thumb side of the wrist. Pain gets worse with gripping or twisting movements. Some people feel a catching or snapping sensation when moving their thumb.
A healthcare provider will do a physical exam to check the symptoms. They might do the Finkelstein test. This test involves bending the thumb into the palm and then bending the wrist toward the little finger. If you feel pain on the thumb side, it’s a positive test.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
While a physical exam is often enough, more tests might be needed. These include:
- X-rays to look for arthritis or fractures.
- MRI or ultrasound to see the tendons and check for inflammation or damage.
These tests confirm de Quervain’s tenosynovitis and help plan treatment.
Differential Diagnosis
It’s important to tell de Quervain’s tenosynovitis apart from other wrist pain causes. Other possible causes include:
|
Condition |
Characteristics |
|---|---|
|
Osteoarthritis |
Joint pain and stiffness, often with a grinding sensation. |
|
Wrist fracture |
Severe pain after trauma, with possible deformity. |
|
Intersection syndrome |
Pain and swelling where the tendons cross, about 2 inches proximal to the wrist. |
“Accurate diagnosis is key to effective management of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. A thorough clinical evaluation, combined with appropriate diagnostic tests, helps in distinguishing this condition from other causes of wrist pain.” –
Orthopedic Specialist
By knowing the signs and using tests, doctors can accurately diagnose de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. They can then create a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
Conservative de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis Treatment Options
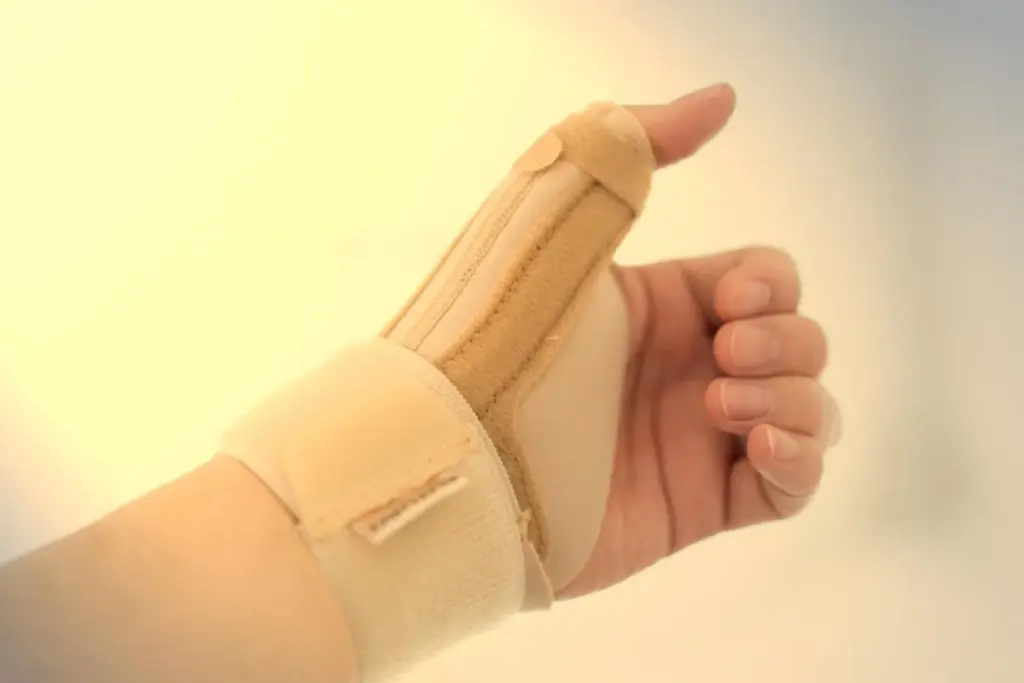
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis can often be managed with conservative treatments. These methods aim to lessen pain, swelling, and injury risk. They help improve wrist function and quality of life.
Rest and Activity Modification
Resting the affected wrist and changing activities are key steps. Avoiding repetitive motions and heavy lifting helps.
By resting the wrist and adjusting daily tasks, patients can reduce tendon strain.
Splinting and Bracing
Splinting or bracing the wrist is another approach. It immobilizes the wrist, easing tendon strain and aiding healing.
A study showed splinting can be an effective first treatment. Many patients find symptom relief.
Anti-inflammatory Medications
Anti-inflammatory medications, like NSAIDs, are used to manage pain and swelling. They are helpful during flare-ups, allowing patients to keep up with daily activities.
Corticosteroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections are a more invasive option. They involve injecting steroids into the tendon sheath to reduce inflammation.
Research indicates these injections can effectively resolve symptoms in many patients.
|
Treatment Option |
Description |
Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
|
Rest and Activity Modification |
Avoiding repetitive motions and heavy lifting |
High |
|
Splinting and Bracing |
Immobilizing the wrist to reduce strain |
High |
|
Anti-inflammatory Medications |
Using NSAIDs to manage pain and inflammation |
Moderate to High |
|
Corticosteroid Injections |
Injecting steroids to reduce inflammation |
High |
A medical expert notes, “Conservative management is a valuable first line for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. It may avoid the need for surgery.”
“The goal of conservative treatment is to alleviate symptoms, promote healing, and restore normal function to the wrist.”
An Orthopedic Specialist
When Surgery Becomes Necessary
In some cases, surgery is needed for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. This is usually a last resort. It’s considered when other treatments don’t work or the condition is severe.
Failed Conservative Treatment
First, doctors try non-surgical treatments like rest and splints. They also use anti-inflammatory drugs and injections. But if these don’t help, surgery might be needed.
Severity Indicators
Some signs show surgery is needed. These include ongoing pain, swelling, and trouble moving the thumb. How much these symptoms affect daily life is key.
Quality of Life Considerations
How de Quervain’s tenosynovitis affects your life is important. If it hampers daily activities, work, or fun, surgery might be the best option. It can help improve your quality of life.
Choosing to have de Quervain’s tenosynovitis surgery should be a team decision. Talk to a de Quervain’s specialist for advice tailored to your situation.
Types of Surgical Procedures for de Quervain’s
There are different ways to surgically treat de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. Each method has its own benefits and drawbacks. The choice depends on how severe the condition is, the patient’s health, and the surgeon’s preference.
Open Surgery Technique
Open surgery is a traditional method for treating de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. It involves making a small incision to release the tendon constriction.
Advantages of Open Surgery:
- Direct visualization of the tendon and surrounding structures
- Ability to address any additional issues, such as tendon damage or scar tissue
- Generally considered a straightforward procedure with a relatively quick recovery
A leading orthopedic surgeon notes, “Open surgery for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a reliable method that has been refined over the years, with a high success rate.”
“The open technique allows for a thorough examination and treatment of the affected area, ensuring that the tendon is properly released and reducing the risk of recurrence.”
An Orthopedic Surgeon
Endoscopic Approach
The endoscopic approach is a less invasive technique. It uses a small camera and specialized instruments to release the tendon through smaller incisions.
Benefits of Endoscopic Surgery:
- Smaller scars and less tissue damage
- Potential for less post-operative pain
- Quicker return to normal activities
|
Surgical Method |
Incision Size |
Recovery Time |
Post-Operative Pain |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Open Surgery |
Larger incision (about 1-2 inches) |
Typically 2-4 weeks |
Moderate to significant |
|
Endoscopic Surgery |
Smaller incisions (about 0.5-1 inch total) |
Often 1-3 weeks |
Less, due to minimal tissue disruption |
Comparing Surgical Methods
Both open and endoscopic surgeries are used to treat de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. The choice depends on the patient’s specific needs and the surgeon’s expertise.
The decision on which method to use should be made after a thorough consultation. It should consider the patient’s condition, lifestyle, and preferences.
Pre-Surgical Preparation
Getting ready for de Quervain’s surgery is key. It makes sure patients are set for the procedure. This helps avoid any problems during and after surgery.
Medical Evaluation
Before surgery, a full medical check-up is needed. This looks at the patient’s health history and current status. The de Quervain’s specialist will also do a physical exam. This helps figure out how bad the condition is and if there are other health issues.
Medication Adjustments
Patients might need to change their meds before surgery. Some drugs, like blood thinners, could increase bleeding risks. It’s important to tell the de Quervain’s specialist about all meds, including supplements and over-the-counter drugs.
Day-of-Surgery Instructions
On surgery day, patients must follow their doctor’s instructions. This includes fasting, arrival times, and what to wear. Also, arrange for someone to drive you home. You might be feeling the effects of anesthesia or pain meds.
|
Preparation Aspect |
Description |
Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
|
Medical Evaluation |
Comprehensive assessment of patient’s health |
de Quervain’s Specialist |
|
Medication Adjustments |
Adjusting medications to minimize risks |
Patient and de Quervain’s Specialist |
|
Day-of-Surgery Instructions |
Following specific instructions for the surgery day |
Patient |
By following these steps, patients can make sure their surgery goes well. And they’ll have an easier recovery.
The Surgical Procedure Duration
De Quervain’s surgery time can vary for several reasons. Knowing these can help patients get ready for their surgery.
Average Time for Standard Cases
For most of Quervain’s tenosynovitis surgeries, it takes about 30 to 60 minutes. This can change a bit based on the surgeon’s skill and the methods used.
Factors That May Extend Surgery Time
Several things can make surgery last longer. These include how complex the case is, any unusual anatomy, and if more procedures are needed. For example, if you’ve had surgery in that area before, it might make things more complicated.
Anesthesia Considerations
The kind of anesthesia used can also affect how long surgery takes. Local anesthesia is often used, which means you can stay awake. Getting ready for surgery and the anesthesia itself can add to the time in the operating room.
|
Factor |
Potential Impact on Surgery Time |
|---|---|
|
Complexity of the Case |
Increased time due to additional care needed |
|
Anatomical Variations |
Potential for longer surgery due to unexpected structures |
|
Type of Anesthesia |
Local anesthesia typically doesn’t add significant time |
|
Surgeon’s Experience |
More experienced surgeons may complete the procedure more efficiently |
Step-by-Step Surgical Process
The surgery for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a detailed process. It needs precision and care. It has several important stages for a good outcome.
Anesthesia Administration
The first step is giving anesthesia. This can be local or regional, based on the patient’s needs and the surgeon’s choice. Local anesthesia is often used to numb the wrist area. This lets the patient stay awake during the surgery.
Incision and Exposure
After anesthesia takes effect, the surgeon makes a small cut in the skin. The cut’s size and place depend on the surgery method. Then, the surgeon carefully opens the tissue to show the first dorsal compartment.
Release of the First Dorsal Compartment
The main part of the surgery is releasing the first dorsal compartment. The surgeon finds the tendon sheath and carefully frees it. This step is key to easing de Quervain’s tenosynovitis symptoms.
Closure and Dressing
After releasing, the surgeon closes the cut with stitches or staples. The wound is then covered with a clean bandage to prevent infection. The patient gets instructions on wound care during recovery.
|
Surgical Step |
Description |
Importance |
|---|---|---|
|
Anesthesia Administration |
Numbs the area to prevent pain |
Crucial for patient comfort |
|
Incision and Exposure |
Allows access to the affected tendon |
Essential for the success of the surgery |
|
Release of the First Dorsal Compartment |
Relieves constriction on the tendons |
Key to alleviating symptoms |
|
Closure and Dressing |
Protects the wound from infection |
Important for recovery |
Immediate Recovery Period
Knowing how to recover right after de Quervain’s surgery is key. The first days are very important for a smooth recovery.
First 24-48 Hours After Surgery
The first 24 to 48 hours are very important. You should rest your hand and keep it up to reduce swelling. Ice packs can help with pain and swelling, as your doctor suggests.
Key actions during the first 24-48 hours include:
- Resting the hand and wrist
- Elevating the hand above the level of the heart
- Applying ice packs as recommended
- Following medication instructions precisely
Pain Management
Pain management is very important right after surgery. You will get pain medicine to help with discomfort. Always follow the dosage your doctor gives you to avoid side effects.
Pain management strategies include:
- Adhering to the prescribed medication regimen
- Monitoring pain levels and reporting any severe pain to the healthcare provider
- Using ice packs to reduce inflammation and pain
Initial Movement Restrictions
Right after surgery, you’ll need to avoid certain movements. Don’t lift heavy things or bend, as it can strain your wrist.
- Avoiding heavy lifting or bending
- Limiting wrist movement as advised by the healthcare provider
- Gradually resuming activities as directed
By following these steps and your doctor’s advice, you can have a smooth recovery. This will help you get better faster.
Long-Term Recovery Timeline
Recovering from De Quervain’s surgery takes time and care. Knowing the recovery timeline helps set realistic goals. It makes the healing process smoother.
First Two Weeks
The first two weeks are key for healing and managing pain. Keep the surgery area clean and dry. Start with gentle exercises to keep fingers moving. Pain usually goes down in the first week, but some discomfort is normal.
Weeks 2-6 Post-Surgery
Weeks 2 to 6 bring big improvements. The wound heals, and most can start to increase their activity slowly. Avoid heavy lifting and repetitive wrist motions.
Return to Normal Activities
Most people return to normal in 6 to 8 weeks. But, recovery times vary. It depends on health, surgery complexity, and following instructions.
“Recovery times can differ, but with proper care, most patients can expect a full recovery,”
An orthopedic surgeon says.
Complete Recovery Expectations
Full recovery takes several months. It’s important to follow a structured rehabilitation program. This includes physical therapy. Knowing the recovery timeline helps prepare for the journey.
Post-Surgical Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation after de Quervain’s tenosynovitis surgery is key to recovery. It helps regain wrist function, reduces pain, and prevents future issues.
Physical Therapy Protocols
Physical therapy is essential in the recovery process. A physical therapist creates a custom plan. This plan includes exercises to improve wrist mobility and strengthen muscles.
Early mobilization is important to avoid stiffness and aid healing.
- Range of motion exercises to maintain flexibility
- Strengthening exercises for the wrist and forearm
- Modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation to reduce pain and inflammation
Home Exercise Programs
A home exercise program is also vital. Patients get daily exercises to do at home. These may include:
- Wrist extensions and flexions
- Forearm rotations
- Finger bends and spreads
Consistency is key. Doing these exercises daily can greatly improve recovery.
Strengthening and Mobility Exercises
As the wrist heals, exercises become more challenging. They may use resistance bands or weights. Gradual progression is important to avoid injury.
Rehabilitation after de Quervain’s surgery is a detailed process. It needs patience, dedication, and a good plan. By doing physical therapy and home exercises, patients can fully recover and get back to their activities.
Potential Complications and Risks
De Quervain’s surgery is usually safe, but there are risks to know. Knowing these can help you decide if surgery is right for you.
Common Minor Complications
Minor issues after de Quervain’s surgery might include:
- Temporary swelling and bruising
- Pain or discomfort at the surgical site
- Minor wound infections
These problems can often be handled with good care and medicine after surgery.
Serious Complications
Though rare, serious problems can happen, such as:
- Nerve damage or neuroma formation
- Infection needing antibiotics or more surgery
- Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS)
It’s important to watch your health after surgery and tell your doctor if you notice any bad signs.
Long-Term Surgical Failure Rates
Failure of surgery, where symptoms don’t go away or come back, is a long-term risk. The failure rate for de Quervain’s surgery can be between 5% to 15%. This depends on the surgery method and how well you recover.
|
Study |
Failure Rate |
Follow-Up Period |
|---|---|---|
|
Study A |
7% |
12 months |
|
Study B |
12% |
24 months |
Knowing about the possible problems with de Quervain’s surgery is key. It helps you understand what might happen and make a better choice for your treatment.
Success Rates and Outcomes
It’s important to know how well de Quervain’s surgery works. This surgery is for a wrist problem that doesn’t get better with other treatments. It helps the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist.
Statistical Success Rates
Research shows de Quervain’s surgery works well for most people. Patients often feel much better after the surgery. This is because the surgery helps the tendons by releasing tension.
- High Success Rate: Over 90% of patients see symptom relief.
- Improved Functionality: Wrist and thumb work better for patients.
- Low Complication Rate: Serious problems are rare, making outcomes good.
Factors Affecting Outcomes
Many things can change how well surgery works. These include how bad the problem was before surgery, the surgery method, and how well the patient recovers.
Surgical Technique: Both open and endoscopic methods work well. The choice depends on the doctor and the patient’s needs.
Patient Satisfaction Studies
Studies show most patients are happy with their surgery results. They feel less pain and can do more things again.
- Most patients are pleased with their surgery results.
- Most can go back to normal activities in a few weeks.
- Studies show symptoms stay better over time.
Cost and Insurance Considerations
People thinking about de Quervain’s surgery often wonder about the costs and insurance. It’s key to know these financial details to make good choices about your health.
Average Cost of de Quervain’s Surgery
The cost of de Quervain’s surgery can change a lot. It depends on where you are, the surgeon’s fees, and the hospital costs. Usually, it’s between $1,000 and $3,000. Here’s a simple cost guide:
|
Service |
Average Cost |
|---|---|
|
Surgeon’s Fee |
$500 – $1,500 |
|
Facility Fee |
$500 – $1,000 |
|
Anesthesia Fee |
$200 – $800 |
|
Total |
$1,200 – $3,300 |
Insurance Coverage Typical Policies
Insurance for de Quervain’s surgery changes with each provider and policy. Most plans cover surgery if other treatments don’t work. It’s important to check your coverage and any costs you might have to pay.
Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Out-of-pocket costs for de Quervain’s surgery include deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. These can differ a lot based on your insurance. For instance, someone with a $500 deductible and 20% coinsurance might have to pay a lot themselves.
Preventing Recurrence After Surgery
To stop de Quervain’s tenosynovitis from coming back, you need a few steps after surgery. You should think about how you work, change your activities, and keep up with self-care. This way, you can avoid problems in the long run.
Ergonomic Considerations
Changing your workspace and daily habits is key to avoiding de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. You should make your workspace better for your wrists and hands.
- Use an ergonomic keyboard and mouse
- Make sure your workspace supports good posture
- Stretch and move around often
Activity Modifications
Changing how you do things is important. You might need to do tasks differently or skip things that hurt your wrists.
|
Activity |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
Lifting heavy objects |
Use proper lifting techniques, avoiding twisting and strain on the wrist |
|
Repetitive tasks |
Take regular breaks, stretch, and vary tasks to avoid repetitive strain |
|
Sports and hobbies |
Adjust techniques to reduce strain on the wrist, consider using supportive devices |
Ongoing Self-Care Strategies
Keeping up with self-care is essential to avoid de Quervain’s tenosynovitis coming back. This means living a healthy life, managing stress, and doing exercises to keep your wrist and hand strong.
- Regular exercise to maintain flexibility and strength
- Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga
- A healthy diet and enough water
By following these tips every day, you can lower the chance of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis coming back after surgery.
How long does de Quervain surgery take?
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a condition that affects the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. It causes pain and discomfort. Surgery is often required to relieve the symptoms when other treatments fail. Understanding the duration of de Quervain’s surgery is key for patients considering surgical treatment options.
The time it takes for de Quervain surgery varies. It usually lasts between 30 to 60 minutes. Several factors can affect this time, including the case’s complexity and the surgeon’s experience.
Key Takeaways
- The duration of de Quervain’s surgery is typically between 30 to 60 minutes.
- Surgery is considered when conservative treatments fail to relieve symptoms.
- The complexity of the case can influence the surgery duration.
- Understanding the surgery duration helps patients prepare for the procedure.
- De Quervain’s tenosynovitis affects the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist.
Understanding de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a condition that affects the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. It causes pain and tenderness, mainly when forming a fist or grasping. This is because of inflammation in the tendons and their sheaths.
Definition and Anatomy
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis affects the tendons of the thumb. The abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendons are involved. These tendons control thumb movement and can become inflamed, causing pain.
The condition was named after Swiss surgeon Fritz de Quervain. The anatomy of the wrist and thumb is key to understanding this condition. The tendons and their sheaths are prone to strain and injury from repetitive motion.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis is not always clear. But it’s linked to repetitive motion and strain on the thumb and wrist. Activities like gardening, typing, or lifting can lead to this condition.
“Repetitive strain on the wrist and thumb can lead to inflammation and pain associated with de Quervain’s tenosynovitis.”
Risk factors include repetitive activities, direct injury to the wrist or thumb, and inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Prevalence and Demographics
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is quite common, affecting those who strain their wrist and thumb. It’s more common in women, often during pregnancy and after giving birth. Hormonal changes and fluid retention are thought to be reasons.
- Women are more likely to be affected than men.
- It is common among individuals aged 30-50 years.
- Activities involving repetitive thumb and wrist motion increase the risk.
Common Symptoms and Diagnosis
Pain and swelling on the thumb side of the wrist are signs of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. This condition often affects people who do repetitive hand tasks, like typing or manual labor.
Characteristic Signs
The main symptoms include pain and tenderness, mainly when forming a fist or grasping. Swelling and warmth on the thumb side of the wrist are also common.
Key symptoms to watch for:
- Pain on the thumb side of the wrist
- Swelling or tenderness near the thumb
- Difficulty moving the thumb or wrist
- Pain when grasping or pinching
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Diagnosing de Quervain’s tenosynovitis involves a physical exam and medical history review. The Finkelstein test is a key diagnostic tool.
The Finkelstein test involves bending the thumb into the palm and then bending the wrist toward the little finger. If this causes pain on the thumb side, it’s likely de Quervain’s tenosynovitis.
“The Finkelstein test is a valuable diagnostic tool for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis, helping clinicians accurately identify the condition.”
Differential Diagnosis
Other conditions like osteoarthritis, ganglion cysts, or intersection syndrome can also cause wrist pain. Accurate diagnosis is key for effective treatment.
Healthcare providers might use X-rays or ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Conservative de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis Treatment Options
When treating de Quervain’s tenosynovitis, doctors often start with non-surgical methods. These methods aim to lessen pain and swelling. They can help manage symptoms without surgery.
Rest and Activity Modification
Resting the wrist and changing how you do things is a key first step. Try to avoid actions that make the problem worse. This means not doing things that repeat the same motion or lifting heavy things.
- Avoiding activities that aggravate the condition
- Modifying work or recreational activities
- Using ergonomic adjustments to reduce strain
Splinting and Bracing
Wearing a splint or brace can help keep the wrist steady. This lessens the pressure on the tendons and helps them heal. You can get splints made just for you or buy them at a store.
Benefits of splinting include:
- Reduced pain and inflammation
- Immobilization of the wrist
- Support during the healing process
Anti-inflammatory Medications
Medicines like NSAIDs can help with pain and swelling. It’s important to take them as directed and talk to a doctor about it.
“NSAIDs are commonly used to manage pain and inflammation associated with de Quervain’s tenosynovitis.” –
Medical Guidelines
Corticosteroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections are another non-surgical option. They can greatly reduce swelling and help with pain.
Key considerations for corticosteroid injections include:
- The possibility of significant pain relief
- The need for possibly more than one injection
- The risk of side effects with repeated use
When Surgery Becomes Necessary
If treatments like rest and splints don’t work for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis, surgery might be needed. Doctors decide this after checking how bad the condition is and how it affects your life.
Failed Conservative Treatment
First, doctors try treatments like rest and splints for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. They also use medicines and injections. If these don’t help after a few months, surgery is considered. This is after trying treatments for a long time.
Severity Indicators
Some signs show you might need surgery for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. These include persistent pain, a lot of swelling, and trouble moving your wrist. How much these symptoms affect your daily life is key in deciding on surgery.
Quality of Life Considerations
Thinking about your quality of life is also important when deciding on surgery. If de Quervain’s tenosynovitis really gets in the way of your daily activities, work, or hobbies, surgery might be a better choice.
“Surgery can greatly improve life for those with severe de Quervain’s tenosynovitis by lessening pain and improving function,”
an expert in hand surgery says.
Choosing surgery is a big decision. It’s made with your doctor, considering your condition, health, and what you prefer.
Types of Surgical Procedures for de Quervain’s
Surgery is an option when other treatments don’t work for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. The main goal is to relieve pressure on the tendons. This helps restore normal function.
Open Surgery Technique
The open surgery method involves a small cut in the skin. This lets the surgeon see and release the tight tendons. It’s a common choice because it’s simple and works well.
- The cut is made in a skin fold to hide the scar.
- The surgeon finds and frees the tight tendon sheath.
- Then, the cut is closed with stitches or staples.
Endoscopic Approach
The endoscopic method is less invasive. It uses a small camera and tools to fix the problem. This way, there’s often less pain and a quicker recovery.
- A small cut is made for the endoscope and tools.
- The tight area is released while being watched on a screen.
- The cut is closed with a few stitches or left open.
Comparing Surgical Methods
Open and endoscopic surgeries have their own pros and cons. The choice depends on the doctor, the patient’s body, and other factors.
|
Surgical Method |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
|
Open Surgery |
Direct view, often used |
More pain, visible scar |
|
Endoscopic Approach |
Less invasive, less pain |
Needs special tools and training |
In summary, both open and endoscopic surgeries can treat de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. The right choice depends on the patient’s needs and the doctor’s advice.
Pre-Surgical Preparation
Getting ready for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis surgery is a big step. It’s important to prepare well to avoid risks and get the best results.
Medical Evaluation
Before surgery, a detailed medical check-up is needed. This check-up looks at your health history and current status. The de Quervain’s specialist will check for any risks or complications.
Tests like blood work might be part of this check-up. The specialist will also look at your medications to see if changes are needed.
Medication Adjustments
Some medicines might need to be changed or stopped before surgery. This includes blood thinners and anti-inflammatory drugs. The de Quervain’s specialist will tell you what to do with your medications.
Telling your specialist about all your medicines is very important. This helps avoid any bad reactions or problems.
Day-of-Surgery Instructions
On the day of surgery, there are important steps to follow. These steps help make the surgery go smoothly. You might need to:
- Fasting or follow certain food rules
- Arrive at a certain time and place
- Bring certain clothes or items
- Do specific things to prepare for surgery
|
Pre-Surgical Preparation Step |
Description |
Importance |
|---|---|---|
|
Medical Evaluation |
Comprehensive review of patient’s medical history and current health status |
High |
|
Medication Adjustments |
Managing medications to avoid complications during surgery |
High |
|
Day-of-Surgery Instructions |
Following specific guidelines for a smooth surgery |
High |
By following these steps, you can help make your surgery a success.
The Surgical Procedure Duration
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis surgery time can vary. Knowing what affects it helps patients get ready and know what to expect.
Average Time for Standard Cases
The usual time for de Quervain’s surgery is 30 to 60 minutes. This can change a bit based on the surgeon’s skill and the methods used.
|
Surgery Type |
Average Duration |
Factors Influencing Time |
|---|---|---|
|
Open Surgery |
45 minutes |
Complexity of the case, surgeon’s experience |
|
Endoscopic Surgery |
30 minutes |
Equipment used, patient’s anatomy |
Factors That May Extend Surgery Time
Several things can make de Quervain’s surgery longer. These include:
- The case’s complexity, like scar tissue or unusual anatomy.
- The need for extra procedures, like tendon repair.
- The surgeon’s experience with the procedure.
Anesthesia Considerations
Anesthesia type also affects surgery time. Local anesthesia is often used for quicker recovery. But, general anesthesia or sedation might be needed in some cases, changing the surgery time.
Understanding what affects de Quervain’s surgery time helps patients prepare. It also helps them know what to expect during and after the surgery.
Step-by-Step Surgical Process
Learning about the steps in de Quervain’s tenosynovitis surgery helps patients get ready. The goal is to ease the tightness in the wrist tendons. This helps reduce pain and improves wrist function.
Anesthesia Administration
The first step is giving anesthesia. It can be local or regional, based on what the patient and doctor decide. Local anesthesia numbs just the area of surgery. Regional anesthesia numbs a bigger area, like from the elbow down. Choosing the right anesthesia is key for comfort during the surgery.
Incision and Exposure
After anesthesia, the surgeon makes a small cut in the skin. The cut’s size and where it is depends on the surgery type. This cut lets the surgeon see and work on the tendons in the first dorsal compartment.
Release of the First Dorsal Compartment
The main part of the surgery is releasing the first dorsal compartment. The surgeon opens the compartment and checks the tendons. Then, they make sure the tendons can move freely by removing any tightness or swelling. This is key to fixing de Quervain’s tenosynovitis symptoms.
Closure and Dressing
After fixing the tendons, the surgeon closes the cut with stitches or staples. Then, they apply a dressing to protect the wound. This dressing stays on for a few days to help the wound start healing.
|
Surgical Step |
Description |
Importance |
|---|---|---|
|
Anesthesia Administration |
Numbs the area to prevent pain during surgery |
Ensures patient comfort |
|
Incision and Exposure |
Allows access to the affected tendons |
Enables the surgeon to perform the necessary repairs |
|
Release of the First Dorsal Compartment |
Relieves constriction on the tendons |
Critical for alleviating symptoms |
|
Closure and Dressing |
Protects the wound and promotes healing |
Essential for recovery |
The steps in de Quervain’s tenosynovitis surgery are carefully planned. Knowing these steps helps patients prepare for the surgery and recovery.
Immediate Recovery Period
The first days after surgery are key for a good recovery from de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. This time is for managing pain, taking care of the wound, and following movement rules to help healing.
First 24-48 Hours After Surgery
In the first 24-48 hours, rest the hand and keep it up to lower swelling. It’s important to follow the doctor’s advice on wound care and dressing changes.
- Keep the wound dry and clean
- Watch for signs of infection, like redness, swelling, or more pain
- Take the pain meds as told by your doctor
Pain Management
Managing pain well is very important right after surgery. Doctors usually give pain meds to help with the pain. It’s key to take the meds as directed by your doctor.
Key aspects of pain management include:
- Stick to the medication schedule
- Report any severe or ongoing pain to your doctor
- Use ice packs to lessen swelling and pain
Initial Movement Restrictions
To help healing, avoid moving the wrist and thumb too much. You might need to wear a splint or bandage to keep it stable.
Avoid heavy lifting, bending, or anything that strains the wrist. Slowly, you can start doing normal things again with your doctor’s okay.
Long-Term Recovery Timeline
Recovering from De Quervain’s surgery takes time and careful care. Knowing the recovery timeline helps patients plan and stick to their rehabilitation plans.
First Two Weeks
The first two weeks are key for healing and managing pain. It’s important to keep the surgery area clean and dry. Also, follow your doctor’s advice on medication.
Key Activities During the First Two Weeks:
- Gentle wrist and thumb movements to prevent stiffness
- Avoiding heavy lifting or bending
- Keeping the hand elevated to reduce swelling
Weeks 2-6 Post-Surgery
Between weeks 2-6, you’ll see big improvements. The pain will lessen, and you’ll move your wrist and thumb more easily.
Physical therapy may be recommended to help you get better. It focuses on strengthening and improving flexibility.
Return to Normal Activities
You can usually go back to your usual activities in 4-6 weeks. This depends on your job and how well you’re recovering.
|
Activity |
Typical Recovery Time |
|---|---|
|
Light Desk Work |
1-2 weeks |
|
Manual Labor |
4-6 weeks |
|
Sports or Heavy Activities |
6-8 weeks |
Complete Recovery Expectations
Full recovery from De Quervain’s surgery can take months. It’s important to be patient and follow your care instructions for the best results.
Knowing the recovery timeline helps you manage your post-surgery journey. It ensures a smooth return to your usual activities.
Post-Surgical Rehabilitation
After de Quervain’s surgery, post-surgical rehabilitation is key. It combines physical therapy and home exercises to strengthen and improve mobility.
A good rehabilitation plan is vital for the best results after surgery. It aims to improve wrist function, reduce pain, and enhance hand and wrist movement.
Physical Therapy Protocols
Physical therapy is a big part of recovery. A physical therapist will make a special exercise plan. This plan helps patients regain wrist and hand strength and movement.
- Gentle exercises to keep flexibility
- Strengthening exercises for the wrist and forearm
- Modalities like heat or cold therapy to manage pain and inflammation
Home Exercise Programs
Patients also get a home exercise plan. This includes daily exercises like:
- Wrist extensions and flexions
- Forearm rotations
- Finger bends and spreads
It’s important to stick to the home exercise plan. Doing these exercises as told by your doctor helps with recovery.
Strengthening and Mobility Exercises
As recovery goes on, exercises focus on getting stronger and moving better. These help the wrist and hand work better, so patients can do their usual activities.
Strengthening exercises might include:
- Resistance band exercises
- Weight training
- Putty or grip strengthening exercises
Mobility exercises are also key. They make sure the wrist and hand can move freely.
Potential Complications and Risks
It’s important to know the possible complications and risks of de Quervain’s surgery. This is true for anyone thinking about this treatment. There are different kinds of complications, from small to serious.
Common Minor Complications
Minor issues after de Quervain’s surgery might include:
- Temporary numbness or tingling around the surgical site
- Mild pain or discomfort
- Swelling or bruising
- Infection (though rare, this can often be treated with antibiotics)
Serious Complications
While not common, serious problems can happen:
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS): A condition with chronic pain and inflammation.
- Nerve Damage: Damage to nerves around the surgery site, causing ongoing numbness or pain.
- Infection: Though rare, infections can be serious and need quick medical care.
Long-Term Surgical Failure Rates
There’s a risk of surgery not working as hoped. Studies show the failure rate is low. But, it can depend on the surgery method and the patient’s health.
|
Complication Type |
Description |
Frequency |
|---|---|---|
|
Minor Complications |
Temporary numbness, mild pain, swelling |
Common |
|
Serious Complications |
CRPS, nerve damage, serious infection |
Rare |
|
Surgical Failure |
Persistence or return of symptoms |
Low |
It’s key for patients to talk to their doctor about these risks. This way, they can understand the specific risks for their situation.
Success Rates and Outcomes
Patients who get de Quervain’s surgery often see big improvements. The surgery releases the tendon sheath in the first dorsal compartment. This is a very effective way to treat de Quervain’s tenosynovitis.
Statistical Success Rates
Research shows that de Quervain’s surgery works well for most people. Between 80% to 90% of patients feel better after the surgery. They say they have less pain and can move their wrists better.
The surgery’s success comes from the careful technique used. Proper surgical intervention helps a lot. It makes it easier for patients to do their daily activities again.
Factors Affecting Outcomes
Several things can change how well the surgery works. These include:
- The severity of the condition before surgery
- Any health problems the patient has
- The surgery method used
- How well the patient follows up with care and exercises after surgery
Patient compliance with after-care is very important. Doing exercises and physical therapy helps a lot. It helps the wrist get strong and move well again.
Patient Satisfaction Studies
Studies show that most patients are very happy with the results of de Quervain’s surgery. They say they feel less pain and can do more things. They also feel better overall.
A study in a top orthopedic journal found that over 90% of patients were happy. They said the surgery helped a lot with pain and function.
Cost and Insurance Considerations
It’s important for patients to know the costs of de Quervain’s surgery. The price can change based on where you are, who does the surgery, and the methods used.
Average Cost of de Quervain’s Surgery
In the United States, de Quervain’s surgery can cost between $1,000 and $3,000. This price usually includes the surgeon’s fee, anesthesia, and the place where the surgery is done. But, costs for tests before surgery, care after, and physical therapy might not be in this first estimate.
“The cost of hand surgery can be high,” says a hand surgeon. “It’s key for patients to know what their insurance pays for. A pre-operative consultation can help clear up these costs.”
Insurance Coverage Typical Policies
Most insurance plans cover de Quervain’s surgery if it’s needed. But, how much they cover can differ a lot. It depends on the insurance company and your policy. It’s best to talk to your insurance to know what you’ll pay for.
- Verify insurance coverage before scheduling surgery
- Understand the deductible and co-pay amounts
- Check if pre-authorization is required
Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Expenses you might have to pay for de Quervain’s surgery include deductibles, co-pays, and costs for services not covered. You should also think about the cost of time off work or arrangements for care after surgery.
Tips for Managing Costs:
- Choose an in-network provider to reduce costs
- Plan for post-operative care to avoid additional expenses
- Review and understand all the charges before the surgery
Preventing Recurrence After Surgery
To stop de Quervain’s tenosynovitis from coming back, you need to make lifestyle changes and ergonomic adjustments. After surgery, it’s important to take steps to ensure success and lower the chance of it happening again.
Ergonomic Considerations
Changing your daily activities to be more ergonomic is key. Look at your workspace, tools, and how you do things to lessen wrist and thumb strain. For example, using an ergonomic keyboard and mouse, stretching regularly, and keeping good posture can help a lot.
- Adjust your workstation to promote good posture.
- Use ergonomic tools and equipment designed to reduce strain.
- Take regular breaks to stretch and move around.
Activity Modifications
Changing activities that make de Quervain’s tenosynovitis worse is also important. You might need to do tasks differently, avoid repetitive actions, and not do things that make you grip or twist. These changes can greatly lower the risk of it coming back.
|
Activity |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
Gardening |
Use adaptive tools with larger grips. |
|
Typing |
Take regular breaks to stretch fingers and wrists. |
|
Lifting |
Avoid lifting heavy objects; use mechanical aids when possible. |
Ongoing Self-Care Strategies
Keeping up with self-care is essential to avoid de Quervain’s tenosynovitis from coming back. This means living a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and doing exercises that strengthen your wrist and thumb. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are also important to catch any problems early.
Self-care tips:
- Engage in regular exercise to maintain flexibility and strength.
- Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation or yoga.
- Monitor your condition and report any changes to your healthcare provider.
By following these tips every day, you can prevent de Quervain’s tenosynovitis from coming back and enjoy lasting relief from symptoms.
Conclusion
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a painful condition that affects the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. It’s important to know its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. This knowledge helps manage the condition effectively.
Conservative treatments like rest, splinting, and corticosteroid injections are often suggested first. But, de Quervain’s surgery might be needed for severe cases or when other treatments don’t work.
The de Quervain’s surgery procedure releases the affected tendons. This helps reduce pain and improve function. With the right de Quervain’s treatment, most people see a big improvement.
The de Quervain’s recovery process starts with a period of rest. Then, rehabilitation exercises help regain strength and mobility.
Understanding the condition and its treatments helps make better care choices. It’s key to talk to a healthcare professional to find the best treatment for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis.
FAQ
What is de Quervain’s tenosynovitis?
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a condition that affects the tendons on the thumb side of your wrist. It happens when these tendons get irritated or constricted at the base of the thumb.
What are the symptoms of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis?
Symptoms include pain and tenderness, mainly when forming a fist, grasping, or turning the wrist. You might also see swelling and redness around the thumb.
How is de Quervain’s tenosynovitis diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose it through a physical exam, like the Finkelstein test. They might also use X-rays or ultrasound to check for other issues.
What are the conservative treatment options for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis?
Treatments include rest, splinting, and anti-inflammatory meds. Corticosteroid injections can also help reduce inflammation and pain.
When is surgery necessary for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis?
Surgery is needed if other treatments don’t work. It’s also considered if the condition is severe and affects daily life a lot.
How long does de Quervain’s surgery take?
Surgery usually lasts 30 to 60 minutes. The exact time depends on the case’s complexity and the surgeon’s experience.
What are the types of surgical procedures for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis?
There are open and endoscopic surgeries. Open surgery makes a bigger incision to release the tendon. Endoscopic surgery uses a smaller incision and a camera.
What is the recovery time after de Quervain’s surgery?
Recovery times vary, but most people can get back to normal in 2 to 6 weeks. It may take a few months to fully recover and regain strength.
What are the possible complications of de Quervain’s surgery?
Complications include infection, nerve damage, and persistent pain. While rare, these serious issues can happen.
How can recurrence be prevented after de Quervain’s surgery?
To prevent recurrence, use ergonomic tools, avoid repetitive motions, and take care of your wrist and thumb.
What is the success rate of de Quervain’s surgery?
Most people find significant relief from symptoms after surgery. Success rates depend on the condition’s severity and the surgery method.
How much does de Quervain’s surgery cost?
Costs vary based on location, surgeon’s fees, and insurance. On average, it can cost several thousand dollars.
Is physical therapy necessary after de Quervain’s surgery?
Yes, physical therapy is often recommended. It helps regain strength, mobility, and function in the wrist and thumb.
Reference
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9375674/[4





