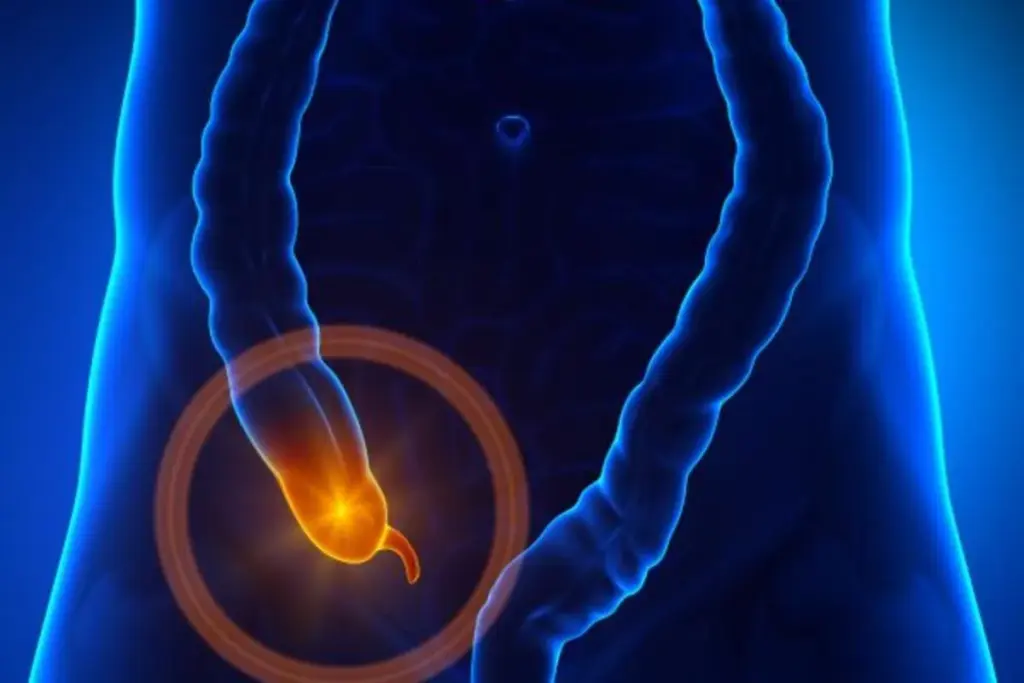
Appendicitis is a serious condition where the appendix, a finger-shaped pouch, gets inflamed. We will look at how this condition progresses, from the first signs of inflammation to serious complications. It’s vital to diagnose and treat it quickly.
Acute appendicitis can get worse fast. Knowing its stages is key to good care. The five stages show why quick medical help is needed.
Hospitals like Liv Hospital stress the importance of team care for appendicitis. Spotting the signs of appendicitis early helps avoid serious problems. Patients get the right treatment on time.
Key Takeaways
- Appendicitis is a serious condition that requires timely medical attention.
- The condition progresses through five distinct stages.
- Understanding these stages is key for good diagnosis and treatment.
- Quickly recognizing signs and appendicitis symptoms can stop severe problems.
- Team care is vital for managing appendicitis well.
Understanding Appendicitis: An Overview
The appendix is a small, tube-like structure attached to the large intestine. It can sometimes become inflamed, leading to appendicitis. This condition causes severe abdominal pain and other complications if not treated promptly.
What is the Appendix and Its Function
The appendix is a narrow, finger-shaped pouch connected to the colon. It’s located on the lower right side of the abdomen. While its exact function is debated, it’s believed to aid in digestion.
Research suggests it may serve as a reservoir for beneficial bacteria. This could help in recovering from diarrheal illnesses according to some studies.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Appendicitis can occur at any age, but it’s most common among those between 10 and 30 years old. Factors that may increase the risk include a family history of the condition, certain gastrointestinal diseases, and a diet low in fiber. Knowing these risk factors can help in early detection and prevention.
What Side is the Appendix On
The appendix is typically located on the lower right side of the abdomen. This is important to note because the location of the pain is often a key indicator of appendicitis. The pain usually starts near the navel and then moves downward to the right lower quadrant of the abdomen.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of appendicitis is key for seeking timely medical intervention. By understanding the appendix’s role, its typical location, and the factors that increase the risk of appendicitis, individuals can better navigate the challenges posed by this condition.
Recognizing Appendicitis Symptoms and Warning Signs
It’s important to know the signs of appendicitis to get help quickly. This condition shows different symptoms that can be tricky to spot. But, knowing these signs is key to getting the right care.
Early Warning Signs
The first signs of appendicitis are often small but important. You might feel sudden pain in the lower right belly, feel sick to your stomach, lose your appetite, and have a low fever. The pain might start near the belly button and then move to the lower right.
Progressive Symptoms
As appendicitis gets worse, the symptoms get more serious. You might feel more pain in your belly, throw up, and have a higher fever. The pain will get more focused in the lower right belly and might hurt when touched.
Differences in Symptoms by Age Group
Appendicitis symptoms can change with age. Kids might feel pain all over their belly, while older adults might not feel pain right away or might have different symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you have severe belly pain, keep throwing up, or have a high fever, get medical help right away. Quick diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve your chances of getting better.
Key Takeaway: Knowing the symptoms and warning signs of appendicitis and when to get medical help is very important. It can greatly improve your treatment outcome.
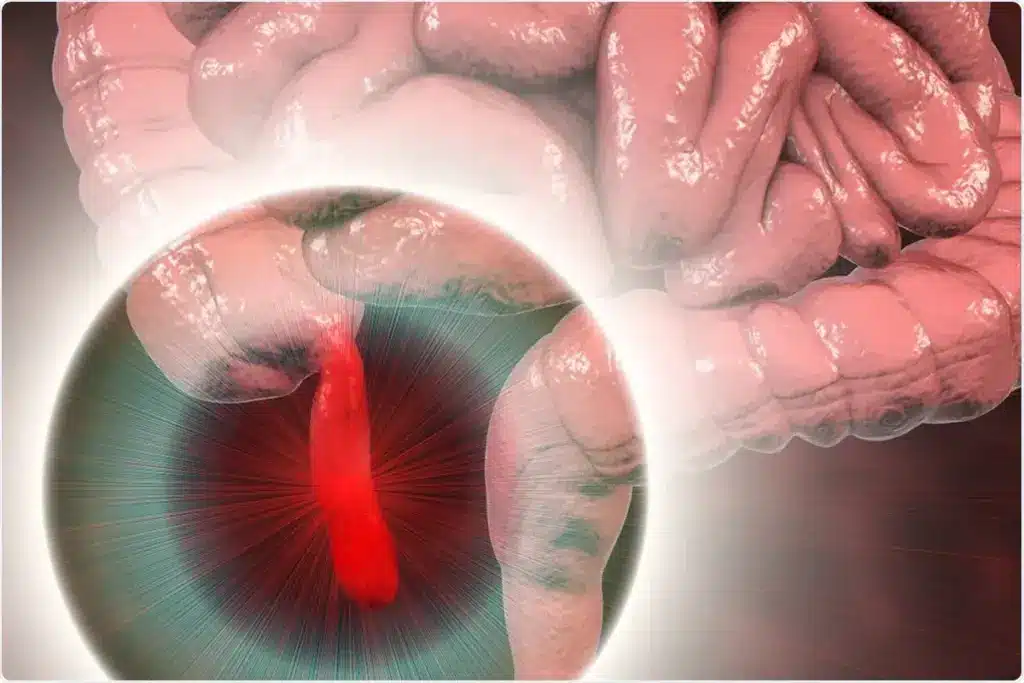
Stage 1: Obstruction of the Appendiceal Lumen
The first stage of appendicitis is when the appendiceal lumen gets blocked. This can happen for many reasons, like lymphoid hyperplasia or a fecalith. This blockage is the main cause of appendicitis.
Common Causes of Appendiceal Obstruction
Obstruction usually comes from lymphoid hyperplasia or a fecalith. Lymphoid hyperplasia makes the lymphoid tissues grow, blocking the appendix. A fecalith is a hard piece of feces that also blocks the appendix. Knowing what causes the appendix to get blocked helps spot early signs of appendicitis.
Initial Inflammatory Response
When the appendiceal lumen gets blocked, the body starts an inflammatory response. This is the body’s way of reacting to the blockage. It brings more blood and white blood cells to the area. This inflammation makes the appendix swell and hurt.
Symptoms During Early Inflammation
In the early stages of inflammation, people might feel appendicitis symptoms like stomach pain, nausea, and not wanting to eat. The pain usually starts near the navel and then moves to the lower right abdomen. Spotting these symptoms early is key to getting medical help quickly.
Understanding the first stage of appendicitis, including its causes and symptoms, is key to diagnosing and treating it well. While we talk about the 4 stages of appendicitis, focusing on the initial blockage is important to avoid more problems.
Stage 2: Suppurative (Phlegmonous) Appendicitis
Appendicitis moves to Stage 2, where it becomes suppurative or phlegmonous. Bacterial growth and swelling are big issues now. The appendix gets more inflamed, causing worse symptoms.
Bacterial Overgrowth and Edema
In this stage, bacterial overgrowth is key, causing more inflammation and swelling. Fluid and white blood cells build up in the appendix wall. This makes things even harder.
Wall Thickening and Neutrophil Infiltration
The appendix wall changes a lot, getting thicker and having neutrophil infiltration. Neutrophils are white blood cells that fight infection. They show the body’s effort to combat the bacteria.
Clinical Manifestations in Stage 2
Symptoms get worse in this stage. People often feel:
- More pain in the lower right abdomen
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
These signs mean the condition is getting worse. A study on PMC says quick action is key to avoid more problems.
Timeframe for Progression
The move from Stage 1 to Stage 2 can take 24 to 48 hours. As inflammation grows, pain gets worse. This pain becomes serious.
Stage 3: Gangrenous Appendicitis
The third stage of appendicitis is called gangrenous appendicitis. It happens when the appendix’s blood vessels get blocked. This causes the tissue to die.
Compromised Blood Supply Mechanisms
When the appendix gets blocked, it can’t get enough blood. This is often because of fecaliths or too much lymphoid tissue. The pressure inside the appendix can squeeze the blood vessels, leading to gangrene.
Tissue Necrosis Development
Without enough blood, the appendix’s tissue starts to die. This dead tissue is easy for bacteria to invade. This makes the problem even worse.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
About 20-30% of appendicitis cases turn into gangrenous appendicitis. Older people and those with vascular disease are at higher risk. Delayed treatment also increases the risk.
Signs of Progression to Gangrenous Stage
Signs of gangrenous appendicitis include severe pain and fever. You might also see signs of a ruptured appendix. It’s important to get medical help quickly if you notice these symptoms.
|
Signs |
Symptoms |
Complications |
|---|---|---|
|
Severe abdominal pain |
Fever, nausea |
Rupture, peritonitis |
|
Increased WBC count |
Abdominal tenderness |
Sepsis, abscess formation |
Stage 4: Perforation and Peritonitis
Appendicitis can reach a critical stage where the appendix bursts. This is a serious situation that needs quick medical help. It involves perforation and peritonitis, which are life-threatening.
Mechanism of Appendix Rupture
The appendix bursts when too much pressure from pus builds up. This pressure tears the appendix wall. Bacteria and other harmful stuff then spill into the belly, causing peritonitis.
Ruptured Appendix Symptoms
Symptoms of a ruptured appendix include:
- Severe abdominal pain that may start in one spot but spread
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal tenderness and muscle tension
- Changes in bowel movements
These symptoms can get worse fast. This shows how urgent it is to see a doctor.
Localized vs. Generalized Peritonitis
Peritonitis can be either localized or spread out. Localized peritonitis is when the infection stays in one area. Generalized peritonitis spreads across the belly, which is more dangerous.
“A burst appendix can lead to peritonitis, a potentially life-threatening condition.”
Increased Complication Rates
If not treated, a burst appendix can cause serious problems. These include abscesses, sepsis, and even death. Quick medical care is key to avoiding these issues.
We know a burst appendix is a serious issue that needs fast action. Recognizing symptoms and understanding the risks helps. This way, people can get medical help quickly, lowering the risk of severe problems.
Stage 5: Abscess Formation and Sepsis
Appendicitis can get worse and lead to serious problems like abscesses and sepsis. If the appendix bursts, an abscess forms. This needs quick medical help to avoid more issues.
Development of Intra-abdominal Abscesses
An intra-abdominal abscess is a pocket of pus in the belly. It happens when the appendix bursts. It causes a lot of pain, fever, and other symptoms. This shows a big infection that needs treatment.
Symptoms of Exploded Appendix Complications
The signs of an exploded appendix are very bad. They include:
- Severe abdominal pain that may radiate to the back
- High fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal tenderness and guarding
These signs mean a serious infection that needs fast medical help.
Systemic Inflammatory Response and Sepsis
Sepsis is a very dangerous condition. It happens when the body’s fight against infection harms its own tissues and organs. If the infection from appendicitis spreads, sepsis can occur. This can cause organs to fail, which is a big emergency.
Mortality Rates in Developed vs. Developing Settings
The death rates from appendicitis problems are different in rich and poor countries. In rich countries, quick surgery and antibiotics lower death rates. But in poor areas, lack of healthcare means more deaths because of late treatment.
|
Setting |
Mortality Rate |
|---|---|
|
Developed Countries |
<1% |
|
Developing Countries |
5-10% |
This shows how important good healthcare is for dealing with appendicitis and its problems.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Appendicitis
Diagnosing acute appendicitis involves several steps. These include clinical checks, scoring systems, and imaging tests. Getting the diagnosis right and fast is key to managing the condition well and avoiding serious problems.
Diagnostic Tools and Scoring Systems
Many tools and scoring systems help spot acute appendicitis. The Alvarado score is a big help. It looks at symptoms, physical checks, and lab results to guess if you have appendicitis.
Alvarado Score and Other Assessment Methods
The Alvarado score is a 10-point system. It uses symptoms, physical checks, and lab tests. A score of 7 or more means you likely have appendicitis. Doctors also look at your history and do a clinical check.
Laboratory Tests and Imaging Techniques
Lab tests like complete blood counts (CBC) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels check for inflammation. Ultrasound and CT scans show the appendix and confirm the diagnosis.
|
Diagnostic Tool |
Description |
Utility in Appendicitis |
|---|---|---|
|
Alvarado Score |
10-point scoring system based on clinical and lab findings |
Assesses likelihood of appendicitis |
|
CBC |
Complete Blood Count |
Indicates inflammation (elevated WBC) |
|
CRP |
C-reactive Protein |
Marker for inflammation |
|
Ultrasound |
Imaging technique using sound waves |
Visualizes appendix, detects inflammation |
|
CT Scan |
Computed Tomography Scan |
Detailed imaging of abdominal structures |
Treatment Options
Acute appendicitis treatment usually means surgery to remove the appendix and antibiotics. The choice between open and laparoscopic surgery depends on the patient’s health and the surgeon’s preference.
Surgical Interventions (Open vs. Laparoscopic)
Laparoscopic appendectomy is less invasive, leading to less pain and quicker recovery. But, open appendectomy might be needed in complex cases or when laparoscopic tools are not available.
Non-Surgical Management in Select Cases
In some cases, like early or simple appendicitis, antibiotics alone might be used. But, this choice needs careful patient selection and close monitoring.
Recovery Timeline and Post-Treatment Care
Recovering from appendicitis surgery takes a few weeks. Patients should gradually return to normal activities. They also need follow-up visits to check on healing and remove stitches or staples.
Getting the diagnosis right and acting fast is linked to survival rates over 99%. Treatment usually includes antibiotics and, often, surgery to remove the appendix.
Conclusion: The Importance of Early Intervention
Knowing the five stages of appendicitis is key for quick medical help. Spotting appendicitis symptoms and signs of appendicitis early can greatly improve treatment results.
Acute appendicitis needs fast medical care to avoid serious problems, as a clinic says. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital for survival rates over 99%. It’s important to know the warning signs and get medical help quickly.
Acting fast can stop appendicitis from getting worse, lowering the chance of serious issues. By knowing the signs of appendicitis and how acute appendicitis progresses, people can seek medical care early. This leads to better health outcomes.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of appendicitis?
Symptoms of appendicitis include abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. You might also feel a loss of appetite and have a fever. The pain usually starts near the belly button and then moves to the lower right side.
What causes appendicitis?
Appendicitis often happens when the appendix gets blocked. This blockage can be caused by feces, undigested food, or other objects. Bacterial growth can also play a role.
What are the 4 stages of appendicitis?
The stages of appendicitis are: Stage 1 is when the appendix gets blocked. Stage 2 is when it becomes inflamed. Stage 3 is when it starts to rot. Stage 4 is when it bursts and causes infection. Stage 5 is when an abscess forms and sepsis occurs.
What side is the appendix on?
The appendix is usually found on the right side of the abdomen. It’s near where the small and large intestines meet.
What are the symptoms of a ruptured appendix?
A ruptured appendix shows severe pain, high fever, and nausea. You might also vomit and feel tenderness in your abdomen. If you have these symptoms, get medical help right away.
How is appendicitis diagnosed?
Doctors use a physical exam, medical history, and tests like blood work and imaging studies. Ultrasound or CT scans are often used to diagnose appendicitis.
What is the treatment for acute appendicitis?
Acute appendicitis is usually treated with surgery to remove the appendix. Sometimes, antibiotics are used for less severe cases.
What are the complications of untreated appendicitis?
Untreated appendicitis can lead to serious problems. These include perforation, peritonitis, abscess formation, and sepsis. These can be very dangerous and even life-threatening.
How long does it take to recover from appendicitis surgery?
Recovery from appendicitis surgery varies. Most people can get back to normal in a few weeks. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions for aftercare.
Can appendicitis be prevented?
While you can’t completely prevent appendicitis, a healthy diet and regular bowel movements can help. Staying hydrated is also important.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8811898/





