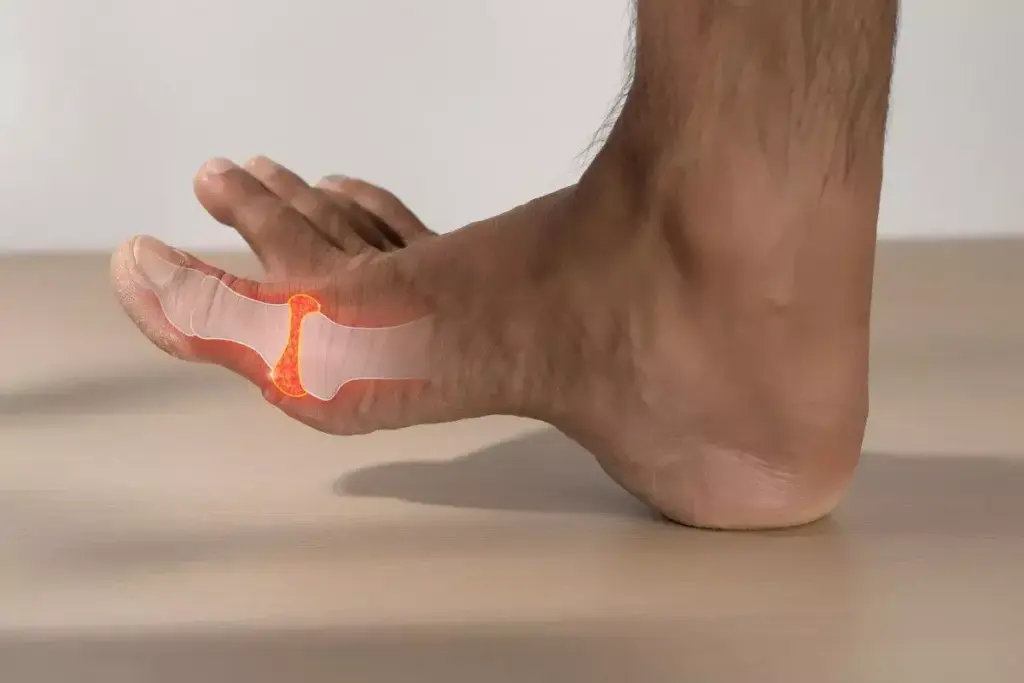
Managing gout well means knowing how food choices affect uric acid levels. Gout is a painful arthritis caused by uric acid crystals in joints. These crystals often come from eating foods high in purines.
For people with gout, making smart food choices is key to a better life. By staying away from foods that can trigger gout, you can handle your condition better.
A gout diet is more than just avoiding some foods. It’s about eating healthy and living a balanced life. Eating the right amounts of healthy foods and cutting down on purine-rich ones can really help manage gout.
Key Takeaways
- Knowing which foods can cause gout attacks is vital for managing it.
- Following a balanced diet and healthy eating habits can help with gout.
- It’s important to reduce foods high in purines to lower uric acid levels.
- Eating moderate amounts of healthy foods can make a big difference.
- Managing gout requires a full approach to diet and lifestyle.
Understanding Gout and the Purine Connection

Purines are substances found in the body and some foods. They play a big role in gout. When purines break down, they turn into uric acid. Usually, uric acid dissolves in the blood and is removed by the kidneys.
But, if there’s too much uric acid or the kidneys don’t remove enough, it can build up. This buildup forms sharp crystals in joints or tissues. These crystals cause pain, swelling, and inflammation.
What Causes Gout Flare-Ups
Gout flare-ups happen when uric acid levels go up. Some things that can raise uric acid levels include:
- Diet: Foods high in purines can increase uric acid.
- Genetics: Family history can influence gout risk.
- Obesity: Being overweight can lead to more uric acid.
- Medical Conditions: Some health issues, like diabetes, can affect uric acid levels.
Knowing what triggers gout is key to managing it. Making smart lifestyle choices can help reduce flare-ups.
How Diet Affects Uric Acid Levels
Diet is very important for managing uric acid. Foods high in purines, like seafood and organ meats, can raise uric acid levels. For example, squid is high in purine and should be eaten in small amounts.
Organ meats, like liver and kidney, are also high in purines. They can make gout symptoms worse. To manage gout, it’s best to limit or avoid these foods.
For instance, tuna has moderate to high purine levels. Gout sufferers should eat no more than 3 ounces of tuna once or twice a week. Drinking plenty of water can also help flush uric acid out of the body and prevent flare-ups.
Understanding the link between purines and gout helps manage the condition. Making smart food choices can reduce painful flare-ups.
Seafood and Gout: Is Tuna Good for Gout?
Seafood is a big part of our diet, but it can affect gout differently. Some seafood is good, while others might make gout worse. Knowing which seafood is safe and how much to eat is key.
Tuna: Consumption Guidelines for Gout Sufferers
Tuna is a favorite, but it has purines. Yet, its purine levels are not as high as some other seafood. Eating tuna in small amounts is a good idea. Start with a 3-ounce serving, about the size of a deck of cards.
Key considerations for tuna consumption:
- Choose skipjack or canned tuna, which tend to have lower purine levels.
- Avoid or limit albacore or yellowfin tuna, as they may have higher purine content.
- Balance tuna with other low-purine protein sources in your diet.
Shellfish to Avoid: Crab, Mussels, Scallops, and Oysters
Crab and other shellfish are healthy but high in purines. Crab meat and gout is a big worry because crab has lots of purines. Mussels, scallops, and oysters also have high purine levels and can cause gout attacks.
It’s important to eat less of these shellfish to control gout. If you do eat them, do it in small amounts and watch your purine intake.
Squid and Other High-Purine Seafood
Squid and seafood like anchovies, sardines, and mackerel have a lot of purines. Squid, in particular, has more purines than tuna. It’s okay to eat squid sometimes, but not too often.
To manage gout well, knowing the purine levels in seafood is key. Making smart choices about seafood can help you enjoy its benefits without gout flare-ups.
Other High-Purine Foods to Limit or Avoid
To manage gout well, knowing which foods to limit is key. Seafood is a known problem, but other foods can also raise uric acid levels. This can lead to more gout attacks.
Organ Meats: Liver, Kidney, and Other Offal
Organ meats like liver and kidney are very high in purines. People with gout should avoid them to keep their condition from getting worse.
Alcoholic Beverages: Red Wine and Beer
Drinking beer and red wine can make gout worse. Beer is a big culprit because it raises uric acid levels a lot. If you like red wine, drinking it in moderation is important to avoid uric acid buildup.
Plant-Based Foods That May Trigger Gout
Even healthy plant-based foods can cause gout because of their purine content. Some legumes and vegetables fall into this category. Knowing which ones to watch out for is important for managing gout.
Additional Foods to Monitor
Other foods can also affect gout, not just high-purine ones. Foods high in sugar and salt can indirectly raise uric acid levels. This can impact your overall health.
| Food Category | Examples | Purine Level |
| Organ Meats | Liver, Kidney | High |
| Alcoholic Beverages | Beer, Red Wine | Variable |
| Plant-Based Foods | Legumes, Certain Vegetables | Moderate |
Conclusion: Managing Gout Through Diet and Hydration
Managing gout well depends on what you eat and how much water you drink. Drinking water helps your kidneys get rid of extra uric acid. This lowers the chance of crystals forming in your joints.
We suggest eating foods low in purines and high in antioxidants, like strawberries. Legumes like green beans, lentils, and mung beans are good too, but eat them in small amounts. Knowing how beans affect gout is important.
Some beans might make gout worse, but mung beans and string beans are okay. They can be part of a diet that helps with gout.
Also, foods like strawberries are not bad for gout if eaten in small amounts. To get rid of uric acid, staying hydrated is key. It’s one of the simplest ways to manage gout.
By choosing the right foods and drinking enough water, people with gout can control their condition. This helps reduce how often they have gout attacks.