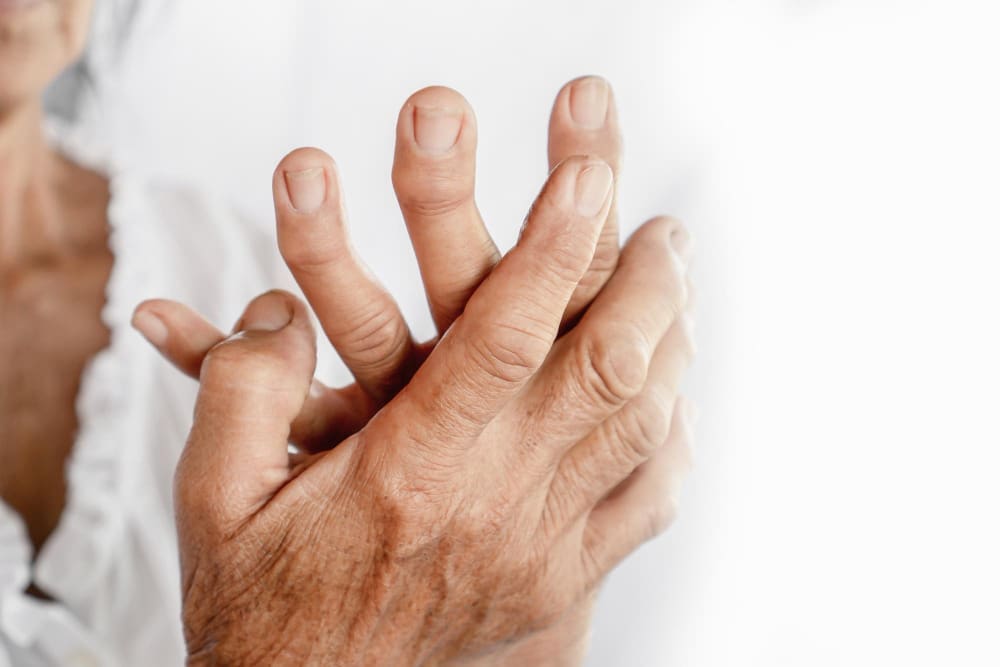

Arthritis is a big problem worldwide, causing chronic pain for millions. At Liv Hospital, we know how important it is to diagnose and treat it right. With over 100 types, knowing the differences is key.
We’ll show you the five main types of arthritis, their special features, and symptoms. New studies show how these conditions affect health globally. This highlights the need for full healthcare services.
Our team works hard to give top-notch healthcare to international patients. By knowing the different arthritis diseases types, we can tailor treatments better.
Key Takeaways
- There are over 100 types of arthritis.
- Five main types of arthritis are commonly diagnosed.
- Understanding symptoms and differences is key for good care.
- Liv Hospital offers complete healthcare services.
- Personalized treatment plans are available for international patients.
The Spectrum of Arthritis Immune Disease
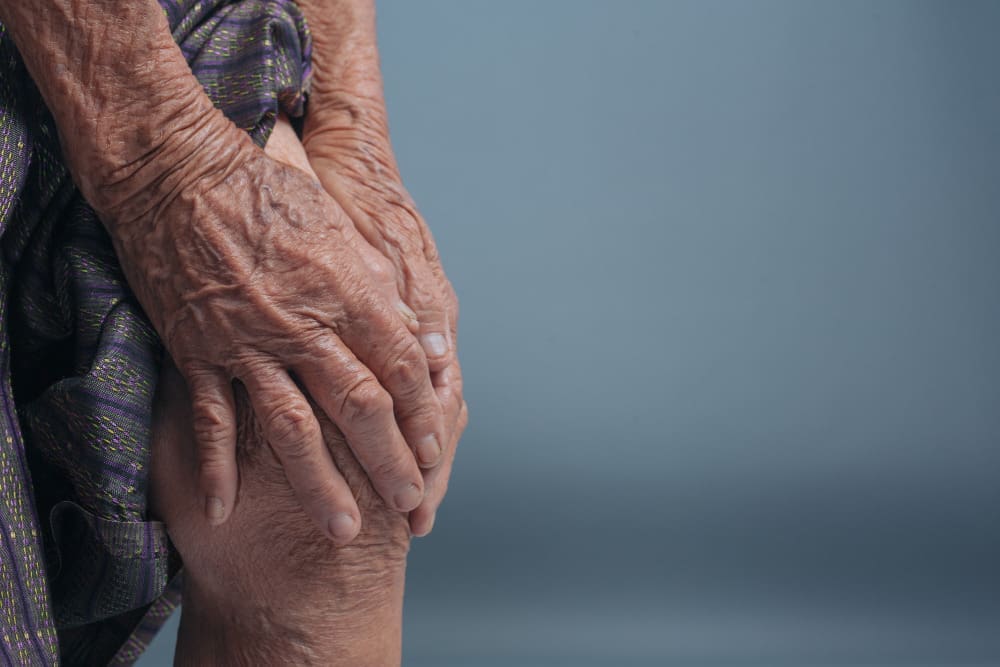

“Arthritis” is a term for over 100 different conditions, many caused by immune system problems. These conditions affect not just the joints but also the tissues around them. This leads to a variety of symptoms and complications.
Over 100 Types of Arthritis
Arthritis includes a wide range of conditions, each with its own set of characteristics and effects on the body. The main categories are inflammatory and non-inflammatory types of arthritis.
Inflammatory arthritis, linked to immune system issues, includes rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. These conditions happen when the immune system attacks healthy tissues. This leads to inflammation and damage to the joints.
Common Mechanisms of Joint Damage
Even though there are many types of arthritis, they share common ways of causing joint damage. In immune-related arthritis, the immune system’s wrong response causes inflammation. This inflammation can damage cartilage, bones, and change the joints in other ways.
The table below shows the main differences and similarities in how joint damage occurs in different types of arthritis:
| Arthritis Type | Primary Mechanism | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | Autoimmune inflammation | Symmetrical joint pain, swelling |
| Psoriatic Arthritis | Immune-mediated inflammation | Joint pain, skin psoriasis |
| Osteoarthritis | Cartilage wear and tear | Joint pain, stiffness |
Knowing these mechanisms is key to creating effective treatments. These treatments aim to address the root causes of joint damage in different arthritis types.
Global Prevalence and Impact of Arthritis
Arthritis is a big health problem worldwide, touching millions of lives. It shows how arthritis affects people, healthcare, and economies. This condition is a major public health issue.
WHO Statistics and Demographics
The World Health Organization says about 18% of adults worldwide have arthritis. This means a lot of people deal with different types of arthritis. Women are more likely to get arthritis than men, and it gets more common with age.
Key demographics affected by arthritis include:
- Older adults, as the condition is more prevalent with increasing age
- Women, who are more likely to develop certain types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis
- Individuals with a family history of arthritis, who may be more susceptible to developing the condition
Economic and Quality of Life Burden
Arthritis has a big economic and quality of life impact. It can cause high healthcare costs, lost work time, and lower quality of life. It’s one of the top causes of disability worldwide, leading to big economic and social costs.
The impact of arthritis on quality of life is wide-ranging, affecting not just the person but also their family and caregivers. It can cause chronic pain, limited movement, and less independence. This makes simple tasks hard. So, it’s key to tackle all types of arthritis to offer full care and support.
How Immune System Dysfunction Leads to Arthritis
To understand how immune system problems cause arthritis, we need to look closely at how joints work and how the immune system responds. The immune system helps keep us safe from germs and harmful substances. But, in arthritis, it starts attacking the wrong targets, causing inflammation and damage to joints.
Normal Joint Physiology
A healthy joint has smooth cartilage and a special membrane that makes fluid to help it move smoothly. The immune system keeps this area safe from attacking itself. But, if this balance is broken, it can start an inflammatory process and damage the joint.
Pathways of Immune-Mediated Inflammation
In autoimmune arthritis, like rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system mistakenly attacks the joint lining. This leads to inflammation and damage. It involves many immune cells and the release of harmful chemicals. For more on treatments like stem cell therapy, check out Liv Hospital’s page on stem cell therapy for.
Genetic and Environmental Triggers
Genetics and the environment both play a part in arthritis. Some people are more likely to get autoimmune arthritis because of their genes. Environmental factors like infections or smoking can also start the disease in people who are at risk.
| Trigger | Description | Impact on Arthritis |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Predisposition | Inherited genetic markers | Increases risk of autoimmune arthritis |
| Environmental Factors | Infections, smoking, etc. | Can trigger disease onset in susceptible individuals |
| Immune System Dysfunction | Failure to maintain tolerance to self-antigens | Leads to autoimmune responses and joint inflammation |
Knowing about these factors helps us see how complex arthritis is. It shows why we need treatments that fix the problem, not just the symptoms.
Osteoarthritis: Degenerative Joint Disease
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis. It happens when cartilage in joints breaks down, causing pain and less mobility. We’ll look at what causes it, who’s at risk, and how cartilage breaks down.
Causes and Risk Factors
Osteoarthritis comes from a mix of genetics and environment. Age is a big risk because joints wear out over time. Other risks include obesity, which adds stress to joints, and previous joint injuries, which can speed up cartilage loss.
Experts and patients say we need better ways to manage arthritis. This is important on World Arthritis Day. You can read more about it here.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Osteoarthritis |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Accumulated wear and tear on joints over time | Increased risk with advancing age |
| Obesity | Additional stress on weight-bearing joints | Accelerates cartilage degradation |
| Previous Joint Injuries | Alters joint mechanics | Leads to accelerated cartilage breakdown |
Cartilage Breakdown Mechanisms
The breakdown of cartilage in osteoarthritis is complex. Enzymatic degradation of cartilage parts is key. Also, abnormal loading of joints can cause more damage.
Characteristic Symptoms and Progression
Osteoarthritis causes joint pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Symptoms get worse over time. If not treated, it can lead to serious disability.
Knowing the causes, risks, and how cartilage breaks down is key. This knowledge helps us find better ways to manage osteoarthritis. It improves life for those with the condition.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Systemic Autoimmune Condition
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a complex disease. It affects the whole body and is hard to diagnose and treat. It causes inflammation and damage to the joints.
Autoantibodies and Immune Dysfunction
RA is marked by the presence of autoantibodies. These include rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs). They play a big role in the disease by causing inflammation.
The body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. This is why these autoantibodies are so harmful.
Key autoantibodies in RA include:
- Rheumatoid Factor (RF)
- Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies (ACPAs)
Symmetrical Joint Involvement Patterns
RA often affects joints in a symmetrical way. This includes the hands, feet, wrists, and knees. This symmetry helps doctors tell RA apart from other arthritis types.
The inflammation from RA can cause pain and swelling. If not treated, it can lead to joint deformity.
Extra-articular Manifestations
RA can also affect other parts of the body. This includes:
- Skin: rheumatoid nodules
- Eyes: dry eyes, scleritis
- Lungs: interstitial lung disease
- Cardiovascular: increased risk of cardiovascular disease
It’s important to know about these extra symptoms. They can greatly affect a person’s quality of life and even their life expectancy.
Managing RA needs a complete approach. We must treat both the joint and extra symptoms. This way, we can improve patients’ lives and well-being.
Psoriatic Arthritis: Skin and Joint Inflammation
Psoriatic arthritis combines skin and joint inflammation. It needs a full treatment plan. We’ll look into this disease, its link to psoriasis, and its unique signs.
Relationship to Psoriasis
Psoriatic arthritis often goes hand in hand with psoriasis. This is a long-term skin issue that causes red, scaly patches. Most people with this arthritis have had psoriasis first. But sometimes, the arthritis starts before the skin problems.
It’s key to know how these two conditions are connected. They share the same inflammation causes. Treating one can help the other.
Five Clinical Subtypes
Psoriatic arthritis comes in five main types, each with its own traits. These types are:
- Distal interphalangeal predominant
- Oligoarticular
- Polyarticular
- Spondylitis
- Arthritis mutilans
Knowing these types helps doctors create the best treatment plan for each patient.
Distinctive Features and Nail Changes
Nail changes are a big sign of psoriatic arthritis. Many patients see pitting, onycholysis, and subungual hyperkeratosis in their nails.
The disease also shows other unique signs. These include dactylitis (swelling of a whole digit) and enthesitis (inflammation where tendons or ligaments meet bone).
| Feature | Description | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Nail Changes | Pitting, onycholysis, subungual hyperkeratosis | 80% |
| Dactylitis | Swelling of an entire digit | 30-50% |
| Enthesitis | Inflammation at tendon/ligament attachment | 40-60% |
Understanding these signs helps doctors diagnose and treat psoriatic arthritis better. This improves patient results.
Gout: Crystalline Arthropathy
Gout is a painful form of arthritis. It happens when uric acid builds up in the blood and forms crystals in the joints. We will look at the causes, symptoms, and treatments for gout. This will give you a full understanding of this condition.
Abnormalities in Uric Acid Metabolism
Gout is caused by problems with uric acid metabolism, leading to too much uric acid in the blood. This can happen because the body makes too much uric acid or the kidneys don’t get rid of it well enough.
Acute Flares vs. Chronic Tophaceous Gout
Gout can show up as acute flares, with sudden and severe joint pain. Or it can be chronic tophaceous gout, where uric acid crystals build up in joints and soft tissues. This leads to long-term inflammation and damage.
Dietary and Lifestyle Connections
Diet and lifestyle are key in managing gout. Eating a diet low in purines, keeping a healthy weight, and drinking plenty of water can help prevent gout flares.
| Characteristics | Acute Flares | Chronic Tophaceous Gout |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Sudden | Gradual |
| Symptoms | Severe pain, redness, swelling | Chronic pain, joint damage |
| Uric Acid Levels | May be normal or elevated | Typically elevated |
We’ve looked at gout, a type of arthritis caused by uric acid problems, and talked about its causes, symptoms, and treatments. To manage gout well, it’s important to understand its different forms and make the right diet and lifestyle changes.
Ankylosing Spondylitis: Axial Inflammation
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic disease that mainly affects the spine. It causes changes in how the spine moves and looks. Understanding this disease involves looking at its genetic roots and how it shows up in people.
HLA-B27 Association and Genetics
Ankylosing spondylitis is linked to the HLA-B27 gene. Many people with this disease have the HLA-B27 gene. But, having this gene doesn’t mean you’ll definitely get the disease. Other genes and factors also matter.
Many genes are involved in ankylosing spondylitis. Scientists are finding more genes that might affect how the disease starts and grows.
Spinal Fusion and Mobility Changes
One key sign of ankylosing spondylitis is the spine fusing together. This fusion makes it harder to move and bend. It can make the spine look like bamboo on X-rays.
- Reduced spinal flexibility
- Chronic back pain
- Potential for spinal deformity
As the disease gets worse, it can make everyday tasks harder because of less mobility.
Extra-spinal Manifestations
Ankylosing spondylitis can also affect other parts of the body. It can cause arthritis in other joints, enthesitis, and uveitis. These extra symptoms can make managing the disease more complex.
- Peripheral arthritis: Joint inflammation beyond the spine
- Enthesitis: Inflammation at the sites of tendon or ligament attachment
- Uveitis: Inflammation of the uveal tract in the eye
It’s important to notice these extra symptoms to give patients the best care.
Comparative Analysis of the 5 Types of Arthritis
It’s important to know the differences between various arthritis types for proper diagnosis and treatment. We’ll look at the five main types of arthritis. We’ll talk about their age of onset, demographics, joint distribution, lab findings, and disease course.
Age of Onset and Demographics
The age and demographics of each arthritis type differ. For example, osteoarthritis mainly affects older adults. On the other hand, rheumatoid arthritis can happen at any age, with women being more likely to get it.
| Type of Arthritis | Typical Age of Onset | Demographic Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Osteoarthritis | 45+ | More common in older adults, slight female predominance |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | 30-60 | Higher prevalence in women, can occur at any age |
| Psoriatic Arthritis | 30-50 | Associated with psoriasis, equal gender distribution |
| Gout | 40-60 (men), post-menopause (women) | More common in men, associated with diet and lifestyle |
| Ankylosing Spondylitis | 20-40 | More common in men, strong genetic association |
Joint Distribution Patterns
The way joints are affected varies among arthritis types. Rheumatoid arthritis often hits the hands and feet equally. Osteoarthritis, on the other hand, usually affects joints that bear weight.
Laboratory Findings
Lab tests are key in diagnosing and differentiating arthritis types. For example, rheumatoid factor is often positive in rheumatoid arthritis. Uric acid levels are high in gout.
Disease Course and Prognosis
The progression and outlook of each arthritis type differ. Knowing these differences helps in managing patient expectations and creating effective treatment plans.
By comparing the different arthritis types, we gain a better understanding of how they affect patients. This knowledge helps healthcare providers offer more tailored and effective care.
Diagnostic Approaches for Different Arthritis Types
Diagnosing different arthritis types requires a detailed strategy. This includes clinical checks, lab tests, and advanced imaging. Our goal is to accurately identify and manage various arthritis types.
Clinical Evaluation and History
At the heart of diagnosing arthritis is a thorough clinical evaluation. We start by taking a detailed patient history. This helps us understand symptoms, their duration, and what makes them better or worse.
Next, we conduct a physical exam. We check for joint swelling, tenderness, and any deformities. This helps us assess the joint’s range of motion.
Key aspects of clinical evaluation include:
- Assessing joint involvement patterns
- Evaluating morning stiffness duration
- Checking for systemic symptoms like fever or weight loss
- Examining for extra-articular manifestations
Laboratory Biomarkers
Laboratory tests are vital in diagnosing and differentiating arthritis types. These tests help identify specific biomarkers for each form of arthritis.
Common laboratory tests include:
- Rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-CCP antibodies for rheumatoid arthritis
- Uric acid levels for gout
- Inflammatory markers like ESR and CRP
- HLA-B27 testing for ankylosing spondylitis
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Advanced imaging techniques offer valuable insights for diagnosing and monitoring arthritis. They help us see joint damage and inflammation.
- X-rays to assess joint damage and bone erosions
- Ultrasound to detect synovitis and early erosions
- MRI for detailed visualization of soft tissues and bone marrow edema
- CT scans for assessing complex bone structures
Differential Diagnosis Challenges
Differential diagnosis in arthritis can be tricky. Symptoms often overlap between types. We must carefully consider various factors to make an accurate diagnosis.
Challenges include:
- Distinguishing between inflammatory and non-inflammatory arthritis
- Identifying overlapping features in mixed connective tissue disease
- Considering the presence of co-existing conditions
- Monitoring response to initial treatments to refine the diagnosis
Modern Treatment Strategies for Arthritis Immune Disease
Modern treatments for arthritis have changed how we care for patients. We now know more about the different types of arthritis and how to treat them. At Liv Hospital, we use the latest research and medical advancements to help our patients.
Disease-Specific Medications
The right medicine depends on the type of arthritis. For example, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are often used for rheumatoid arthritis. Biologic agents are used for psoriatic arthritis.
We make sure each patient gets the right medicine for their needs. This helps manage their condition effectively.
Biologic and Targeted Therapies
Biologic therapies have changed how we treat arthritis. These therapies target specific molecules in the inflammatory process. They help patients who don’t get better with usual treatments.
Targeted therapies, like Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, offer more options for managing arthritis. They are helpful for those with moderate to severe disease.
Liv Hospital’s Academic Approach to Arthritis Care
At Liv Hospital, we focus on academic care for arthritis. Our team keeps up with the latest research and guidelines. This ensures our patients get the best care available.
We work with international experts and join clinical trials. This helps us understand arthritis better and find new treatments.
Multidisciplinary Management
Arthritis care needs a team effort. This includes rheumatologists, orthopedic surgeons, physical therapists, and more.
We work with our patients to create personalized plans. These plans address their specific needs and improve their quality of life.
| Treatment Approach | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Disease-Specific Medications | Tailored medication plans based on arthritis type | Effective management of symptoms and disease progression |
| Biologic and Targeted Therapies | Targeted treatment for inflammatory processes | Significant relief for patients unresponsive to conventional treatments |
| Multidisciplinary Management | Collaborative care involving various healthcare professionals | Personalized treatment plans and improved patient outcomes |
Conclusion
It’s important to know the different kinds of arthritis to manage the immune disease well. We’ve looked at five main types, each with its own traits and treatments. Knowing which type you have is key to the right treatment.
At Liv Hospital, we offer top-notch care for patients from around the world. We use the latest treatments to meet each patient’s needs. Our team works together to help patients live better lives.
Understanding arthritis’s complexities helps us manage symptoms and slow the disease. We aim to improve our patients’ health and well-being. Our goal is to provide the best healthcare with full support for our patients
FAQ
What are the main types of arthritis immune disease?
The main types are osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, gout, and ankylosing spondylitis. We’ll look at each, covering causes, symptoms, and treatments.
How many types of arthritis are there?
Over 100 types of arthritis exist, each with its own traits and symptoms. We focus on the five main ones, but knowing the full range is key.
What is the impact of arthritis on global health?
Arthritis affects millions worldwide, causing economic and quality of life issues. Understanding and managing it is vital.
How does immune system dysfunction contribute to arthritis?
Immune system issues lead to joint damage and inflammation in arthritis. We’ll discuss genetic and environmental triggers.
What are the symptoms of osteoarthritis?
Symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. We’ll cover causes, risk factors, and cartilage breakdown.
What is the difference between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease, while osteoarthritis is a degenerative condition. We’ll compare their symptoms and features.
How is psoriatic arthritis related to psoriasis?
Psoriatic arthritis often occurs with psoriasis, causing skin and joint inflammation. We’ll explore their connection and unique symptoms.
What causes gout?
Gout results from uric acid metabolism issues, leading to joint inflammation. We’ll discuss dietary and lifestyle factors and treatment options.
How is ankylosing spondylitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, biomarkers, and imaging. We’ll discuss the challenges and importance of accurate diagnosis.
What are the modern treatment strategies for arthritis immune disease?
Treatments include specific medications and biologic therapies. Liv Hospital emphasizes a multidisciplinary approach for international patients.
Are there different kinds of arthritis?
Yes, over 100 types exist, with the five main ones discussed in detail. Knowing the different types is essential for effective management.
What are the different types of arthritis?
Types include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, gout, and ankylosing spondylitis. We’ve covered their unique features and symptoms.
What are the main types of arthritis immune disease?
The main types are osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, gout, and ankylosing spondylitis. We’ll look at each, covering causes, symptoms, and treatments.
How many types of arthritis are there?
Over 100 types of arthritis exist, each with its own traits and symptoms. We focus on the five main ones, but knowing the full range is key.
What is the impact of arthritis on global health?
Arthritis affects millions worldwide, causing economic and quality of life issues. Understanding and managing it is vital.
How does immune system dysfunction contribute to arthritis?
Immune system issues lead to joint damage and inflammation in arthritis. We’ll discuss genetic and environmental triggers.
What are the symptoms of osteoarthritis?
Symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. We’ll cover causes, risk factors, and cartilage breakdown.
What is the difference between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease, while osteoarthritis is a degenerative condition. We’ll compare their symptoms and features.
How is psoriatic arthritis related to psoriasis?
Psoriatic arthritis often occurs with psoriasis, causing skin and joint inflammation. We’ll explore their connection and unique symptoms.
What causes gout?
Gout results from uric acid metabolism issues, leading to joint inflammation. We’ll discuss dietary and lifestyle factors and treatment options.
How is ankylosing spondylitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, biomarkers, and imaging. We’ll discuss the challenges and importance of accurate diagnosis.
What are the modern treatment strategies for arthritis immune disease?
Treatments include specific medications and biologic therapies. Liv Hospital emphasizes a multidisciplinary approach for international patients.
Are there different kinds of arthritis?
Yes, over 100 types exist, with the five main ones discussed in detail. Knowing the different types is essential for effective management.
What are the different types of arthritis?
Types include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, gout, and ankylosing spondylitis. We’ve covered their unique features and symptoms.
References
Physiotattva. The 5 Most Common Types of Arthritis. https://www.physiotattva.com/blog/the-5-most-common-types-of-arthritis
Arthritis Australia. Types of Arthritis. https://arthritisaustralia.com.au/what-is-arthritis/types-of-arthritis/
Rheumatology Associates Houston. How Different Types of Arthritis Affect Your Health. https://rheumatologyassociateshouston.com/how-different-types-of-arthritis-affect-your-health/
Arthritis Foundation. Sources of Arthritis Pain. https://www.arthritis.org/health-wellness/healthy-living/managing-pain/understanding-pain/sources-of-arthritis-pain










