Did you know that hydrocephalus affects thousands of children worldwide? It causes too much cerebrospinal fluid in the brain.
If not treated, hydrocephalus in children can cause serious problems. These include high brain pressure, brain damage, and even death. We will look at what happens if this condition is not treated, stressing the need for early action.
When a child is found to have hydrocephalus, quick medical help is key. Without it, hydrocephalus symptoms can lead to big delays in growth and disabilities.
Key Takeaways
- Untreated hydrocephalus can lead to severe complications in children.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are key to avoid long-term harm.
- Hydrocephalus symptoms can cause big delays in growth if not treated.
- Quick medical help is vital for children with hydrocephalus.
- Untreated hydrocephalus can cause high brain pressure and brain damage.
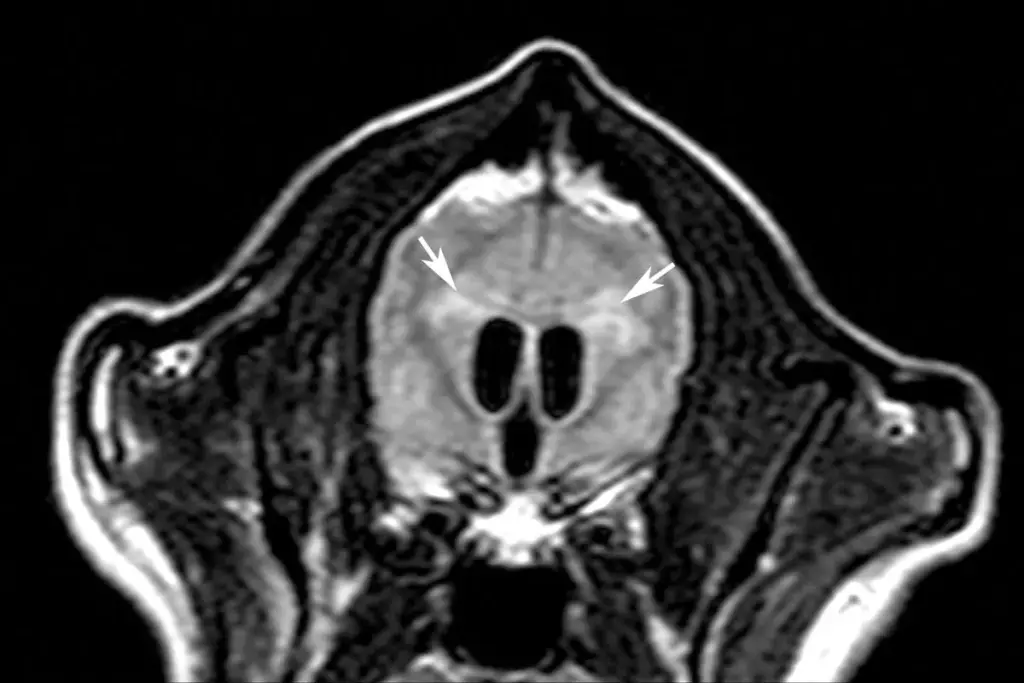
To understand hydrocephalus in kids, we need to know what it is and how cerebrospinal fluid works. Hydrocephalus is when too much cerebrospinal fluid builds up in the brain. This causes the brain to get too much pressure.
Definition and Cerebrospinal Fluid Dynamics
Cerebrospinal fluid is very important for the brain. It protects the brain and helps get rid of waste. Normally, the brain makes and absorbs CSF at the same rate. But in hydrocephalus, this balance is broken.
This can happen because of a blockage in CSF flow or problems with absorption. The way CSF moves is complex. It’s made in the ventricles, flows through the brain, and then gets absorbed. Knowing this helps us understand how hydrocephalus starts and grows. CSF is mainly made in the choroid plexus of the ventricles.
Prevalence and Incidence in Pediatric Populations
Hydrocephalus can happen at any age, but it’s a big deal for kids. It affects their growth and development. About 1 to 2 kids out of 1,000 are born with hydrocephalus.
Some kids get it because of infections, injuries, or tumors. Knowing how common hydrocephalus is in kids helps doctors plan better care. Early treatment can really help kids with hydrocephalus. So, it’s a key area in pediatric neurology.
Types of Hydrocephalus That Affect Children

Children can have different kinds of hydrocephalus, including rare ones. Knowing about these types is key for good care and treatment.
Congenital Hydrocephalus
Congenital hydrocephalus is present at birth. It’s linked to developmental issues, like neural tube defects. This condition can come from genetic mutations or environmental factors during fetal development. It might be found before birth or soon after.
Acquired Hydrocephalus
Acquired hydrocephalus starts after birth. It’s often caused by infections, trauma, or tumors. Infections like meningitis can cause inflammation that leads to hydrocephalus. It can happen at any age and might need different treatment than congenital hydrocephalus.
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus in Rare Pediatric Cases
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH) is rare in kids. It’s when cerebrospinal fluid builds up in the brain’s ventricles without high pressure. NPH can cause symptoms like gait problems, cognitive decline, and urinary incontinence. Finding NPH in children is hard and needs careful checking.
Knowing the type of hydrocephalus is vital for the right treatment. We’ll look at causes, symptoms, and treatments for hydrocephalus in kids next.
Causes of Hydrocephalus in the Pediatric Population
It’s important to know why hydrocephalus happens in kids. This condition is when too much cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up in the brain. It can come from different reasons.
Developmental Abnormalities and Arachnoid Cysts
Developmental problems are a big reason for hydrocephalus in children. Arachnoid cysts, which are fluid-filled sacs in the brain, can block CSF flow. This leads to hydrocephalus.
Other issues like neural tube defects can also cause hydrocephalus. These problems need early treatment to avoid brain damage.
Infections and Inflammatory Processes
Infections and inflammation are also big causes of hydrocephalus in kids. Meningitis, for example, can cause inflammation that blocks CSF pathways. This leads to hydrocephalus.
- Meningitis
- Encephalitis
- Ventriculitis
These infections can cause inflammation and scarring in CSF pathways. This results in hydrocephalus. Early diagnosis and treatment are very important.
Trauma and Other Acquired Causes
Trauma is a big cause of hydrocephalus in kids. Head injuries can cause bleeding or inflammation that blocks CSF flow. “
Other causes include tumors, cysts, and vascular malformations that block CSF pathways. Knowing these causes helps in making good treatment plans.
Signs and Symptoms of Hydrocephalus in Children
Hydrocephalus shows up differently in infants, toddlers, and older kids. It’s key to spot these signs early for the best treatment.
Presentation in Infants and Toddlers
In babies and toddlers, hydrocephalus has clear signs. A big head or fast head growth is often seen at doctor visits. Other signs include:
- Visible Symptoms: Bulging fontanelles, prominent scalp veins, and an upward gaze limitation (also known as “setting sun” eyes).
- Behavioral Changes: Irritability, poor feeding, and vomiting.
- Developmental Delays: Delays in achieving developmental milestones.
Manifestations in Older Children
In older kids, hydrocephalus symptoms can be tricky to spot. They might look like other problems. Common signs include:
- Headaches and Vomiting: Often worse in the morning, these can be signs of increased intracranial pressure.
- Visual Disturbances: Blurred vision, double vision, or difficulty with eye movements.
- Cognitive and Behavioral Changes: Decline in school performance, memory issues, and changes in personality or behavior.
- Coordination and Balance Problems: Difficulty with walking or maintaining balance.
Older kids might say they have headaches or nausea. These can be mistaken for other issues. A detailed doctor’s check-up is needed to find out if it’s hydrocephalus.
Diagnosis of Pediatric Hydrocephalus
Diagnosing hydrocephalus in children requires advanced neuroimaging and clinical assessments. These methods help us identify hydrocephalus and plan treatment.
Neuroimaging Studies of Brain Ventricles
Neuroimaging is key in diagnosing hydrocephalus. We use ultrasound, CT, and MRI to see the brain’s ventricles. This helps us check their size and shape.
Ultrasound is great for infants because it’s safe and doesn’t use radiation. It can spot enlarged ventricles, a sign of hydrocephalus.
CT scans give detailed brain images and can quickly spot ventricular enlargement. But, they do use radiation.
MRI is very sensitive and shows brain details without radiation. It’s good for looking at CSF pathways and finding blockages.
|
Imaging Modality |
Advantages |
Limitations |
|---|---|---|
|
Ultrasound |
Non-invasive, no radiation |
Limited detail, operator-dependent |
|
CT Scan |
Quick, detailed images |
Involves radiation |
|
MRI |
Highly detailed, no radiation |
Time-consuming, may require sedation |
Clinical Evaluation and Assessment
Neuroimaging isn’t the only thing we use. A detailed clinical evaluation is also vital. We look at symptoms, medical history, and developmental milestones.
During the clinical evaluation, we check for signs of increased intracranial pressure. This includes bulging fontanelles in infants or headaches and vomiting in older kids. We also check cognitive and motor development for any delays or issues.
By combining neuroimaging and clinical findings, we can accurately diagnose hydrocephalus. Then, we create a treatment plan that meets the child’s specific needs.
Standard Treatment Options for Pediatric Hydrocephalus
Pediatric hydrocephalus has well-known and effective treatments. We’ll look at these treatments closely. We’ll discuss how they work, their benefits, and their role in managing hydrocephalus.
Shunt Systems and Their Function
A shunt system helps treat hydrocephalus by removing extra cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the brain. It sends the CSF to other parts of the body where it can be absorbed. The system has three key parts: a proximal catheter, a valve, and a distal catheter.
The proximal catheter goes into the brain’s ventricle to drain CSF. The valve controls how fast CSF flows, preventing it from draining too quickly or too slowly. The distal catheter is placed in a spot where CSF can be absorbed, like the abdominal cavity.
|
Component |
Function |
|---|---|
|
Proximal Catheter |
Drains excess CSF from the brain ventricle |
|
Valve |
Regulates CSF flow |
|
Distal Catheter |
Directs CSF to a location for absorption (e.g., abdominal cavity) |
Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV) Procedures
Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV) is a surgery for hydrocephalus. It creates a new path for CSF to leave the brain. This is done by making a small hole in the third ventricle, helping CSF bypass any blockage.
ETV is an option for some patients with hydrocephalus, mainly those with obstructive hydrocephalus. The success of ETV depends on the patient’s age and the cause of hydrocephalus.
Both shunt systems and ETV procedures are key in treating pediatric hydrocephalus. The right treatment depends on the patient’s condition, the cause of hydrocephalus, and other factors.
Immediate Consequences of Untreated Hydrocephalus
Not treating hydrocephalus quickly can cause serious health problems in kids. It can lead to many issues that affect a child’s health and growth.
Increased Intracranial Pressure and Cerebral Edema
Untreated hydrocephalus raises intracranial pressure (ICP). This happens when cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up and presses on the brain. This can cause cerebral edema, where the brain swells from too much fluid.
This swelling puts more pressure on the brain. It can lead to severe brain damage if not treated fast.
Symptoms include headaches, vomiting, and changes in consciousness. In babies, you might see a bigger head, bulging fontanelles, and fussiness.
|
Symptoms |
Infants |
Older Children |
|---|---|---|
|
Headaches |
Irritability, bulging fontanelles |
Headaches, vomiting |
|
Altered Consciousness |
Lethargy, poor feeding |
Confusion, drowsiness |
Acute Neurological Deterioration
Untreated hydrocephalus can also cause acute neurological deterioration. It can damage the brain, leading to a drop in brain function. This can show as a decrease in thinking skills, movement problems, and seizures.
“Prompt treatment of hydrocephalus is critical to avoid long-term brain damage and improve life quality for kids.” – Pediatric Neurologist
Early treatment is key to avoid permanent damage. Delaying it can cause lasting harm, showing why early diagnosis and treatment are so important.
In summary, untreated hydrocephalus has severe and lasting effects on a child’s health and growth. Knowing these effects stresses the urgent need for quick and effective treatment.
Short-term Complications When Hydrocephalus Remains Untreated
When hydrocephalus is not treated in children, it causes many short-term problems. These issues affect their growth and health. They can be seen in how a child thinks, develops, and physically.
Cognitive and Developmental Impacts
Untreated hydrocephalus can harm a child’s brain and growth. Some major effects include:
- Delayed Developmental Milestones: Kids might not reach important steps like sitting, standing, or walking on time.
- Cognitive Impairments: Hydrocephalus can make it hard for kids to remember things, focus, and solve problems.
- Learning Disabilities: Without treatment, kids might struggle in school and have trouble keeping up with their classmates.
Physical Manifestations and Symptoms
Untreated hydrocephalus also causes physical signs and symptoms. These can be:
- Increased Head Size: Babies might have a head that’s too big because of extra cerebrospinal fluid.
- Vision Problems: Hydrocephalus can lead to blurry or double vision.
- Motor Skill Impairments: Kids might find it hard to move and balance, making everyday tasks tough.
It’s very important for kids with hydrocephalus to get the right treatment quickly. This helps avoid these problems and gives them the best chance for a good future.
Long-term Effects of Untreated Hydrocephalus
Untreated hydrocephalus can cause serious long-term health issues in children. It can lead to permanent brain damage and lifelong disabilities. The buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) increases pressure in the brain. This can harm the brain’s delicate structures.
Permanent Brain Damage and Neural Tissue Compression
The prolonged compression of neural tissue from untreated hydrocephalus can cause permanent brain damage. This damage can impact a child’s development in many ways. It can affect their thinking, movement, and emotional control.
The longer the condition lasts, the more severe the damage. The brain’s neural pathways can be destroyed. This makes it hard for the child to grow normally. The compression can also cause neural atrophy, making the child’s neurological outlook worse.
Lifelong Disabilities and Functional Limitations
Children with untreated hydrocephalus face a high risk of lifelong disabilities. These disabilities can include cognitive and learning issues, as well as physical and motor problems. The severity of these disabilities may require ongoing medical care, therapy, and educational support.
Living with hydrocephalus can be tough. Without treatment, it can greatly affect a child’s quality of life. Families may need to make big changes to support their child. They might need to include various therapies and interventions in their daily routine.
Understanding the long-term effects of untreated hydrocephalus is key. It shows why early and effective treatment is so important. Early intervention can greatly improve a child’s life. It can reduce the risk of permanent damage and improve their overall well-being.
Neurological Consequences of Untreated Hydrocephalus
Untreated hydrocephalus in children can cause serious problems. It affects their motor skills, thinking abilities, and growth. Without treatment, it can lead to many serious health issues.
Motor Function Impairments
One big problem is motor function issues. Children might have trouble with:
- Coordination and balance
- Muscle weakness or spasticity
- Difficulty with fine motor skills, like writing or using utensils
These issues can make daily tasks hard. It can also lead to long-term disabilities.
Cognitive and Intellectual Disabilities
Untreated hydrocephalus can also cause cognitive and intellectual problems. Children might struggle with:
- Learning disabilities, affecting schoolwork
- Memory and information processing issues
- Difficulty focusing on tasks
These problems can affect their education and social life. Early treatment is very important.
Sensory Processing Disorders
Sensory processing disorders are another issue. Children might be overly sensitive to:
- Certain sounds, sights, or textures
- Difficulty processing sensory information, leading to overwhelming feelings
- Challenges with self-regulation, affecting their emotions and behavior
It’s key to address these disorders to improve their quality of life.
In summary, untreated hydrocephalus can have many serious effects. It can impact a child’s development and well-being. It’s vital for healthcare providers and families to know these risks. This way, they can get help early and ensure the best care.
Mortality Risks Associated with Untreated Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus can be very dangerous if not treated. It causes too much fluid in the brain. This can lead to serious brain problems and even death.
Survival Statistics and Prognosis
The outlook for people with untreated hydrocephalus depends on several factors. These include the cause, how severe it is, and any other health issues. Children with this condition face a higher risk of death, with rates sometimes as high as 60% in the first few years.
Survival rates can change based on many things. These include access to healthcare, other health problems, and the success of treatments.
Fatal Complications and End-stage Manifestations
Untreated hydrocephalus can cause serious problems. These include increased intracranial pressure, brain herniation, and brain damage. These issues happen because of too much fluid in the brain, which presses on and harms brain tissues.
In the worst cases, people may lose control of their muscles, have trouble thinking, and even stop breathing. This can be fatal.
It’s critical to get medical help early to avoid these dangers. This can help improve life quality for those with hydrocephalus.
Quality of Life Impact for Children with Untreated Hydrocephalus
Untreated hydrocephalus affects many parts of a child’s life. It impacts their development, daily life, education, and social interactions. Not treating this condition has serious effects that go beyond just health issues.
Educational Challenges and Accommodations
Children with untreated hydrocephalus face big educational hurdles. The condition can cause problems with thinking, focusing, and remembering. Special educational accommodations are key to help them succeed.
These accommodations might include special plans, extra help, and technology to aid learning. Schools and teachers play a big role in helping these kids. They can make learning environments more inclusive and supportive.
Social Development and Peer Relationships
Untreated hydrocephalus can also hurt a child’s social skills and friendships. Kids might struggle with understanding social cues, talking, and managing their feelings. This can lead to social isolation if not handled right.
It’s important to give these kids chances to socialize and learn social skills. Family, caregivers, and teachers can help by setting up playdates and activities. This helps kids build friendships and feel connected.
Family Burden and Caregiver Stress
Diagnosing hydrocephalus and choosing not to treat it can be very hard on families and caregivers. The emotional, physical, and financial stress is huge. Caregiver stress is a big worry, as it can make it hard for caregivers to support their child well.
Families need help and support to deal with this stress. Counseling, support groups, and respite care can be very helpful. They give caregivers the tools and breaks they need to care for their child and stay healthy themselves.
Preventing Complications When Treatment Is Delayed
When hydrocephalus treatment is delayed, certain steps can help lower risks. It’s tough to delay treatment, but the right steps can lessen some problems.
Medical Management Strategies
Medical care is key in preventing issues when treatment is delayed. Monitoring intracranial pressure and managing symptoms are very important. We use medicines to control symptoms like headaches and nausea.
Regular visits to healthcare providers are also vital. They help track the condition and adjust plans as needed.
Using acetazolamide is another part of medical management. It can temporarily lower cerebrospinal fluid production, easing some pressure. But, it’s not a permanent fix and must be watched closely by doctors.
Positioning and Physical Interventions
Positioning and physical steps are also important when treatment is delayed. The right positioning of the child can help lower intracranial pressure. For babies, this might mean tilting the head of the bed to help cerebrospinal fluid drain better.
Physical therapy can also help. Gentle exercises and stretches keep muscles flexible and strong. This can lessen some symptoms of hydrocephalus. Physical therapy also helps in keeping the child comfortable and avoiding problems like contractures or skin issues.
By combining medical care with the right positioning and physical therapy, we can prevent more complications when treatment is delayed. It’s important to work with healthcare providers to make these plans fit each child’s needs.
Scenarios Where Hydrocephalus Treatment May Be Delayed
There are several reasons why hydrocephalus treatment might be delayed. This can affect how the condition progresses. It’s important for healthcare providers and families to understand these reasons.
Medical Contraindications and Risks
At times, certain medical conditions can make immediate treatment risky. For example, if a child has an active infection, surgery for hydrocephalus might be postponed until the infection is treated.
Other conditions, like severe heart or breathing problems, can also delay treatment. This is because the risks of surgery and anesthesia might be too high.
|
Medical Contraindication |
Description |
Impact on Treatment |
|---|---|---|
|
Active Infection |
Presence of an untreated infection |
Treatment delayed until infection is resolved |
|
Cardiac Instability |
Severe heart condition |
Surgery postponed until cardiac status stabilizes |
|
Respiratory Instability |
Significant breathing difficulties |
Treatment delayed until respiratory status improves |
Access to Healthcare Barriers and Solutions
Barriers to healthcare can also delay treatment for hydrocephalus. These can include living far from care, not having insurance, or facing financial challenges.
For those in remote or underserved areas, getting to specialized care is hard. Telemedicine can help with initial checks and follow-ups. Programs that help with travel costs to care centers are also helpful.
Improving healthcare access and creating fair policies are key to reducing delays in hydrocephalus treatment.
|
Barrier |
Description |
Potential Solution |
|---|---|---|
|
Geographical Constraints |
Distance to healthcare facilities |
Telemedicine, transportation assistance |
|
Lack of Insurance |
Inability to afford care |
Financial assistance programs, insurance support |
|
Socioeconomic Factors |
Economic status affecting care access |
Social services support, community resources |
Monitoring and Managing Untreated Hydrocephalus
Managing untreated hydrocephalus is complex. It needs close watch and quick action in emergencies. We’ll look at how to monitor and manage this condition to help children.
Clinical Surveillance Protocols
Watching over children with untreated hydrocephalus is key. We do frequent neurological checks and imaging studies. These help us see if the condition is getting worse.
We also keep an eye out for signs like headache, vomiting, and changes in consciousness. This way, we can act fast if the child’s condition worsens.
Warning Signs of Deterioration
It’s important to know when a child’s condition is getting worse. Look for increased irritability, changes in appetite, and sleep issues. Also, watch for weakness, vision problems, and coordination issues.
Parents and caregivers are key in spotting these signs. Teaching them what to look for helps them get help quickly if needed.
Emergency Interventions
Being ready for emergencies is vital in managing untreated hydrocephalus. If a child’s condition suddenly gets worse, quick medical help is needed. This might include medicines to lower pressure or emergency surgery.
Having a plan for emergencies is important. It helps us avoid serious problems and improve outcomes for children with untreated hydrocephalus.
Conclusion
Hydrocephalus is a complex condition that needs quick medical care to avoid serious problems. We’ve looked at hydrocephalus in kids, including what it is, its types, causes, signs, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes.
Getting a diagnosis and treatment early is key to avoiding complications. This helps improve the life of kids with hydrocephalus. Without treatment, kids face big challenges in thinking, moving, and feeling emotions. But, with the right treatment, they can do much better.
Knowing the dangers of not treating hydrocephalus and the good it can do helps families and doctors. They can work together to give kids the best care. We also need more research, awareness, and support for those with hydrocephalus.
FAQ
What is hydrocephalus in children?
Hydrocephalus is when too much cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up in the brain. This causes the brain pressure to go up.
What are the different types of hydrocephalus that can affect children?
Children can get different types of hydrocephalus. These include congenital, acquired, and rare cases of normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH).
What causes hydrocephalus in children?
Hydrocephalus in kids can come from many things. This includes birth defects, cysts, infections, inflammation, and head injuries.
How is hydrocephalus diagnosed in children?
Doctors use special brain scans to check the ventricles. They also do a full check-up to find out if a child has hydrocephalus.
What are the signs and symptoms of hydrocephalus in infants and toddlers?
Babies and toddlers with hydrocephalus might have a big head. They might also vomit, get irritable, and feel very tired.
What are the treatment options for pediatric hydrocephalus?
Doctors use shunt systems or a procedure called endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) to treat hydrocephalus in kids.
What happens if hydrocephalus is left untreated in children?
If hydrocephalus isn’t treated, it can cause a lot of problems. This includes high brain pressure, swelling, and serious brain damage.
What are the short-term complications of untreated hydrocephalus?
Untreated hydrocephalus can cause problems right away. This includes delays in learning and physical issues.
What are the long-term effects of untreated hydrocephalus?
Untreated hydrocephalus can lead to serious long-term problems. This includes permanent brain damage, disabilities, and limited abilities.
How does untreated hydrocephalus impact a child’s quality of life?
Untreated hydrocephalus can really affect a child’s life. It can hurt their school work, social skills, and make life hard for families and caregivers.
What are the mortality risks associated with untreated hydrocephalus?
Untreated hydrocephalus can be very dangerous. It can even be life-threatening if not treated.
How can complications be prevented when treatment for hydrocephalus is delayed?
When treatment is delayed, doctors can use other ways to help. This includes medicine and physical treatments to prevent problems.
What are the scenarios where hydrocephalus treatment may be delayed?
Treatment might be delayed for some kids. This can happen if there are health reasons or if it’s hard to get to a doctor.
How is untreated hydrocephalus monitored and managed?
Doctors keep a close eye on kids with untreated hydrocephalus. They look for signs of getting worse and are ready to act fast if needed.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8082886/[1





