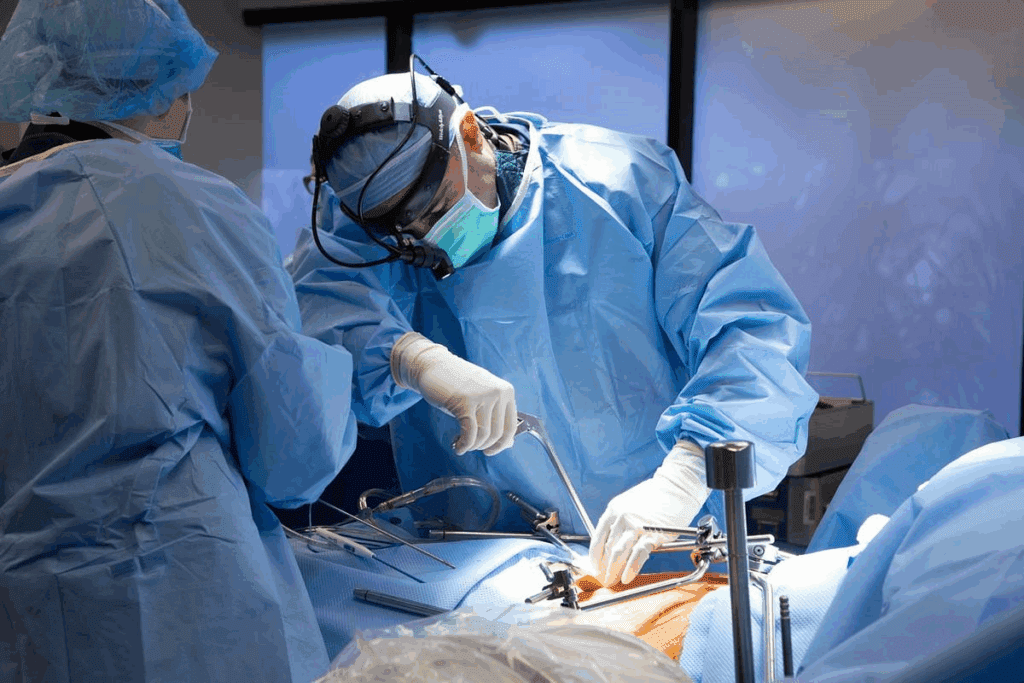
Thoracic surgery is a complex and delicate procedure that requires careful planning. The patient position for thoracic surgery is crucial for achieving optimal results, as it affects surgical access, patient physiology, and overall success.
Research shows that the correct patient position for thoracic surgery reduces the risk of complications and supports faster recovery. As a leading healthcare provider, we emphasize precise positioning to ensure exceptional care for patients from around the world.
Key Takeaways
- Optimal patient positioning is critical for successful thoracic surgery.
- Proper positioning enhances surgical access and reduces complications.
- Correct positioning improves patient recovery times and overall outcomes.
- Our healthcare team prioritizes precise positioning for exceptional patient care.
- Advanced positioning techniques are used to minimize risks and ensure the best results.
The Importance of Proper Positioning in Thoracic Surgery
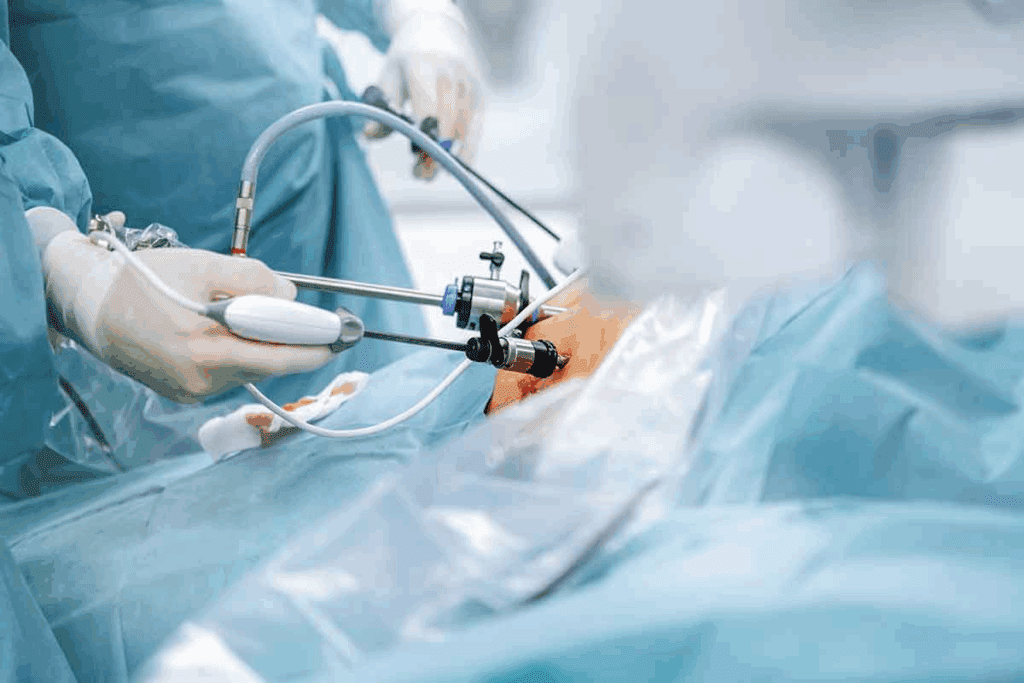
In thoracic surgery, the right patient position is key. It affects how well the surgeon can see and how the patient’s body reacts. We know that effective thoracic surgery needs the patient to be positioned just right for the best results.
Proper positioning is vital. It helps the surgical team get the best view of the thoracic cavity. This improves the surgery’s outcome. It also keeps the patient’s body stable during the operation.
Impact on Surgical Access and Visualization
The patient’s position greatly affects surgical access and visualization in thoracic surgery. By adjusting the patient’s position, surgeons can see the area they need to operate on better. This is essential for the surgery’s success.
Good positioning makes it easier to reach the thoracic cavity. This simplifies the surgery and may lower the risk of problems. It lets the surgical team work more accurately and with more control.
Effect on Patient Physiology and Hemodynamics
Patient positioning also deeply affects patient physiology and hemodynamics in thoracic surgery. The patient’s position can change how their body breathes and pumps blood. This affects how well they get oxygen and manage their blood pressure.
We think carefully about how different positions affect the patient’s body. We choose a position that supports the patient’s health during the surgery. We also watch for any changes in blood flow that might happen because of the position.
Patient Position for Thoracic Surgery: An Overview
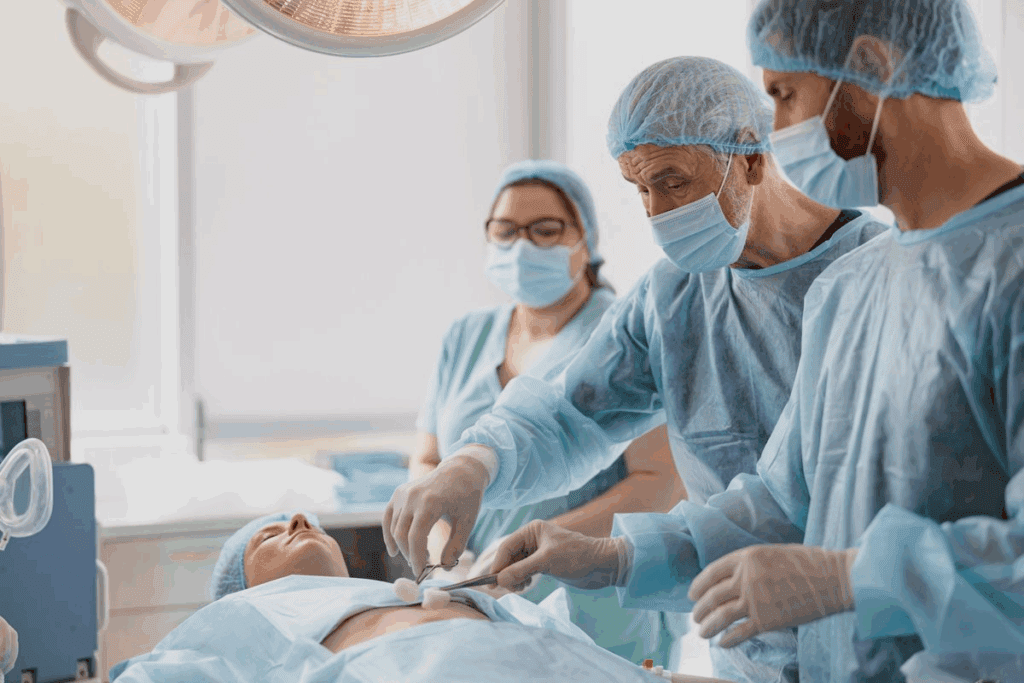
Positioning patients for thoracic surgery has changed a lot over time. It’s now more important than ever. The right position is key for better surgery access, patient safety, and results.
Common Positions Used in Modern Thoracic Procedures
Today, several positions are used in thoracic surgery. Each has its own use and benefits. The lateral decubitus position is often used for thoracotomy, giving great access to the chest area. The supine position is best for surgeries on the front of the chest and some minimally invasive ones. The prone position is also popular for certain surgeries, improving exposure.
We pick the best position for each patient, considering their health, the surgery type, and the surgeon’s choice. This flexibility helps us tailor care for each patient, aiming for the best results.
Evolution of Positioning Techniques
Positioning techniques in thoracic surgery have seen big improvements. In the past, options were limited. But, as surgery techniques got better, so did how we position patients.
Now, we use many techniques, from the traditional lateral decubitus to the prone position. These changes aim to improve surgery access, lower risks, and keep patients safer. We keep working to make positioning better, using new tech and our experience to improve care.
Lateral Decubitus Position: The Standard for Thoracotomy
The lateral decubitus position is key in thoracic surgery, like thoracotomy. It involves putting the patient on their side. This is important for getting to the thoracic cavity.
Proper Patient Alignment in Lateral Decubitus
Getting the patient’s position right in the lateral decubitus is vital for thoracotomy success. We make sure the spine is straight and the hips are bent. This helps us get to the thoracic area better.
The upper arm is placed on an armrest or supported. This prevents nerve or vessel damage.
Key elements of proper alignment include:
- Maintaining the spine in a neutral position
- Flexing the hips to improve access to the thorax
- Supporting the upper arm to prevent nerve damage
Advantages for Lung and Pleural Access
The lateral decubitus position has big benefits for lung and pleural procedures. By having the patient on their side, we get better views of the thoracic cavity. This makes surgeries easier.
| Advantages | Description |
| Better Exposure | Improved access to the lungs and pleura |
| Enhanced Visualization | Clearer view of the surgical site |
| Facilitated Surgical Access | Easier manipulation of surgical instruments |
Potential Complications and Prevention
Even though the lateral decubitus position is great, it can have risks. These include nerve injuries and breathing problems. We work hard to avoid these by carefully positioning the patient and watching them closely.
Strategies for preventing complications include:
- Regularly checking for nerve compression
- Adjusting the patient’s position to optimize respiratory function
- Using supportive devices to maintain stable positioning
Supine Position in Thoracic Surgery
The supine position is key in thoracic surgeries, mainly for anterior approaches. It’s chosen for its simplicity and access to the thoracic cavity. We’ll look at when to use it, its role in anterior procedures, and monitoring patients during surgery.
Indications for Supine Positioning
The supine position is best for surgeries needing access to the front of the thoracic area. Common reasons include:
- Mediastinal surgeries
- Anterior thoracic spine procedures
- Certain types of thymectomy
- Some lung surgeries where the front is easier to reach
We decide on the supine position based on the patient’s body, the surgery type, and benefits for both the patient and the team.
Anterior Thoracic Procedures
In anterior thoracic surgeries, the supine position gives great exposure. It makes access straightforward. This is great for:
- Thymectomy, where the thymus gland is removed
- Mediastinoscopy, for checking the mediastinum
- Certain lung resections needing an anterior approach
The supine position helps by giving a clear view of the area. This makes the surgery safer and more effective.
Patient Monitoring Considerations
When patients are on their backs for thoracic surgery, watching them closely is vital. Important things to monitor include:
- Respiratory function to avoid lung issues
- Hemodynamic status to catch blood pressure or heart changes
- Positioning of limbs to prevent nerve or blood vessel problems
We stress the need for constant monitoring to keep patients safe and get the best results.
Prone Position for Specialized Thoracic Procedures
For some thoracic surgeries, the prone position is key to success. This position, where the patient lies on their stomach, is used for complex surgeries. It helps achieve the best results.
Indications for Prone Positioning
The prone position is best for certain thoracic surgeries. It gives unique access to the body. Esophageal surgery and posterior mediastinal mass resections are examples where it’s beneficial.
We look at the patient’s body and the surgery’s needs to decide if prone positioning is right.
Technique for Safe Prone Positioning
Safe prone positioning needs careful attention to avoid problems. We make sure the patient’s airway is safe and sensitive areas aren’t pressed.
- We use careful padding and support to protect pressure points.
- The patient’s limbs are placed to avoid nerve injury.
- We keep a close eye on the patient during the surgery.
Managing Complications in Prone Position
The prone position has its challenges. We’re ready to handle issues like respiratory difficulties or hemodynamic instability.
| Complication | Management Strategy |
| Respiratory difficulties | Adjust ventilation parameters and ensure secure airway management. |
| Hemodynamic instability | Monitor vital signs closely and be prepared to adjust fluid management or administer vasoactive medications as needed. |
Knowing about prone positioning’s benefits, techniques, and risks helps us improve patient results in thoracic surgeries.
Modified Positions for Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery
Modified positions are key to the success of minimally invasive thoracic surgery. They improve surgical access and patient outcomes. Understanding these positions is vital as we move forward in this field.
Minimally invasive thoracic surgery includes Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS) and robotic-assisted surgery. Each method needs specific patient positions. This ensures the best surgical conditions and reduces risks.
Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS) Positioning
VATS is a key method for treating thoracic conditions. It’s less invasive than traditional surgery. Proper positioning is essential for good exposure and vision of the thoracic cavity.
Patients usually lie on their side for VATS, like in open thoracotomy. But, the exact position and supports used can change. This helps place trocars and move during surgery.
Robotic-Assisted Thoracic Surgery Positioning
Robotic-assisted thoracic surgery is a new step in minimally invasive surgery. It offers better precision and control. The positioning for this surgery is similar to VATS, with the patient lying on their side.
Robotic systems need special considerations. This includes making sure there’s enough space for the robotic arms. The patient’s position might need to be adjusted for the robotic system to dock properly. This might involve using special supports and changing the operating table.
By carefully planning and executing patient positioning for minimally invasive thoracic surgery, we can improve outcomes. We can also reduce patient trauma and speed up recovery. As technology improves, we expect to see even better positioning techniques for these innovative surgeries.
Positioning for Specific Thoracic Procedures
Thoracic surgery includes many procedures, each needing its own positioning. The way patients are positioned is key for success. It affects how well surgeons can see and work, and keeps patients safe.
Lung Resection Positioning
Lung surgeries, like lobectomies and segmentectomies, use the lateral decubitus position. This position helps surgeons reach the lung’s hilum. It also makes it easier to work on pulmonary vessels and bronchi. We make sure patients are aligned and stable to avoid movement during surgery.
“The lateral decubitus position is a cornerstone in thoracic surgery, providing unparalleled access to the thoracic cavity,” as emphasized by thoracic surgeons worldwide.
Esophagectomy Positioning
Esophagectomies need different positions based on the approach. For example, a left lateral decubitus position is used for some thoraco-abdominal approaches. Others might prefer a prone position for minimally invasive surgeries. The goal is to get the best view of the esophagus while reducing risks.
Mediastinal Mass Resection
Positioning for removing mediastinal masses depends on the mass’s location and size. For anterior masses, a supine position with arms up is common. This allows for a median sternotomy or anterior thoracotomy. We carefully plan to avoid harming the mass during setup.
Chest Wall Procedures
Chest wall surgeries, like pectus excavatum repair or tumor removal, need specific positioning. This might be supine or prone, depending on the procedure and the chest area involved.
In conclusion, positioning for thoracic surgeries varies greatly. It must match the specific needs of each procedure. By understanding these needs, we can achieve the best results for our patients.
Anesthesia Considerations During Patient Positioning
Anesthesia is key to keeping patients safe when they’re positioned for thoracic surgery. It’s vital for managing the body’s changes during positioning.
Airway Management During Position Changes
Keeping the airway clear is a big part of anesthesia care during positioning. We make sure the endotracheal tube stays in place and ventilation is good during changes.
- Secure fixation of the endotracheal tube to prevent displacement
- Continuous monitoring of airway pressures and ventilation parameters
- Careful assessment of the patient’s respiratory status during and after positioning
By focusing on airway management, we lower the risk of breathing problems. This ensures the patient gets enough oxygen during surgery.
Hemodynamic Monitoring and Management
Watching the heart is important during patient positioning. We keep an eye on blood pressure, heart rate, and cardiac output. This helps keep the patient’s heart stable.
Key aspects of hemodynamic management include:
- Continuous blood pressure monitoring, preferably using invasive arterial lines
- Heart rate and rhythm monitoring to detect arrhythmias
- Assessment of cardiac output and vascular resistance
By closely monitoring the heart, we can quickly spot and fix any problems. This keeps the patient’s heart stable during the surgery.
Preventing Positioning-Related Complications
Keeping patients safe during thoracic surgery is key. We focus on careful steps to avoid risks linked to how patients are positioned.
Getting patient positioning right is vital in thoracic surgery. We plan and execute carefully to avoid complications.
Pressure Point Protection
Protecting pressure points is a big part of avoiding complications. We use special padding to spread out pressure and prevent tissue damage.
We use special padding for sensitive spots like elbows, heels, and the sacrum. We check these areas often during surgery to make sure they’re safe.
Nerve Injury Prevention
Nerve injuries can happen if patients are positioned wrong. We work hard to prevent this by avoiding nerve compression or stretching.
We position limbs carefully to avoid nerve issues. We also use supports and watch for nerve problems during surgery.
Vascular Compression Avoidance
Vascular compression can cause serious problems like deep vein thrombosis. We use supports and change positions to avoid this.
Keeping patients in the right position helps blood flow. This reduces the chance of vascular issues.
Joint and Muscle Protection
It’s important to protect joints and muscles during surgery. This helps prevent pain and mobility problems later. We use supports to keep joints neutral and avoid muscle strain.
Our team makes sure patient positioning is right for surgery and comfort. This helps avoid complications.
We plan carefully, execute precisely, and monitor closely to lower complication risks in thoracic surgery. Patient safety and comfort are our top priorities.
Special Considerations for High-Risk Patients
Thoracic surgery for high-risk patients comes with its own set of challenges. We focus on obese, elderly, and patients with musculoskeletal conditions. Our goal is to ensure safe and effective surgery for these groups.
Obese Patients
Obese patients face challenges like smaller lung volumes and higher respiratory risks. We start by improving their lung function before surgery. We also plan the surgery carefully to manage these risks.
Key considerations for obese patients include:
- Preoperative weight loss when feasible
- Careful positioning to avoid pressure points
- Enhanced monitoring during surgery
- Postoperative respiratory support
Elderly Patients
Elderly patients often have many health issues that make surgery riskier. We do detailed checks before surgery to find and plan for these risks.
| Consideration | Strategy |
| Cardiovascular Comorbidity | Cardiac evaluation and optimization |
| Respiratory Comorbidity | Pulmonary function testing and rehabilitation |
| Renamed Functional Status | Preoperative physical therapy |
Patients with Pre-existing Musculoskeletal Conditions
Patients with musculoskeletal issues need special care during surgery. We use special tools and methods to support them.
For example, those with severe arthritis might need extra support and padding. This helps prevent discomfort and injury during long surgeries.
We tailor our approach to meet the unique needs of high-risk patients. This way, we can improve outcomes and provide top-notch care for all thoracic surgery patients.
Equipment and Devices for Optimal Positioning
Advanced equipment and positioning aids are key for good thoracic surgery results. We use a variety of specialized devices. They help make sure patients are positioned right, making the surgery safer and more effective.
Positioning Aids and Supports
Positioning aids and supports are vital for keeping patients in the right spot during surgery. They include:
- Inflatable pillows and wedges for precise patient alignment
- Straps and restraints to secure the patient in place
- Adjustable armrests and leg supports for comfort and accessibility
These tools help keep the patient in the best position. This reduces the chance of problems and makes the surgery easier.
Modern Operating Tables and Attachments
Modern operating tables offer flexibility and precision in patient positioning. Key features include:
- Adjustable height and tilt to facilitate optimal surgical access
- Attachments for securing positioning aids and supports
- Integrated technology for monitoring patient position and vital signs
Choosing high-quality operating tables and attachments is vital for better patient safety and surgery results. We suggest picking equipment that’s both flexible and dependable. It should handle the needs of complex thoracic surgeries well.
By using the latest positioning aids with modern operating tables, we can greatly improve care for our patients having thoracic surgery.
The Role of the Surgical Team in Patient Positioning
Working together, the surgical team makes sure patients are positioned right. This team effort involves surgeons, anesthesiologists, and nurses. They all play a key role in getting the patient ready for surgery.
Surgeon’s Responsibility
The surgeon is key in picking the best position for surgery. They think about how to get to the area, seeing clearly, and keeping the patient safe.
Key responsibilities of the surgeon include:
- Determining the optimal patient position
- Communicating positioning requirements to the team
- Ensuring that the position does not compromise the surgical site
Anesthesiologist’s Role
The anesthesiologist keeps an eye on how the patient reacts to being moved. They watch the patient’s vital signs and adjust the anesthesia to keep them stable.
The anesthesiologist’s key tasks include:
- Monitoring patient vital signs during positioning
- Adjusting anesthesia to maintain patient stability
- Ensuring airway security during position changes
Nursing and Support Staff Contributions
Nurses and support staff are essential in putting the patient in the right position. They work with the surgeon and anesthesiologist to make sure the patient is safe and in the correct position.
| Team Member | Key Responsibilities |
| Surgeon | Determining optimal position, communicating requirements |
| Anesthesiologist | Monitoring vital signs, adjusting anesthesia |
| Nursing Staff | Executing patient position, ensuring safety |
Good communication and teamwork are vital for successful patient positioning. By working together, we can give our patients the best care during thoracic surgery.
Conclusion
Proper patient positioning is key for successful thoracic surgery. We’ve looked at the importance of the right position, common positions used, and the surgical team’s role.
Different positions, like lateral decubitus, supine, and prone, are used for various thoracic procedures. Careful planning and precise execution are vital for the best results. Understanding patient positioning helps healthcare professionals improve access, reduce complications, and aid in patient recovery.
As medical technology and techniques evolve, optimal patient positioning remains essential. By focusing on the best positioning, we can achieve better surgical outcomes. This ensures top-notch healthcare and support for our patients.
FAQ
What is the most common position used for thoracic surgery?
The lateral decubitus position is often used for thoracic surgery. It’s great for lung and pleura procedures.
Why is proper patient positioning so important in thoracic surgery?
Proper positioning is key in thoracic surgery. It affects access, visibility, and patient health. It helps avoid complications and keeps patients safe.
What are the benefits of the lateral decubitus position in thoracic surgery?
The lateral decubitus position is excellent for lung and pleura surgeries. It offers better visibility and control over thoracic structures.
How is patient safety ensured during positioning for thoracic surgery?
Safety is ensured through careful planning and monitoring. This includes protecting pressure points and avoiding nerve injuries. It also involves preventing vascular compression and protecting joints and muscles.
What are the specific positioning requirements for minimally invasive thoracic surgery?
Minimally invasive surgeries need specific positions for access and visibility. Modified positions are used to expose the surgical site better.
How do anesthesiologists contribute to patient positioning in thoracic surgery?
Anesthesiologists manage airway changes and monitor blood pressure. They ensure patient stability during the procedure.
What are the challenges of positioning high-risk patients for thoracic surgery?
High-risk patients, like the obese or elderly, pose challenges. Specialized positioning strategies are needed to ensure their safety.
What equipment is used to achieve optimal patient positioning in thoracic surgery?
Equipment like positioning aids and modern operating tables are used. High-quality equipment improves patient safety and outcomes.
How does the surgical team collaborate to achieve optimal patient positioning?
The team works together for precise positioning. Surgeons, anesthesiologists, and nurses ensure patient safety and monitoring throughout the surgery.
Reference
- Yost, C. C. (2023). A primer for the student joining the general thoracic surgery service. PMC – National Institutes of Health. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10328966/
























