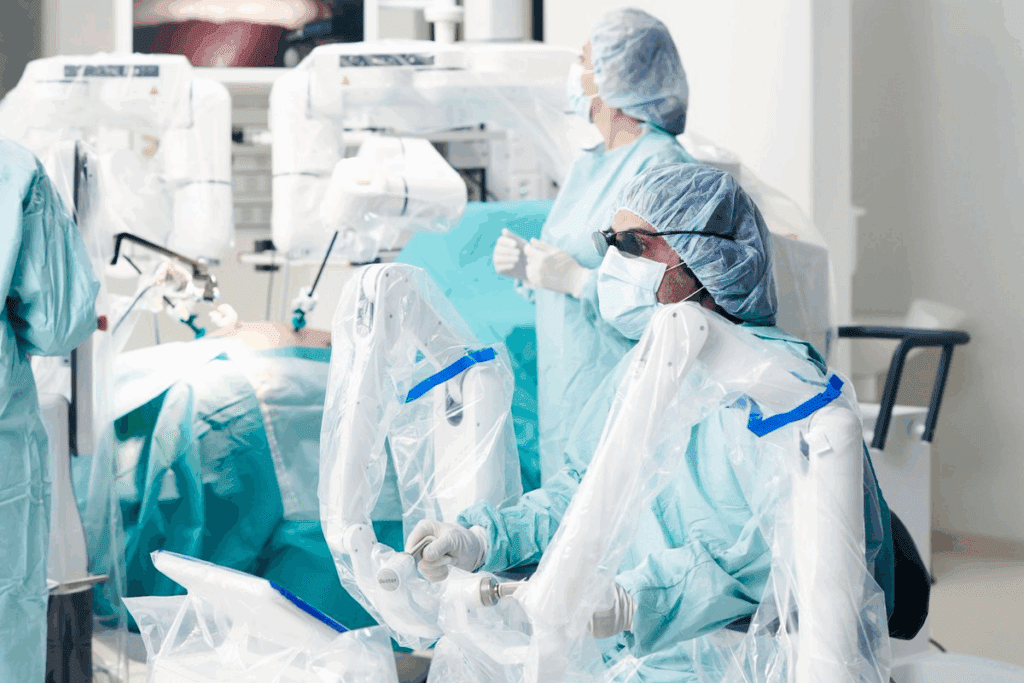
In 2020, over 877,000 robotic surgeries were performed, marking a major shift in how complex operations are carried out. Is robotic surgery becoming the new standard in modern medicine? Its growing use suggests a transformation in surgical precision and patient outcomes.
Robotic-assisted surgery has revolutionized the medical world, allowing surgeons to perform procedures with enhanced precision, flexibility, and control. However, with such rapid advancement, it’s essential to ask: Is robotic surgery truly safe and effective for all patients?
The FDA plays a crucial role in ensuring safety. The clearance process for robotic surgery systems is extremely strict, involving extensive testing and evaluation to confirm that these systems meet the highest performance and safety standards.
Key Takeaways
- The FDA is key in making sure robotic surgery systems are safe and work well.
- Robotic-assisted surgery gives surgeons better precision, flexibility, and control.
- The FDA clearance process is very strict, with lots of testing.
- Robotic surgery is getting more popular, with over 877,000 procedures in 2020.
- FDA approval is very important for robotic surgery systems to be released to the market.
The Evolution of Robotic Surgery in Modern Medicine
Robotic surgery started with new technology and has become key in today’s surgery. It has changed how we treat many health issues, making treatments less invasive.
From Concept to Clinical Reality
The journey of robotic surgery from idea to use in hospitals was long. At first, people doubted robots in surgery. But as tech got better, robots became a part of surgeries.
Key technological advancements included better robotic arms, improved views for surgeons, and controls that made surgeries easier. These changes let surgeons do complex surgeries with more precision and less harm.
Key Milestones in Surgical Robotics Development
Robotic surgery has seen many important moments. Knowing these helps us see how it became a big part of medicine today.
| Year | Milestone | Description |
| 1990s | Initial Development | First robotic surgical systems were developed, marking the beginning of robotic surgery. |
| 2000 | FDA Clearance | The first robotic surgical system received FDA clearance, paving the way for clinical use. |
| 2010s | Technological Advancements | Significant improvements in robotic technology, including enhanced visualization and robotic arms. |
The evolution of robotic surgery keeps going. There’s always new research and tech to make it better and use it for more things.
Understanding FDA Approval for Medical Devices
It’s important to know how the FDA approves medical devices. This includes the tough tests and checks that robotic surgical systems go through. The FDA makes sure these devices are safe and work well.
The FDA’s process balances new ideas with keeping patients safe. They sort devices by risk and use, which decides how closely they’re watched.
The FDA Classification System for Medical Devices
The FDA puts medical devices into three groups based on risk. Class I devices are the least risky and have the least rules. Class II devices are a bit riskier and need more checks. Class III devices, like many robotic systems, are the riskiest and face the toughest rules, needing approval before they can be used.
Regulatory Pathways for Surgical Technologies
Surgical techs, like robotic systems, can get FDA approval in different ways. The usual way is the 510(k) pre-market notification, which shows a device is as good as one already on the market. For new tech, the Pre-Market Approval (PMA) is needed, which requires more detailed clinical data.
Knowing these paths helps us see how robotic systems get the green light for use in hospitals. The FDA’s careful checks make sure these devices are safe and work well before they’re used on patients.
Is Robotic Surgery FDA Approved? Current Status and Regulations
To know if robotic surgery is FDA approved, we need to look at the rules for medical devices. The terms “FDA approval” and “FDA clearance” are often mixed up. But they mean different things in the world of medical devices.
Definition of FDA Approval vs. Clearance
FDA approval and clearance are two different steps for medical devices. Approval is needed for high-risk devices (Class III). It means a deep review of the device’s safety and how well it works.
Clearance is for lower-risk devices (Class II and some Class I). It means the device is similar to one that’s already approved.
Robotic surgical systems usually need FDA clearance. They go through the 510(k) pre-market notification process. This checks if the new device is similar to one that’s already on the market.
Regulatory Framework for Robotic Surgical Systems
The rules for robotic surgical systems include several important parts:
- Classification: These systems are usually Class II devices, needing a 510(k) clearance.
- Pre-Market Notification: Makers must send in a 510(k) application. It shows the device is similar to one already approved.
- Clinical Data: Sometimes, clinical data is needed to prove the device is safe and works well.
- Post-Market Surveillance: Makers must watch for and report any bad events linked to their devices.
| Regulatory Pathway | Description | Device Classification |
| 510(k) Clearance | Pre-market notification for substantial equivalence | Class II |
| PMA Approval | Rigorous review for safety and effectiveness | Class III |
The rules today let robotic surgical systems get cleared for market through the 510(k) process. It’s key to know the difference between FDA approval and clearance. As the field grows, keeping up with the rules is important for doctors and patients.
The Da Vinci Surgical System: FDA Clearance History
The Da Vinci Surgical System got its first FDA approval in 2000. It has led to big steps in robotic surgery. Intuitive Surgical made it, and it’s key in robotic-assisted surgery today.
Initial FDA Clearance in 2000 and Original Applications
The Da Vinci System got its first FDA okay in 2000 for laparoscopic surgical procedures. This was a big deal for robotic surgery. It started with general surgery and urology.
Its new tech meant better precision, flexibility, and control in surgery. This was a big step forward.
The first approval let doctors use it for cholecystectomy and nephrectomy. This made robotic surgery a real option instead of traditional surgery.
Subsequent Clearances and Expanded Surgical Indications
After the first approval, the Da Vinci System got more FDA okay for more surgeries. Now, it’s used in gynecological, thoracic, and cardiac surgeries.
Studies showed it’s safe and works well for many surgeries. So, it’s used in many hospitals in the U.S.
The Da Vinci System keeps getting better and more approved for surgeries. It’s leading the way in robotic surgery.
Other FDA-Cleared Robotic Surgical Platforms
Several robotic surgical platforms have received FDA clearance, aside from the Da Vinci Surgical System. These options are available for surgeons and patients.
Intuitive Surgical’s Additional Systems
Intuitive Surgical, the creators of the Da Vinci System, have developed more robotic platforms. These include the Ion Endoluminal System and the SP Surgical System.
The Ion Endoluminal System is for minimally invasive lung cancer procedures. It helps surgeons navigate the lungs precisely for diagnosis and treatment.
The SP Surgical System is a big step forward in robotic surgery. It uses a single port, reducing the number of incisions needed for complex surgeries.
Medtronic’s Hugo and Mazor X Platforms
Medtronic has also made significant contributions to robotic surgery. The Hugo Robotic-Assisted Surgery (RAS) system is for complex procedures, providing flexibility and precision.
The Mazor X system is designed for spinal surgery. It offers advanced navigation and tools, improving the accuracy of spinal procedures.
Stryker, Smith & Nephew, and Other Approved Systems
Stryker and Smith & Nephew are also major players in robotic surgery. They have FDA-cleared systems for various surgical specialties.
| Manufacturer | System Name | Surgical Specialty |
| Intuitive Surgical | Ion Endoluminal System | Pulmonary |
| Intuitive Surgical | SP Surgical System | General Surgery |
| Medtronic | Hugo RAS | General, Gynecological, Urological |
| Medtronic | Mazor X | Spinal Surgery |
| Stryker | Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery | Orthopedic |
| Smith & Nephew | Corin T3 | Orthopedic |
The availability of these FDA-cleared robotic platforms is a big step forward in surgery. It offers patients and surgeons many options for different needs and procedures.
The FDA Approval Process for Robotic Surgical Systems
It’s important to know how the FDA approves robotic surgical systems. They use two main ways: the 510(k) clearance for devices similar to others, and the Pre-Market Approval (PMA) for new or risky devices.
Pre-Market Notification (510(k)) Requirements and Examples
The 510(k) clearance lets manufacturers show their device is similar to one already approved. They must send a 510(k) notification with details about the device and how it compares to the predicate device.
Key requirements for 510(k) clearance include:
- Demonstrating substantial equivalence to a predicate device
- Providing detailed device descriptions and labeling
- Submitting performance data to support substantial equivalence
Devices like the da Vinci Surgical System from Intuitive Surgical have gotten 510(k) clearance. They’re used for surgeries in urology, gynecology, and general surgery.
Pre-Market Approval (PMA) Pathway for Novel Systems
The PMA pathway is for new or high-risk devices that don’t match existing ones. It requires a lot of scientific evidence, including clinical trials, to prove the device is safe and works well.
The PMA pathway involves several key steps:
- Pre-submission interactions with the FDA to discuss the proposed PMA application
- Submission of the PMA application, including detailed device information and clinical data
- FDA review of the PMA application, which may include an advisory committee meeting
The FDA says the PMA process is the strictest for device approval. It’s key to make sure new robotic surgical systems are safe and effective before they’re used on patients.
In summary, the FDA checks the safety and effectiveness of robotic surgical systems through the 510(k) or PMA pathways. Knowing these steps is vital for manufacturers, surgeons, and patients.
FDA-Approved Robotic Surgery Procedures and Applications
The FDA has cleared many robotic surgery procedures for various medical uses. This has changed the way we do surgery today. Robotic surgery is now approved for many procedures in fields like urology, gynecology, and general surgery.
Approved Urological and Gynecological Procedures
Robotic surgery is key in urology and gynecology because it’s precise and less invasive. The FDA has okayed robotic systems for:
- Prostatectomies
- Nephrectomies
- Hysterectomies
- Myomectomies
- Sacrocolpopexy
These surgeries benefit from the robotic system’s better dexterity and view. This leads to better results for patients.
Approved General, Thoracic, and Cardiac Applications
Robotic surgery is also approved for general, thoracic, and cardiac procedures. These include:
- Cholecystectomies
- Hernia repairs
- Lobectomies
- Mitral valve repairs
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
Robotic systems in these areas promise to cut down recovery times and boost surgical accuracy.
| Surgical Specialty | Approved Procedures | Benefits |
| Urology | Prostatectomies, Nephrectomies | Enhanced precision, Less blood loss |
| Gynecology | Hysterectomies, Myomectomies | Minimal scarring, Faster recovery |
| General Surgery | Cholecystectomies, Hernia repairs | Reduced trauma, Shorter hospital stays |
| Thoracic Surgery | Lobectomies | Improved visualization, Less post-operative pain |
| Cardiac Surgery | Mitral valve repairs, CABG | Precision in complex procedures, Reduced risk of complications |
The table above shows FDA-approved robotic surgery procedures across different specialties. It highlights their benefits. As robotic technology advances, we’ll see more procedures and applications approved.
Safety Monitoring and Post-Market Surveillance of Surgical Robots
Keeping robotic surgical systems safe is a big deal for the FDA and makers. After they get the green light, it’s important to keep watching them. This helps find and fix any problems that might come up.
FDA’s MAUDE Database and Adverse Event Reporting
The FDA’s MAUDE (Manufacturer and User Facility Device Experience) database is key for tracking bad events with medical devices. It helps the FDA see how devices are doing, spot safety issues, and act if needed.
It’s a must for makers to report bad events. Doctors and hospitals should also tell the FDA about any problems. The MAUDE database has info on failures, injuries, and deaths. It shows how safe and good robotic surgery systems are.
Manufacturer Reporting Requirements and Recalls
Manufacturer reporting requirements are vital for watching devices after they’re sold. Makers must tell the FDA about failures, serious harm, and deaths. This helps the FDA find and fix safety problems, like by recalling devices.
If a robotic system is found to be bad or risky, makers might recall it. The FDA helps make sure recalls work well. This means fixing or removing the bad devices from use.
With strong safety checks and watching devices after they’re sold, the FDA and makers can keep robotic surgery safe and working well.
Risks and Complications of FDA-Approved Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery is becoming more common. It’s important to know its risks and complications for safety and making informed choices. FDA-approved systems have been tested well, but they can have risks.
Documented Adverse Events and Technical Malfunctions
Robotic surgery systems, like any complex tech, can have problems. Documented adverse events include:
- Injury to surrounding tissues or organs
- Bleeding complications
- Infection
- Conversion to open surgery
- Equipment failure
Technical issues can be software or hardware problems. It’s key for hospitals and surgical teams to have backup plans for these issues.
FDA Safety Communications and Manufacturer Responses
The FDA sends out safety alerts for medical devices, including robotic surgery. These alerts are based on data from the FDA’s MAUDE database. It tracks adverse events and malfunctions.
Manufacturer responses to risks may include:
- Software updates for safety
- Hardware changes for reliability
- Training for surgeons and staff
- Better patient selection
Knowing these risks and how to handle them helps patients and healthcare providers make better choices about robotic surgery.
Benefits and Clinical Outcomes of FDA-Cleared Robotic Procedures
FDA-cleared robotic procedures are becoming more popular. They offer many advantages, like shorter recovery times and better precision. This has changed the way we do surgery.
Evidence-Based Advantages for Patients and Surgeons
Robotic surgery brings many benefits. Patients see less blood loss, smaller cuts, and less pain after surgery. Surgeons get better views, more control, and finer movements.
Research shows robotic surgery means shorter hospital stays and quicker recovery. This is great for complex surgeries where time is key.
Comparative Effectiveness with Traditional Surgical Approaches
Studies compare robotic surgery to traditional methods. They find robotic surgery often has better results. This includes fewer complications and faster recovery for patients.
In surgeries like urology and gynecology, robotic methods have fewer problems and better results. General surgery also sees less harm and death with robotic procedures.
The evidence backs up robotic surgery as a safe and effective choice. It offers many benefits for both patients and surgeons.
Robotic Surgery Training and Certification Requirements
Robotic surgery is growing, and knowing the training and certification needs is key. Surgeons and hospitals must understand this. The complex robotic systems need thorough training to ensure surgeons can use them well.
FDA Recommendations for Surgeon Training and Proficiency
The FDA stresses the need for good training for surgeons using robotic systems. It doesn’t certify surgeons itself but gives training guidelines. These guidelines cover:
- Comprehensive didactic training on the robotic system’s components and operation
- Practical hands-on experience with simulated surgeries or under the guidance of an experienced surgeon
- Observation and participation in actual robotic surgeries
- Ongoing evaluation and feedback on the surgeon’s proficiency
Surgeon training programs aim to make sure surgeons can use the robotic system well. They learn both theory and practical skills.
Hospital Credentialing Processes and Volume Requirements
Hospital credentialing is vital to check if surgeons are ready for robotic surgeries. It includes:
- Reviewing the surgeon’s training and experience with robotic surgical systems
- Evaluating the surgeon’s performance during initial robotic surgeries
- Requiring a minimum number of robotic surgeries per year to maintain privileges
Many hospitals also set volume requirements to keep surgeons skilled. Below is a table showing typical hospital credentialing needs for robotic surgery.
| Credentialing Requirement | Description | Typical Threshold |
| Initial Training | Completion of a robotic surgery training program | Yes/No |
| Proctoring | Observation by an experienced surgeon during initial cases | 3-5 cases |
| Annual Volume | Minimum number of robotic surgeries per year | 20-50 cases |
| Ongoing Evaluation | Regular assessment of surgical outcomes and complications | Ongoing |
By following these training and credentialing rules, hospitals can make sure their surgeons are ready for robotic surgeries. This leads to better care for patients.
Patient Considerations for FDA-Approved Robotic Procedures
Thinking about FDA-approved robotic procedures? There are important things to know. Robotic surgery has many benefits but also unique aspects. Understanding these can help you make a good choice for your care.
Questions to Ask Your Surgeon About Robotic Surgery Options
Talk to your surgeon about robotic surgery. Ask about their experience, the benefits and risks for your case, and what recovery will be like.
- What experience do you have with robotic surgery?
- What are the benefits and risks of robotic surgery for my condition?
- How will I be monitored during and after the procedure?
- What is the expected recovery time, and what kind of post-operative care will I need?
These questions can help you understand your options better. This way, you can decide if robotic surgery is right for you.
Insurance Coverage, Cost Implications, and Accessibility
It’s important to know the financial side of robotic surgery. Insurance coverage can vary. Check with your insurance to see what’s covered.
| Insurance Provider | Coverage for Robotic Surgery | Out-of-Pocket Costs |
| Medicare | Generally covers FDA-approved robotic procedures | Varies based on plan and deductible |
| Private Insurers | Coverage varies by provider and policy | Depends on copay, deductible, and coinsurance |
| Medicaid | Coverage varies by state and program | May have minimal or no out-of-pocket costs |
Also, think about the cost of robotic surgery. There might be extra costs for the technology. The availability of robotic systems and surgeon expertise in your area also matters.
In summary, patients should weigh their options carefully. Discuss with your surgeon and understand the costs. Being informed helps you choose the best for your health.
Conclusion
Robotic surgery has changed the way we do medicine, bringing many benefits to both patients and doctors. We’ve seen how different robotic systems have been approved by the FDA for various surgeries. This shows how important it is to know the rules that guide these new technologies.
Looking into the FDA’s approval process gives us a clear picture of the high standards robotic surgery must meet. Systems like the Da Vinci Surgical System and others from Intuitive Surgical, Medtronic, Stryker, and Smith & Nephew have opened up new possibilities in surgery.
As robotic surgery keeps growing, we must think about what’s next. This includes better training for surgeons, more patient options, and keeping an eye on safety and success. By wrapping up the main points and looking ahead, we can see how robotic surgery will shape healthcare’s future.
FAQ
What is robotic surgery and how does it differ from traditional surgery?
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, is a new way to do surgery. It uses a robotic system to help with the procedure. This method is different from traditional surgery because it uses advanced technology.
This technology allows for better precision, flexibility, and control during surgery.
Is the Da Vinci Surgical System FDA-approved?
The Da Vinci Surgical System, made by Intuitive Surgical, got its first FDA clearance in 2000. It has also gotten clearances for more uses in surgery. Even though “approval” and “clearance” are similar, the Da Vinci System is FDA-cleared.
What are the benefits of robotic surgery compared to traditional surgical approaches?
Robotic surgery has many benefits. It can lead to less recovery time, less blood loss, and better precision. Studies have shown these advantages compared to traditional surgery.
Are there any risks or complications associated with robotic surgery?
Like any surgery, robotic surgery has risks and complications. These can include bad outcomes and technical problems. The FDA watches these through its MAUDE database and issues warnings when needed.
What training is required for surgeons to perform robotic surgery?
The FDA says surgeons need thorough training and certification for robotic surgery. Hospitals also check surgeons’ skills and how often they do robotic surgery. This ensures they are good at it.
How do I know if robotic surgery is right for me?
If you’re thinking about robotic surgery, talk to your surgeon. They can explain the good and bad parts, including costs and insurance. It’s important to ask questions and think if robotic surgery is right for you.
Are there other FDA-cleared robotic surgical systems beside the Da Vinci Surgical System?
Yes, there are other robotic systems cleared by the FDA. Companies like Intuitive Surgical, Medtronic, Stryker, and Smith & Nephew have them. These options are available for surgeons and patients.
What is the difference between FDA clearance and FDA approval?
FDA clearance and approval are often confused, but they mean different things. Clearance means a device is similar to one already on the market. Approval is for new or high-risk devices.
How does the FDA monitor the safety of robotic surgical systems?
The FDA watches the safety of robotic systems after they’re on the market. They use the MAUDE database to track problems. Manufacturers also have to report certain issues and follow FDA rules.
Can robotic surgery be used for various surgical specialties?
Yes, robotic surgery is cleared for many types of surgery. This includes urology, gynecology, general surgery, thoracic surgery, and cardiac surgery.
Reference:
PMC – Levels of autonomy in FDA-cleared surgical robots: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11053143




































