
At LivHospital, we use Fluoro Deoxy Glucose (FDG) for advanced medical imaging. It helps us diagnose and manage serious diseases. FDG is key in oncology, neurology, and cardiology.
We know how important FDG is. Fluorodeoxyglucose (18F) shows how the body’s cells work. It helps us spot problems and plan treatments.
We focus on our patients, giving them the best care. With FDG PET scans, we make sure our patients get the right treatment.
Key Takeaways
- FDG is a critical radiopharmaceutical in PET scanning.
- It’s used to diagnose and manage diseases in oncology, neurology, and cardiology.
- FDG PET scans help visualize metabolic processes in the body.
- Our hospital uses FDG in advanced medical imaging.
- We provide complete care, from diagnosis to treatment.
Understanding Fluoro Deoxy Glucose: The Glucose Analog

Fluoro Deoxy Glucose (FDG) is a key tool in medical imaging. It acts as a glucose analog to detect diseases. As a glucose molecule with fluorine-18, FDG is vital in PET scans. It shows how the body’s cells use energy.
Chemical Structure and Properties
FDG is a glucose-like molecule with fluorine-18. This makes it perfect for studying how cells use glucose. It’s not fully broken down, which helps in tracing glucose use in the body.
The 18F-FDG structure is close to glucose. This lets it enter cells like glucose does. Inside, it’s turned into FDG-6-phosphate but can’t be broken down further. This makes it stay in cells, showing where glucose is used most.
How FDG Mimics Glucose Metabolism
FDG is taken up by cells like glucose. The more a cell uses glucose, the more FDG it takes up. This is why FDG PET scans are great for finding and tracking cancer.
FDG’s ability to mimic glucose use is key for medical imaging. With 18F-FDG in PET scans, doctors can see how active tissues are. This helps in diagnosing and tracking diseases like cancer and neurological disorders.
The Role of Fluorine-18 in Imaging
The fluorine-18 in FDG is what makes imaging possible. When it decays, it releases positrons that create gamma rays. These rays are what PET scanners use to make detailed images.
The use of 18F-FDG in PET scans has changed medicine. It gives doctors a deep look into how tissues work. This helps in diagnosing diseases early and accurately, and in tracking treatment success.
The Science Behind FDG PET Scanning Technology
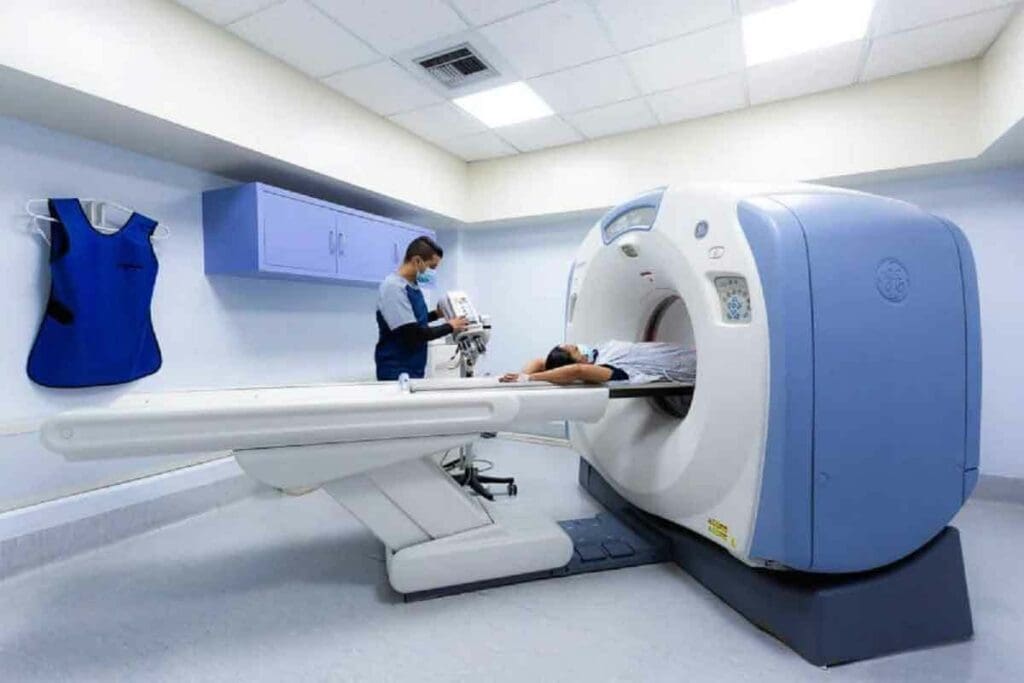
FDG PET scanning technology works by finding metabolic activity in the body. This is key for spotting and managing diseases like cancer and neurological issues.
How PET Detects FDG in the Body
PET scans use 18F-FDG, a special radioactive sugar, to see how cells work. When 18F-FDG is given to the body, it goes to cells that use a lot of sugar. This includes cancer cells. The PET scanner then spots the radioactive signals, showing where the activity is.
The Production Process of 18F-FDG
Making 18F-FDG is a detailed process. It begins with creating fluorine-18 in a cyclotron. This isotope is then linked to glucose to make 18F-FDG. The whole process is carefully watched to make sure it’s safe and works well.
| Step | Description |
| 1. Cyclotron Production | Fluorine-18 is produced in a cyclotron. |
| 2. Synthesis | Fluorine-18 is attached to a glucose molecule. |
| 3. Quality Control | The final product is tested for purity and sterility. |
Why Metabolic Imaging Matters
Metabolic imaging with FDG PET shows how tissues are working. This info is vital for finding diseases, checking if treatments are working, and tracking how diseases change. FDG PET scans help doctors make better choices for their patients.
In summary, the science of FDG PET scanning is both interesting and complex. By knowing how PET finds FDG, how 18F-FDG is made, and why metabolic imaging is important, we see how FDG PET is a key part of today’s medicine.
The Complete FDG PET Scan Procedure
Knowing what to expect during an FDG PET scan can make you feel less anxious. It’s important to understand the process to make your experience better. We’re here to walk you through every step of the FDG PET scan procedure.
Patient Preparation Requirements
Before your FDG PET scan, there are some steps you need to take. These steps help ensure accurate results and a smooth process. Here’s what you need to do:
- Fasting: You’ll need to fast for 4-6 hours before the scan. This helps keep your glucose levels stable.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water is encouraged. It helps keep you hydrated before the scan.
- Avoid Strenuous Exercise: Try not to do any strenuous exercise for 24 hours before. This prevents muscles from taking up too much glucose.
- Medication and Diabetes Management: Tell your healthcare provider about any medications you’re taking. This includes if you have diabetes. Proper management of diabetes is key to controlling your glucose levels.
The Injection and Uptake Period
When you arrive at the imaging facility, a small amount of Fluoro Deoxy Glucose (FDG) will be injected into your vein. This is usually done in your arm. The FDG is absorbed by cells in your body, with active areas like cancers taking up more.
After the injection, you’ll need to wait for about 60 minutes. This allows the FDG to spread throughout your body. Try to stay as quiet and motionless as possible during this time to avoid muscle uptake.
The Scanning Process and Duration
The scanning itself takes between 30 to 60 minutes. You’ll lie on a table that slides into the PET scanner. The scanner will then detect the FDG in your cells, creating detailed images of your body’s metabolic activity.
It’s important to stay as motionless as possible during the scan. This ensures the images are clear and accurate. Our team will be there to support you and answer any questions you might have.
By following these steps, you can help make your FDG PET scan successful. This will give your healthcare team the information they need to make accurate diagnoses.
Oncology Applications: How FDG Revolutionized Cancer Detection
FDG has changed how we see and treat cancer. We use 18F-FDG PET scans a lot in oncology. They help us find, stage, and check how well treatments work in different cancers.
These scans give us metabolic info that goes with the body images from other scans. This gives us a full picture of cancer.
Increased FDG Uptake in Cancer Cells
Cancer cells take up more FDG because they use a lot of glucose. This is called the Warburg effect. So, cancer cells show up more on PET scans than normal cells.
Cancer Types Most Effectively Detected
FDG PET scans are great for finding and managing many cancers. These include:
- Lymphoma
- Lung cancer
- Colorectal cancer
- Melanoma
- Head and neck cancers
These cancers usually take up a lot of FDG. This makes FDG PET scans key for diagnosis and planning.
Staging and Treatment Planning with FDG
FDG PET scans are key for cancer staging. They show how far the disease has spread. This info is important for planning treatment.
It helps decide if surgery, chemo, radiation, or a mix is best.
Neurological Disorders Diagnosed with Fluoro Deoxy Glucose
Fluoro Deoxy Glucose (FDG) is key in neurology for diagnosing and managing neurological disorders. We use 18F-FDG PET scans to understand brain metabolism. This helps us diagnose and treat complex brain conditions better.
Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia Patterns
FDG PET is vital in diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias. FDG PET scans show glucose hypometabolism patterns in the brain, which are signs of Alzheimer’s. These patterns often involve reduced FDG uptake in the temporal and parietal cortices.
Using FDG PET for Alzheimer’s diagnosis has many benefits. It allows for early detection of metabolic changes and differentiates Alzheimer’s from other dementias. It also helps monitor disease progression and treatment response.
- Early detection of metabolic changes before significant neuronal loss occurs
- Differential diagnosis between Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia
- Monitoring disease progression and response to treatment
Epilepsy Focus Localization
FDG PET is essential in evaluating epilepsy, helping to find seizure foci in patients with refractory epilepsy. During the interictal period, brain areas involved in seizures show reduced glucose metabolism. This appears as hypometabolic regions on FDG PET scans.
The information from FDG PET scans is vital for:
- Identifying possible epileptogenic zones
- Guiding surgical planning for epilepsy treatment
- Correlating with other diagnostic modalities like EEG and MRI
Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders
In Parkinson’s disease and other movement disorders, FDG PET aids in differential diagnosis and assessing disease severity. While Parkinson’s is mainly diagnosed clinically, FDG PET offers insights into brain metabolism patterns linked to the disease.
| Movement Disorder | Characteristic FDG PET Pattern | Clinical Utility |
| Parkinson’s Disease | Increased metabolism in putamen and globus pallidus | Differential diagnosis, disease severity assessment |
| Multiple System Atrophy | Hypometabolism in putamen and cerebellum | Differential diagnosis from Parkinson’s disease |
| Progressive Supranuclear Palsy | Hypometabolism in midbrain and frontal cortex | Differential diagnosis, assessing disease extent |
FDG PET scans provide insights into metabolic patterns of various neurological disorders. They are essential in neurology, improving our ability to diagnose, manage, and study complex brain diseases.
Cardiovascular Applications of Fludeoxyglucose F 18
Fluoro Deoxy Glucose (FDG) is key in diagnosing and treating heart diseases. The use of 18F-FDG PET scans in cardiology has greatly helped us understand heart conditions. It has also improved how we care for patients.
Myocardial Viability Assessment
FDG PET is vital in checking if heart muscle is alive or scarred. FDG uptake shows if tissue is alive. This helps doctors choose the best treatment for heart disease or after a heart attack.
Doctors can see if a patient needs procedures like CABG or PCI. This helps in making the best treatment plans and improving patient results.
Detecting Cardiac Inflammation
FDG PET scans are also great for finding heart inflammation. Increased FDG uptake means inflammation. This helps in early diagnosis and treatment of conditions like myocarditis or cardiac sarcoidosis.
This ability to spot inflammation is very important. It lets doctors start the right treatments and check if they work.
Vascular Inflammation Imaging
Vascular inflammation is a big part of atherosclerosis, or plaque buildup in arteries. FDG PET imaging finds vascular inflammation. This helps understand how severe atherosclerosis is.
By finding inflammation, doctors can spot high-risk patients. They can then suggest lifestyle changes or medicines. This could lower the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Treatment Response Monitoring: The FDG Advantage
Monitoring how well treatments work is key in fighting cancer. 18F-FDG PET scans have changed this field. They show how cancer cells use glucose, helping us see if treatments are effective.
Measuring Therapy Effectiveness in Cancer
FDG PET scans are great for checking if cancer treatments are working. The change in metabolic activity as measured by FDG uptake tells us a lot. It shows if the treatment is effective.
For example, if FDG uptake goes down after starting treatment, it’s a good sign. But if it stays the same or goes up, it might mean the treatment isn’t working well.
Optimal Timing for Follow-up Scans
When to do follow-up FDG PET scans is very important. Scans are usually done after a few cycles of chemotherapy or at the midpoint of treatment. This helps us see how the treatment is doing at first.
| Treatment Type | Typical Timing for Follow-up FDG PET Scan | Purpose |
| Chemotherapy | After 2-3 cycles | Assess initial response to treatment |
| Radiation Therapy | 6-8 weeks post-treatment | Evaluate treatment outcome |
| Targeted Therapy | Varies; often at 8-12 weeks | Monitor response and adjust treatment plan |
Interpreting Changes in Metabolic Activity
Understanding changes in metabolic activity from FDG PET scans needs skill. A significant reduction in FDG uptake usually means the treatment is working well. But stable or increased uptake might mean we need to change the treatment plan.
By using FDG PET scans, doctors can make better choices about treatment. This helps improve how well patients do.
Safety Profile and Risks of F 18 FDG PET Scans
The safety of FDG PET scans is a complex topic. It includes radiation exposure, things you shouldn’t do, and how to take care of patients. Understanding these aspects is key to knowing how safe and effective F 18 FDG PET scans are.
Radiation Exposure Considerations
F 18 FDG PET scans use a small amount of radiation because of Fluorine-18. The dose is usually around 7-10 mSv. This is similar to what you get from other imaging tests like CT scans.
Radiation Exposure Comparison
| Imaging Procedure | Typical Effective Dose (mSv) |
| FDG PET Scan | 7-10 |
| CT Scan (Abdomen and Pelvis) | 10-20 |
| Chest X-ray | 0.1 |
Contraindications and Precautions
FDG PET scans are mostly safe, but there are some things to watch out for. If you’re pregnant, it’s a big no-go unless it’s really needed. Women who are breastfeeding should stop for a bit after the scan.
Precautions for FDG PET Scans
- Patients with diabetes need special management (discussed in the next section)
- Recent chemotherapy or radiation therapy may affect results
- Patients should avoid strenuous exercise before the scan
Managing Diabetic Patients
Diabetic patients need extra care with FDG PET scans. High blood sugar can mess up the scan by making tumors harder to see. So, it’s important to keep blood sugar in check before the scan.
Guidelines for Diabetic Patients
| Parameter | Guideline |
| Blood Glucose Level | Less than 200 mg/dL (preferably) |
| Insulin Administration | Avoid short-acting insulin 4-6 hours before scan |
| Long-acting Insulin | Adjust as per patient’s usual regimen, but consider the timing |
Limitations and Challenges in FDG PET Imaging
FDG PET is a powerful tool for diagnosing diseases. Yet, it has its own set of challenges. It’s important to know these to use it effectively.
False Positives from Inflammatory Conditions
FDG PET can sometimes show false positives. This happens when inflammation increases glucose uptake, like in cancer. This can make it hard to read the scans, making diagnosis tricky.
Conditions like sarcoidosis or post-surgery inflammation can cause this. It’s key to look at the whole picture and use other imaging too. This helps get a clearer diagnosis.
Normal Physiological Uptake Patterns
Knowing how FDG PET works in normal tissues is critical. Different parts of the body take up glucose at different rates. This can sometimes look like disease.
The brain, heart, liver, and muscles all take up glucose in their own ways. Knowing this helps doctors tell real disease from normal activity.
Technical and Interpretive Challenges
There are technical and interpretive hurdles in FDG PET imaging. Things like how the patient is prepared and when the scan is done can affect the results.
| Challenge | Description | Impact on FDG PET |
| Patient Preparation | Inadequate fasting or high blood glucose levels | Reduced image quality and diagnostic accuracy |
| Scan Timing | Variability in uptake period | Affects comparability of scans and diagnostic reliability |
| Technological Factors | Scanner resolution and sensitivity | Influences detection of small lesions and accuracy of SUV measurements |
Reading FDG PET scans also needs skill. Small changes in uptake can mean a lot for treatment. Keeping up with training and guidelines is important.
In summary, FDG PET is a valuable tool but has its limits. Knowing these helps us use it better. This leads to better care for patients.
Advanced Applications: Beyond Standard FDG Imaging
FDG PET imaging is now used in new ways to improve diagnosis and care. We’re seeing more techniques like dual-time-point imaging and combining it with CT and MRI. These methods help doctors get better information for patients.
Dual-Time-Point Imaging
Dual-time-point imaging takes PET scans at two times after FDG injection. It helps spot cancer better, even when the first scan is unclear. This way, doctors can tell if something is cancer or not.
Combination with CT and MRI (PET/CT and PET/MRI)
Using FDG PET with CT and MRI has changed how we diagnose. PET/CT shows where tumors are and how they’re growing. PET/MRI gives even more detail, which is great for brain and some cancer cases.
Quantitative Analysis Techniques
Quantitative analysis measures how much FDG is in tissues. This tells doctors about tumor activity. New methods like texture analysis and machine learning are making FDG PET even better.
These new uses of FDG PET are helping doctors make better choices for patients. As technology gets better, we’ll see even more ways to use FDG PET.
The Future of Fluoro Deoxy Glucose in Precision Medicine
FDG is playing a bigger role in precision medicine, with new uses and tech coming up. As medical imaging gets better, FDG PET scans are leading the way. They give us a peek into metabolic processes we couldn’t see before.
Emerging Clinical Applications
FDG PET is being looked at for new uses, like checking inflammatory diseases and neurological disorders. For example, it might help diagnose and track conditions like sarcoidosis and vasculitis. These are diseases where inflammation is a big part of the problem.
A recent study found that “FDG PET/CT is a valuable tool for checking disease activity and how well treatments work in patients with large vessel vasculitis”
Large vessel vasculitis is a condition where inflammation happens in the blood vessels. FDG PET/CT can help see how much inflammation there is.
| Emerging Application | Description | Potential Benefit |
| Inflammatory Disease Assessment | Using FDG PET to evaluate inflammation in conditions like sarcoidosis and vasculitis. | Improved diagnosis and monitoring of disease activity. |
| Neurological Disorder Diagnosis | Exploring FDG PET for diagnosing and monitoring neurological conditions. | Enhanced understanding of disease progression and treatment response. |
Technological Advancements
New tech is making FDG PET scans better. Better scanners and new image algorithms are giving us clearer images. For more on PET scanning tech, check out RadiologyInfo.org.
Also, combining PET/CT and PET/MRI systems is making FDG PET scans even more useful. This lets doctors pinpoint metabolic activity better and manage patients more effectively.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence
The future of FDG PET is linked to artificial intelligence (AI). AI can make sense of the data from FDG PET scans, making diagnoses more accurate and treatments more tailored. This way, doctors can understand metabolic processes better and make better decisions.
As we go forward, combining FDG PET with AI will lead to big leaps in precision medicine. This will mean better care for patients.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into how Fluoro Deoxy Glucose (FDG) helps in medical imaging. It’s key for spotting and treating many diseases. This tool, 18F-FDG, has changed nuclear medicine, mainly in cancer, brain, and heart studies.
FDG is great for finding cancer, seeing how treatments work, and checking brain and heart health. It shows how active cells are, helping doctors a lot. It’s also good for spotting Alzheimer’s, epilepsy, and heart problems.
In the end, FDG is a big deal for doctors. It helps them decide the best care for patients. As imaging tech gets better, FDG will keep being a key player. It will help make patients’ health better.
FAQ
What is Fluoro Deoxy Glucose (FDG) and how is it used in medical imaging?
Fluoro Deoxy Glucose (FDG) is a glucose-like substance used in PET scans. It helps show how active cells are in the body. This is very useful in finding diseases like cancer, studying the brain, and checking the heart.
How does FDG mimic glucose metabolism in the body?
FDG acts like glucose but isn’t broken down further. This lets it build up in cells that are very active, like cancer cells. This makes it useful for finding these cells.
What is the role of Fluorine-18 in FDG PET scanning?
Fluorine-18 is a radioactive part of FDG. It lets PET scanners see where FDG is in the body. This gives clear images of where cells are most active.
How is 18F-FDG produced?
18F-FDG is made by hitting oxygen-18 with protons. This creates Fluorine-18. Then, it’s added to a glucose molecule.
What are the applications of FDG in oncology?
In oncology, FDG helps find and check how far cancer has spread. It’s used for cancers like lymphoma, lung cancer, and melanoma. It also helps see how well treatments are working.
How is FDG used in neurology?
Neurology uses FDG to spot and track diseases like Alzheimer’s. It also helps find where seizures start in people with epilepsy.
What are the cardiovascular applications of FDG?
In cardiology, FDG checks if heart muscle is alive. It also finds heart inflammation and looks at blood vessel inflammation.
Is FDG PET scanning safe?
FDG PET scans are mostly safe. But, they do expose you to a little radiation. People with diabetes need to be careful.
What are the limitations and challenges of FDG PET imaging?
FDG PET scans can sometimes show false positives. This can happen with inflammation or normal cell activity. There are also technical and reading challenges.
How is FDG used to monitor treatment response?
FDG tracks how well treatments are working. If cells use less FDG, it means the treatment is effective.
What are the emerging clinical applications of FDG?
New uses for FDG include precision medicine and combining with other scans. It’s also being used with artificial intelligence.
What is dual-time-point imaging with FDG?
Dual-time-point imaging takes scans at two times after FDG is given. This helps make diagnoses more accurate and understand what’s happening in the body.
How is FDG PET imaging combined with other modalities like CT and MRI?
FDG PET scans can be used with CT and MRI. This gives more information and helps doctors make better diagnoses. It’s seen in PET/CT and PET/MRI scans.
Reference
- RadiologyInfo.org, 2025, PET/CT – Positron Emission Tomography.
Comprehensive patient-friendly info on PET procedures and FDG use.










