Radiotherapy is a treatment that uses targeted radiation to destroy cancer cells. It’s a vital part of cancer care, helping to treat various cancers and relieve symptoms.
Understanding how long does radiotherapy lasts is important for patients preparing for treatment. The duration can vary depending on the type of cancer, its stage, and the patient’s overall health.
At Liv Hospital, patients receive advanced, personalized radiotherapy care delivered by an experienced team. This approach ensures effective treatment while managing side effects and supporting overall well-being. Knowing what to expect helps patients face radiotherapy with confidence.
Key Takeaways
- Radiotherapy is a targeted cancer treatment that destroys cancerous cells.
- It is used to treat various cancers and ease symptoms.
- Liv Hospital offers advanced cancer care with a personalized approach.
- Understanding the treatment process helps patients prepare and cope.
- Radiation therapy can cure, prevent, or slow cancer growth.
Understanding Radiotherapy: Purpose and Applications
Radiotherapy is used for many medical conditions, including cancers and non-cancerous growths. It kills or controls cancer cells with ionizing radiation. It’s also used for non-cancerous conditions to destroy or shrink abnormal cells.
Definition and Basic Principles of Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy, or radiotherapy, is a cancer treatment. It uses high doses of radiation to kill cancer cells or slow their growth. The goal is to target the area precisely, protecting healthy tissues.
The therapy damages the DNA of targeted cells, stopping them from dividing and leading to cell death. This helps shrink tumors, ease symptoms, and improve patients’ quality of life.
Types of Conditions Treated with Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy treats many cancers, like breast, prostate, lung, and brain tumors. It’s also used for non-cancerous conditions, such as benign tumors and eye diseases like thyroid eye disease.
The choice to use radiotherapy depends on the tumor’s type, size, and location, and the patient’s health. It can be used alone or with surgery and chemotherapy.
Radiotherapy for Malignant vs. Benign Conditions
For malignant conditions, radiotherapy aims to cure cancer, prevent recurrence, or ease symptoms. For benign conditions, it’s used when symptoms are severe and other treatments fail.
For example, it treats some benign brain tumors that can’t be removed surgically. It also helps with symptoms from non-cancerous conditions like keloid scars or vascular malformations.
How Long Does Radiotherapy Last: Treatment Duration Explained
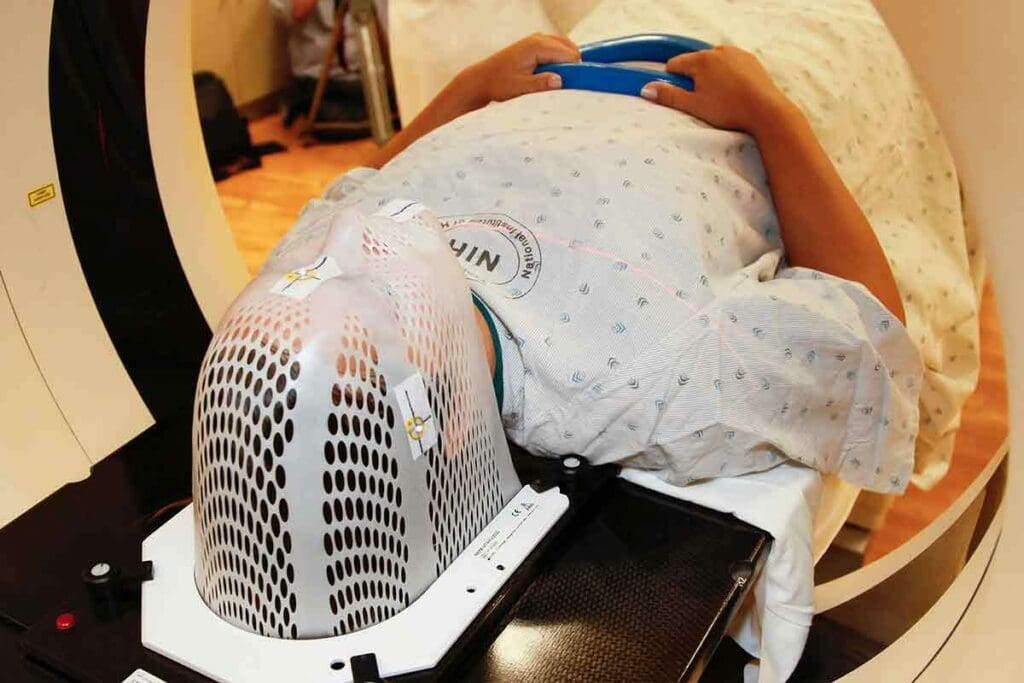

Knowing how long radiotherapy lasts is key for patients. It helps them get ready for their treatment. The time it takes varies a lot. This depends on the condition, treatment goals, and the type of radiotherapy.
Standard Treatment Schedules
Radiotherapy is often given five days a week for five or six weeks. This is common for many cancers. But, the time can change based on the patient’s needs and the cancer type.
For example, radiation treatment duration can differ for various cancers. Knowing this helps manage what patients expect.
Factors Affecting Treatment Length
Several things can change how long radiotherapy lasts. These include:
- The type and stage of cancer
- The treatment goals, whether curative or palliative
- The overall health of the patient
- The specific radiotherapy technique being used
Abbreviated Schedules for Specific Conditions
For some cases, treatments are shorter. This is true for palliative care or certain tumors. These shorter schedules can help quickly relieve symptoms or manage them without much disruption.
| Treatment Type | Typical Duration | Frequency |
| Curative Radiotherapy | 5-6 weeks | 5 days a week |
| Palliative Radiotherapy | 1-2 weeks | Varies |
| Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy | 1-5 fractions | Once a day or every other day |
The table shows how treatment times can vary. It’s important for patients to talk to their healthcare provider. This way, they know what to expect from their treatment.
Types of Radiotherapy Administration Methods
Radiotherapy comes in different forms, each suited for different needs. The method chosen depends on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health. It also depends on the treatment goals.
External Beam Radiation Therapy
External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) uses a machine outside the body to send radiation to the tumor. This method targets tumors well while protecting healthy tissues. EBRT is used for many cancers, like those in the brain, breast, and prostate.
Internal Radiation Therapy (Brachytherapy)
Internal radiation therapy, or brachytherapy, places radioactive material inside or near the tumor. It’s great for treating cancers like prostate and cervical cancer. The treatment can be temporary or permanent, based on the plan.
Liquid Radiotherapy and Its Applications
Liquid radiotherapy uses radioactive substances swallowed or injected into the body. It’s used for thyroid cancer and other cancers where it targets cancer cells well. This method needs careful planning and monitoring for safety and effectiveness.
The choice of radiotherapy method depends on many factors. These include the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health. Each method has its own benefits and is chosen based on the patient’s needs.
The Radiotherapy Planning Process
The success of radiotherapy starts with careful planning. This planning ensures the treatment hits the tumor right, making it more effective. It also keeps healthy tissues safe.
Initial Consultation and Assessment
The planning starts with a first meeting between the patient and the radiation oncologist. The doctor checks the patient’s health, looks at images, and talks about treatment goals. This meeting is key to picking the right radiotherapy.
The doctor looks at the patient’s medical history, cancer type and stage, and other important details. They might also ask for more tests or images to learn more.
Simulation and Treatment Mapping
After the first meeting, the patient has a simulation session. This session is vital for mapping the treatment area. It uses CT scans to find the tumor’s exact spot. The patient is placed on a table, and devices are used to keep them in the same position for each treatment.
The data from the simulation helps create a detailed map of the treatment area. This map includes the tumor and the tissues around it. It’s key for making a good treatment plan.
Treatment Plan Development
Next, a personalized treatment plan is made. A team of experts, like radiation oncologists and medical physicists, work together. They figure out the best dose and how to deliver it.
| Factors Considered | Description |
| Tumor Size and Location | The size and location of the tumor are critical in determining the radiotherapy dose and delivery technique. |
| Patient’s Overall Health | The patient’s overall health and medical history are taken into account to minimize possible side effects. |
| Type of Cancer | The type and stage of cancer influence the treatment plan, including the dose and fractionation schedule. |
The plan shows how much radiation to use, how many times, and when. It’s made just for the patient, aiming for the best results.
What Happens During a Typical Radiotherapy Session
Knowing what happens during a radiotherapy session can ease anxiety for patients. A radiotherapy session is a detailed process. It involves several steps to make sure the treatment is done right and works well.
Preparation Before Each Treatment
Before each radiotherapy session, patients need to prepare in certain ways. This helps make sure the treatment works well. They might:
- Arrive at the treatment facility on time
- Change into a hospital gown
- Take off any jewelry or items that could get in the way
The radiation therapist will then put the patient on a treatment table. They use special devices to keep the patient in the right spot during treatment.
The Treatment Room Experience
In the treatment room, the patient lies on a table. The radiation therapist leaves before starting the treatment. They talk to the patient through an intercom. The treatment is painless and usually lasts between 2 and 15 minutes for external radiotherapy.
Duration of Individual Sessions
The length of radiotherapy sessions can change based on the treatment type and case complexity. Here’s a quick look:
| Type of Radiotherapy | Typical Session Duration |
| External Beam Radiation Therapy | 2-15 minutes |
| Internal Radiation Therapy (Brachytherapy) | Varies, sometimes several days for implant placement |
It’s key for patients to know that while the treatment itself is short, getting ready and positioned can take longer.
Precision and Safety Measures in Modern Radiotherapy
Modern radiotherapy has made big strides, focusing on precision and safety. It aims to hit the tumor with the right dose of radiation. At the same time, it tries to avoid harming healthy tissues nearby.
Targeting Techniques to Spare Healthy Tissue
Modern radiotherapy uses advanced targeting methods. Three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3D-CRT) shapes the radiation beam to fit the tumor’s shape. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) changes the radiation beam’s intensity. This way, it gives the tumor a stronger dose while protecting healthy tissue.
These methods help lower side effects and improve treatment results. By precisely targeting the tumor, radiotherapy can work better, even when the tumor is close to important areas.
Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT)
Image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) is a big step forward in radiotherapy. It uses imaging like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI to guide the radiation. This makes sure the radiation hits the tumor right, even if it moves during treatment.
IGRT makes radiotherapy more precise by allowing adjustments in real-time. This is key for tumors that move, like those in the lung or prostate.
Quality Assurance Protocols
Quality assurance protocols are key to safe and effective radiotherapy. They involve testing and checking the equipment and treatment plans. Regular checks help find and fix problems before they harm patients.
By following strict quality assurance rules, radiotherapy centers keep treatments precise and safe. This includes keeping equipment in top shape, training staff, and watching treatment closely.
In summary, modern radiotherapy uses many safety and precision steps to treat patients well. With advanced targeting, image-guided therapy, and quality checks, radiotherapy keeps getting better and safer.
Managing Side Effects During Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is a common cancer treatment. It can cause side effects, and knowing how to manage them is key. Each patient’s experience is different, so understanding these effects is important.
Common Short-Term Side Effects
Patients may feel very tired during radiotherapy. This is called fatigue. They might also notice skin changes like redness or dryness in the treated area. Hair loss can happen if the scalp is treated.
Nausea and vomiting can occur, mainly if the stomach area is treated. Mouth sores and dry mouth are common in head and neck treatments.
Site-Specific Reactions
Side effects differ based on the treated area. For example, the pelvic area treatment might lead to frequent urination. The chest area treatment can cause swallowing or coughing issues.
Knowing these specific reactions helps patients prepare. Healthcare providers should talk about these effects before treatment starts.
Supportive Care During Treatment
Supportive care is essential for managing radiotherapy side effects. This includes eating smaller meals to avoid nausea or using creams for skin issues.
Staying hydrated, resting well, and doing gentle exercises are also important. Emotional support from loved ones or support groups helps a lot.
By understanding side effects and using supportive care, patients can handle radiotherapy better.
After Treatment: What to Expect When Radiotherapy Ends
When radiotherapy ends, patients often wonder what’s next. This marks a big milestone but also starts a new recovery phase.
Immediate Post-Treatment Period
Right after treatment, patients might feel many emotions. They could feel relieved or worried about the future. This time is key for managing side effects and starting recovery. It’s important to keep up with follow-up appointments to check progress and solve any issues.
Some patients might want to get back to normal quickly. Others might need more time. Always listen to your healthcare team’s advice on rest, exercise, and activities.
Are You Radioactive After Treatment?
Most people aren’t radioactive after external beam radiation therapy. This therapy sends radiation from outside the body, and it stops once treatment ends. But, with internal radiation therapy (brachytherapy), where a radioactive source is inside the body, there’s a small risk of radiation exposure to others.
It’s very important to follow the safety precautions given by your healthcare team if you had brachytherapy. The risk is usually low, and steps are taken to keep exposure to a minimum.
How Long Do Radiotherapy Effects Last?
The effects of radiotherapy can last differently for everyone. Some side effects might go away quickly, while others take longer. Your healthcare team will guide you on what to expect and how to handle any ongoing side effects.
| Side Effect | Typical Duration | Management Tips |
| Fatigue | Several weeks to months | Rest, gentle exercise, nutrition counseling |
| Skin Reactions | Few weeks to several months | Topical creams, avoiding irritants |
| Hair Loss | Permanent or regrowth within a year | Wigs, scalp cooling, gentle hair care |
Knowing about side effects and how to manage them is important for the post-radiotherapy period. Keeping in touch with your healthcare providers is key to getting the best results.
Special Considerations for Different Types of Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is not just for cancer. It helps with non-cancerous conditions and palliative care too. It’s flexible and can be adjusted for different needs.
Radiotherapy for Non-Cancerous Conditions
Radiotherapy is used for more than just cancer. It treats benign tumors, vascular conditions, and non-cancerous growths. These treatments aim to ease symptoms and prevent complications.
- Benign tumors that cause discomfort or affect organ function
- Certain vascular conditions, such as arteriovenous malformations
- Some non-cancerous growths that cause pain or discomfort
The dosage and plan for non-cancerous conditions are adjusted to reduce side effects. This ensures the best outcome.
Palliative Radiotherapy Approaches
Palliative radiotherapy helps patients with advanced cancer or serious conditions. It aims to relieve symptoms and improve life quality. The National Cancer Institute says it can help with pain, bleeding, and breathing issues.
Some common methods include:
- Short-course radiotherapy for quick symptom relief
- Targeted treatment to protect healthy tissue
- Combination therapy with other treatments, like pain meds
Pediatric Radiotherapy Considerations
Radiotherapy for kids needs special care because of their sensitive tissues and long-term effects. Pediatric radiotherapy aims to:
- Use the lowest dose needed
- Use advanced techniques to protect healthy tissue
- Watch for long-term effects and provide follow-up care
The treatment is customized for each child. It considers their age, size, and condition. This approach aims to be effective while minimizing side effects.
Conclusion: Navigating Your Radiotherapy Journey
Understanding radiotherapy can make a big difference for patients. It’s a complex treatment that needs careful planning and execution.
By learning the basics of radiotherapy, patients can prepare better for treatment. Knowing what happens during a session and how to handle side effects can reduce anxiety. This improves the overall experience.
Navigating radiotherapy is more than just treatment. It’s about being informed and proactive. With the right knowledge and support, patients can make informed decisions and take control of their journey.
As radiotherapy evolves with new technology and research, staying updated is key. This helps patients navigate their treatment more effectively.
FAQ
What is radiotherapy used for?
Radiotherapy treats many medical conditions, like cancer and non-cancerous tumors. It can be used alone or with other treatments like surgery and chemotherapy.
How is radiotherapy performed?
There are different ways to do radiotherapy. You can get it through external beam radiation, internal radiation (brachytherapy), or liquid radiotherapy. The method chosen depends on the condition and where it is.
How long does radiotherapy last?
Radiotherapy’s length varies. It depends on the condition, treatment method, and patient factors. Treatments can last from a few days to weeks or even months.
Are you radioactive after radiotherapy?
Most people aren’t radioactive after external beam radiation. But, after brachytherapy, you might be for a short time. This depends on the radioactive material used.
What happens during a typical radiotherapy session?
During a session, you lie on a table. The machine sends radiation to the right spot. Sessions are usually painless and can take from minutes to an hour.
How effective is radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy’s success varies. It depends on the condition, treatment method, and patient factors. It can work well for some cancers and non-cancerous conditions.
Does radiotherapy shrink tumors?
Yes, it can. Radiotherapy damages cancer cells’ DNA, stopping them from growing. How well it works depends on the tumor type, stage, and treatment.
What are the common side effects of radiotherapy?
Side effects include fatigue, skin reactions, and site-specific issues like hair loss or mouth sores. Supportive care can help manage these.
How long do the effects of radiotherapy last?
Effects vary. Some side effects go away soon after treatment. Others can last months or years.
Can radiotherapy be used for non-cancerous conditions?
Yes, it can treat non-cancerous conditions like benign tumors or vascular malformations. The treatment and dose might differ from cancer treatments.
What is liquid radiotherapy?
Liquid radiotherapy uses radioactive liquids to treat conditions, including cancer. It targets specific areas or cells directly.
How is radiotherapy planned?
Planning involves several steps. These include a consultation, simulation, treatment mapping, and creating a personalized plan. This ensures accurate and effective radiation delivery.
References
- National Cancer Institute. (2018). Radiation therapy for cancer.
https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/types/radiation-therapy
- American Cancer Society. (2025). Radiation therapy.
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/managing-cancer/treatment-types/radiation.html
- National Cancer Institute. (2018). External beam radiation therapy for cancer.
https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/types/radiation-therapy/external-beam










