Modern surgical techniques have evolved significantly, offering patients a range of options for their medical care. One of the key advancements is the introduction of robotic precision in surgical procedures.
A surgeon controls robotic arms with extreme precision, allowing for more complex operations to be performed with greater accuracy. In contrast, manual technique relies on the skill and experience of the surgeon.
Understanding the differences between these two approaches is crucial for informed decision-making. By weighing the benefits of one against the risks of the other, patients can make more informed choices about their care.
Key Takeaways
- Robotic surgery offers enhanced precision and accuracy.
- Manual surgery relies on the surgeon’s skill and experience.
- The choice between robotic and manual surgery depends on various factors.
- Understanding the benefits and risks is crucial for informed decision-making.
- Patients should discuss their options with their healthcare provider.
Understanding Surgical Approaches
The landscape of surgery has been shaped by two distinct methodologies: traditional manual techniques and robotic-assisted innovations. Understanding these approaches is crucial for evaluating their effectiveness and applicability in various surgical contexts.
Defining Traditional Manual Surgery
Traditional manual surgery involves procedures performed directly by a surgeon’s hands, utilizing basic surgical instruments. This method has been the cornerstone of surgical practice for centuries, relying on the skill, precision, and experience of the surgeon.
Key characteristics of manual surgery include:
- Direct human control over surgical instruments
- Tactile feedback allowing surgeons to feel tissue resistance and texture
- Flexibility in handling unexpected situations during surgery
The Emergence of Robotic-Assisted Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery represents a significant advancement in surgical technology, where a robotic system is controlled by a surgeon to perform procedures. This approach has evolved over the past few decades, offering enhanced precision and minimal invasiveness.
The development of robotic-assisted surgery has been driven by:
- Advancements in robotic technology and miniaturization
- The need for greater precision and reduced human error
- The potential for minimally invasive procedures to reduce recovery time
Key Distinctions at a Glance
The differences between manual and robotic-assisted surgery can be summarized in the following table:
| Feature | Manual Surgery | Robotic-Assisted Surgery |
| Control Mechanism | Direct human control | Surgeon-controlled robotic system |
| Tactile Feedback | Direct tactile feedback | Limited tactile feedback, enhanced visualization |
| Precision and Accuracy | Highly dependent on surgeon skill | Enhanced precision with robotic assistance |
| Invasiveness | Can be more invasive | Often minimally invasive |
The Evolution of Surgical Techniques
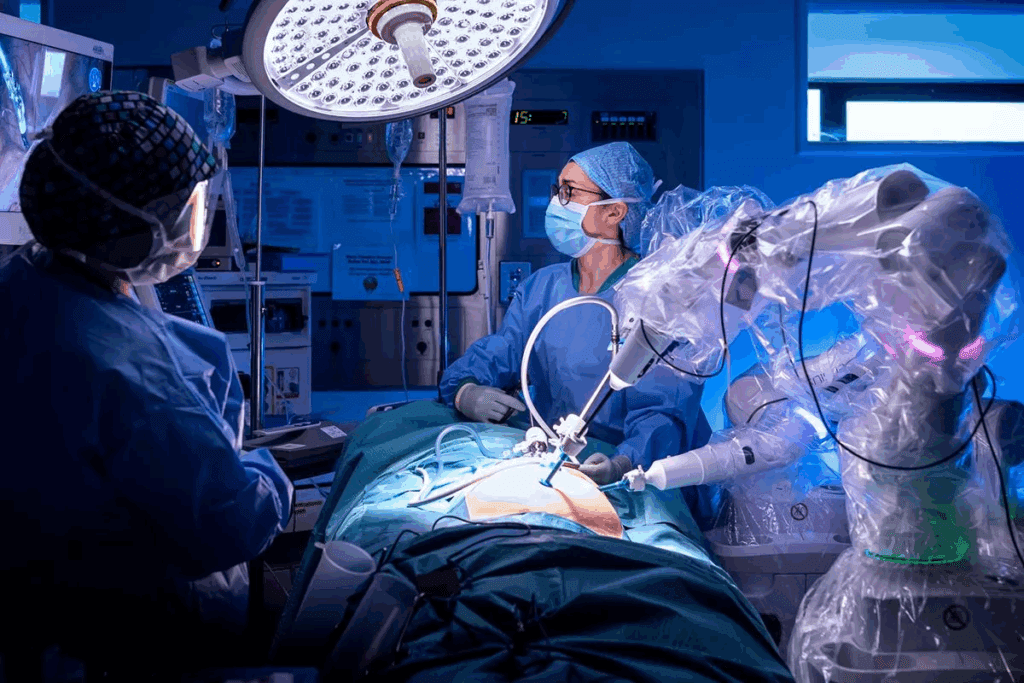
The history of surgery is marked by continuous innovation, from traditional manual surgical procedures to the development of robotic surgical systems. This evolution reflects the medical community’s ongoing quest for precision, safety, and patient comfort.
The development of surgical techniques has been influenced by various factors, including technological advancements, the need for greater precision, and the desire to minimize recovery times. As a result, both manual and robotic surgical methods have evolved significantly over time.
History of Manual Surgical Procedures
Manual surgical procedures have a long history, dating back to ancient civilizations. Early surgical techniques were often crude and performed without the benefit of modern anesthesia or antiseptic practices. Over time, manual surgery evolved through the introduction of new tools and techniques, significantly improving patient outcomes.
The development of surgical instruments, such as forceps and scalpels, played a crucial role in the advancement of manual surgery. Surgeons have continually refined their techniques, incorporating new materials and technologies to enhance their capabilities.
Development of Robotic Surgical Systems
Robotic surgical systems represent a significant innovation in the field of surgery. The first robotic surgical system was approved for use in the late 1990s, marking the beginning of a new era in surgical care. Since then, robotic surgery has continued to evolve, with advancements in technology leading to greater precision and control.
Robotic surgical systems offer several advantages, including enhanced visualization, improved dexterity, and the ability to perform complex procedures with minimal invasion. These systems have been particularly beneficial in specialties such as urology and gynecology.
As robotic technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further improvements in surgical outcomes and patient recovery times. The ongoing development of robotic surgical systems is a testament to the innovative spirit of the medical community.
How Robotic Surgery Works
Robotic-assisted surgery is a sophisticated technique that enables surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater accuracy. This advanced method involves a combination of cutting-edge technology and skilled surgical expertise.
Components of Robotic Surgical Systems
A robotic surgical system consists of several key components, including the surgeon’s console, the patient-side cart, and the vision system. The surgeon’s console is where the surgeon controls the robotic arms, using a high-definition 3D display to visualize the surgical site.
The patient-side cart houses the robotic arms that perform the surgery. These arms are equipped with surgical instruments that can be changed as needed during the procedure. The vision system provides a clear, magnified view of the operating area, allowing for precise dissection and suturing.
Surgeon Control and Interface
The surgeon’s control over the robotic system is facilitated through the console, which translates the surgeon’s hand movements into precise actions by the robotic arms. According to Klause, MD, FACS, “The console provides an ergonomic environment for the surgeon, reducing fatigue and improving control.” The interface is designed to be intuitive, allowing surgeons to focus on the procedure without being distracted by the technology.
“The integration of robotics in surgery has enhanced our ability to perform complex procedures with a high degree of precision and minimal invasiveness.” A MD, FACS
Technological Capabilities
The technological capabilities of robotic surgical systems are a significant advancement in the field of surgery. These systems offer enhanced precision, improved dexterity, and greater flexibility compared to traditional surgical methods. The robotic arms can rotate 360 degrees, allowing for complex maneuvers that would be difficult or impossible with manual instruments.
The combination of robotic precision and robotic accuracy enables surgeons to perform delicate procedures with confidence. As technology continues to evolve, the capabilities of robotic surgical systems are expected to expand, further enhancing patient outcomes.
The Art of Manual Surgery
The art of manual surgery is deeply rooted in the training and expertise of the surgeon. Manual surgery relies on the surgeon’s skill and experience, providing direct tactile feedback, which is crucial for the success of the procedure.
Surgeon Training and Skill Development
Surgeons undergo rigorous training to develop the manual skills required for surgical procedures. This training includes years of education, practice, and hands-on experience in the operating room. As one expert notes,
“The development of manual skill is a continuous process that requires dedication, patience, and a willingness to learn from both successes and failures.”
The training process for manual surgeons is comprehensive, covering various techniques, patient care, and decision-making. It is through this extensive training that surgeons develop the manual dexterity and precision needed to perform complex surgeries.
Tactile Feedback and Direct Control
One of the key advantages of manual surgery is the tactile feedback it provides. Surgeons can feel the tissue and instruments, allowing for more precise control during the procedure. This direct control enables surgeons to make real-time adjustments, enhancing the overall outcome of the surgery.
The ability to receive tactile feedback is crucial in manual surgery, as it allows surgeons to assess the texture, tension, and resistance of tissues. This information is vital for making informed decisions during the procedure.
Adaptability in the Operating Room
Manual surgery requires a high degree of adaptability. Surgeons must be able to adjust their techniques based on the specific needs of the patient and the complexity of the procedure. As noted in a study on robotic knee replacement vs. traditional surgery, manual surgery’s adaptability is one of its significant advantages.
The adaptability required in manual surgery is not just about technical skills; it also involves being able to manage unexpected complications and make critical decisions under pressure. Surgeons must be able to think on their feet and adjust their approach as needed.
Robotic vs Manual Surgery: A Comprehensive Comparison
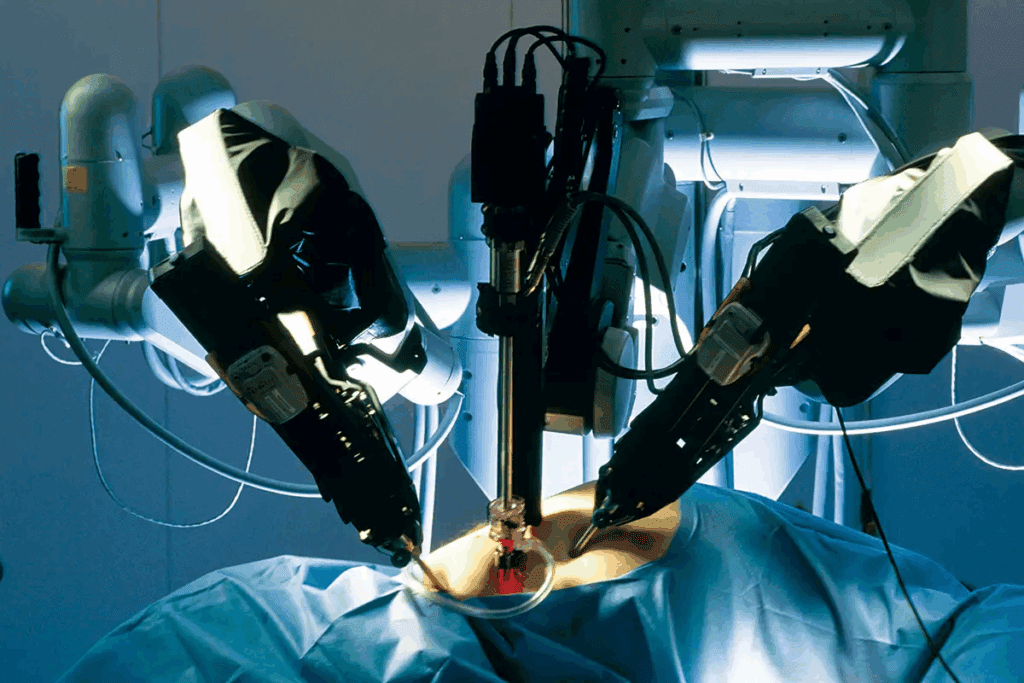
The choice between robotic and manual surgery depends on several factors, including precision, range of motion, and the surgeon’s expertise. As medical technology continues to evolve, understanding the differences between these two surgical approaches is crucial for making informed decisions.
Precision and Accuracy Factors
Robotic surgery has been shown to offer greater precision and accuracy compared to traditional manual surgery. Studies have highlighted that the robotic system’s ability to filter out hand tremors and provide a three-dimensional view enhances the surgeon’s capability to perform complex procedures with greater accuracy.
Key Precision and Accuracy Factors:
- Enhanced visualization
- Tremor filtration
- Improved dexterity
Range of Motion and Accessibility
Robotic systems provide surgeons with a greater range of motion and accessibility to confined spaces within the body. This is particularly beneficial in procedures that require intricate maneuvers in tight spaces.
The flexibility of robotic arms allows for more versatile movement, enabling surgeons to perform complex tasks with ease.
Learning Curve for Surgeons
The learning curve for robotic surgery is generally steeper than for manual surgery. Surgeons must undergo specialized training to master the robotic system’s interface and controls.
However, once proficient, surgeons can leverage the robotic system’s capabilities to perform procedures with enhanced precision and minimal invasiveness.
Operational Workflow Differences
The operational workflow differs significantly between robotic and manual surgery. Robotic surgery requires the setup and calibration of the robotic system, which can add to the overall procedure time.
| Aspect | Robotic Surgery | Manual Surgery |
| Precision | High, with tremor filtration | Dependent on surgeon’s skill |
| Range of Motion | Enhanced flexibility | Limited by human anatomy |
| Learning Curve | Steeper, requires training | More familiar for surgeons |
| Operational Workflow | Requires system setup | More straightforward |
Understanding these differences is crucial for surgeons and medical institutions when deciding which surgical approach to adopt for various procedures.
Benefits of Robotic-Assisted Surgery
With its cutting-edge technology, robotic-assisted surgery offers several advantages over traditional methods. This modern surgical approach has been increasingly adopted due to its potential to improve patient outcomes and enhance the surgical experience.
Enhanced Visualization and Magnification
One of the significant benefits of robotic-assisted surgery is its ability to provide enhanced visualization and magnification. The robotic system offers a high-definition, 3D view of the surgical site, allowing surgeons to see the area more clearly and precisely.
According to MD, FACS, “The improved visualization provided by robotic systems enables surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater accuracy.” This enhanced view is crucial in delicate surgeries where precision is paramount.
Minimally Invasive Capabilities
Robotic-assisted surgery is often associated with minimally invasive procedures, which result in smaller incisions compared to traditional open surgery. This leads to less tissue damage and trauma to the patient.
The benefits of minimally invasive surgery include reduced risk of infection, less postoperative pain, and quicker recovery times. These advantages contribute to improved patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Reduced Hand Tremor and Stability
The robotic surgical system is designed to reduce hand tremors and provide stability during procedures. The system’s advanced technology filters out any unintended movements, allowing for smoother and more precise surgery.
Ergonomic Advantages for Surgeons
Robotic-assisted surgery also provides ergonomic benefits for surgeons. The console where the surgeon operates is designed to reduce fatigue and improve comfort during long procedures.
A study comparing surgeon fatigue in robotic versus traditional surgeries found that surgeons experienced less fatigue when using robotic systems. This ergonomic advantage can lead to improved performance and reduced risk of errors during surgery.
| Benefits | Robotic-Assisted Surgery | Traditional Surgery |
| Visualization | High-definition, 3D view | Limited by human vision |
| Invasiveness | Minimally invasive | More invasive |
| Hand Tremor | Reduced | Present |
| Surgeon Ergonomics | Ergonomic design | Variable |
Advantages of Traditional Manual Techniques
The art of manual surgery is rooted in its ability to provide direct tactile feedback, a feature that remains invaluable in modern surgical practices. This tactile sensation allows surgeons to better understand the anatomy they are operating on, making more informed decisions during the procedure.
Direct Tactile Feedback
One of the primary advantages of manual surgery is the direct tactile feedback it provides. Surgeons can feel the tissue and structures they are operating on, which is crucial for assessing the texture, tension, and other critical characteristics of the anatomy. This sensory input is essential for complex procedures where precision is paramount.
Tactile feedback enables surgeons to make subtle adjustments during surgery, potentially reducing the risk of complications. It allows for a more nuanced understanding of the surgical site, which can be particularly valuable in delicate or intricate operations.
Freedom from Technical Malfunctions
Manual surgery is not dependent on complex technology, which means it is less susceptible to technical malfunctions that can occur with robotic systems. This reliability can be a significant advantage in situations where technological failures could have serious consequences.
“The simplicity of manual surgery can be a significant advantage, as it eliminates the risk of mechanical failures that can complicate robotic-assisted procedures.”
Lower Procedural Costs
Manual surgery typically involves lower procedural costs compared to robotic surgery. The absence of expensive robotic equipment and the associated maintenance costs can make manual surgery a more economical choice for both healthcare providers and patients.
| Cost Factor | Manual Surgery | Robotic Surgery |
| Equipment Costs | Lower | Higher |
| Maintenance Costs | Minimal | Significant |
| Training Costs | Standard surgical training | Specialized training required |
Versatility Across Conditions
Manual techniques are versatile and can be applied across a wide range of surgical conditions. Surgeons are trained to adapt their manual skills to various situations, making manual surgery a flexible option for different types of procedures.
The benefits of traditional manual surgery techniques, including direct tactile feedback, freedom from technical malfunctions, lower procedural costs, and versatility across conditions, make it a valuable approach in modern surgical practice.
Patient Outcomes and Recovery
The distinction between robotic and manual surgery extends to patient recovery and outcomes, areas where subtle differences can have significant implications. As surgical techniques continue to evolve, understanding these differences is crucial for both surgeons and patients.
Comparing Recovery Timelines
Recovery timelines vary significantly between robotic and manual surgery. Robotic surgery often results in faster recovery times due to its minimally invasive nature, reducing tissue trauma and promoting quicker healing. According to MD, FACS, robotic surgery can lead to shorter hospital stays and faster return to normal activities.
Pain Management Differences
Pain management is another critical aspect where robotic and manual surgery differ. Robotic surgery tends to result in less pain for patients due to smaller incisions and reduced tissue damage. This can lead to a reduction in the need for postoperative pain medication, contributing to a more comfortable recovery.
Scarring and Cosmetic Results
The cosmetic outcomes of surgery are increasingly important to patients. Robotic surgery, with its smaller and more precise incisions, generally offers better cosmetic results, reducing scarring and improving patient satisfaction with the surgical outcome.
Long-term Functional Outcomes
Long-term functional outcomes are a key consideration in evaluating the success of surgical procedures. Studies have shown that robotic surgery can lead to comparable or, in some cases, superior long-term functional outcomes compared to manual surgery, particularly in complex procedures.
In conclusion, the choice between robotic and manual surgery has a profound impact on patient outcomes and recovery. By understanding the differences in recovery timelines, pain management, scarring, and long-term functional outcomes, patients and surgeons can make more informed decisions.
Surgical Specialties and Applications
The integration of robotic technology in surgery has expanded its applications across multiple medical disciplines. Robotic-assisted surgery is now a vital component in various surgical specialties, offering enhanced precision, flexibility, and improved patient outcomes.
Urology and Prostate Surgery
Robotic surgery has significantly impacted urology, particularly in prostate surgeries. Procedures like robotic-assisted prostatectomy have become increasingly common due to their minimally invasive nature and reduced recovery times. The enhanced visualization and precision offered by robotic systems allow for better preservation of surrounding tissues and nerves.
Gynecological Procedures
In gynecology, robotic surgery is used for a range of procedures, including hysterectomies and endometriosis treatments. The robotic system’s ability to filter out hand tremors and provide a three-dimensional view of the operating area enhances the surgeon’s capability to perform complex procedures with greater accuracy.
Cardiac and Thoracic Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery is also making inroads in cardiac and thoracic surgery. Procedures such as mitral valve repair and coronary artery bypass grafting are being performed with robotic assistance, offering patients the benefits of minimally invasive surgery, including less pain and quicker recovery.
General Surgery Applications
General surgery is another area where robotic-assisted surgery is being increasingly adopted. Procedures like cholecystectomies and hernia repairs are being performed robotically, benefiting from the enhanced dexterity and visualization provided by the robotic systems.
As robotic technology continues to evolve, its applications across various surgical specialties are expected to expand, offering new possibilities for improving surgical outcomes and patient care.
Risk Assessment: Complications and Safety
Assessing the risks associated with surgical procedures is crucial for informed decision-making. Both robotic and manual surgeries have their unique set of risks and complications.
Common Complications in Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery, despite its advancements, comes with its own set of potential complications. These include:
- Technical malfunctions or system failures during the procedure.
- Increased risk of certain types of injuries due to the lack of direct tactile feedback.
- Potential for longer operating times, especially during the initial phase of a surgeon’s learning curve.
Understanding these risks is crucial for both surgeons and patients to make informed decisions.
Risks Associated with Manual Procedures
Manual surgery, while traditional and widely practiced, also has its associated risks, including:
- Higher risk of hand tremors and fatigue affecting precision.
- Increased risk of infection or tissue damage due to larger incisions in some cases.
- Potential for longer recovery times due to the invasiveness of the procedure.
These risks highlight the importance of skilled surgeons and proper patient care.
Safety Protocol Differences
The safety protocols for robotic and manual surgeries differ significantly. Robotic surgery relies heavily on:
- Pre-operative checks of the robotic system to ensure functionality.
- Training programs for surgeons to adapt to the robotic interface.
- Intra-operative monitoring to quickly address any technical issues.
In contrast, manual surgery focuses on:
- The skill and experience of the surgeon.
- Proper sterilization and infection control measures.
- Effective patient monitoring during and after the procedure.
Complication Management Strategies
Effective management of complications is critical in both robotic and manual surgeries. Strategies include:
- Prompt recognition and addressing of complications as they arise.
- Having a contingency plan in place for potential technical failures or surgical complications.
- Post-operative care protocols to minimize the risk of infection or other complications.
By understanding the risks and implementing robust safety protocols, surgeons can significantly improve patient outcomes.
The Economic Perspective
Understanding the economic perspective of surgical approaches is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients. The financial implications of choosing between robotic and manual surgery are significant and multifaceted.
Initial Investment and Maintenance Costs
Robotic surgery requires a substantial initial investment, including the cost of the robotic system itself, training for surgeons and staff, and necessary infrastructure modifications to the operating room. For instance, the da Vinci Surgical System, a commonly used robotic platform, can cost between $1.5 million to $2.5 million. Additionally, maintenance costs, which can range from $100,000 to $200,000 annually, must be considered.
Maintenance costs include regular software updates, hardware maintenance, and repair costs. These expenses contribute to the overall cost of owning and operating a robotic surgical system.
Per-Procedure Expenses
The cost per surgical procedure using robotic systems is generally higher than traditional manual surgery. Expenses include the cost of disposable instruments, maintenance fees, and potentially longer operating room times. A study comparing the costs of robotic and open surgery found that robotic procedures were significantly more expensive.
| Cost Component | Robotic Surgery | Manual Surgery |
| Initial Equipment Cost | $1.5 million – $2.5 million | $0 (existing equipment) |
| Maintenance Cost (Annual) | $100,000 – $200,000 | $0 – $50,000 |
| Disposable Instruments per Procedure | $1,000 – $2,000 | $500 – $1,000 |
Insurance Coverage and Patient Financial Impact
Insurance coverage for robotic surgery varies by provider and policy. While many insurance plans cover robotic surgery for certain procedures, patients may still face higher out-of-pocket costs compared to traditional surgery. The financial impact on patients includes not only the direct costs of the procedure but also potential costs associated with longer recovery times or complications.
It’s essential for patients to understand their insurance coverage and potential out-of-pocket expenses when considering robotic versus manual surgery.
Long-term Economic Considerations
When evaluating the long-term economic implications, factors such as recovery time, complication rates, and the need for additional surgeries must be considered. Robotic surgery, while potentially reducing recovery time and complications in some cases, may not always result in long-term cost savings.
The economic perspective on robotic versus manual surgery is complex, involving initial investment, per-procedure costs, insurance coverage, and long-term outcomes. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is crucial for making informed decisions.
Surgeon Perspectives and Preferences
Surgeons’ preferences for robotic or manual surgery vary widely based on their specialty, experience, and the specific demands of their practice. Understanding these preferences is crucial for appreciating the complexities of modern surgical practice.
Survey of Surgical Specialists
A survey of surgical specialists reveals diverse opinions on the utility of robotic versus manual surgery. While some surgeons appreciate the enhanced precision and minimal invasiveness of robotic surgery, others value the direct tactile feedback and flexibility of traditional methods.
Training Requirements and Adaptation
The training required for robotic surgery is generally more extensive than for manual surgery, involving both theoretical knowledge and hands-on practice. Surgeons must adapt to new interfaces and technologies, which can be challenging but ultimately rewarding.
Career Satisfaction Comparisons
Career satisfaction among surgeons can be influenced by their choice between robotic and manual surgery. Factors such as the complexity of cases, the success rate of procedures, and the ergonomic benefits of robotic systems can all impact a surgeon’s job satisfaction.
Specialty-Specific Preferences
Different surgical specialties exhibit unique preferences for robotic or manual surgery. For instance, urologists and gynecologists often favor robotic surgery for its precision in delicate procedures, while general surgeons may prefer manual techniques for their versatility.
| Surgical Specialty | Preferred Method | Reasons |
| Urology | Robotic | Precision, minimal invasiveness |
| General Surgery | Manual | Versatility, direct tactile feedback |
| Gynecology | Robotic | Precision, reduced recovery time |
Patient Decision-Making Factors
The choice between robotic and manual surgery is a significant one, influenced by various factors that patients must carefully weigh. Understanding these factors is crucial in making an informed decision that aligns with the patient’s health needs and personal preferences.
When to Choose Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery may be the preferred option for certain procedures, particularly those that require high precision and minimal invasiveness. Conditions that benefit from robotic surgery include certain types of urological, gynecological, and cardiac procedures.
- Complex surgeries that require precise dissection and suturing
- Procedures where minimal invasiveness can lead to quicker recovery times
- Cases where the surgeon’s experience and comfort with robotic systems can enhance outcomes
When Manual Surgery May Be Preferable
Manual surgery remains the standard for many procedures, especially where direct tactile feedback is crucial or in situations where the complexity of the case doesn’t necessitate the advanced technology of robotic systems.
- Emergency surgeries where time is of the essence and robotic systems may not be readily available
- Procedures that require direct manual manipulation, such as certain orthopedic or neurosurgical operations
- Cases where cost considerations are a significant factor, and the benefits of robotic surgery do not outweigh the additional costs
Essential Questions to Ask Your Surgeon
Patients should engage in thorough discussions with their surgeons to understand the rationale behind the recommended surgical approach. Key questions to ask include:
| Question | Why It Matters |
| What are the benefits of robotic surgery for my condition? | Understanding the specific advantages of robotic surgery for the patient’s particular condition. |
| Are there any risks or complications associated with robotic surgery? | Identifying potential risks to make an informed decision. |
| How will the choice of surgical technique affect my recovery? | Understanding the impact on recovery time, pain management, and overall outcome. |
Understanding Your Surgical Options
Ultimately, the decision between robotic and manual surgery should be based on a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s health status, the nature of the procedure, and the potential outcomes of each surgical approach.
By carefully considering these factors and discussing them with healthcare providers, patients can make informed decisions that best suit their needs.
Future Innovations in Surgical Technology
Surgical technology is on the cusp of a revolution, driven by innovations in robotic systems, manual surgical tools, and the incorporation of artificial intelligence.
Next-Generation Robotic Systems
The development of next-generation robotic systems is expected to bring about significant advancements in surgical precision and flexibility. These systems will likely feature enhanced visualization capabilities, improved dexterity, and more intuitive control interfaces.
Key Features of Next-Generation Robotic Systems:
- Enhanced visualization with 3D imaging
- Improved robotic arms with increased degrees of freedom
- Advanced haptic feedback systems
- Integration with AI for real-time decision support
Advancements in Manual Surgical Tools
While robotic surgery is advancing, manual surgical tools are also being improved. Innovations include ergonomic design enhancements, materials that reduce tissue trauma, and the development of smart tools that provide real-time feedback to surgeons.
Examples of Advanced Manual Surgical Tools:
- Ergonomically designed handles to reduce surgeon fatigue
- Instruments with integrated sensors for precision
- Materials that minimize adhesion and promote healing
AI and Machine Learning Integration
The integration of AI and machine learning into surgical practices is poised to revolutionize patient care. AI can assist in preoperative planning, provide real-time guidance during surgery, and enhance postoperative care through predictive analytics.
| AI Application | Description | Benefit |
| Preoperative Planning | AI-assisted imaging and simulation | Improved surgical accuracy |
| Intraoperative Guidance | Real-time data analysis and feedback | Enhanced decision-making |
| Postoperative Care | Predictive analytics for patient recovery | Reduced complications |
Augmented Reality in the Operating Room
Augmented reality (AR) is set to transform the operating room by providing surgeons with real-time, interactive data. AR can enhance visualization, guide surgical instruments, and improve patient outcomes.
As these technologies continue to evolve, they are expected to significantly impact the future of surgery, improving both the precision and outcomes of surgical procedures.
Global Adoption and Accessibility
The availability of robotic surgery varies significantly across different regions and countries. This disparity is influenced by factors such as the level of healthcare infrastructure, economic conditions, and the availability of trained professionals.
Robotic Surgery Availability Worldwide
Robotic surgery has gained significant traction in developed countries, with many hospitals and surgical centers adopting this technology. However, its availability remains limited in many parts of the world, particularly in low-income and resource-constrained settings.
A study on the global distribution of robotic surgery systems revealed that the majority are installed in North America and Europe, with a growing presence in Asia and Latin America. Despite this progress, there are still significant disparities in access to robotic surgery within and between countries.
Training Infrastructure Challenges
One of the major challenges in the global adoption of robotic surgery is the development of adequate training infrastructure. Surgeons and surgical teams require specialized training to effectively use robotic systems, but opportunities for such training are not uniformly available worldwide.
To address this challenge, many organizations and companies are developing training programs and resources. These include simulation-based training, hands-on workshops, and online educational materials. However, more needs to be done to ensure that all surgeons who wish to learn robotic surgery have access to high-quality training.
Bridging the Technology Gap
Bridging the technology gap is crucial for ensuring equitable access to robotic surgery. This involves not only making robotic systems more widely available but also ensuring that they are integrated into healthcare systems in a way that is sustainable and beneficial to patients.
| Region | Robotic Surgery Availability | Training Infrastructure |
| North America | High | Well-established |
| Europe | Moderate to High | Developing |
| Asia | Growing | Emerging |
| Latin America | Limited | Limited |
| Africa | Very Limited | Minimal |
Ethical Considerations in Surgical Access
The global adoption of robotic surgery raises important ethical considerations, particularly regarding equitable access to this technology. Ensuring that the benefits of robotic surgery are available to all who need them, regardless of their geographical location or economic status, is a critical challenge.
Addressing these ethical considerations will require a multifaceted approach that includes policy changes, investment in healthcare infrastructure, and efforts to make robotic surgery more affordable and accessible. By working together, it is possible to ensure that the advantages of robotic surgery are available to patients worldwide.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Surgical Choice
Choosing between robotic and manual surgery is a critical decision that depends on various factors, including the type of procedure, individual patient needs, and the surgeon’s expertise. Throughout this article, we have explored the differences between robotic-assisted surgery and traditional manual techniques, highlighting their respective benefits and limitations.
When considering robotic vs manual surgery, it’s essential to weigh the advantages of enhanced precision and minimally invasive capabilities against the benefits of direct tactile feedback and cost-effectiveness. By understanding the key distinctions between these surgical approaches, patients can engage in informed surgical decision-making with their healthcare providers.
Ultimately, making an informed surgical choice requires careful consideration of individual circumstances, medical needs, and the latest technological advancements in surgical care. By staying informed and discussing options with a qualified surgeon, patients can make the best decision for their specific situation.
FAQ
What is the main difference between robotic and manual surgery?
Robotic surgery utilizes a robotic system controlled by a surgeon to perform procedures, whereas manual surgery is performed directly by a surgeon’s hands using traditional instruments.
How does robotic surgery enhance precision and accuracy?
Robotic surgery enhances precision and accuracy through its advanced technological capabilities, including high-definition visualization, precise instrumentation, and the elimination of hand tremors.
What are the benefits of manual surgery?
Manual surgery provides direct tactile feedback, is free from technical malfunctions associated with robotic systems, often has lower procedural costs, and offers versatility across various surgical conditions.
Are there differences in recovery timelines between robotic and manual surgery?
Yes, recovery timelines can differ. Robotic surgery, being minimally invasive, often results in shorter recovery times compared to traditional manual surgery, which may involve larger incisions.
How do robotic and manual surgeries compare in terms of pain management?
Robotic surgery typically results in less tissue trauma and smaller incisions, potentially leading to reduced postoperative pain compared to manual surgery.
What are the economic implications of choosing robotic over manual surgery?
Robotic surgery involves higher initial investment and maintenance costs, but per-procedure expenses can vary. Insurance coverage and long-term economic considerations also play a role in the overall cost.
Can robotic surgery be used for all types of surgical procedures?
While robotic surgery is versatile and used in various specialties, including urology, gynecology, cardiac, and thoracic surgery, not all procedures are suitable for robotic surgery. The choice depends on the specific condition, patient factors, and surgeon expertise.
How do surgeons decide between robotic and manual surgery?
Surgeons consider factors such as the patient’s condition, the complexity of the procedure, their own training and experience with robotic or manual techniques, and the potential benefits and risks associated with each approach.
What should patients consider when deciding between robotic and manual surgery?
Patients should consider their individual needs, the nature of their condition, the potential benefits and risks of each surgical approach, and discuss their options thoroughly with their surgeon to make an informed decision.
Are there any advancements in robotic surgery technology?
Yes, next-generation robotic systems are being developed with advancements in AI, machine learning, and augmented reality, which are expected to further enhance the precision, safety, and outcomes of robotic surgery.
How is the future of surgical technology shaping up?
The future of surgical technology is moving towards more precise, minimally invasive, and technologically advanced procedures, with ongoing innovations in both robotic and manual surgical techniques, as well as the integration of AI and augmented reality.
References
- Wang, Y., et al. (2023). Systematic review and meta-analysis of economic and clinical outcomes in robotic versus manual total knee arthroplasty. Journal of Arthroplasty, 38(1), 145–157.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37819597/

































