Did you know that having gout significantly increases your risk of developing kidney stones? Both conditions come from too much uric acid in your body. Knowing this can help you prevent both painful conditions by managing your health and lifestyle.
Studies show that people with gout are more likely to get kidney stones. High uric acid levels cause both problems. So, it’s important to check and prevent these conditions in people at risk.
Key Takeaways
- Gout increases the risk of developing kidney stones due to excess uric acid.
- Both conditions share a common underlying cause: hyperuricemia.
- Proper management and lifestyle modifications can help prevent both conditions.
- Comprehensive evaluation is key for patients at risk.
- Preventive strategies can lower the risk of kidney stones in gout patients.
Understanding Gout and Kidney Stones Individually
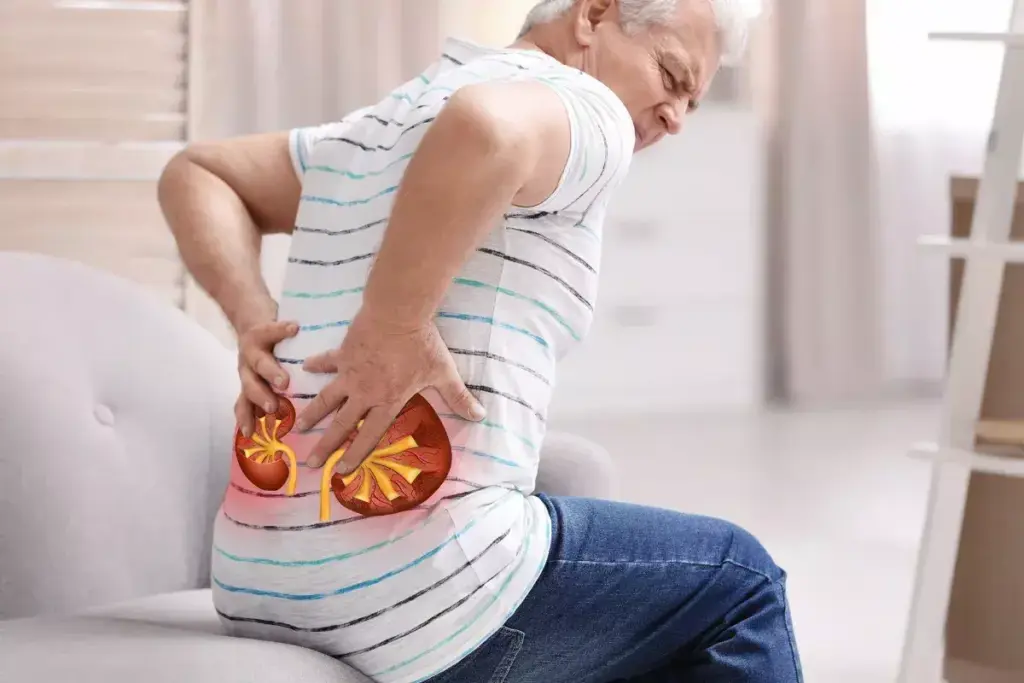
First, let’s understand what gout and kidney stones are. Both are serious health issues that affect many people. They cause a lot of pain and can lead to bigger problems if not treated right.
What is Gout?
Gout is a type of arthritis that causes sudden, severe pain. It often hits the joint at the base of the big toe. Gout happens when there’s too much uric acid in the blood. This forms sharp crystals in joints or tissues, causing pain and swelling. Uric acid is a waste product from breaking down certain substances in the body and some foods.
The symptoms of gout are very painful. They include intense pain, redness, and swelling in the affected joint. To manage gout, you can change your lifestyle, diet, and take medicine to lower uric acid levels.
What are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are hard deposits that form in the kidneys. The most common type is calcium oxalate, but there are others like uric acid stones. These stones can cause severe pain, usually in the side or back, below the ribs.
| Type of Kidney Stone | Cause | Characteristics |
| Calcium Oxalate Stones | Excess calcium and oxalate in the urine | Most common type, often associated with diet and hydration levels |
| Uric Acid Stones | Excess uric acid in the urine | Associated with gout and conditions that lead to high uric acid levels |
| Struvite Stones | Urinary tract infections | Can grow quickly and become quite large, sometimes with few symptoms |
Kidney stones are very painful and might need medical help to remove or break down. To prevent them, you can change your diet, drink more water, and take medicine if needed.
The Connection Between Gout and Kidney Stones
To understand the link between gout and kidney stones, we need to look at their common causes. Both are linked to how our body handles uric acid. Studies show a strong connection between them.
Hyperuricemia: The Common Denominator
High levels of uric acid in the blood are key for both gout and kidney stones. Uric acid crystals can cause gout in joints and kidney stones. If uric acid levels get too high, it can lead to crystals forming in both places.
Hyperuricemia is a big deal for both gout and kidney stones. Keeping uric acid levels in check is vital to avoid both conditions. It’s why managing hyperuricemia is so important for patients with gout and those at risk for kidney stones.
Statistical Evidence of the Relationship
Research has found a strong link between gout and kidney stones. For example, having gout can make you twice as likely to get kidney stones. Also, about half of gout patients develop uric acid stones, compared to 20 percent without gout.
| Condition | Incidence of Kidney Stones | Percentage of Uric Acid Stones |
| Gout | Double the risk | 50% |
| Without Gout | Normal risk | 20% |
The stats clearly show a strong link between gout and kidney stones. This highlights the need to watch and manage uric acid levels in gout patients to stop kidney stones.
Pathophysiology and Risk Factors
Uric acid crystals are key in gout and kidney stones. They form due to genetics, diet, and medical conditions. This shows a common cause for both issues.
How Uric Acid Crystals Form in Joints and Kidneys
When there’s too much uric acid, called hyperuricemia, crystals form. These crystals can cause gout in joints or kidney stones. The process includes:
- The breakdown of purines into uric acid.
- The accumulation of uric acid due to overproduction or underexcretion.
- The crystallization of uric acid in joints or kidneys.
Shared Risk Factors for Both Conditions
Many factors increase the risk of gout and kidney stones. These include:
- Being overweight or obese, which increases uric acid production.
- Consuming a diet high in purines, such as organ meats and certain seafood.
- Drinking alcohol, mainly beer, which can raise uric acid levels.
- Having a family history of gout or kidney stones.
Knowing these risk factors helps prevent both conditions.
Uric Acid Nephrolithiasis in Gout Patients
Uric acid stones in the kidneys are a big worry for gout patients. The risk is higher because of shared causes like hyperuricemia. Keeping uric acid levels in check is key to avoid these stones.
We suggest gout patients and those at risk of kidney stones work with their doctors. This helps manage their condition and lower the risk of problems.
Conclusion: Prevention and Management Strategies
Managing gout and kidney stones well needs a full plan. This includes changing your lifestyle, eating differently, and using medicine. Knowing how these two issues are linked helps us find better ways to stop them from happening.
Drinking plenty of water and eating less purine are key steps. These actions help control uric acid levels, which are important for both gout and kidney stones. Taking medicines like allopurinol can also lower uric acid, making complications less likely.
We aim to help people manage their gout and kidney stones better. By eating right, staying at a healthy weight, and following treatment plans, people can live better lives. Our goal is to give people the tools they need to handle their conditions well.
We believe in a mix of medical care and lifestyle changes for the best results. This approach helps manage gout and prevent kidney stones effectively.
FAQ
Are gout and kidney stones related?
Can gout cause kidney stones?
What is the role of hyperuricemia in gout and kidney stones?
How do uric acid crystals form in joints and kidneys?
What are the shared risk factors for gout and kidney stones?
Can lifestyle changes help prevent gout and kidney stones?
How can I manage gout and kidney stones?
Is there a link between uric acid levels and kidney stone formation?
Can dietary changes help reduce uric acid levels?
References
Nature. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.nature.com/articles/s41584-019-0280-5