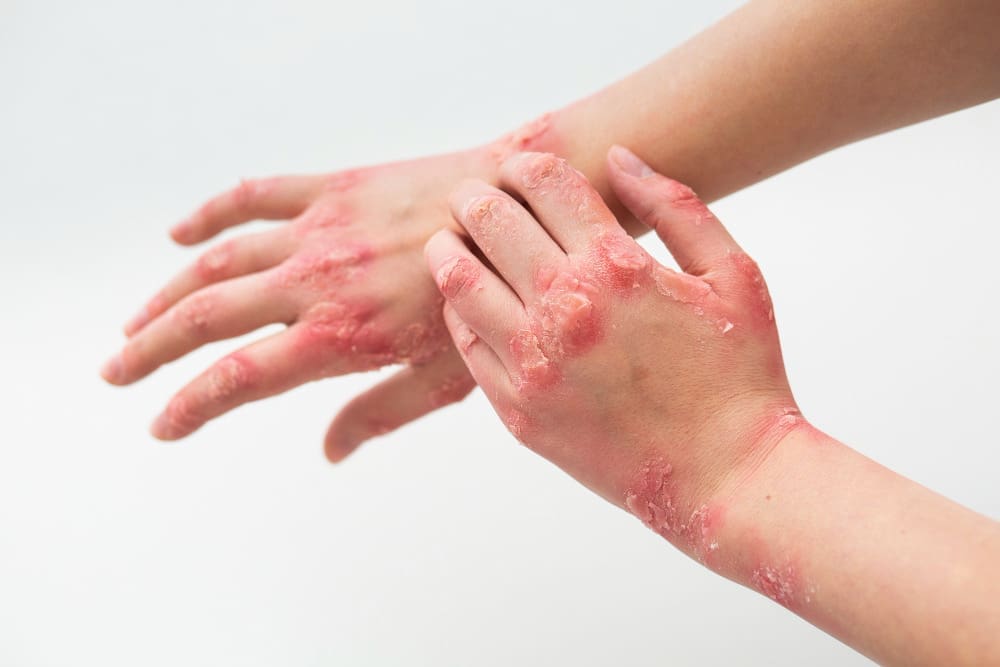
At Liv Hospital, we get how tough autoimmune diseases are. They happen when the immune system goes wrong and attacks healthy parts of the body. This leads to long-lasting health problems.
There are more than 80 kinds of autoimmune disorders. They affect a lot of people. In fact, they hit 5–8% of the population and are a big reason for chronic illness. We’ll look at 7 common autoimmune disease examples and dive into what makes them so complex.
Key Takeaways
- Autoimmune diseases affect 5-8% of the population worldwide.
- There are over 80 types of autoimmune disorders.
- Autoimmune diseases are the third most common cause of chronic illness.
- Understanding autoimmune diseases is key to helping patients.
- Liv Hospital is committed to top-notch care for autoimmune disorders.
Understanding Autoimmune Disorders: When the Body Attacks Itself
Autoimmune diseases happen when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s healthy tissues. This is because the immune system’s defense against pathogens goes wrong.
The immune system is a complex network that defends the body against invaders. In autoimmune disorders, it fails to tell self from non-self. This leads to an attack on the body’s own cells and tissues. This can cause a variety of diseases, each with its own symptoms and challenges.
The Immune System Gone Rogue
In a healthy person, the immune system fights off pathogens like bacteria and viruses. But in autoimmune disorders, it sees the body’s own tissues as foreign. This results in inflammation, tissue damage, and different symptoms depending on the disease and affected organs.
For example, in Type 1 Diabetes, the immune system attacks the pancreas’s insulin-producing cells. This causes high blood sugar levels. Understanding how the immune system goes wrong is key to finding treatments. Research is ongoing to learn more about autoimmune diseases, including the role of genetics, environment, and immune system imbalance. For more on treatments like stem cell therapy, visit our dedicated page.
The Scope of Autoimmune Conditions
There are over 80 recognized autoimmune disorders, affecting millions globally. Women are three times more likely than men to get these diseases. The exact reasons for this are not fully understood but involve genetics, hormones, and environment.
Autoimmune diseases have a big impact on individuals and society. They can cause chronic illness, disability, and lower quality of life. They also strain healthcare systems due to ongoing care, lost productivity, and management costs.
It’s important to understand the scope and impact of autoimmune disorders. This helps raise awareness, fund research, and develop better management strategies. By recognizing the challenges faced by those with autoimmune diseases, we can improve their care and support.
What Are the 7 Autoimmune Diseases Most Commonly Diagnosed?

Knowing the most common autoimmune diseases is key for good care. These diseases happen when the body’s immune system attacks itself. Some diseases are diagnosed more often than others.
Overview of Prevalence and Impact
The seven most common autoimmune diseases are type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Each affects different parts of the body. They have different effects on people’s lives.
Type 1 diabetes happens when the immune system destroys the insulin-making cells in the pancreas. This means people with this disease need insulin for life. Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, causes inflammation and damage to the joints. If not treated well, it can lead to severe disability.
Demographics and Risk Factors
Autoimmune diseases can happen to anyone, at any age or gender. But, some groups are more likely to get certain diseases. For example, women are more likely to get SLE and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis than men.
To understand who gets these diseases, let’s look at some data:
| Autoimmune Disease | Prevalence | Common Demographics |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1 Diabetes | 0.3-0.5% globally | Children and young adults |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | 0.5-1% globally | Women, aged 40-60 |
| Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) | 0.05% globally | Women of childbearing age |
| Multiple Sclerosis | 0.1% globally | Young adults, more common in women |
| Psoriasis | 2-3% globally | Affects all ages, peaks in 20-50 age group |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease | 0.3-0.5% globally | Young adults, equal gender distribution |
| Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis | 1-2% globally | More common in women, middle-aged |
Knowing who gets these diseases helps doctors diagnose and treat them better. By understanding these conditions, doctors can give better care and support.
Diagnosing Autoimmune Conditions
We use many tools to find autoimmune conditions. Finding these conditions can be hard because their symptoms are not clear and the immune system is complex.
Blood Tests and Antibody Markers
Blood tests are key in finding autoimmune diseases. They look for specific antibodies linked to these diseases. For example, antinuclear antibodies (ANA) show Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), while rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated protein antibody (anti-CCP) point to Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). These markers help us tell apart different autoimmune diseases and decide on treatments.
Challenges in Diagnosis
Even with better tests, finding autoimmune diseases is tricky. Symptoms can look the same in different diseases, and some people might not show the usual antibodies. Doctors must look at the whole picture, mixing clinical checks with lab results.
“The diagnosis of autoimmune diseases is not just about identifying a specific antibody; it’s about understanding the patient’s overall clinical picture.”
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you have ongoing or strange symptoms like joint pain, tiredness, or skin issues, see a doctor. Early treatment can make a big difference for people with autoimmune diseases. We urge anyone with worrying symptoms to talk to a healthcare expert.
Type 1 Diabetes: When the Immune System Targets the Pancreas
Type 1 diabetes happens when the immune system attacks the pancreas’s insulin-making cells. It’s a serious autoimmune disease. It’s one of the 7 common autoimmune diseases that greatly affect people’s lives. It shows how the body’s defense can go wrong and attack itself.
Type 1 diabetes is caused by the immune system destroying the insulin-making beta cells in the pancreas. This leads to not enough insulin, causing blood sugar to be too high. Knowing about this disease means understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Pathophysiology and Symptoms
Type 1 diabetes is caused by the immune system destroying the pancreas’s beta cells. This is often due to genetics and the environment. Without enough beta cells, the pancreas can’t make enough insulin. This causes blood sugar to rise.
Symptoms of Type 1 diabetes can appear quickly, often in a few weeks. They include:
- Increased thirst and urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Unexplained weight loss
It’s important to notice these symptoms early to get a diagnosis and start treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches
To diagnose Type 1 diabetes, doctors do blood tests to check blood sugar and for autoantibodies. Treatment mainly involves insulin therapy to replace the insulin the body can’t make. New insulin delivery systems, like continuous glucose monitors and insulin pumps, help manage the disease better.
For more on managing Type 1 diabetes, including new technologies like the artificial pancreas, see this article.
Living with Type 1 Diabetes
Managing Type 1 diabetes means checking blood sugar often, adjusting insulin, eating right, and staying active. It’s challenging, but many people with Type 1 diabetes live full lives. New medical technologies and treatments are making life easier for those with this disease.
Autoimmune diseases like Type 1 diabetes show why we need to keep researching their causes and treatments. Understanding and managing these diseases can greatly improve people’s lives.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Joint Inflammation and Destruction
Rheumatoid arthritis happens when the immune system attacks the lining of the joints. This leads to ongoing pain and inflammation. It’s a common autoimmune disease that damages joints.
“Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic condition that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life if not properly managed,” says a leading rheumatologist.
Mechanism of Joint Damage
The immune system’s attack on the synovium causes inflammation. This attracts immune cells, leading to thickening of the synovium. A layer of inflammatory tissue, called a pannus, forms and invades the joint.
This inflammation can damage cartilage and bones. It can lead to loss of joint function and severe disability.
The process involves complex interactions between immune cells, cytokines, and other inflammatory mediators. Understanding these mechanisms is key to finding effective treatments.
Symptoms and Progression
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. These symptoms often affect the hands and feet. The disease can progress at different rates.
Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to preventing long-term damage. Symptoms can also include fatigue, fever, and loss of appetite. This shows the disease’s systemic nature.
Modern Treatment Strategies
Modern treatments for rheumatoid arthritis combine disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic agents. These aim to reduce inflammation and slow disease progression.
- DMARDs, such as methotrexate, are often the first line of treatment.
- Biologic agents, including TNF-alpha inhibitors, target specific components of the immune response.
- Early intervention with these treatments can significantly improve outcomes.
“The introduction of biologic therapies has revolutionized the management of rheumatoid arthritis, bringing new hope to patients with severe disease,” notes a recent medical review.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): The Great Imitator
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a complex autoimmune disease. It affects many parts of the body, making it hard to diagnose and treat.
Multi-System Involvement
SLE can harm organs like the skin, joints, kidneys, and brain. This wide impact makes the disease very challenging to manage.
The disease’s effects on different parts of the body cause a variety of symptoms. This makes it hard to diagnose. If not treated, SLE can cause lasting damage.
Characteristic Symptoms and Flares
SLE patients often have joint pain, skin rashes, and fever. The disease goes through periods of flares and remission. The severity of symptoms varies from person to person.
Common symptoms include:
- Joint pain and swelling
- Skin rashes, like the butterfly-shaped rash on the face
- Fever and fatigue
- Hair loss
- Sensitivity to sunlight
Diagnosis Challenges and Management
Diagnosing SLE can be tricky because it’s similar to other diseases. Doctors use a combination of clinical evaluation, lab tests, and patient history to make a diagnosis.
Managing SLE requires a detailed treatment plan. This may include medicines to reduce inflammation and prevent flares. Lifestyle changes, like avoiding sunlight and staying healthy, are also key.
| Treatment Approach | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Medications | Corticosteroids and immunosuppressants | Reduce inflammation and prevent flares |
| Lifestyle Adjustments | Avoiding sunlight, healthy diet, and exercise | Improve overall health and reduce symptom severity |
Understanding SLE’s complexities and working with healthcare providers can help patients manage their condition. This improves their quality of life.
Multiple Sclerosis: Attacking the Nervous System
Multiple sclerosis happens when the immune system attacks the myelin, the protective layer of nerve fibers. This damage stops electrical impulses from flowing properly. It causes many neurological symptoms.
The Demyelination Process
The main problem in multiple sclerosis is demyelination. The immune system attacks the myelin sheath, causing inflammation and damage. This can lead to lesions in the central nervous system, affecting many bodily functions.
Demyelination causes symptoms like numbness, weakness, vision problems, and tremors. The damage’s extent varies among people, making each case different.
Types and Progression Patterns
Multiple sclerosis comes in different forms. Knowing these types helps find the best treatment.
- Relapsing-remitting MS has periods of relapses followed by recovery.
- Secondary progressive MS gets worse over time, with occasional flare-ups.
- Primary progressive MS gets worse from the start, with no clear relapses.
- Progressive-relapsing MS gets worse steadily, with some flare-ups.
Treatment Innovations
Treatment for multiple sclerosis has improved a lot. Now, there are disease-modifying therapies to reduce relapses. These include:
- Disease-modifying therapies that target the immune system to reduce inflammation and slow disease progression.
- Symptomatic treatments for symptoms like spasticity, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties.
- Rehabilitation therapies, including physical, occupational, and speech therapy, to help maintain function and quality of life.
Understanding multiple sclerosis, including demyelination and progression patterns, shows the need for new treatments. These help manage this autoimmune disease.
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: When the Thyroid Comes Under Attack
When the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, it leads to Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. This is a common autoimmune disorder. It makes the thyroid gland unable to make enough thyroid hormones, causing hypothyroidism.
Thyroid Function and Autoimmunity
The thyroid gland is key for metabolism and energy. In Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, the immune system makes antibodies that harm the thyroid. This causes inflammation and a drop in thyroid hormone production.
This condition can really affect someone’s life, causing tiredness, weight gain, and feeling cold. It’s important to understand Hashimoto’s thyroiditis to manage it well.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis vary but often include tiredness, dry skin, hair loss, and feeling cold. Doctors diagnose it by checking thyroid hormone levels and looking for specific antibodies.
Getting diagnosed early is key to avoid serious problems. Tests may include:
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test
- Free thyroxine (FT4) and free triiodothyronine (FT3) tests
- Thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPO) test
Treatment and Management
Treatment for Hashimoto’s thyroiditis usually means taking thyroid hormone to balance hormone levels. We help find the right dosage and check how well it works.
Managing Hashimoto’s also means making lifestyle changes. This includes eating well and managing stress. A healthy diet and regular exercise are important for overall health.
The following table summarizes key aspects of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Autoimmune Response | Immune system attacks the thyroid gland |
| Symptoms | Fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, hair loss |
| Diagnosis | TSH, FT4, FT3 tests, TPO antibody test |
| Treatment | Thyroid hormone replacement therapy |
Other Common Autoimmune Conditions
Autoimmune diseases are more than just a few well-known ones. Conditions like psoriatic arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease also pose challenges. They affect patients and healthcare providers in unique ways.
Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriasis is a chronic condition that causes skin inflammation. It leads to scaly, red patches on the skin. It affects about 2-3% of the world’s population.
When psoriasis causes joint inflammation, it’s called psoriatic arthritis. This can damage joints if not treated.
Symptoms of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis
- Skin redness and scaling
- Joint pain and swelling
- Nail changes, such as thickening or pitting
- Fatigue
Doctors diagnose it by looking at skin and joint symptoms. Treatment includes topical therapies, medications, and lifestyle changes. These help manage symptoms and prevent joint damage.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. These conditions cause chronic inflammation in the GI tract. Symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss.
Types of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
| Condition | Primary Area Affected | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Crohn’s Disease | Any part of the GI tract, from mouth to anus | Diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight loss |
| Ulcerative Colitis | Colon and rectum | Diarrhea with blood, urgency, abdominal pain |
Managing IBD involves reducing inflammation and preventing relapse. Medications and lifestyle changes are key. Dietary changes help control symptoms.
It’s important to understand these autoimmune conditions for better care. Recognizing the different ways autoimmune diseases manifest helps us support patients better. This improves their quality of life.
Conclusion: Advances in Autoimmune Disease Management
Medical science has made big strides in managing autoimmune diseases. These are conditions where the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues. Knowing about these diseases and their effects on patients is key to good care.
There has been a lot of progress in immunology. This includes better ways to diagnose and treat diseases like Type 1 Diabetes, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. These advances have greatly improved the lives of patients around the world.
As we keep studying autoimmune diseases, it’s clear that more research and awareness are needed. Supporting research and education can help us better understand and manage these conditions. This will improve the lives of those dealing with immunology significant diseases.
FAQ
What are autoimmune diseases?
Autoimmune diseases happen when the immune system attacks healthy body tissues. This leads to various conditions that can harm different organs and systems.
How many types of autoimmune disorders are there?
There are over 80 types of autoimmune disorders. These conditions affect a large number of people worldwide.
What are some common examples of autoimmune diseases?
Common autoimmune diseases include type 1 diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis. Others are systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), multiple sclerosis, and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease are also examples.
Why are women more likely to be affected by autoimmune diseases?
Women are more likely to get autoimmune diseases. Hormonal and genetic factors might explain this difference.
How are autoimmune diseases diagnosed?
Diagnosing autoimmune diseases is tricky. But, blood tests that find specific antibodies are key for making a diagnosis.
What is the role of the immune system in autoimmune diseases?
In autoimmune diseases, the immune system gets confused. It attacks healthy tissues, causing damage and symptoms.
Can autoimmune diseases be treated?
There’s no cure for autoimmune diseases. But, treatments like medications and lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms and slow the disease.
What is the impact of autoimmune diseases on quality of life?
Autoimmune diseases can greatly affect a person’s life. They can harm both physical and emotional health. Getting the right care is key to managing these conditions.
How can I manage my autoimmune disease?
Managing an autoimmune disease needs a detailed plan. This includes medication, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups. These steps help prevent complications and improve life quality.
What are the latest advances in autoimmune disease management?
Research is always improving our understanding of autoimmune diseases. New treatments, like biologic agents, are being developed. These aim to better manage and treat these conditions.
What are autoimmune diseases?
Autoimmune diseases happen when the immune system attacks healthy body tissues. This leads to various conditions that can harm different organs and systems.
How many types of autoimmune disorders are there?
There are over 80 types of autoimmune disorders. These conditions affect a large number of people worldwide.
What are some common examples of autoimmune diseases?
Common autoimmune diseases include type 1 diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis. Others are systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), multiple sclerosis, and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease are also examples.
Why are women more likely to be affected by autoimmune diseases?
Women are more likely to get autoimmune diseases. Hormonal and genetic factors might explain this difference.
How are autoimmune diseases diagnosed?
Diagnosing autoimmune diseases is tricky. But, blood tests that find specific antibodies are key for making a diagnosis.
What is the role of the immune system in autoimmune diseases?
In autoimmune diseases, the immune system gets confused. It attacks healthy tissues, causing damage and symptoms.
Can autoimmune diseases be treated?
There’s no cure for autoimmune diseases. But, treatments like medications and lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms and slow the disease.
What is the impact of autoimmune diseases on quality of life?
Autoimmune diseases can greatly affect a person’s life. They can harm both physical and emotional health. Getting the right care is key to managing these conditions.
How can I manage my autoimmune disease?
Managing an autoimmune disease needs a detailed plan. This includes medication, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups. These steps help prevent complications and improve life quality.
What are the latest advances in autoimmune disease management?
Research is always improving our understanding of autoimmune diseases. New treatments, like biologic agents, are being developed. These aim to better manage and treat these conditions.
References
Healthline. Autoimmune Disease: Types, Symptoms, Causes, and More. https://www.healthline.com/health/autoimmune-disorders
Bass Medical Group. 15 Autoimmune Disorders to Be Aware Of. https://www.bassmedicalgroup.com/blog-post/15-autoimmune-disorders-to-be-aware-of
Medical News Today. List of Autoimmune Diseases. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/list-of-autoimmune-diseases


































