Toddler ear infections, also known as acute otitis media, are very common in young kids. The National Institutes of Health says five out of six children will get an ear infection before they are three years old.
It’s important to know the signs of an ear infection to get help quickly. Toddlers with an ear infection might be more irritable, cry a lot, and pull at their ear. They might also have trouble sleeping.
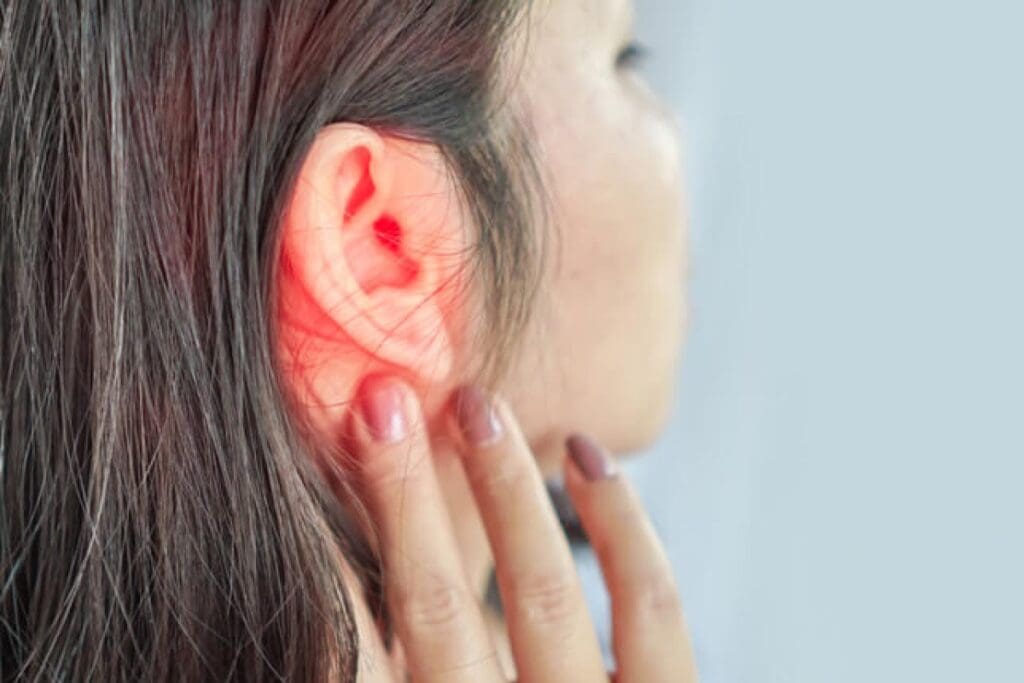
You might see the outer ear looking red and swollen. In serious cases, you might see yellow or white fluid coming out of the ear canal. This means the eardrum might have burst. Learn what ear infection looks like in toddlers and the common signs you should watch for. so lets check it out now.
Key Takeaways
- Ear infections are very common in toddlers, affecting five out of six children before age three.
- Signs include irritability, crying, tugging at the ear, and sleep disturbances.
- Physical symptoms can include redness, swelling, and discharge.
- Timely recognition is key to avoiding serious problems.
- Knowing these signs helps in giving the right care.
Understanding Toddler Ear Infections
It’s important to know about ear infections in toddlers to catch them early. These infections, known as acute otitis media, are common in young kids. They cause a lot of pain for both children and their parents.
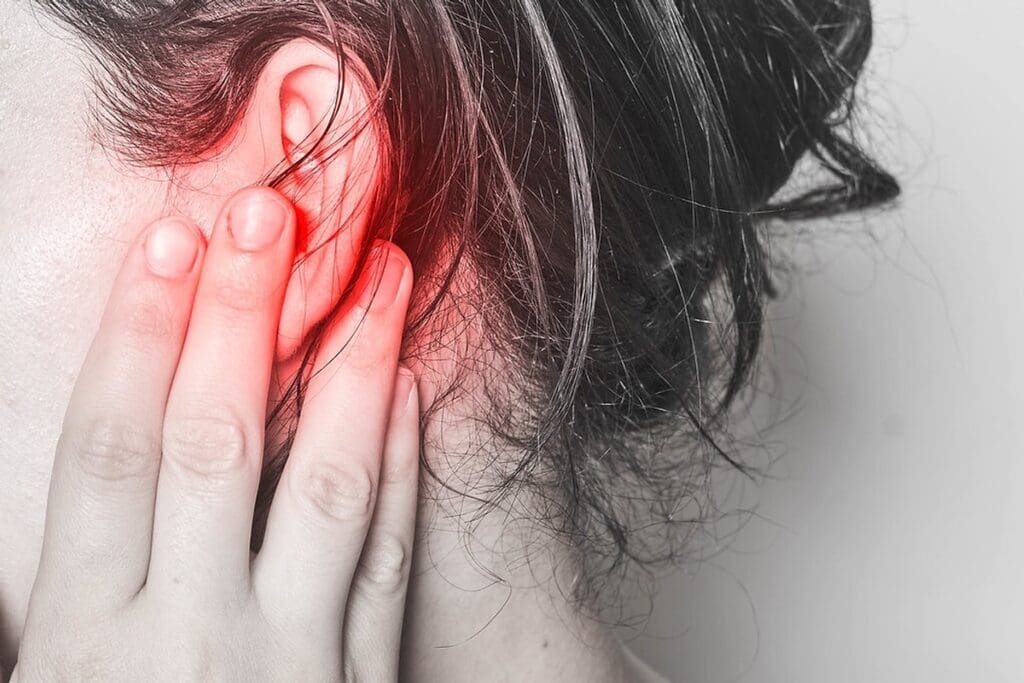

Acute otitis media happens when fluid builds up behind the eardrum. This makes parts of the middle ear infected and swollen. Kids get these infections often because their immune systems are not fully grown. Their eustachian tubes are also smaller and more horizontal, making them more likely to get sick.
What is Acute Otitis Media?
Acute otitis media is when the middle ear becomes inflamed, usually from a bacterial or viral infection. The eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the back of the nose and throat, is key in this condition. If this tube is blocked or not working right, fluid can build up and cause an infection.
Statistics on Ear Infection Prevalence
About 80% of children will get at least one ear infection by the age of three. Most ear infections happen between 6 months and 2 years. This shows how common ear infections are in young kids.
Age and Gender Differences
Studies show that boys are slightly more likely to get ear infections than girls. Younger kids are also more at risk. This is because their immune systems are not fully developed and their body structure is different.
Knowing the signs of ear infection is key to getting the right ear infection treatment. Parents should watch for ear ache, fever, and irritability. These signs can mean a child has an ear infection.
Visual Signs of a Toddler’s Ear Infection
Ear infections in toddlers can show through changes in the ear’s look. Parents should watch for these signs to catch infections early.
Redness and Inflammation of the Ear
Redness and inflammation of the outer ear are common signs. The ear might look swollen or larger than before. This can make the child feel uncomfortable and irritable.
Fluid Discharge: What It Means
Severe ear infections can cause yellow or white fluid to come out of the ear. This means the eardrum has a hole, letting fluid out. Seeing this fluid means it’s time to see a doctor.
Changes in Eardrum Appearance
Parents who use an otoscope might see changes in the eardrum. An infected eardrum looks red, bulging, or retracted. There might also be fluid behind it. Knowing these signs can help spot infections, but always check with a doctor for sure.
Spotting these signs early is key to treating ear infections in toddlers. If you think your child has an ear infection, get them to a doctor fast. This can stop bigger problems later.
Behavioural Symptoms That Indicate an Ear Infection
Toddlers with ear infections may show certain behaviours that mean they need to see a doctor. These signs are usually due to the pain or discomfort from the infection.
Increased Irritability and Persistent Crying
One common sign of an ear infection in toddlers is being more irritable and crying a lot. The pain makes them fussy and hard to calm down. It’s important for parents to realize this could mean there’s an ear infection, if other symptoms are present too.
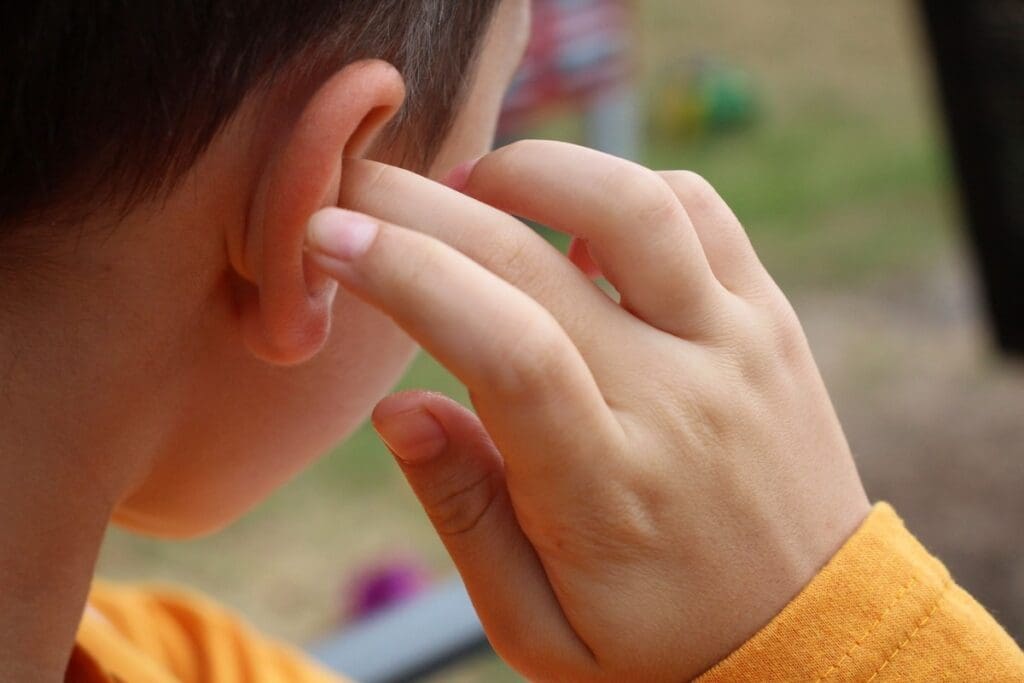
Ear Tugging or Pulling Behaviours
Toddlers with ear infections might tug or pull at their ears. This is their body’s way of trying to ease the pain or pressure. Even though ear tugging can have other reasons, it’s a key sign to watch for with ear infection symptoms.

Sleep Disturbances and Positioning
Ear infections can make it hard for toddlers to sleep well. They might have trouble falling asleep or wake up a lot at night. Some kids might try to sleep better by changing how they lie or holding their ear.
Signs of Temporary Hearing Loss
Ear infections can sometimes cause temporary hearing loss because of fluid in the middle ear. Toddlers might not hear their name or usual sounds around the house. For more info on ear infections and their effects, check NHS.uk.
Spotting these behavioral signs is key to catching ear infections early. If you think your toddler has an ear infection, seeing a doctor is a must. They can help figure out the problem and tell you how to treat ear infection right.
Physical Symptoms and Complications
Toddlers with ear infections show many physical signs. It’s key to spot these early to avoid bigger problems. These symptoms can affect the whole body or just the ear.
Fever Patterns in Bacterial vs. Viral Infections
Fever is a big sign of ear infections, often from bacteria. Bacterial infections usually cause higher fevers than viruses. Knowing this helps doctors choose the right treatment.
For example, antibiotics might be needed for bacterial infections. But viruses might need something else.
Balance Issues and Coordination Changes
Ear infections can mess with balance and coordination. Toddlers might trip more or have trouble walking. These signs are usually short-lived but can worry parents.
It’s important to watch for these signs. They show how serious the infection is.
Reduced Appetite and Other Systemic Symptoms
Ear infections can also make toddlers lose their appetite. The pain or discomfort makes eating hard. This can lead to eating less.
Other signs include feeling tired, cranky, or just not feeling well. These can really affect a toddler’s health.
Potential Complications of Untreated Ear Infections
Not treating ear infections can cause big problems. The infection might spread to other parts of the ear or even the head. This can lead to serious issues like mastoiditis or meningitis.
It’s vital to see a doctor if symptoms don’t get better or get worse. This helps avoid serious complications.
Risk Factors for Recurrent Ear Infections
Several risk factors can make toddlers more likely to get ear infections. It’s important to know these factors. Knowing them can help prevent and manage ear infections.
Anatomical Considerations
Toddlers are more likely to get ear infections because of their body shape. Their Eustachian tubes are shorter and more horizontal. This makes it easier for bacteria to get into the middle ear.
The Eustachian tubes help drain fluid from the middle ear. When they don’t work right, fluid builds up. This is a perfect place for infections to start. As kids grow, their tubes change, which can help reduce infections.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to smoke is a big risk for ear infections in kids. Smoke can hurt how the Eustachian tubes work and weaken the immune system.
Other things like pollution and allergens can also cause ear infections.
Daycare Attendance and Exposure
Kids in daycare are more likely to get ear infections. They are exposed to more respiratory viruses and bacteria. Being close to other kids means they can catch infections more easily.
- Increased exposure to pathogens
- Higher risk of respiratory infections
- Potential for inadequate hygiene practices
Genetic Predispositions
Some kids might be more likely to get ear infections because of their genes. If a family has a history of ear infections, a child might be more at risk.
Knowing about genetic risks can help parents watch for signs of ear infections. It can also help them get help early.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Ear Infections
Knowing when to get medical help for your toddler’s ear infection is key. It helps them get better and avoid serious problems. Ear infections can be caused by viruses or bacteria. Knowing the difference is important for the right treatment.
Warning Signs Requiring Immediate Care
Some symptoms mean you need to see a doctor right away. Look out for a high fever (over 102°F), severe ear pain, or discharge from the ear. Also, if your child seems confused, dizzy, or has trouble hearing, get help fast.
Severe symptoms that need quick attention include:
- High fever
- Severe ear pain
- Discharge or fluid leakage from the ear
- Signs of confusion or dizziness
Symptoms That Can Wait for a Regular Appointment
Not every ear infection symptom is an emergency. Mild ear pain, a slight fever (less than 102°F), and irritability can be watched at home first. But, if these get worse or last too long, see a pediatrician.
The American Academy of Pediatrics suggests waiting and watching for some cases. This is for kids over 6 months with mild symptoms. They also recommend pain relief.
What to Expect During the Medical Examination
A doctor will use an otoscope to look into your child’s ear during an exam. This helps find infections, fluid, or other issues.
The doctor will also check your child’s overall health. They’ll look for fever and ask about ear pain or hearing problems.
Diagnostic Procedures for Ear Infections
Tests like tympanometry might be done to check the eardrum and middle ear muscles. Sometimes, a hearing test is needed to see if there’s hearing loss.
If the infection is bacterial and serious, antibiotics might be prescribed. It’s important to finish all the antibiotics as told by the doctor.
For help with how to get rid of ear infection symptoms, consider pain relief. Use acetaminophen for kids over 3 months or ibuprofen for kids over 6 months. Always ask a healthcare provider first.
Conclusion: Prevention and Management Strategies
To prevent ear infections in toddlers, we need to take several steps. These include regular vaccinations, good hygiene, and a clean environment. By knowing the risks and acting early, parents can lower the chance of ear infections in their kids.
Getting regular shots, like the flu and pneumococcal vaccines, helps fight off harmful germs. Staying away from cigarette smoke and washing hands often also helps. For more tips, check out Drome Clinic’s guide on ear infection symptoms, causes, and prevention.
Managing ear infections well means treating them quickly and sometimes needing surgery. Doctors might give pain meds and antibiotics to help. By using these strategies, parents can keep their child’s hearing and health safe.
FAQ’s:
What are the common signs of an ear infection in toddlers?
Signs include irritability and ear tugging. Toddlers may also have fever and fluid from the ear. They might sleep poorly and show signs of hearing loss.
How can I identify an ear infection in my toddler using an otoscope?
An otoscope can show redness and inflammation. You might see a bulging eardrum or fluid. But, always check with a doctor for a sure diagnosis.
What are the risk factors for recurrent ear infections in toddlers?
Risk factors include a shorter Eustachian tube. Exposure to tobacco smoke and daycare also play a part. Genetic predispositions are another factor.
When should I seek medical attention for my toddler’s ear infection?
Get help right away for severe symptoms like high fever and severe pain. For milder symptoms, make an appointment with your doctor.
What can happen if an ear infection is left untreated?
Untreated infections can cause hearing loss and other serious problems. It’s important to get medical help if you think your toddler has an infection.
How are ear infections typically treated?
Treatment often includes antibiotics for bacterial infections. Your doctor may also suggest pain relief and watch for complications.
Can ear infections be prevented?
While prevention is not always possible, reducing risk factors helps. Avoiding tobacco smoke and good hygiene can lower the chance of infections.
How can I manage my toddler’s ear infection symptoms at home?
You can help by giving pain relief and keeping their head up while sleeping. A warm compress can also ease ear pain
Reference
- American Academy of Pediatrics. (2013). The diagnosis and management of acute otitis media. Pediatrics, 131(3), e964-e999. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2012-3659
- John, C. C., & Anthony, J. M. (2016). Acute otitis media in children: Diagnosis and management. American Family Physician, 94(6), 469–476.
- Kerschner, J. E., & Preciado, D. (2019). Otitis media in children: Diagnosis and treatment. Journal of the American Medical Association, 321(4), 365–379. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.19694
- National Institutes of Health. (2019). Ear infections in children. National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/ear-infections-children
- Paradise, J. L., Rockette, C. J., Colborn, D. K., Bernard, B. S., Smith, C. G., & Janosky, J. E. (2009). Otitis media in young children. The New England Journal of Medicine, 360(14), 1409–1417. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0805342


































