When sinus congestion happens, it can cause more than just a stuffy nose. Many people feel ear discomfort because of the link between the sinuses and the ear.
The eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the nose. It’s key for keeping ear pressure right and draining fluids. A sinus infection can cause swelling and mucus, blocking the tube and causing ear pain.
At Liv Hospital, our team gets how sinusitis and ear pain are connected. We offer full care to find and fix the root of sinus-related ear issues.
Key Takeaways
- The eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the nose, regulating ear pressure and draining fluids.
- A sinus infection can cause inflammation and mucus buildup, obstructing the eustachian tube and leading to ear pain.
- Understanding the connection between sinusitis and ear pain is key for good diagnosis and treatment.
- Liv Hospital offers full care for those with sinus-related ear discomfort.
- Our team is committed to patient-centered care with the latest medical methods.
The Anatomical Connection Between Sinuses and Ears
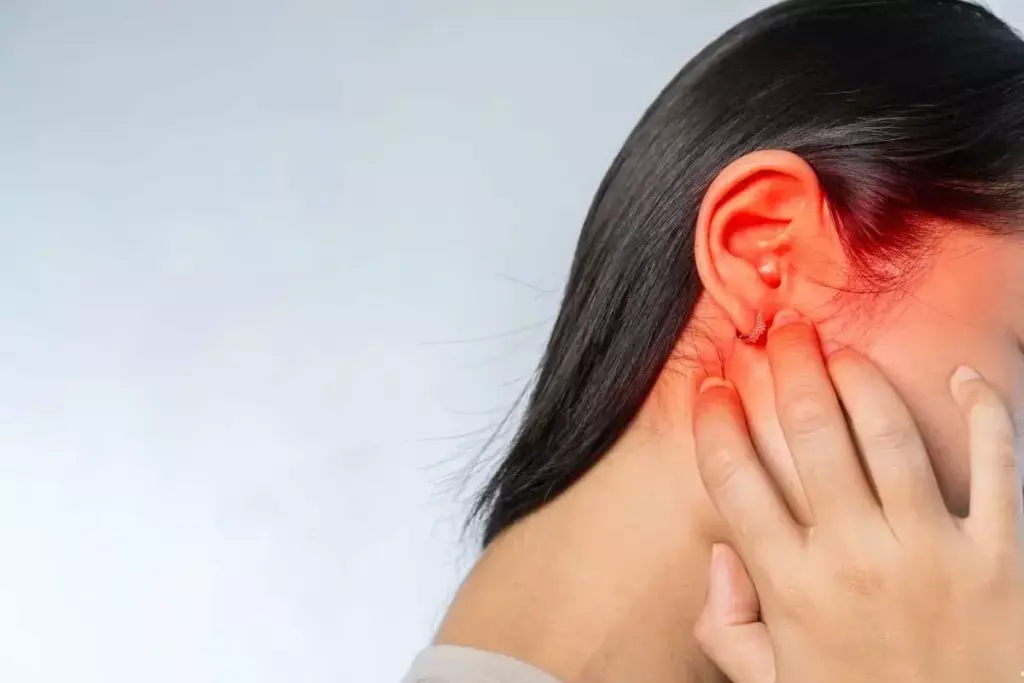

Our sinuses and ears are closely linked, which is why sinus infections can cause ear pain. This connection is not just about being close. It’s about the shared paths that can affect both systems at the same time.
Understanding Sinus and Ear Anatomy
To understand how sinus infections lead to ear pain, we need to know about the sinuses and ears. The sinuses are air-filled spaces in our nose. They help humidify the air and filter out dust. The ears, on the other hand, are complex organs for hearing and balance.
The ears have three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. The middle ear is key because it connects to the back of the nose through the Eustachian tube.
The Critical Role of Eustachian Tubes
The Eustachian tube connects the nose to the middle ear. It’s vital for ear pressure and draining fluids. It lets air pass from the ear to the sinuses, balances pressure, and drains excess fluid.
When a sinus infection happens, the Eustachian tube can get blocked. This leads to pressure and pain in the ear. This is known as earache from congestion.
How Inflammation Affects Both Systems
When we get a sinus infection, it causes inflammation and mucus buildup in the sinuses. This inflammation can spread to the Eustachian tube, blocking it and causing ear pain. This is known as sinus infection earache.
The link between nasal congestion and earache is clear. The Eustachian tube’s problem is a big part of it. Knowing this connection helps us see why sinus infections often cause ear pain and discomfort.
Can Sinus Infection Cause Ear Pain? Exploring the Mechanisms
Sinus infections can cause ear pain in several ways. The swelling and blockage from a sinus infection can affect the Eustachian tubes. These tubes are key for keeping ear pressure balanced.
Pressure Buildup and Ear Discomfort
The Eustachian tubes link the middle ear to the back of the nose and throat. If these tubes get blocked by sinusitis, it can cause pressure buildup in the middle ear. This leads to pain and discomfort.
Nasal Congestion Blocking Drainage Pathways
Nasal congestion from sinus infections can block the Eustachian tubes’ drainage pathways. This blockage can cause fluid to build up in the middle ear. This buildup can make ear pain worse and may lead to other problems.
Secondary Ear Infections from Trapped Fluid
Fluid trapped in the middle ear due to blocked Eustachian tubes can lead to secondary ear infections. When bacteria or viruses infect this fluid, it causes more inflammation and pain.
Temporary Hearing Loss and Other Symptoms
Sinus infections can also cause temporary hearing loss by disrupting sound transmission. Other symptoms like dizziness and a feeling of fullness in the ear can also occur. These symptoms come from the pressure imbalance and fluid buildup.
Understanding how sinus infections affect the ear is key to treating ear pain. By treating both the sinus infection and its effects on the ear, we can offer better care for patients with ear pain from sinusitis.
Conclusion: Managing and Preventing Sinus-Related Ear Pain
Sinus-related ear pain can be really tough, but there are ways to handle it. Treating the sinus infection is key to easing ear pain from sinusitis.
Warm compresses, decongestants, and steam therapy can ease sinus pressure and ear pain. Sometimes, doctors will give antibiotics for bacterial sinus infections. This can help lessen ear pain symptoms.
To avoid ear pain from sinus issues, drinking plenty of water is important. It helps thin out mucus and eases congestion. Using saline nasal sprays can also clear mucus and reduce congestion. Knowing how sinus infections and ear pain are linked helps people manage their symptoms better. This way, they can prevent future sinusitis and ear pain headaches.
FAQ:
Can a sinus infection cause ear pain?
Yes, sinus infections can cause ear pain due to pressure buildup and Eustachian tube dysfunction.
How does a sinus infection lead to ear pain?
Ear pain occurs when inflamed sinuses block the Eustachian tube, creating pressure and discomfort in the middle ear.
Can sinus pressure cause earache?
Yes, increased sinus pressure can radiate to the ears, causing a dull or throbbing ache.
Can a sinus infection cause temporary hearing loss?
Yes, fluid buildup and Eustachian tube blockage from sinus infection can temporarily reduce hearing.
What are the other symptoms related to sinus-related ear pain?
Symptoms can include nasal congestion, headache, facial pressure, muffled hearing, and sometimes ringing in the ears.
How can sinus-related ear pain be managed and prevented?
Management includes decongestants, saline rinses, pain relievers, steam inhalation, and allergy control to prevent recurrence.
Do ears hurt with sinus infection?
Yes, ear discomfort is common with sinus infections due to pressure changes and fluid buildup.
Can nasal congestion cause earache?
Yes, congestion can block the Eustachian tube, leading to ear pain or pressure.
Can sinusitis cause ear pain?
Yes, sinusitis can cause ear pain through Eustachian tube blockage and sinus pressure.
References:
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482338/[9